简介
Trie是一种用来高效存储字符串以及搜索字符串的结构。当我们使用一般的平衡查找二叉树来完成这个任务时,一般的时间复杂度为M*log(N), 其中M为字符串的长度,N为字符串的数量。而当我们用Trie的时候,复杂度可以降到O(M).
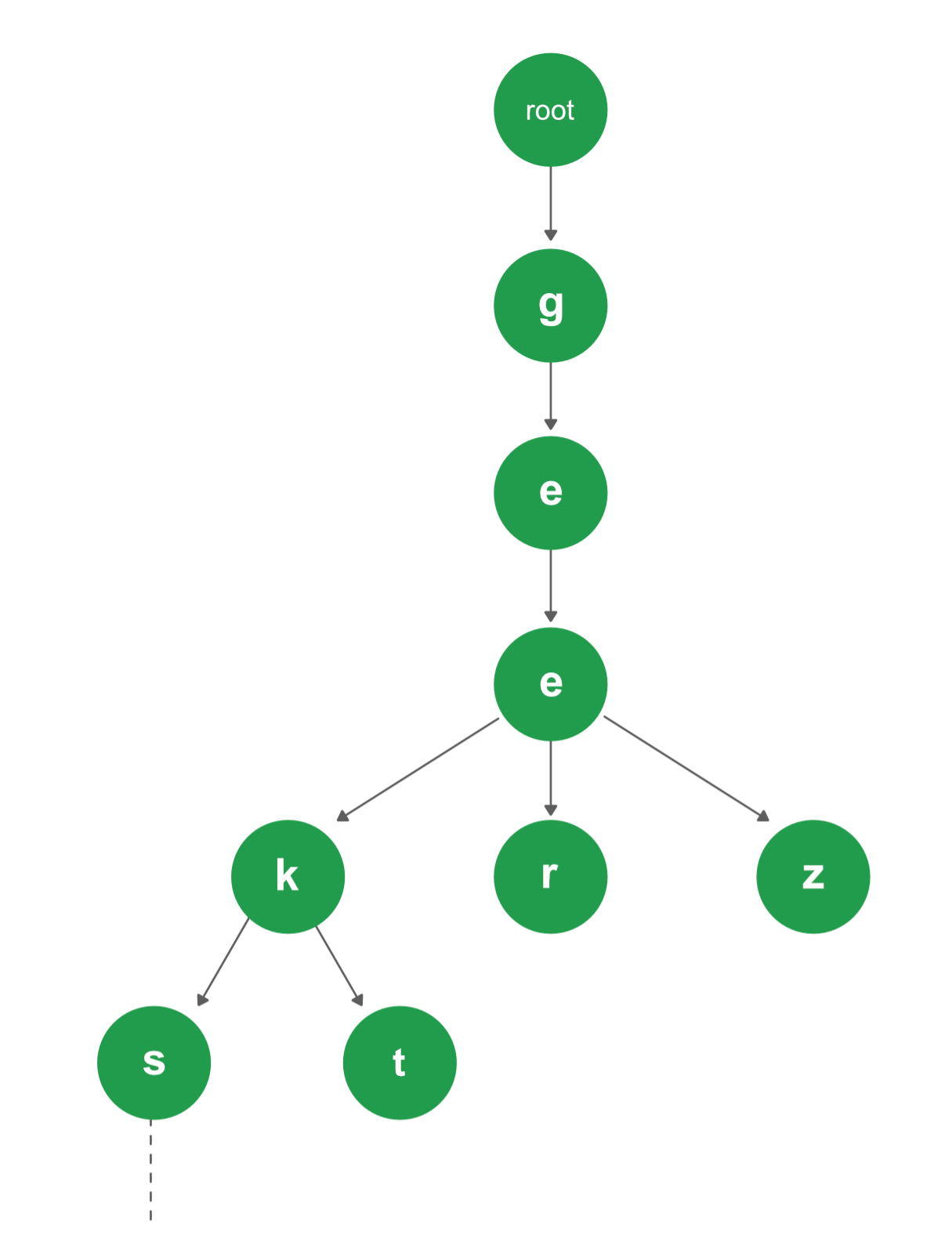
Trie的ADT
// Trie node
struct TrieNode
{
struct TrieNode *children[ALPHABET_SIZE];
// isEndOfWord is true if the node
// represents end of a word
bool isEndOfWord;
};
isEndOfWord的布尔值用以指示字符串末尾的那个char.
Trie的插入
直接插入children的数组,如果不存在这个char则新建一个TrieNode, 如果已经是末尾字符就把isEndOfWord设为True.
Trie的搜索
自顶向下的搜索,通过isEndOfWord来判断命中情况.
Java实现(来自Leetcode)
class TrieNode {
// R links to node children
private TrieNode[] links;
private final int R = 26;
private boolean isEnd;
public TrieNode() {
links = new TrieNode[R];
}
public boolean containsKey(char ch) {
return links[ch -'a'] != null;
}
public TrieNode get(char ch) {
return links[ch -'a'];
}
public void put(char ch, TrieNode node) {
links[ch -'a'] = node;
}
public void setEnd() {
isEnd = true;
}
public boolean isEnd() {
return isEnd;
}
}
class Trie {
private TrieNode root;
public Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
// Inserts a word into the trie.
public void insert(String word) {
TrieNode node = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char currentChar = word.charAt(i);
if (!node.containsKey(currentChar)) {
node.put(currentChar, new TrieNode());
}
node = node.get(currentChar);
}
node.setEnd();
}
// search a prefix or whole key in trie and
// returns the node where search ends
private TrieNode searchPrefix(String word) {
TrieNode node = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char curLetter = word.charAt(i);
if (node.containsKey(curLetter)) {
node = node.get(curLetter);
} else {
return null;
}
}
return node;
}
// Returns if the word is in the trie.
public boolean search(String word) {
TrieNode node = searchPrefix(word);
return node != null && node.isEnd();
}
// Returns if there is any word in the trie
// that starts with the given prefix.
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
TrieNode node = searchPrefix(prefix);
return node != null;
}
}
实例1: LeetCode 211
class TrieNode(object):
def __init__(self):
self.trienode = {}
self.end = False
def containsKey(self, ch):
return self.trienode.get(ch) != None
class WordDictionary:
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
"""
self.root = TrieNode()
def addWord(self, word):
"""
Adds a word into the data structure.
:type word: str
:rtype: void
"""
start = self.root
for i in word:
if(not start.containsKey(i)):
start.trienode[i] = TrieNode()
start = start.trienode[i]
start.end = True
# def searchPrefix(self, word):
# """
# Returns true if the prefix is included in the data structure.
# :type word:str
# :rtype: str
# """
def search(self, word, curr = None):
"""
Returns if the word is in the data structure. A word could contain the dot character '.' to represent any one letter.
:type word: str
:rtype: bool
"""
if not curr:
curr = self.root
for i, c in enumerate(word):
is_last_char = i == len(word) - 1
if c == ".":
if is_last_char:
return self.wildcard_terminate(curr)
else:
return self.wildcard_recursive(word[i+1:], curr)
else:
if not curr.containsKey(c):
return False
curr = curr.trienode[c]
return curr.end == True
def wildcard_recursive(self, word, node):
return any(map(lambda x: self.search(word, x), node.trienode.values()))
def wildcard_terminate(self, node):
return any(map(lambda x: x.end, node.trienode.values()))
# Your WordDictionary object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = WordDictionary()
# obj.addWord(word)
# param_2 = obj.search(word)