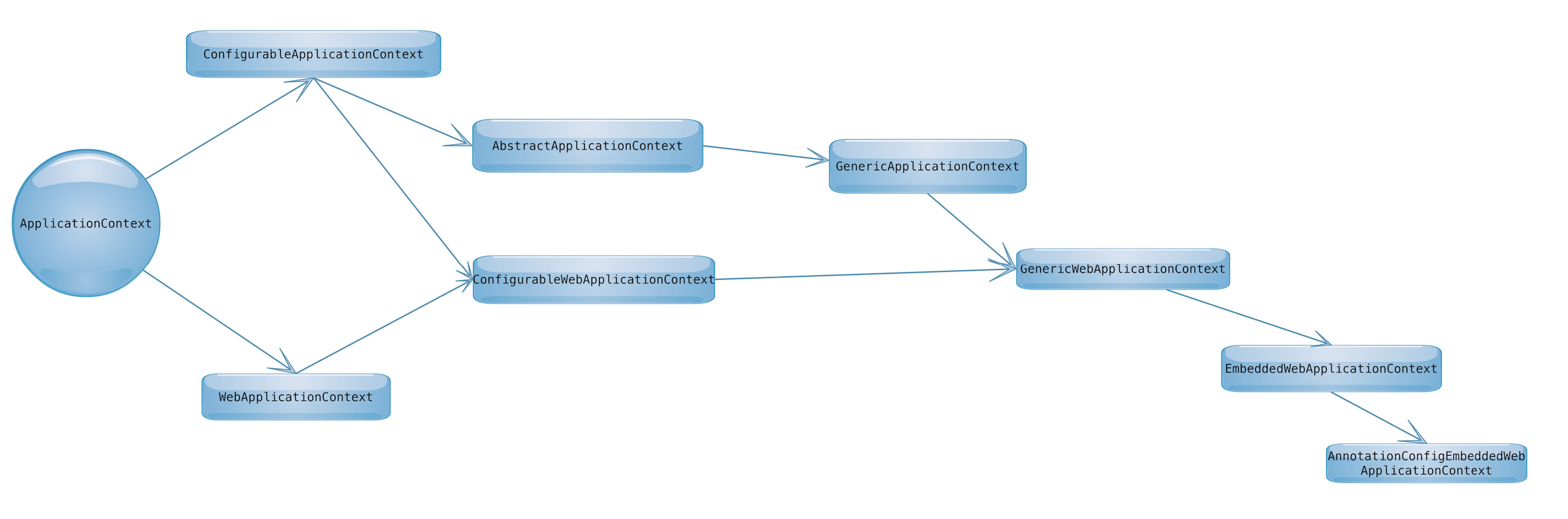
applicationContext家族
applicationContext家族绝对是spring大剧场的核心成员,spring的几大核心特性都涉及到的applicationContext,spring官网明白的写着applicationContext所能做的事情,如下
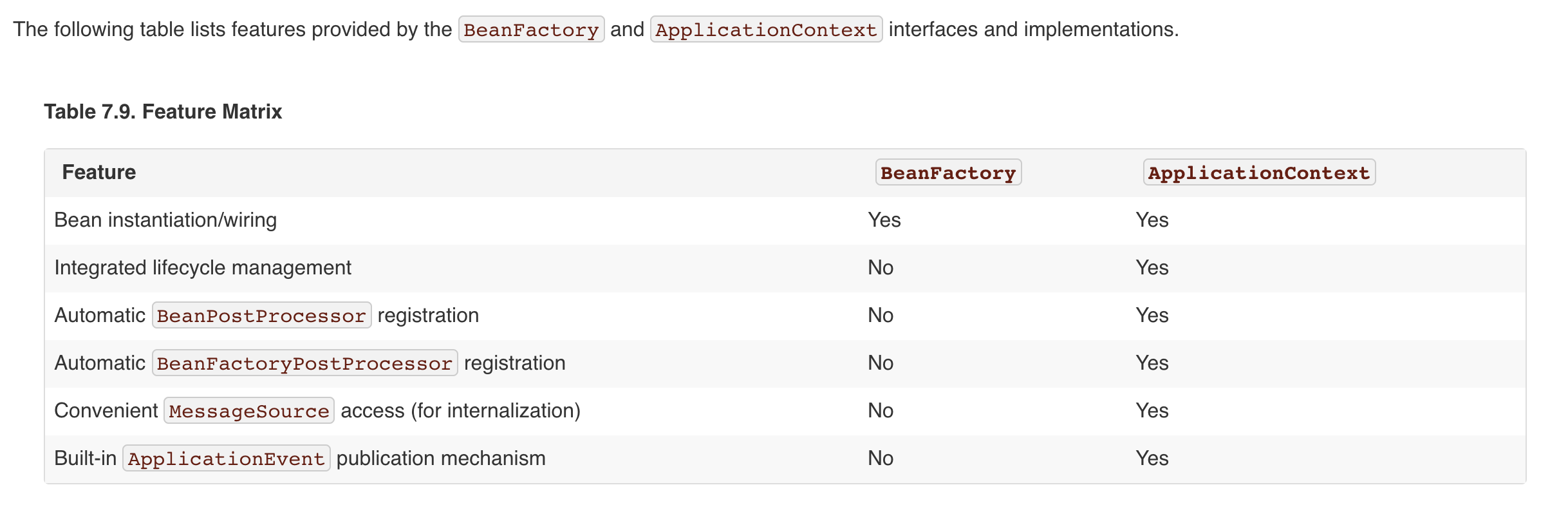
applicationContext家族绝对是中原第一大家族,分支众多,盘根错杂。ApplicationContext类是其家族族长,排名第一位。下面给出applicationContext家族图谱,借此试图缕清applicationContext家族,家族成员间的关系如图谱所示,主要成员的各自功能下面一一说来
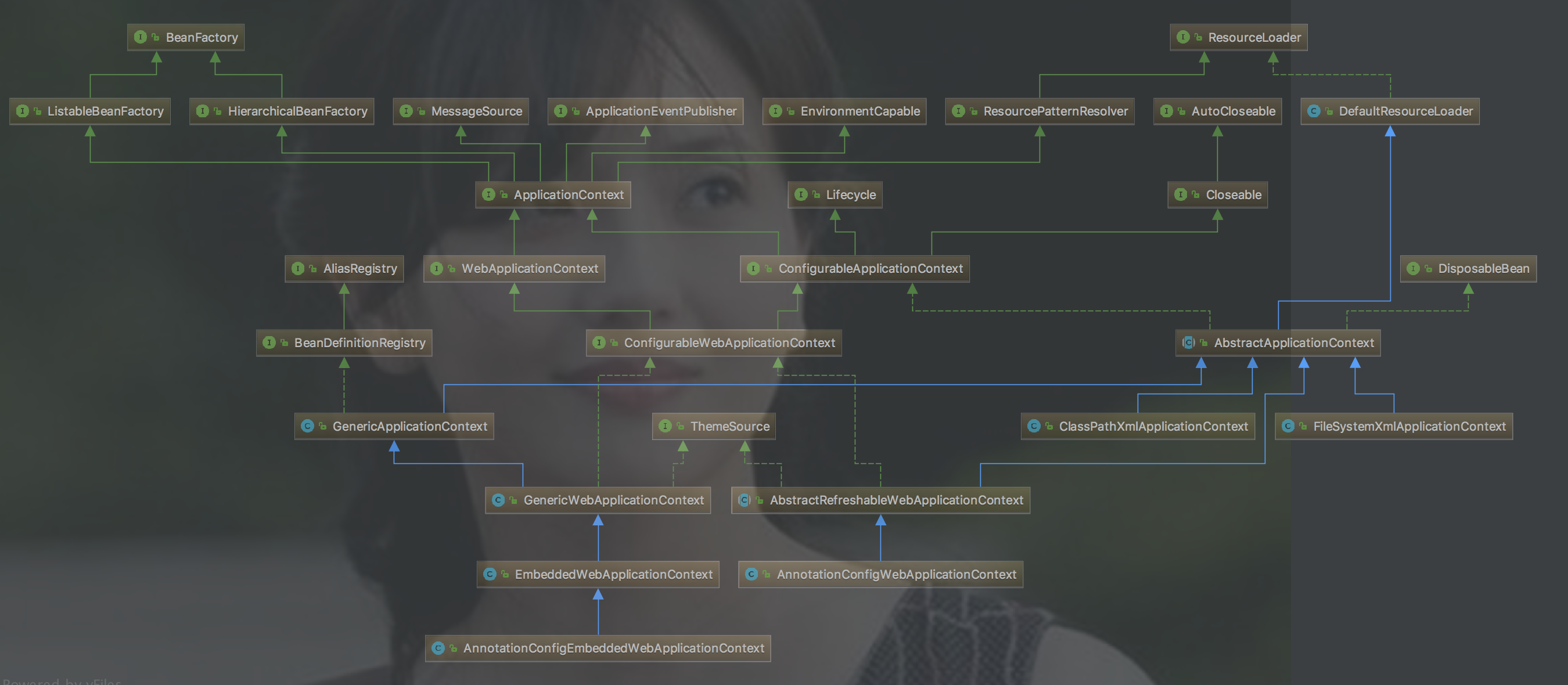
另一个维度
├── ApplicationContext
└── ConfigurableApplicationContext
│ └── AbstractApplicationContext
│ │ └── GenericApplicationContext
│ │ │ └── GenericWebApplicationContext
│ │ │ │ └── EmbeddedWebApplicationContext
│ │ │ │ │ └── AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext
│ │ │ │ │ └── XmlEmbeddedWebApplicationContext
│ │ │ └── GenericXmlApplicationContext
│ │ │ └── ResourceAdapterApplicationContext
│ │ │ └── StaticApplicationContext
│ │ │ │ └── StaticWebApplicationContext
│ │ └── AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext
│ │ │ └── AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext
│ │ │ │ └── AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext
│ │ │ │ │ └── AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext
│ │ │ │ │ └── XmlWebApplicationContext
│ │ │ └── AbstractXmlApplicationContext
│ │ │ │ │ └── ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
│ │ │ │ │ └── FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
│ └── ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
│ │ └── AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext
│ │ │ │ └── ......
