论文来源:NAACL 2016
论文链接:Hierarchical Attention Networks for Document Classification
有点老但是很经典的一篇论文,最近重新读了一遍。
HAN (Hierarchical Attention Networks for Document Classification) 是一个针对文本分类任务的层次化 attention 模型。它有两个显著的特点:
- 通过"词-句子-文章"的层次化结构来表示一篇文本。
- 该模型有两个层次的 attention 机制,分别存在于词层次 (word level) 和句子层次 (sentence level)。从而使该模型具有对文本中重要性不同的句子和词的能力给予不同 "注意力" 的能力。
HAN 模型的灵感来源于人在阅读 document 的时候,不同的词和句子对人理解 document 信息有不同的影响。因为,词和句子的重要性是和上下文息息相关的,即使是相同的词和句子,在不同的上下文中重要性也不一样。人在阅读一篇文章时,对 document 不同的内容是有着不同的注意度的。
由此,本文在 attention 机制的基础上,联想到 document 是一个层次化的结构,提出用词向量来表示句子向量,再由句子向量表示 document 向量,并且在词层次和句子层次分别引入 attention 操作的模型。实验表明,HAN 模型相比与它同时期的其他模型,实验指标大幅提升。
今天,我们来介绍一下 HAN 模型。
模型概述
HAN 的模型结构如下所示,它包含一个词序列编码器,一个 word level 的 attention 层,一个句子序列编码器,一个 sentence level 的 attention 层。
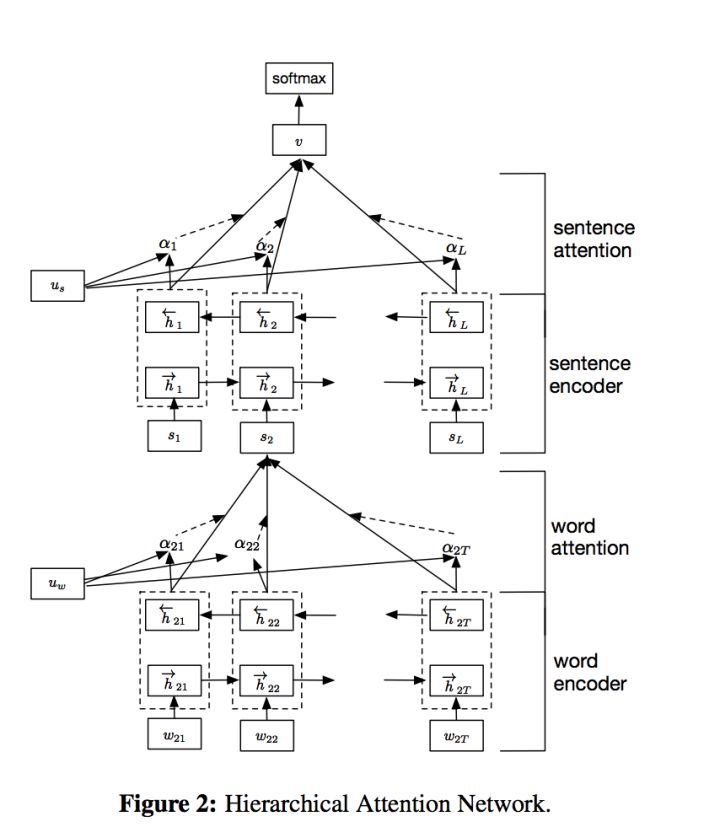
基于 GRU 的词序列编码器
不再赘述了,以前介绍过好多遍,一个简单的 BiGRU。
层次化 attention
词编码器(Word Encoder)
由词序列组成 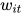 ,
,![t\in [0,T]](https://p1-jj.byteimg.com/tos-cn-i-t2oaga2asx/gold-user-assets/2019/1/6/1682333e531526cf~tplv-t2oaga2asx-jj-mark:3024:0:0:0:q75.png) 组成的句子,首先把词转化成词向量,
组成的句子,首先把词转化成词向量,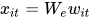 ,然后用双向的 GRU 网络,可以将正向和反向的上下文信息结合起来,获得隐藏层输出。
,然后用双向的 GRU 网络,可以将正向和反向的上下文信息结合起来,获得隐藏层输出。
![x_{it}=W_{e}w_{it},t\in[1,T]](https://p1-jj.byteimg.com/tos-cn-i-t2oaga2asx/gold-user-assets/2019/1/6/1682333e5329924b~tplv-t2oaga2asx-jj-mark:3024:0:0:0:q75.png)
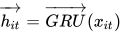
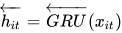
对于一个给定的词语 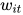 , 经过 GRU 网络后,获得了一种新的表示:
, 经过 GRU 网络后,获得了一种新的表示: ![h_{it}=[\overrightarrow{h_{it}},\overleftarrow{h_{it}}]](https://p1-jj.byteimg.com/tos-cn-i-t2oaga2asx/gold-user-assets/2019/1/6/1682333e53536926~tplv-t2oaga2asx-jj-mark:3024:0:0:0:q75.png)
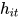 包含了
包含了 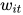 周围两个方向的信息。
周围两个方向的信息。
self.word_rnn = nn.GRU(emb_size, word_rnn_size, num_layers=word_rnn_layers,
bidirectional=True, dropout=dropout, batch_first=True)词级别的 attention
attention 的目的是要把一个句子中,对句子的含义影响最大的词语找出来。论文通过将 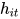 输入到一个 dense 网络中得到的结果
