
微信公众号:深广大数据Club关注可了解更多大数据相关资讯。问题或建议,请公众号留言;如果你觉得深广大数据Club对你有帮助,欢迎转发朋友圈
本文主要讲述Apache Flink流处理过程中,StreamGraph的生成过程。
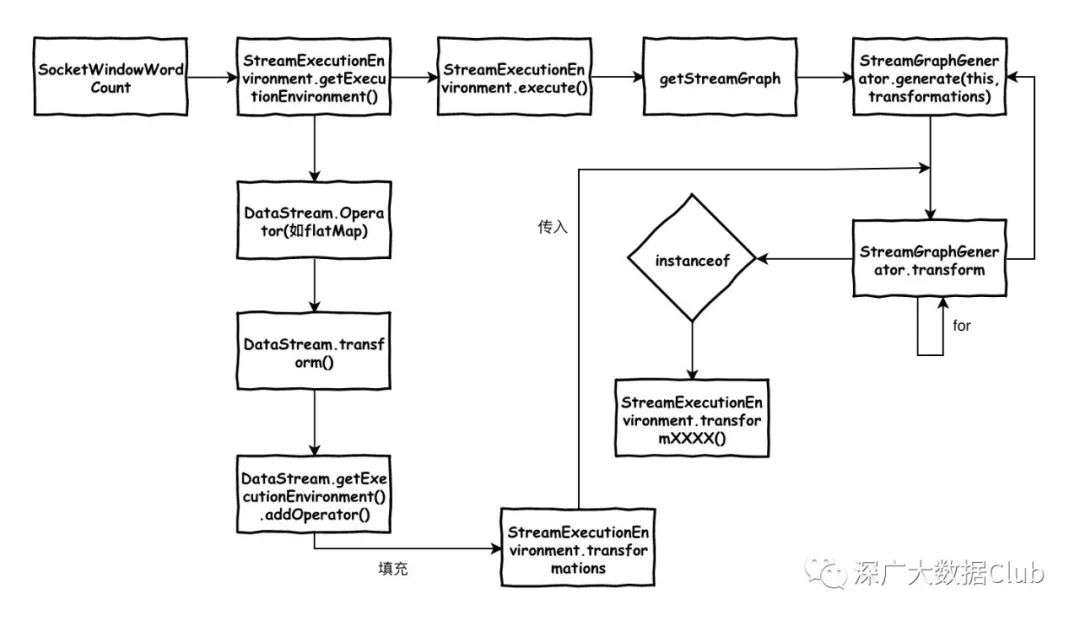
以上这张图片为生成StreamGraph的代码调用流程图,接下来我们还是从example入手来学习理解StreamGraph的生成过程吧。
启动环境
这里我们同样从SocketWindowWordCount入手。我们这里先将Apache Flink启动起来,然后将example部署到Flink上运行。
至于如何启动的过程我们这里就不做赘述,详细的可以看本地部署的文章。《Apache Flink本地安装及Example运行》
从前面几篇文章我们可以了解到。Apache Flink要运行首先需要创建对应的Environment,stream对应的StreamExecutionEnvironment,batch的对应的ExecutionEnvironment。
SocketWindowWordCount
由于我们这里运行的是local模式,所以SocketWindowWordCount的Environment为LocalStreamEnvironment
// get the execution environmentfinal StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();...env.execute("Socket Window WordCount");通过LocalStreamEnvironment.execute()方法来执行任务。
public JobExecutionResult execute(String jobName) throws Exception { // transform the streaming program into a JobGraph StreamGraph streamGraph = getStreamGraph(); streamGraph.setJobName(jobName); ...}这里我们关注的是StreamGraph,所以execute()方法中后续的内容这里就不讲,在后续的文章中会做进一步讲解。
execute方法调用getStreamGraph()获取StreamGraph实例。
public StreamGraph getStreamGraph() { if (transformations.size() <= 0) { throw new IllegalStateException("No operators defined in streaming topology. Cannot execute."); } return StreamGraphGenerator.generate(this, transformations);}getStreamGraph()方法调用StreamGraphGenerator.generate()生成StreamGraph。从这里开始就是我们重点要讲的内容。
StreamGraphGenerator.generate()包含两个参数。
-
this //指定Environment为当前的LocalStreamEnvironment
-
transformations
检查LocalStreamEnvironment的父类StreamExecutionEnvironment可以发现,在StreamExecutionEnvironment变量中包含transformations,是一个List类型。
protected final List<StreamTransformation<?>> transformations = new ArrayList<>();那这个List在哪里被填充?