│ │ └── GenericWebApplicationContext
│ │ │ └── ......
│ │ └── StaticWebApplicationContext
├── WebApplicationContext
│ │ └── ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
│ │ │ └── ......
│ │ └── StubWebApplicationContext
从图中可以看,在ApplicationContext家族族长上面还有几个大人物,如果ApplicationContext是和珅,那么这几大人物就是乾隆、皇后、太后等。 先介绍这几大人物
BeanFactory
BeanFactory其实也是一个大家族,家族主要负责实例化bean,其详细介绍见BeanFactory传
MessageSource
ApplicationEventPublisher
EnvironmentCapable
ResourcePatternResolver
ResourceLoader
下面正式介绍ApplicationContext加入成员
ApplicationContext
/**
* 这个核心接口为一个应用提供了配置,当应用正在执行时,他是仅读的;但是如果实现类支持的话可以被重载。
* An ApplicationContext provides:
* 1.访问应用组件的Bean factory methods,继承自ListableBeanFactory
* 2.以通用的方式加载file resources的能力,继承自ResourceLoader interface
* 3.发布事件给注册的listeners的能力,继承自ApplicationEventPublisher interface
* 4.resolve messages,支持i18n的能力,继承自MessageSource interface
* 5.继承parent context,后代context中的定义始终优先。这意味着,例如,整个Web应用程序可以使用单个parent context,而每个servlet都有自己的子context,该context独立于任何其他servlet的context.
* 除了有BeanFactory的生命周期的能力外,ApplicationContext实现类们检查和调用 ApplicationContextAware beans、ResourceLoaderAware beans、 ApplicationEventPublisherAware beans、MessageSourceAware beans.
*/
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,
MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
/**
* Return the unique id of this application context.
*/
String getId();
/**
* Return a name for the deployed application that this context belongs to
*/
String getApplicationName();
/**
* return a display name for this context (never {@code null})
*/
String getDisplayName();
/**
* Return the timestamp when this context was first loaded.
* @return the timestamp (ms) when this context was first loaded
*/
long getStartupDate();
/**
* Return the parent context, or {@code null} if there is no parent
* and this is the root of the context hierarchy.
*/
ApplicationContext getParent();
/**
* 为此context暴露AutowireCapableBeanFactory功能。它通常不被应用程序代码使用。除了实例化那些存活在application context之外的bean instances的目的,将Spring bean生命周期(全部或部分)应用于它们。
* 可替代的,由ConfigurableApplicationContext接口暴露的内部BeanFactory也提供对 AutowireCapableBeanFactory接口的访问权限。本方法主要用作ApplicationContext接口上方便的特定工具
AutowireCapableBeanFactory getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
WebApplicationContext
- 主要增加了servletContext、contextParameters、contextAttributes属性和getServletContext()方法
/**
* 这个接口增加getServletContext() 方法给通用的ApplicationContext interface, 和定义了一个众所周知的application attribute name,这个name必须和the root context绑定。
* 像通用的application contexts一样, web application contexts也是有层级的,
* 每个应用程序都有一个根上下文, 而在the application中每个servlet都有他自己的子(包括dispatcher servlet)。
* 除了标准的application context 生命周期能力,WebApplicationContext 实现类需要检查和ServletContextAware beans和调用setServletContext method
*/
public interface WebApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext {
/**
* Context attribute to bind root WebApplicationContext to on successful startup.
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils#getRequiredWebApplicationContext和getWebApplicationContext
*/
String ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT";
/**
* Scope identifier for request scope: "request".
*/
String SCOPE_REQUEST = "request";
/**
* Scope identifier for session scope: "session".
*/
String SCOPE_SESSION = "session";
/**
* Scope identifier for global session scope: "globalSession".
*/
String SCOPE_GLOBAL_SESSION = "globalSession";
/**
* Scope identifier for the global web application scope: "application".