输入到一个 dense 网络中得到的结果 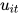 作为
作为 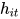 的隐含表示。
的隐含表示。
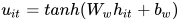
为了衡量单词的重要性,这里用 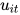 和一个随机初始化的上下文向量
和一个随机初始化的上下文向量 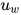 的相似度来表示,然后经过 softmax 操作获得了一个归一化的 attention 权重矩阵
的相似度来表示,然后经过 softmax 操作获得了一个归一化的 attention 权重矩阵 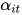 ,代表句子
,代表句子 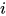 中第
中第 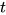 个词的权重。
个词的权重。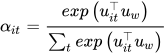
(下面代码实现中,在 softmax 之前多了一步 normalization 操作,去最大值。)
得到了 attention 权重矩阵之后,句子向量 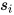 可以看作这些词向量的加权求和。这里的上下文向量
可以看作这些词向量的加权求和。这里的上下文向量 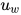 是在训练网络的过程中学习获得的。我们可以把
是在训练网络的过程中学习获得的。我们可以把 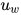 当作一种询问的高级表示,比如"哪些词含有比较重要的信息?"
当作一种询问的高级表示,比如"哪些词含有比较重要的信息?"
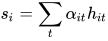
WordAttention 部分代码如下:
class WordAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, emb_size, word_rnn_size, word_rnn_layers, word_att_size, dropout):
"""
:param vocab_size: number of words in the vocabulary of the model
:param emb_size: size of word embeddings
:param word_rnn_size: size of (bidirectional) word-level RNN
:param word_rnn_layers: number of layers in word-level RNN
:param word_att_size: size of word-level attention layer
:param dropout: dropout
"""
super(WordAttention, self).__init__()
# Embeddings (look-up) layer
self.embeddings = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, emb_size)
# Bidirectional word-level RNN
self.word_rnn = nn.GRU(emb_size, word_rnn_size, num_layers=word_rnn_layers, bidirectional=True,
dropout=dropout, batch_first=True)
# Word-level attention network
self.word_attention = nn.Linear(2 * word_rnn_size, word_att_size)
# Word context vector to take dot-product with
self.word_context_vector = nn.Linear(word_att_size, 1, bias=False)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, sentences, words_per_sentence):
"""
Forward propagation.
