在CSS中,
下面先来列出目前博主了解的CSS属性:
1. opacity
opacity居然也能让
结论: 当opacity不为1或0时,z-index会生效
2. transform
结论:
3. flexbox
结论:
总结
让z-index生效:
如有疑问,欢迎在下方评论区留言!
z-index会影响元素的层叠关系。当然,这是有前提,最常用的就是设置元素的position值为relative/absolute/fixed。不过,这篇文章不是来介绍这些的,而是介绍一下影响z-index生效的其他CSS属性。下面先来列出目前博主了解的CSS属性:
- opacity
- transform
- flexbox
1. opacity
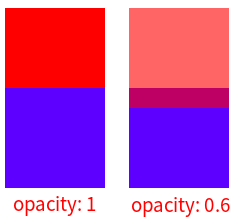
opacity居然也能让
z-index生效,真是莫名其妙。<style>
.back,
.front {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.back {
background: red;
z-index: 10;
opacity: 0.5;
}
.front {
background: blue;
margin-top: -20px;
}
</style>
<div class="box">
<div class="back"></div>
<div class="front"></div>
</div>
结论: 当opacity不为1或0时,z-index会生效
2. transform
<style>
.back,
.front {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.back {
background: red;
z-index: 10;
transform: rotate(10deg);
}
.front {
background: blue;
margin-top: -20px;
}
</style>
<div class="box">
<div class="back"></div>
<div class="front"></div>
</div>

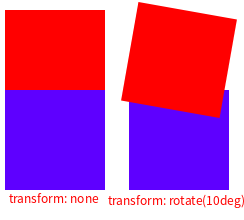
结论:
当transform不为none时,z-index会生效。3. flexbox
<style>
.box {
display: flex;
}
.back,
.front {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.back {
background: red;
z-index: 10;
}
.front {
background: blue;
margin-left: -20px;
}
</style>
<div class="box">
<div class="back"></div>
<div class="front"></div>
</div>

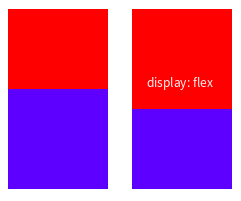
结论:
当父元素设置display: flex | inline-flex时,子元素设置z-index生效。总结
让z-index生效:
- 设置元素的position值为relative/absolute/fixed
- 当opacity不为1或0时
- 当transform不为none时
- 当父元素设置display: flex | inline-flex时,子元素设置z-index
如有疑问,欢迎在下方评论区留言!