*/
String SCOPE_APPLICATION = "application";
/**
* Name of the ServletContext environment bean in the factory.
* @see javax.servlet.ServletContext
*/
String SERVLET_CONTEXT_BEAN_NAME = "servletContext";
/**
* Name of the ServletContext/PortletContext init-params environment bean in the factory.
* ServletConfig parameters override ServletContext parameters of the same name.
* @see javax.servlet.ServletContext#getInitParameterNames()
* @see javax.servlet.ServletContext#getInitParameter(String)
* @see javax.servlet.ServletConfig#getInitParameterNames()
* @see javax.servlet.ServletConfig#getInitParameter(String)
*/
String CONTEXT_PARAMETERS_BEAN_NAME = "contextParameters";
/**
* Name of the ServletContext/PortletContext attributes environment bean in the factory.
* @see javax.servlet.ServletContext#getAttributeNames()
* @see javax.servlet.ServletContext#getAttribute(String)
*/
String CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTES_BEAN_NAME = "contextAttributes";
/**
* Return the standard Servlet API ServletContext for this application.
* <p>Also available for a Portlet application, in addition to the PortletContext.
*/
ServletContext getServletContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext
- 主要增加了systemProperties、systemEnvironment属性和addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(BeanFactoryPostProcessor)、addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?>)、refresh()、ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory()方法
/**
* 这个一个SPI接口,由大多数应用程序实现。
* 除了ApplicationContext interface的方法外,提供了配置an application context 的工具
* 这里封装了配置和生命周期方法以避免使它们对ApplicationContext客户端代码可见. 这些方法通过startup and shutdown code被使用
*/
public interface ConfigurableApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext, Lifecycle, Closeable {
/**
* 在一个字符串中多个context config paths的分隔符
* @see org.springframework.context.support.AbstractXmlApplicationContext#setConfigLocation
* @see org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader#CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM
* @see org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#setContextConfigLocation
*/
String CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS = ",; \t\n";
/**
* Name of the ConversionService bean in the factory.
*/
String CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME = "conversionService";
/**
* Name of the LoadTimeWeaver bean in the factory.
*/
String LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME = "loadTimeWeaver";
/**
* Name of the {@link Environment} bean in the factory.
*/
String ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME = "environment";
/**
* Name of the System properties bean in the factory.
* @see java.lang.System#getProperties()
*/
String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME = "systemProperties";
/**
* Name of the System environment bean in the factory.
* @see java.lang.System#getenv()
*/
String SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME = "systemEnvironment";
/**
* Set the unique id of this application context.
* @since 3.0
*/
void setId(String id);
/**
* Set the parent of this application context
*/
void setParent(ApplicationContext parent);
/**
* Set the {@code Environment} for this application context.
*/
void setEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment);
/**
* Return the {@code Environment} for this application context
*/
@Override
ConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment();
/**
* 增加一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,在refresh和在bean definitions被评估的时候,这个BeanFactoryPostProcessor被应用在内部的bean factory of this application context. To be invoked during context configuration.
*/
void addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor);
/**
* 增加一个在context事件中被通知的ApplicationListener,如context refresh 和context shutdown事件
* @see org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent
* @see org.springframework.context.event.ContextClosedEvent
*/
void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener);
/**
* Register the given protocol resolver with this application context,
* allowing for additional resource protocols to be handled.
*/
void addProtocolResolver(ProtocolResolver resolver);
/**
* 加载或刷新the configuration的持久化形式,configuration可以是an XML file, properties file, or 一个database schema.
* <p>由于这是一个startup方法,这个方法调用后要么全部要么没有singletons被实例化.
*/
void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;
/**
* Register a shutdown hook with the JVM runtime, closing this context
* on JVM shutdown unless it has already been closed at that time.
*/
void registerShutdownHook();
/**
* Close this application context, releasing all resources and locks that the implementation might hold.
*/
@Override
void close();
/**
* @return whether the context is still active
*/
boolean isActive();
/**
* Return the internal bean factory of this application context.
* Can be used to access specific functionality of the underlying factory.
* <p>Note: Do not use this to post-process the bean factory; singletons
* will already have been instantiated before. Use a BeanFactoryPostProcessor
* to intercept the BeanFactory setup process before beans get touched.
* <p>Generally, this internal factory will only be accessible while the context
* is active, that is, inbetween refresh() and close().
* The isActive() flag can be used to check whether the context
* is in an appropriate state.
