
微信公众号:深广大数据Club关注可了解更多大数据相关的技术资讯。问题或建议,请公众号留言;如果你觉得深广大数据Club对你有帮助,欢迎点击右上角转发朋友圈
本文主要讲述JobGraph的生成过程,JobGraph是通过streamGraph.getJobGraph生成。建议看这这篇文章之前先看下前一篇文章Flink源码解析 | 从Example出发:理解StreamGraph的生成过程
从上一篇文章中,我们了解了StreamGraph的生成过程,现在我们接着讲解JobGraph的生成。
先来看下StreamGraph与JobGraph的转换图。
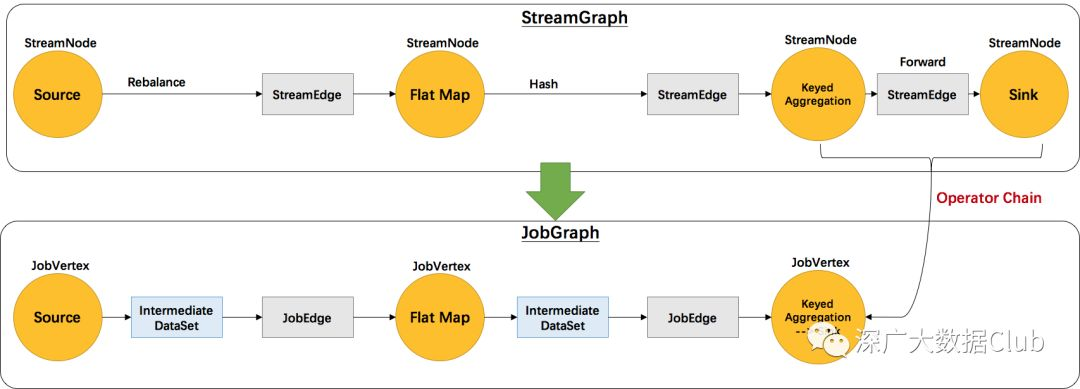
StreamGraph 和 JobGraph 都是在 Client 端生成的,我们可以在 IDE 中通过断点调试观察 StreamGraph 和 JobGraph 的生成过程。
JobGraph的生成流程
StreamGraph生成之后,代码中通过streamGraph.getJobGraph()来获取JobGraph实例。
JobGraph jobGraph = streamGraph.getJobGraph();jobGraph.setAllowQueuedScheduling(true);getJobGraph()方法中,调用StreamingJobGraphGenerator.createJobGraph()方法来创建JobGraph
public JobGraph getJobGraph(@Nullable JobID jobID) { // temporarily forbid checkpointing for iterative jobs if (isIterative() && checkpointConfig.isCheckpointingEnabled() && !checkpointConfig.isForceCheckpointing()) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException( "Checkpointing is currently not supported by default for iterative jobs, as we cannot guarantee exactly once semantics. " + "State checkpoints happen normally, but records in-transit during the snapshot will be lost upon failure. " + "\nThe user can force enable state checkpoints with the reduced guarantees by calling: env.enableCheckpointing(interval,true)"); } return StreamingJobGraphGenerator.createJobGraph(this, jobID);}createJobGraph方法中会实例化一个StreamingJobGraphGenerator的实例,创建实例时传入之前生成的streamGraph和jobId,再调用createJobGraph()方法创建
public static JobGraph createJobGraph(StreamGraph streamGraph, @Nullable JobID jobID) { return new StreamingJobGraphGenerator(streamGraph, jobID).createJobGraph();}我们来看看StreamingJobGraphGenerator的构造方法做了哪些事情。
private StreamingJobGraphGenerator(StreamGraph streamGraph, @Nullable JobID jobID) { this.streamGraph = streamGraph; this.defaultStreamGraphHasher = new StreamGraphHasherV2(); this.legacyStreamGraphHashers = Arrays.asList(new StreamGraphUserHashHasher()); this.jobVertices ID:JobVertex = new HashMap<>(); this.builtVertices = new HashSet<>(); this.chainedConfigs = new HashMap<>(); this.vertexConfigs = new HashMap<>(); this.chainedNames = new HashMap<>(); this.chainedMinResources = new HashMap<>(); this.chainedPreferredResources = new HashMap<>(); this.physicalEdgesInOrder = new ArrayList<>(); jobGraph = new JobGraph(jobID, streamGraph.getJobName());}构造方法中创建了一系列hashmap后,创建了一个基础JobGraph对象,此处只给JobGraph的jobId以及JobName做了赋值,其他的信息是在createJobGraph()方法中进行填充。
HashMap介绍
-
jobVertices id -> JobVertex
-
builtVertices 已构建的JobVertex的ID集合
-
chainedConfigs 保存chain信息,部署时用来构建 OperatorChain,startNodeId -> (currentNodeId -> StreamConfig)
-
vertexConfigs 所有节点的配置信息,id -> StreamConfig
-
chainedNames 保存每个节点的名字,id -> chainedName
-
chainedMinResources 保存每个节点的最小资源 id -> ResourceSpec
-
chainedPreferredResources 保存每个节点的首选资源 id -> ResourceSpec
-
physicalEdgesInOrder 物理边集合(排除了chain内部的边), 按创建顺序排序