:param sentences: encoded sentence-level data, a tensor of dimension (n_sentences, word_pad_len, emb_size)
:param words_per_sentence: sentence lengths, a tensor of dimension (n_sentences)
:return: sentence embeddings, attention weights of words
"""
# Sort sentences by decreasing sentence lengths (SORTING #2)
words_per_sentence, sent_sort_ind = words_per_sentence.sort(dim=0, descending=True)
sentences = sentences[sent_sort_ind] # (n_sentences, word_pad_len, emb_size)
# Get word embeddings, apply dropout
sentences = self.dropout(self.embeddings(sentences)) # (n_sentences, word_pad_len, emb_size)
# Re-arrange as words by removing pad-words (SENTENCES -> WORDS)
words, bw = pack_padded_sequence(sentences,
lengths=words_per_sentence.tolist(),
batch_first=True)
# (n_words, emb_size), bw is the effective batch size at each word-timestep
(words, _), _ = self.word_rnn(PackedSequence(words, bw)) # (n_words, 2 * word_rnn_size), (max(sent_lens))
# Find attention vectors by applying the attention linear layer
att_w = self.word_attention(words) # (n_words, att_size)
att_w = F.tanh(att_w) # (n_words, att_size)
# Take the dot-product of the attention vectors with the context vector (i.e. parameter of linear layer)
att_w = self.word_context_vector(att_w).squeeze(1) # (n_words)
max_value = att_w.max()
att_w = torch.exp(att_w - max_value) # (n_words)
# Re-arrange as sentences by re-padding with 0s (WORDS -> SENTENCES)
att_w, _ = pad_packed_sequence(PackedSequence(att_w, bw), batch_first=True)
# (n_sentences, max_sent_len_in_batch)
# Calculate softmax values
word_alphas = att_w / torch.sum(att_w, dim=1, keepdim=True)
# (n_sentences, max_sent_len_in_batch)
# Similarly re-arrange word-level RNN outputs as sentences by re-padding with 0s (WORDS -> SENTENCES)
sentences, _ = pad_packed_sequence(PackedSequence(words, bw), batch_first=True)
# (n_sentences, max_sent_len_in_batch, 2 * word_rnn_size)
# Find sentence embeddings
sentences = sentences * word_alphas.unsqueeze(2) # (n_sentences, max_sent_len_in_batch, 2 * word_rnn_size)
sentences = sentences.sum(dim=1) # (n_sentences, 2 * word_rnn_size)
# Unsort sentences into the original order (INVERSE OF SORTING #2)
_, sent_unsort_ind = sent_sort_ind.sort(dim=0, descending=False) # (n_sentences)
sentences = sentences[sent_unsort_ind] # (n_sentences, 2 * word_rnn_size)
word_alphas = word_alphas[sent_unsort_ind] # (n_sentences, max_sent_len_in_batch)
return sentences, word_alphas语句编码器 (Sentence Encoder)
得到了句子向量表示 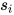 以后,可以用类似的办法获得文档向量:
以后,可以用类似的办法获得文档向量:
![\overrightarrow{h_{i}}=\overrightarrow{GRU}(s_{i}),i\in[1,L]](https://p1-jj.byteimg.com/tos-cn-i-t2oaga2asx/gold-user-assets/2019/1/6/1682333e530586a3~tplv-t2oaga2asx-jj-mark:3024:0:0:0:q75.png)
![\overleftarrow{h_{i}}=\overleftarrow{GRU}(s_{i}),i\in[L,1]](https://p1-jj.byteimg.com/tos-cn-i-t2oaga2asx/gold-user-assets/2019/1/6/1682333e53ad199b~tplv-t2oaga2asx-jj-mark:3024:0:0:0:q75.png)
对于给定的句子 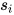 ,相应的句子表示为
,相应的句子表示为
![h_{i}=[\overrightarrow{h_{i}},\overleftarrow{h_{i}}]](https://p1-jj.byteimg.com/tos-cn-i-t2oaga2asx/gold-user-assets/2019/1/6/1682333e53bacc78~tplv-t2oaga2asx-jj-mark:3024:0:0:0:q75.png)
这样,可以获得包含两个方向的上下文信息的表示。
self.sentence_rnn = nn.GRU(2 * word_rnn_size, sentence_rnn_size, num_layers=sentence_rnn_layers,
bidirectional=True, dropout=dropout, batch_first=True)句子级别的 attention
和 word level 的 attention 类似,对于 document,也有一个句子级别的上下文向量 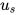 ,来衡量一个句子相对于 document 的重要性。
,来衡量一个句子相对于 document 的重要性。
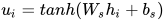
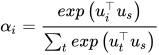
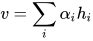
SentenceAttention 部分代码如下:
class SentenceAttention(nn.Module):
"""
The sentence-level attention module.