*/
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
}
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
- 主要增加了setConfigLocations(String...configLocations)、setServletContext(ServletContext)、setServletConfig(ServletConfig)方法
/**
* 接口被可配置的web application contexts实现
*
* <p>Note: 这个接口的setters方法需要在ConfigurableApplicationContext.refresh方法调用之前被调用
* @see ContextLoader#createWebApplicationContext
* @see org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#createWebApplicationContext
*/
public interface ConfigurableWebApplicationContext extends WebApplicationContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext {
/**
* Prefix for ApplicationContext ids that refer to context path and/or servlet name.
*/
String APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ":";
/**
* Name of the ServletConfig environment bean in the factory.
*/
String SERVLET_CONFIG_BEAN_NAME = "servletConfig";
/**
* Set the ServletContext for this web application context.
* <p>refresh()需要这个方法调用后调用
*/
void setServletContext(ServletContext servletContext);
/**
* Set the ServletConfig for this web application context.
* refresh()需要这个方法调用后调用
*/
void setServletConfig(ServletConfig servletConfig);
/**
* Return the ServletConfig for this web application context, if any.
*/
ServletConfig getServletConfig();
/**
* Set the namespace for this web application context
*/
void setNamespace(String namespace);
/**
* Return the namespace for this web application context, if any.
*/
String getNamespace();
/**
* Set the config locations for this web application context in init-param style,即 被逗号,分号,空格分隔
*/
void setConfigLocation(String configLocation);
/**
* Set the config locations for this web application context.
*/
void setConfigLocations(String... configLocations);
/**
* Return the config locations for this web application context,
* or {@code null} if none specified.
*/
String[] getConfigLocations();
}
AbstractApplicationContext
- 这个类的具体功能就比较全了
- 增加的主要属性有
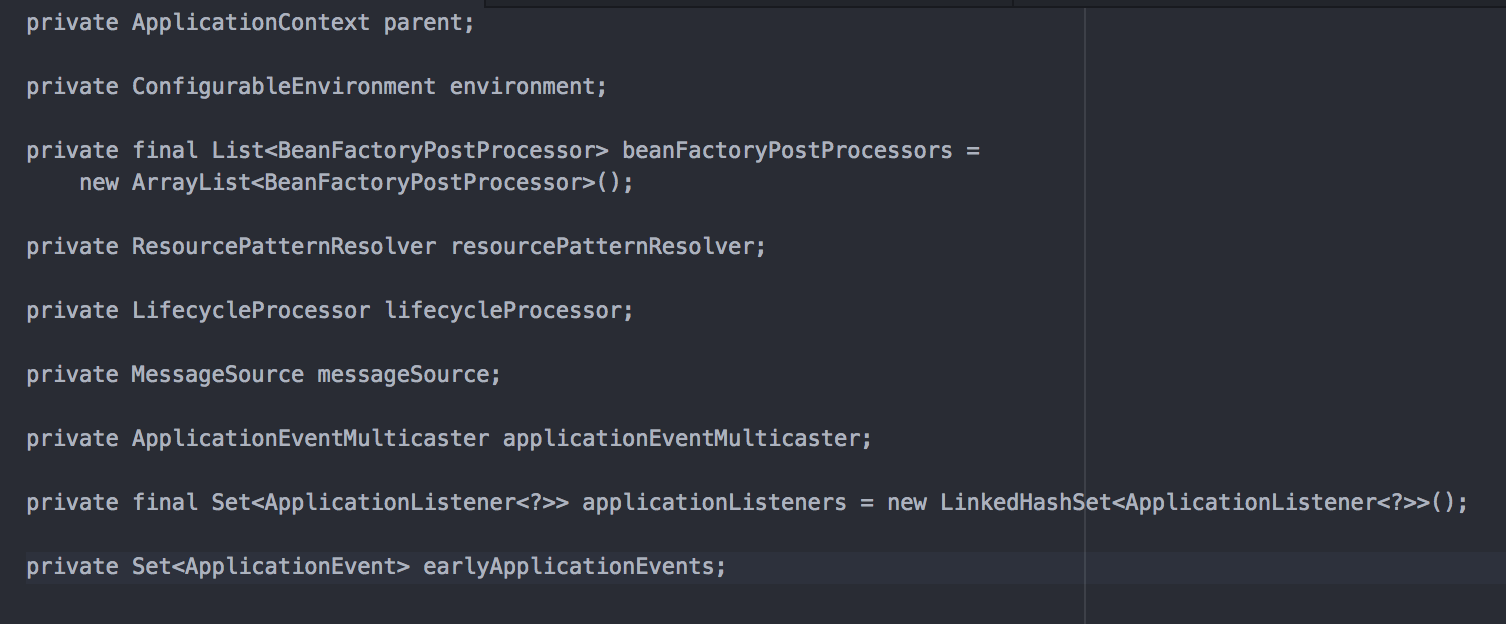
- 增加的主要方法有
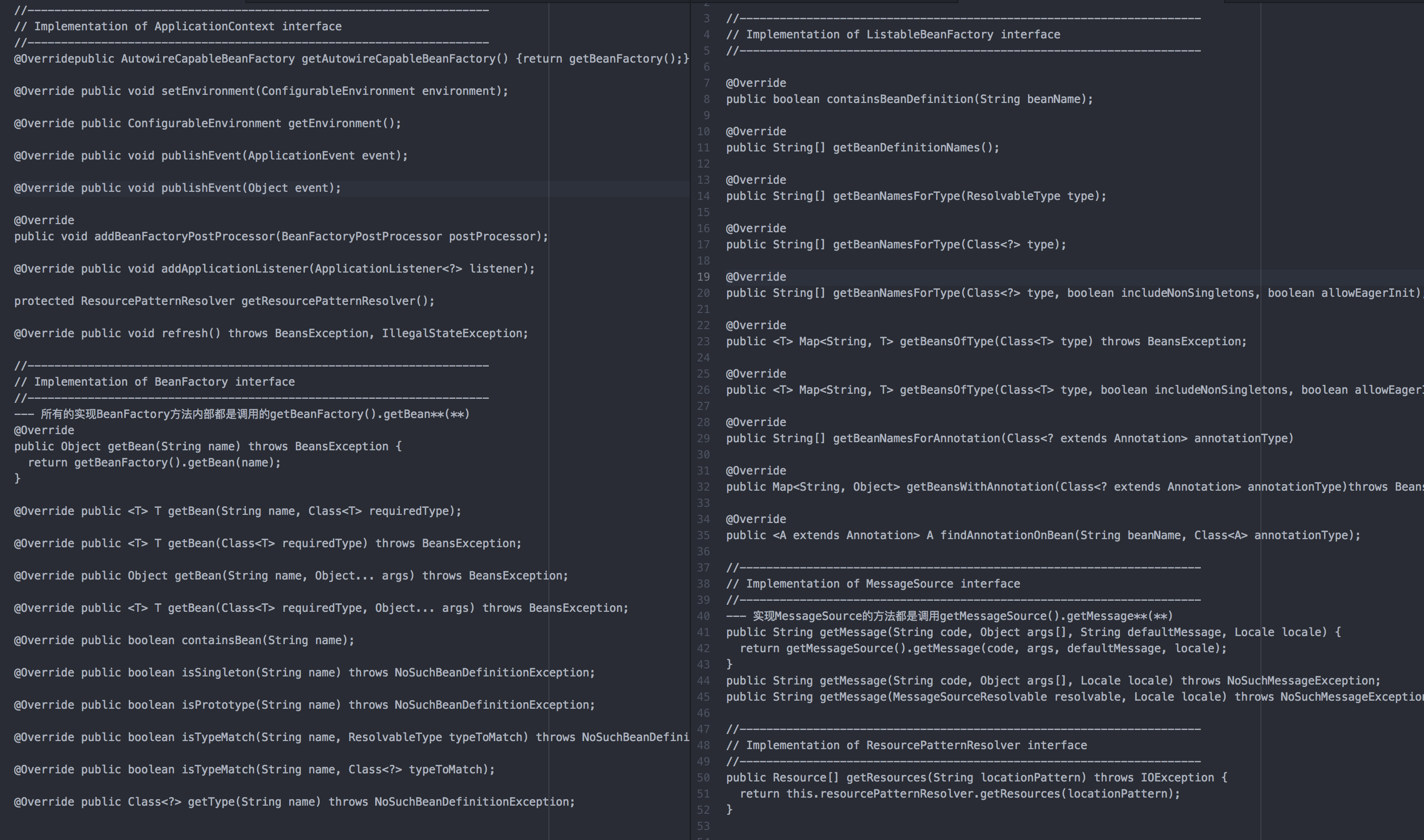
上图列出了主要的方法,可以看出这些方法都是实现了其他类的方法,具有了很多的功能,我们实际开发中可以直接使用这些方法完成我们的需求,这也是我们的终极目的:不仅了解了原理,还能灵活使用,鉴于AbstractApplicationContext的功能完备,我们就需要特别关注AbstractApplicationContext及其子类了,实际开发用的上
/**
* 不强制要求用于配置的存储类型,只需实现常见的context功能,使用Template Method设计模式,需要具体的子类来实现抽象方法。
* 与普通BeanFactory相比,ApplicationContext应该检测在其内部bean工厂中定义的特殊bean:因此,该类自动注册BeanFactoryPostProcessors,BeanPostProcessors和ApplicationListeners,它们在context中定义为bean。
* MessageSource可以在这个context中应用,如果没有MessageSource,则message resolution会委托给父context.
* 此外,ApplicationEventMulticaster类被应用到这个context, 否则, 默认的SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster将被应用.