Transformations列表填充
我们回到SocketWindowWordCount,从这里入手来理解这个List是怎么被填充的。
DataStream<WordWithCount> windowCounts = text .flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<String, WordWithCount>() { @Override public void flatMap(String value, Collector<WordWithCount> out) { for (String word : value.split("\\s")) { out.collect(new WordWithCount(word, 1L)); } } }) .keyBy("word") .timeWindow(Time.seconds(5)) .reduce(new ReduceFunction<WordWithCount>() { @Override public WordWithCount reduce(WordWithCount a, WordWithCount b) { eturn new WordWithCount(a.word, a.count + b.count); } });先看text.flatMap()
public <R> SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> flatMap(FlatMapFunction<T, R> flatMapper) { TypeInformation<R> outType = TypeExtractor.getFlatMapReturnTypes(clean(flatMapper), getType(), Utils.getCallLocationName(), true); return transform("Flat Map", outType, new StreamFlatMap<>(clean(flatMapper)));}flatMap()方法调用transform()方法,传入operatorName="Flat Map"
public <R> SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> transform(String operatorName, TypeInformation<R> outTypeInfo, OneInputStreamOperator<T, R> operator) { // read the output type of the input Transform to coax out errors about MissingTypeInfo transformation.getOutputType(); OneInputTransformation<T, R> resultTransform = new OneInputTransformation<>( this.transformation, operatorName, operator, outTypeInfo, environment.getParallelism()); @SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" }) SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> returnStream = new SingleOutputStreamOperator(environment, resultTransform); getExecutionEnvironment().addOperator(resultTransform); return returnStream; }-
获取resultTransform对象
-
通过environment、resultTransform生成returnStream
-
getExecutionEnvironment()获取Environment,此处获取的是LocalStreamEnvironment
-
返回
重点在第三步:getExecutionEnvironment().addOperator(resultTransform)
@Internalpublic void addOperator(StreamTransformation<?> transformation) { Preconditions.checkNotNull(transformation, "transformation must not be null."); this.transformations.add(transformation);}transformations列表的填充就是通过Environment的addOperator方法进行数据填充。在execute方法执行之前,会将用户编写的DataStream操作代码转换为一个transformations列表。在execute执行的时候传入transformations生成SteamGraph。
StreamGraphGenerator
接下来我们继续看StreamGraphGenerator.generate()的内容
private StreamGraph generateInternal(List<StreamTransformation<?>> transformations) { for (StreamTransformation<?> transformation: transformations) { transform(transformation); } return streamGraph;}方法主体是一个for循环,循环遍历transformations列表,并将单项transformation传入transform方法。
private Collection<Integer> transform(StreamTransformation<?> transform) { if (alreadyTransformed.containsKey(transform)) { return alreadyTransformed.get(transform); } LOG.debug("Transforming " + transform); if (transform.getMaxParallelism() <= 0) { // if the max parallelism hasn't been set, then first use the job wide max parallelism // from theExecutionConfig. int globalMaxParallelismFromConfig = env.getConfig().getMaxParallelism(); if (globalMaxParallelismFromConfig > 0) { transform.setMaxParallelism(globalMaxParallelismFromConfig); } } // call at least once to trigger exceptions about MissingTypeInfo transform.getOutputType(); Collection<Integer> transformedIds; if (transform instanceof OneInputTransformation<?, ?>) { transformedIds = transformOneInputTransform((OneInputTransformation<?, ?>) transform); } else if (transform instanceof TwoInputTransformation<?, ?, ?>) { transformedIds = transformTwoInputTransform((TwoInputTransformation<?, ?, ?>) transform); } else if (transform instanceof SourceTransformation<?>) { transformedIds = transformSource((SourceTransformation<?>) transform); } else if (transform instanceof SinkTransformation<?>) { transformedIds = transformSink((SinkTransformation<?>) transform); } else if (transform instanceof UnionTransformation<?>) { transformedIds = transformUnion((UnionTransformation<?>) transform); } else if (transform instanceof SplitTransformation<?>) { transformedIds = transformSplit((SplitTransformation<?>) transform); } else if (transform instanceof SelectTransformation<?>) { transformedIds = transformSelect((SelectTransformation<?>) transform); } else if (transform instanceof FeedbackTransformation<?>) { transformedIds = transformFeedback((FeedbackTransformation<?>) transform); } else if (transform instanceof CoFeedbackTransformation<?>) { transformedIds = transformCoFeedback((CoFeedbackTransformation<?>) transform); } else if (transform instanceof PartitionTransformation<?>) { transformedIds = transformPartition((PartitionTransformation<?>) transform); } else if (transform instanceof SideOutputTransformation<?>) { transformedIds = transformSideOutput((SideOutputTransformation<?>) transform); } else { throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown transformation: " + transform); } // need this check because the iterate transformation adds itself before // transforming the feedback edges if (!alreadyTransformed.containsKey(transform)) { alreadyTransformed.put(transform, transformedIds); } if (transform.getBufferTimeout() >= 0) { streamGraph.setBufferTimeout(transform.getId(), transform.getBufferTimeout()); } if (transform.getUid() != null) { streamGraph.setTransformationUID(transform.getId(), transform.getUid()); } if (transform.getUserProvidedNodeHash() != null) { streamGraph.setTransformationUserHash(transform.getId(), transform.getUserProvidedNodeHash()); } if (transform.getMinResources() != null && transform.getPreferredResources() != null) { streamGraph.setResources(transform.getId(), transform.getMinResources(), transform.getPreferredResources()); } return transformedIds; }transform()根据传入的transform的类型不同调用不同的transformXXX方法并返回transformedIds,并添加到transformedIds列表中,最终返回给上一层。
相关文章
《Flink源码解析 | 从Example出发:读懂本地任务执行流程》
《Flink源码解析 | 从Example出发:读懂集群任务执行流程》
《Flink源码解析 | 从Example出发:读懂Flink On Yarn任务执行流程》
《Flink源码解析 | 从Example出发:读懂start-start-shell.sh任务执行流程》
关注公众号

友情链接
HBase技术社区