到此就是创建JobGraph的大体流程。不过我们再更深入一步来了解createJobGraph()方法的详细内容。
CreateJobGraph分解
private JobGraph createJobGraph() { // make sure that all vertices start immediately //streaming 模式下,调度模式是所有节点(vertices)一起启动 jobGraph.setScheduleMode(ScheduleMode.EAGER); // Generate deterministic hashes for the nodes in order to identify them across // submission iff they didn't change. // 广度优先遍历 StreamGraph 并且为每个SteamNode生成hash id, // 保证如果提交的拓扑没有改变,则每次生成的hash都是一样的 Map<Integer, byte[]> hashes = defaultStreamGraphHasher.traverseStreamGraphAndGenerateHashes(streamGraph); // 为向后兼容性生成遗留版本Hash List<Map<Integer, byte[]>> legacyHashes = new ArrayList<>(legacyStreamGraphHashers.size()); for (StreamGraphHasher hasher : legacyStreamGraphHashers) { legacyHashes.add(hasher.traverseStreamGraphAndGenerateHashes(streamGraph)); } //用于保存遗留hash与当前primary之间的对应关系 Map<Integer, List<Tuple2<byte[], byte[]>>> chainedOperatorHashes = new HashMap<>(); // 最重要的函数,生成JobVertex,JobEdge等,并尽可能地将多个节点chain在一起 setChaining(hashes, legacyHashes, chainedOperatorHashes); // 将每个JobVertex的入边集合也序列化到该JobVertex的StreamConfig中 // (出边集合已经在setChaining的时候写入了) setPhysicalEdges(); // 根据group name,为每个 JobVertex 指定所属的 SlotSharingGroup // 以及针对 Iteration的头尾设置 CoLocationGroup setSlotSharingAndCoLocation(); // 配置checkpoint configureCheckpointing(); //为JobGraph添加用户Artifact Entries JobGraphGenerator.addUserArtifactEntries(streamGraph.getEnvironment().getCachedFiles(), jobGraph); // set the ExecutionConfig last when it has been finalized try { //从streamGraph获取Execution并设置到jobGraph中 jobGraph.setExecutionConfig(streamGraph.getExecutionConfig()); } catch (IOException e) { throw new IllegalConfigurationException("Could not serialize the ExecutionConfig." + "This indicates that non-serializable types (like custom serializers) were registered"); } return jobGraph;}我们先来看下调度模式,ScheduleMode中包含两种模式:LAZY_FROM_SOURCES和EAGER。
-
LAZY_FROM_SOURCES 延迟启动
-
EAGER 立即全部启动
public enum ScheduleMode { /** 从源开始延迟地安排任务。一旦下游任务的输入数据准备好,下游任务就会启动 */ LAZY_FROM_SOURCES, /** 调度所有任务立即启动. */ EAGER; /** * Returns whether we are allowed to deploy consumers lazily. */ public boolean allowLazyDeployment() { return this == LAZY_FROM_SOURCES; }}Chain创建过程
接下来我们重点分析下setChaining方法
private void setChaining(Map<Integer, byte[]> hashes, List<Map<Integer, byte[]>> legacyHashes, Map<Integer, List<Tuple2<byte[], byte[]>>> chainedOperatorHashes) { for (Integer sourceNodeId : streamGraph.getSourceIDs()) { createChain(sourceNodeId, sourceNodeId, hashes, legacyHashes, 0, chainedOperatorHashes); }}private List<StreamEdge> createChain( Integer startNodeId, Integer currentNodeId, Map<Integer, byte[]> hashes, List<Map<Integer, byte[]>> legacyHashes, int chainIndex, Map<Integer, List<Tuple2<byte[], byte[]>>> chainedOperatorHashes) { if (!builtVertices.contains(startNodeId)) { // 过渡用的出边集合, 用来生成最终的JobEdge, 注意不包括 chain 内部的边 List<StreamEdge> transitiveOutEdges = new ArrayList<StreamEdge>(); List<StreamEdge> chainableOutputs = new ArrayList<StreamEdge>(); List<StreamEdge> nonChainableOutputs = new ArrayList<StreamEdge>(); // 将当前节点的出边分成 chainable 和 nonChainable 两类 for (StreamEdge outEdge : streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId).getOutEdges()) { if (isChainable(outEdge, streamGraph)) { chainableOutputs.add(outEdge); } else { nonChainableOutputs.add(outEdge); } } //递归调用 for (StreamEdge chainable : chainableOutputs) { transitiveOutEdges.addAll( createChain(startNodeId, chainable.getTargetId(), hashes, legacyHashes, chainIndex + 1, chainedOperatorHashes)); } for (StreamEdge nonChainable : nonChainableOutputs) { transitiveOutEdges.add(nonChainable); createChain(nonChainable.getTargetId(), nonChainable.getTargetId(), hashes, legacyHashes, 0, chainedOperatorHashes); } List<Tuple2<byte[], byte[]>> operatorHashes = chainedOperatorHashes.computeIfAbsent(startNodeId, k -> new ArrayList<>()); byte[] primaryHashBytes = hashes.get(currentNodeId); // 循环填充primaryHash与legacyHash的对应关系 for (Map<Integer, byte[]> legacyHash : legacyHashes) { operatorHashes.add(new Tuple2<>(primaryHashBytes, legacyHash.get(currentNodeId))); } // 生成当前节点的显示名,如:"Keyed Aggregation -> Sink: Unnamed" chainedNames.put(currentNodeId, createChainedName(currentNodeId, chainableOutputs)); //设置当前节点的最小资源 chainedMinResources.put(currentNodeId, createChainedMinResources(currentNodeId, chainableOutputs)); //设置当前节点的首选资源 chainedPreferredResources.put(currentNodeId, createChainedPreferredResources(currentNodeId, chainableOutputs)); // 如果当前节点是起始节点, 则直接创建 JobVertex 并返回 StreamConfig, 否则先创建一个空的 StreamConfig // createJobVertex 函数就是根据 StreamNode 创建对应的 JobVertex, 并返回了空的 StreamConfig StreamConfig config = currentNodeId.equals(startNodeId) ? createJobVertex(startNodeId, hashes, legacyHashes, chainedOperatorHashes) : new StreamConfig(new Configuration()); // 设置 JobVertex 的 StreamConfig, 基本上是序列化 StreamNode 中的配置到 StreamConfig 中. // 其中包括 序列化器, StreamOperator, Checkpoint 等相关配置 setVertexConfig(currentNodeId, config, chainableOutputs, nonChainableOutputs); if (currentNodeId.equals(startNodeId)) { // 如果是chain的起始节点。(不是chain中的节点,也会被标记成 chain start) config.setChainStart(); config.setChainIndex(0); config.setOperatorName(streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId).getOperatorName()); // 我们也会把物理出边写入配置, 部署时会用到 config.setOutEdgesInOrder(transitiveOutEdges); config.setOutEdges(streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId).getOutEdges()); // 将当前节点(headOfChain)与所有出边相连 for (StreamEdge edge : transitiveOutEdges) { // 通过StreamEdge构建出JobEdge,创建IntermediateDataSet,用来将JobVertex和JobEdge相连 connect(startNodeId, edge); } // 将chain中所有子节点的StreamConfig写入到 headOfChain 节点的 CHAINED_TASK_CONFIG 配置中 config.setTransitiveChainedTaskConfigs(chainedConfigs.get(startNodeId)); } else { // 如果是 chain 中的子节点 