* 通过扩展DefaultResourceLoader实现资源加载. 因此,将非URL资源路径(non-URL resource paths)视为类路径资源(class path resources)
*/
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext, DisposableBean {
··· 略 ···
// 这里特别列出refresh()方法,因为在spring application启动、实例化的很多功能都是通过此方法完成的
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}finally {
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
}
GenericApplicationContext
- 继承了AbstractApplicationContext,拥有AbstractApplicationContext的全部强大功能
- 相比AbstractApplicationContext,GenericApplicationContext重要的点是它又实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,即拥有了处理BeanDefinition的功能;同时他有两个重要的属DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory、ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
/**
* Generic ApplicationContext的实现类持有一个内部的DefaultListableBeanFactory instance和不会假定一个指定的bean definition格式. 实现BeanDefinitionRegistry interface为了应用任意bean definition readers给GenericApplicationContext
* 典型的使用是通过BeanDefinitionRegistry register各种各样的bean definitions。 然后调用#refresh()去实例化those beans,带着application context语法(处理ApplicationContextAware, 自动检查BeanFactoryPostProcessors等
* 与为每次刷新创建新的内部BeanFactory实例的其他ApplicationContext实现相比,此上下文的内部BeanFactory从一开始就可用,以便能够在其上注册bean定义。 refresh()只能调用一次。
* 对于想以刷新的方式读取指定的bean definition formats的那些自定义的 application context实现类,考虑使用AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext来获取
*/
public class GenericApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext implements BeanDefinitionRegistry {
private final DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
private final AtomicBoolean refreshed = new AtomicBoolean();
public GenericApplicationContext() {
this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
}
public GenericApplicationContext(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory){
Assert.notNull(beanFactory, "BeanFactory must not be null");
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
public final DefaultListableBeanFactory getDefaultListableBeanFactory() {
return this.beanFactory;
}
@Override
public AutowireCapableBeanFactory getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return this.beanFactory;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Implementation of BeanDefinitionRegistry
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
this.beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
@Override
public void removeBeanDefinition(String beanName);
@Override
public BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String beanName);
@Override
public boolean isBeanNameInUse(String beanName);
@Override
public void registerAlias(String beanName, String alias);
@Override
public void removeAlias(String alias);
@Override
public boolean isAlias(String beanName);
GenericWebApplicationContext
- 除了拥有GenericApplicationContext的功能,由于还实现了ConfigurableWebApplicationContext接口,所以它可以操作ServletContext类、ServletConfig和setConfigLocations,相当于由于还实现了ConfigurableWebApplicationContext接口的具体方法实现;同时它重写了postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory),放入ServletContext相关类(ServletContextAwareProcessor、ServletContextAware)
/**
* 适用于web environments的GenericApplicationContext子类
* 实现ConfigurableWebApplicationContext的目的被设计用来用于程序化设置, 例如用于构建内部的contexts或者和WebApplicationInitializers一起使用
* 如果你想实现一个可以从配置文件读取bean definitions的WebApplicationContext
考虑使用AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext.loadBeanDefinitions方法
*/
public class GenericWebApplicationContext extends GenericApplicationContext
implements ConfigurableWebApplicationContext, ThemeSource {
private ServletContext servletContext;
private ThemeSource themeSource;
public GenericWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
this.servletContext = servletContext;
}
public GenericWebApplicationContext(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
super(beanFactory);
}
public GenericWebApplicationContext(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory, ServletContext servletContext) {
super(beanFactory);
this.servletContext = servletContext;
}
@Override
public void setServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
this.servletContext = servletContext;
}
@Override
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ServletContextAwareProcessor(this.servletContext));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, this.servletContext);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory, this.servletContext);
}
@Override
protected void initPropertySources() {
ConfigurableEnvironment env = getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(this.servletContext, null);
}
}
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Pseudo-implementation of ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
... ...
}
EmbeddedWebApplicationContext
- 这个context继承了GenericWebApplicationContext。它关联一个EmbeddedServletContainerFactory,所以这个类不仅可以操作继承GenericWebApplicationContext的ServletContext、ServletConfig相关方法,还可以操作EmbeddedServletContainer、ServletContextInitializer。而EmbeddedServletContainer、ServletContextInitializer是用来产生ServletContext、ServletConfig实例的
/**
* 它是一个包含EmbeddedServletContainerFactory类,用于自启动的WebApplicationContext子类。
* 这个context可以通过在ApplicationContext本身中搜索单个EmbeddedServletContainerFactory bean来创建、实例化、运行一个EmbeddedServletContainer。EmbeddedServletContainerFactory不受standard Spring concepts(such as dependency injection, lifecycle callbacks and property placeholder variables)的影响
* 此外,定义在context里的任何Servlet和Filter beans都将自动注册到嵌入式Servlet容器中。
* 单个Servlet bean时,'/' mapping被使用。多个Servlet beans时,小写的bean name将作为mapping prefix。名字叫dispatcherServlet的Servlet总是mapped to '/'。Filter beans mapping to all URLs ('/*')
* 对于更多高级的配置,the context能改为定义实现ServletContextInitializer接口的beans(最常见的是ServletRegistrationBeans和/或FilterRegistrationBeans).