"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size, emb_size, word_rnn_size, sentence_rnn_size, word_rnn_layers, sentence_rnn_layers,
word_att_size, sentence_att_size, dropout):
"""
:param vocab_size: number of words in the vocabulary of the model
:param emb_size: size of word embeddings
:param word_rnn_size: size of (bidirectional) word-level RNN
:param sentence_rnn_size: size of (bidirectional) sentence-level RNN
:param word_rnn_layers: number of layers in word-level RNN
:param sentence_rnn_layers: number of layers in sentence-level RNN
:param word_att_size: size of word-level attention layer
:param sentence_att_size: size of sentence-level attention layer
:param dropout: dropout
"""
super(SentenceAttention, self).__init__()
# Word-level attention module
self.word_attention = WordAttention(vocab_size, emb_size, word_rnn_size, word_rnn_layers, word_att_size,
dropout)
# Bidirectional sentence-level RNN
self.sentence_rnn = nn.GRU(2 * word_rnn_size, sentence_rnn_size, num_layers=sentence_rnn_layers,
bidirectional=True, dropout=dropout, batch_first=True)
# Sentence-level attention network
self.sentence_attention = nn.Linear(2 * sentence_rnn_size, sentence_att_size)
# Sentence context vector to take dot-product with
self.sentence_context_vector = nn.Linear(sentence_att_size, 1, bias=False)
# this performs a dot product with the linear layer's 1D parameter vector, which is the sentence context vector
# You could also do this with:
# self.sentence_context_vector = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(1, sentence_att_size))
# self.sentence_context_vector.data.uniform_(-0.1, 0.1)
# And then take the dot-product
# Dropout
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, documents, sentences_per_document, words_per_sentence):
"""
Forward propagation.
:param documents: encoded document-level data, a tensor of dimensions (n_documents, sent_pad_len, word_pad_len)
:param sentences_per_document: document lengths, a tensor of dimensions (n_documents)
:param words_per_sentence: sentence lengths, a tensor of dimensions (n_documents, sent_pad_len)
:return: document embeddings, attention weights of words, attention weights of sentences
"""
# Sort documents by decreasing document lengths (SORTING #1)
sentences_per_document, doc_sort_ind = sentences_per_document.sort(dim=0, descending=True)
documents = documents[doc_sort_ind] # (n_documents, sent_pad_len, word_pad_len)
words_per_sentence = words_per_sentence[doc_sort_ind] # (n_documents, sent_pad_len)
# Re-arrange as sentences by removing pad-sentences (DOCUMENTS -> SENTENCES)
sentences, bs = pack_padded_sequence(documents,
lengths=sentences_per_document.tolist(),
batch_first=True)
# (n_sentences, word_pad_len), bs is the effective batch size at each sentence-timestep
# Re-arrange sentence lengths in the same way (DOCUMENTS -> SENTENCES)
words_per_sentence, _ = pack_padded_sequence(words_per_sentence,
lengths=sentences_per_document.tolist(),
batch_first=True)
# (n_sentences), '_' is the same as 'bs' in the earlier step
# Find sentence embeddings by applying the word-level attention module
sentences, word_alphas = self.word_attention(sentences, words_per_sentence)
# (n_sentences, 2 * word_rnn_size), (n_sentences, max_sent_len_in_batch)
sentences = self.dropout(sentences)
(sentences, _), _ = self.sentence_rnn(
PackedSequence(sentences, bs)) # (n_sentences, 2 * sentence_rnn_size), (max(sent_lens))
# Find attention vectors by applying the attention linear layer
att_s = self.sentence_attention(sentences) # (n_sentences, att_size)
att_s = F.tanh(att_s) # (n_sentences, att_size)
# Take the dot-product of the attention vectors with the context vector (i.e. parameter of linear layer)
att_s = self.sentence_context_vector(att_s).squeeze(1) # (n_sentences)