Map<Integer, StreamConfig> chainedConfs = chainedConfigs.get(startNodeId); if (chainedConfs == null) { chainedConfigs.put(startNodeId, new HashMap<Integer, StreamConfig>()); } config.setChainIndex(chainIndex); StreamNode node = streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId); config.setOperatorName(node.getOperatorName()); // 将当前节点的StreamConfig添加到该chain的config集合中 chainedConfigs.get(startNodeId).put(currentNodeId, config); } config.setOperatorID(new OperatorID(primaryHashBytes)); if (chainableOutputs.isEmpty()) { config.setChainEnd(); } // 返回连往chain外部的出边集合 return transitiveOutEdges; } else { return new ArrayList<>(); }}StreamGraph以及JobGraph都是在客户端生成的。客户端提交任务时发送给JobManager和TaskManager的则是一个个JobVerex,每一个每个 JobVertex 都会对应一个可序列化的 StreamConfig。TaskManager运行Task任务时,会将序列化的配置信息进行反序列化,其中就包括了含有用户代码的StreamOperator。
此处setChainning会对source调用 createChain方法。createChain方法递归调用下游节点,构建出node chains.具体的流程如下:
-
createChain会分析当前节点的出边,根据Operator Chains中的chainable条件,将出边分成chainalbe和noChainable两类,并分别递归调用自身方法。
//递归调用for (StreamEdge chainable : chainableOutputs) { transitiveOutEdges.addAll( createChain(startNodeId, chainable.getTargetId(), hashes, legacyHashes, chainIndex + 1, chainedOperatorHashes));}-
配置operatorHashes用于故障恢复
-
设置当前节点资源
-
将StreamNode中的配置信息序列化到StreamConfig中
-
判断是否为chain子节点
-
是,将StreamConfig添加到该chain的config集合中
-
否,构建 JobVertex 和 JobEdge相连
-
一个node chains,除了 headOfChain node会生成对应的 JobVertex,其余的nodes都是以序列化的形式写入到StreamConfig中,并保存到headOfChain的 CHAINED_TASK_CONFIG 配置项中
public void setTransitiveChainedTaskConfigs(Map<Integer, StreamConfig> chainedTaskConfigs) { try { InstantiationUtil.writeObjectToConfig(chainedTaskConfigs, this.config, CHAINED_TASK_CONFIG); } catch (IOException e) { throw new StreamTaskException("Could not serialize configuration.", e); }}JobVerex创建过程
private StreamConfig createJobVertex( Integer streamNodeId, Map<Integer, byte[]> hashes, List<Map<Integer, byte[]>> legacyHashes, Map<Integer, List<Tuple2<byte[], byte[]>>> chainedOperatorHashes) { JobVertex jobVertex; StreamNode streamNode = streamGraph.getStreamNode(streamNodeId); byte[] hash = hashes.get(streamNodeId); if (hash == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot find node hash. " + "Did you generate them before calling this method?"); } JobVertexID jobVertexId = new JobVertexID(hash); List<JobVertexID> legacyJobVertexIds = new ArrayList<>(legacyHashes.size()); for (Map<Integer, byte[]> legacyHash : legacyHashes) { hash = legacyHash.get(streamNodeId); if (null != hash) { legacyJobVertexIds.add(new JobVertexID(hash)); } } List<Tuple2<byte[], byte[]>> chainedOperators = chainedOperatorHashes.get(streamNodeId); List<OperatorID> chainedOperatorVertexIds = new ArrayList<>(); List<OperatorID> userDefinedChainedOperatorVertexIds = new ArrayList<>(); if (chainedOperators != null) { for (Tuple2<byte[], byte[]> chainedOperator : chainedOperators) { chainedOperatorVertexIds.add(new OperatorID(chainedOperator.f0)); userDefinedChainedOperatorVertexIds.add(chainedOperator.f1 != null ? new OperatorID(chainedOperator.f1) : null); } } //如用户自定义了UserFunction且属于InputFormatSourceFunction,则通过InputFormatVertex创建JobVertex if (streamNode.getInputFormat() != null) { jobVertex = new InputFormatVertex( chainedNames.get(streamNodeId), jobVertexId, legacyJobVertexIds, chainedOperatorVertexIds, userDefinedChainedOperatorVertexIds); TaskConfig taskConfig = new TaskConfig(jobVertex.getConfiguration()); taskConfig.setStubWrapper(new UserCodeObjectWrapper<Object>(streamNode.getInputFormat())); } else { jobVertex = new JobVertex( chainedNames.get(streamNodeId), jobVertexId, legacyJobVertexIds, chainedOperatorVertexIds, userDefinedChainedOperatorVertexIds); } jobVertex.setResources(chainedMinResources.get(streamNodeId), chainedPreferredResources.get(streamNodeId)); jobVertex.setInvokableClass(streamNode.getJobVertexClass()); //设置并行度 int parallelism = streamNode.getParallelism(); if (parallelism > 0) { jobVertex.setParallelism(parallelism); } else { parallelism = jobVertex.getParallelism(); } //设置最大并行度 jobVertex.setMaxParallelism(streamNode.getMaxParallelism()); if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) { LOG.debug("Parallelism set: {} for {}", parallelism, streamNodeId); } //设置streamNodeID与jobVertex的映射 jobVertices.put(streamNodeId, jobVertex); //将streamNodeId添加到已构建列表 builtVertices.add(streamNodeId); //将jobVertex添加到JobGraph中 jobGraph.addVertex(jobVertex); return new StreamConfig(jobVertex.getConfiguration()); }创建流程其实是将StreamNode转换为JobVerex的过程。主要内容在中间创建JobVerex段,判断用户是否自定义UserFunction且属于InputFormatSourceFunction,是,则通过InputFormatVertex创建JobVertex;否,则通过JobVertex构造方法创建。
public JobVertex(String name, JobVertexID primaryId, List<JobVertexID> alternativeIds, List<OperatorID> operatorIds, List<OperatorID> alternativeOperatorIds) { Preconditions.checkArgument(operatorIds.size() == alternativeOperatorIds.size()); this.name = name == null ? DEFAULT_NAME : name; this.id = primaryId == null ? new JobVertexID() : primaryId; //JobVertex的可选id this.idAlternatives.addAll(alternativeIds); // 该JobVertex中包含的所有运算符ID this.operatorIDs.addAll(operatorIds); //该JobVertex中包含的所有运算符的备选ID。 this.operatorIdsAlternatives.addAll(alternativeOperatorIds); }注意:这里的idAlternatives仅为向后兼容版本< 1.3而保留。将在未来被移除。目前在新版本已经没有使用了。
总结
本文主要对 Flink 中将 StreamGraph 转变成 JobGraph 的核心源码进行了分析。根据开头所给出的转换图片结合代码,整理如下:
-
StreamNode转成JobVertex
-
StreamEdge转成JobEdge
-
JobEdge和JobVertex之间创建IntermediateDataSet 来连接
最后一步是关键所在。感兴趣的童鞋可以进行代码调试,更清晰的了解转换的过程。
系列相关文章
Flink源码解析 | 从Example出发理解Flink-Flink启动
Flink源码解析 | 从Example出发:读懂本地任务执行流程
Flink源码解析 | 从Example出发:读懂集群任务执行流程
Flink源码解析 | 从Example出发:读懂Flink On Yarn任务执行流程
Flink源码解析 | 从Example出发:读懂start-start-shell.sh任务执行流程
Flink源码解析 | 从Example出发:理解StreamGraph的生成过程
关注公众号

友情链接
HBase技术社区