* 尽管这个context能直接用,但是大部分开发者应该使用AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext或XmlEmbeddedWebApplicationContext
*/
public class EmbeddedWebApplicationContext extends GenericWebApplicationContext {
public static final String DISPATCHER_SERVLET_NAME = "dispatcherServlet";
private volatile EmbeddedServletContainer embeddedServletContainer;
private ServletConfig servletConfig;
@Override
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(
new WebApplicationContextServletContextAwareProcessor(this));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class);
}
@Override
public final void refresh() {super.refresh();}
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
createEmbeddedServletContainer();}
}
@Override
protected void finishRefresh();
@Override
protected void onClose() {
super.onClose();
stopAndReleaseEmbeddedServletContainer();
}
private void createEmbeddedServletContainer();
protected EmbeddedServletContainerFactory getEmbeddedServletContainerFactory();
private ServletContextInitializer getSelfInitializer();
private void selfInitialize(ServletContext servletContext);
protected Collection<ServletContextInitializer> getServletContextInitializerBeans() {
return new ServletContextInitializerBeans(getBeanFactory());
}
protected void prepareEmbeddedWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext);
private EmbeddedServletContainer startEmbeddedServletContainer();
private void stopAndReleaseEmbeddedServletContainer();
public void setServletConfig(ServletConfig servletConfig);
public EmbeddedServletContainer getEmbeddedServletContainer();
AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext
这是spring boot默认实例化和使用的context- 这个context继承了EmbeddedWebApplicationContext,所有它拥有EmbeddedWebApplicationContext的能力。此外他有个非常重要的功能:扫描和读取annotated bean classes和classPath下的classes。分别通过AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader和ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner来实现
/**
* 这个context接受annotated classes作为输入,尤其是@Configuration-annotated classes, @Component 和@inject classes. 逐一注册classes(指定class names作为 config location) 和指定base packages作为config location).
* Note: 当有多个@Configuration classes时, 较晚加载的@Bean definitions将会重写较早加载的
*/
public class AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext
extends EmbeddedWebApplicationContext {
// 可以扫描有两个重要的属性
private final AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader;
private final ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner;
private Class<?>[] annotatedClasses;
private String[] basePackages;
public AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext() {
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
public AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
this();
register(annotatedClasses);
refresh();
}
public AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext(String... basePackages) {
this();
scan(basePackages);
refresh();
}
@Override
public void setEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
super.setEnvironment(environment);
this.reader.setEnvironment(environment);
this.scanner.setEnvironment(environment);
}
/**
* 提供一个自定义的BeanNameGenerator给AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader and/or ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
* Any call to this method must occur prior to calls to #register(Class...) and/or #scan(String...)
*/
public void setBeanNameGenerator(BeanNameGenerator beanNameGenerator) {
this.reader.setBeanNameGenerator(beanNameGenerator);
this.scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(beanNameGenerator);
this.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton(
AnnotationConfigUtils.CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR,
beanNameGenerator);
}
public void setScopeMetadataResolver(ScopeMetadataResolver scopeMetadataResolver) {
this.reader.setScopeMetadataResolver(scopeMetadataResolver);
this.scanner.setScopeMetadataResolver(scopeMetadataResolver);
}
/**
* 注册一个或多个要处理的带注释的类。Register one or more annotated classes to be processed. Note:必须调用refresh()才能使the context完全处理新类.对register的调用是幂等的
*/
public final void register(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
this.annotatedClasses = annotatedClasses;
}
/**
* 对指定的base packages执行scan(扫描). Note:同register方法
*/
public final void scan(String... basePackages) {
this.basePackages = basePackages;
}
@Override
protected void prepareRefresh() {
this.scanner.clearCache();
super.prepareRefresh();
}
// 后置处理来执行scan and/or register方法
@Override
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
super.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
if (this.basePackages != null && this.basePackages.length > 0) {
this.scanner.scan(this.basePackages);
}
if (this.annotatedClasses != null && this.annotatedClasses.length > 0) {
this.reader.register(this.annotatedClasses);
}
}
}
总结
- 本文沿着一个层级线介绍了一个线级的ApplicationContext,所以有小部分的子类没有介绍到。spring boot就是通过这个线来完成自己的强大的功能的。下面总结一下这个层级线