max_value = att_s.max() # scalar, for numerical stability during exponent calculation
att_s = torch.exp(att_s - max_value) # (n_sentences)
# Re-arrange as documents by re-padding with 0s (SENTENCES -> DOCUMENTS)
att_s, _ = pad_packed_sequence(PackedSequence(att_s, bs),
batch_first=True) # (n_documents, max_doc_len_in_batch)
# Calculate softmax values
sentence_alphas = att_s / torch.sum(att_s, dim=1, keepdim=True) # (n_documents, max_doc_len_in_batch)
# Similarly re-arrange sentence-level RNN outputs as documents by re-padding with 0s (SENTENCES -> DOCUMENTS)
documents, _ = pad_packed_sequence(PackedSequence(sentences, bs),
batch_first=True)
# (n_documents, max_doc_len_in_batch, 2 * sentence_rnn_size)
# Find document embeddings
documents = documents * sentence_alphas.unsqueeze(
2) # (n_documents, max_doc_len_in_batch, 2 * sentence_rnn_size)
documents = documents.sum(dim=1) # (n_documents, 2 * sentence_rnn_size)
# Also re-arrange word_alphas (SENTENCES -> DOCUMENTS)
word_alphas, _ = pad_packed_sequence(PackedSequence(word_alphas, bs),
batch_first=True)
# (n_documents, max_doc_len_in_batch, max_sent_len_in_batch)
# Unsort documents into the original order (INVERSE OF SORTING #1)
_, doc_unsort_ind = doc_sort_ind.sort(dim=0, descending=False) # (n_documents)
documents = documents[doc_unsort_ind] # (n_documents, 2 * sentence_rnn_size)
sentence_alphas = sentence_alphas[doc_unsort_ind] # (n_documents, max_doc_len_in_batch)
word_alphas = word_alphas[doc_unsort_ind] # (n_documents, max_doc_len_in_batch, max_sent_len_in_batch)
return documents, word_alphas, sentence_alphas在获得了整篇文章的层次化向量表示之后,就可以使用全连接的 softmax 层进行分类。
最后这部分代码如下:
class HierarchialAttentionNetwork(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_classes, vocab_size, emb_size, word_rnn_size, sentence_rnn_size, word_rnn_layers,
sentence_rnn_layers, word_att_size, sentence_att_size, dropout=0.5):
"""
:param n_classes: number of classes
:param vocab_size: number of words in the vocabulary of the model
:param emb_size: size of word embeddings
:param word_rnn_size: size of (bidirectional) word-level RNN
:param sentence_rnn_size: size of (bidirectional) sentence-level RNN
:param word_rnn_layers: number of layers in word-level RNN
:param sentence_rnn_layers: number of layers in sentence-level RNN
:param word_att_size: size of word-level attention layer
:param sentence_att_size: size of sentence-level attention layer
:param dropout: dropout
"""
super(HierarchialAttentionNetwork, self).__init__()
self.sentence_attention = SentenceAttention(vocab_size, emb_size, word_rnn_size, sentence_rnn_size,
word_rnn_layers, sentence_rnn_layers, word_att_size,
sentence_att_size, dropout)
# Classifier
self.fc = nn.Linear(2 * sentence_rnn_size, n_classes)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, documents, sentences_per_document, words_per_sentence):
"""
Forward propagation.
:param documents: encoded document-level data, a tensor of dimensions (n_documents, sent_pad_len, word_pad_len)
:param sentences_per_document: document lengths, a tensor of dimensions (n_documents)
:param words_per_sentence: sentence lengths, a tensor of dimensions (n_documents, sent_pad_len)
:return: class scores, attention weights of words, attention weights of sentences
"""
# (n_documents, 2 * sentence_rnn_size)
# (n_documents, max_doc_len_in_batch, max_sent_len_in_batch)
# (n_documents, max_doc_len_in_batch)
document_embeddings, word_alphas, sentence_alphas = self.sentence_attention(documents, sentences_per_document, words_per_sentence)
# (n_documents, n_classes)
scores = self.fc(self.dropout(document_embeddings))
return scores, word_alphas, sentence_alphas参考资料
滨城之恋:Hierarchical Attention Networks for Document Classification 阅读笔记