如今javascript已经成为众多程序必备的一门语言,在web、某些小桌面应用、移动端H5应用都已经出现javascript的影子,如今的javascript还加上了node.js让它可以让你的工作工程化。而且html5 的 画布 也已经已经成型了,我敢推断未来数据显示的这一块更多的企业会在前端去成实现这一块的内容。
比如现在的 echarts charts no-charts 等库的出现。
作为一个前端工程师,如果未来不学点数据结构 和 算法的话, 如果没有一定的数据模型在脑海里很难实现一些事情。如果你还想停了在
使用一些 React , Vue ,Jq + ajax 去实现一些增删改成的话。那就没必要学...哈哈哈。
今天说的是最简单的一种 链表数据结构。其实这种数据类型是你用的最多的,比如你每天使用的Array 就是 基于这样一种链表结构实现。
单向链表
首先在来看看概念 来源于 百度百科
首先我们实现一个类 和 这个类应该实现那些内容
function LinkedNode() {
//创建一个Node类
let Node = function (element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
}
let head = null, //存放整条单向链表的数据结构
length = 0; //链表的结构
this.append = (element) => { };
this.insert = (position, element) => { };
this.removeAt = function () { };
this.remove = (element) => { };
this.indexOf = (element) => { };
this.isEmpty = () => { };
this.size = () => { };
this.toString = () => { };
this.print = () => { };
this.getHead = () => { return head; };
}
我们接下来实现一下append,向我们这个单链表添加数据
this.append = (element) => {
let node = new Node(element);//创建数据类型 默认next的指针为null
let current = null;
if (head == null) {
//如果这个链表没有数据
head = node;
} else {
current = head;
while (current.next) {
//一直遍历 知道是最后一个 为止 null
current = current.next;
}
//这个时候的 next 为null 让它等于 node 我们新的元素
current.next = node;
}
length++;
};
然我们打印一下我们现在看到的数据结构
let list = new LinkedList();
list.append(15);
list.append(10);
list.append(20);
console.log(list.getHead());
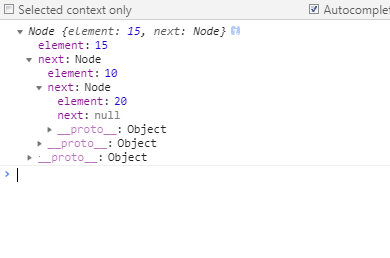 image.png
image.png
如果显示,现在明白javascript中如何实现一个指针了吧,哈哈哈
现在实现指定位置的插入数据
this.insert = (position, element) => {
//首先我们插入的为止必须为 0 和这条链表长度内
if (position >= 0 && position <= length) {
let node = new Node(element),
current = head,
previous, // 插入数据前的一个
index = 0;
if (position == 0) {
node.next = current;
head = node;
} else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next; //插入数据的后一位
}
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
//这里是张previous 和 current 的数据类型做跟换,具体为什么head 会变化,也是因为上面有一步 head = current;然后你后面的 current只要有变动 javscript 也会在内容中 把更改到head中
}
length++;
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
};
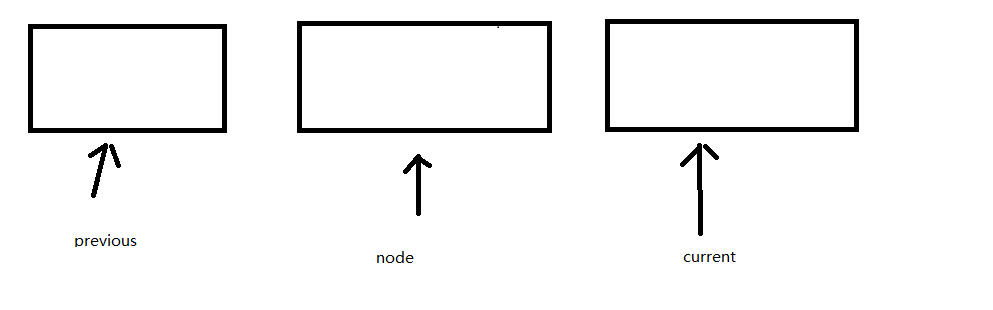 image.png
image.png
如图所示 同理实现removeAt
this.removeAt = (position) => {
if (position > -1 && position < length) {
let current = head,
previous,
index = 0;
if (position === 0) {
head = current.next;
} else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
previous.next = current.next; //直接把上next 知道 当前current.next 属性就好了
}
length--;
return current.element;
}
else {
return null;
}
};
this.indexOf = (element) => {
let current = head,
index = 0;
while (current) {
if (current.element == element) {
return index;
}
index++;
current = current.next;
}
return -1;
};
this.remove = (element) => {
let index = this.indexOf(element);
return this.removeAt(index);
};
this.isEmpty = () => length === 0;
this.size= () => length ;
this.toString= () => {
let current = head;
string = '';
while (current) {
string += current.element + (current.next ? ',' : '');
current = current.next;
}
return string;
};
this.print = function () {
this.toString();
};