- volatile则是通知jvm当前变量在寄存器或者cpu中的值是不确定的,需要从主存中读取。不会阻塞线程。
- synchronized是通过锁机制来控制变量是否可以访问。当变量被锁时,其他线程访问变量将被阻塞,直至锁释放。
volatile
- volatile保证其他线程对这个变量操作时是立即可见的,即操作的是从内存中读取的最新值
- 无法保证原子性
- 只能修饰变量
public class Test {
private volatile int count;
public void increase() {
count++;
System.out.println("----" + count);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Test test = new Test();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread() {
public void run() {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
test.increase();
}
};
}.start();
}
}
}
- 控制台输出:
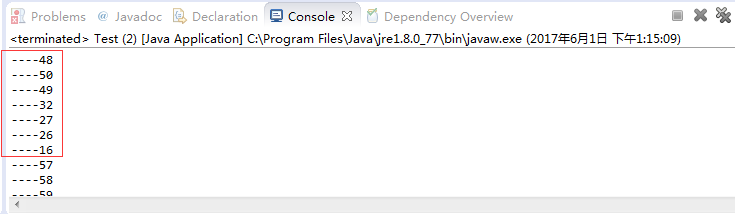
- 使用场景(DCL双重检测锁):
class Singleton{
private volatile static Singleton instance = null;
private Singleton() {}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
if(instance==null) {
synchronized (Singleton.class) {
if(instance==null)
instance = new Singleton();
}
}
return instance;
}
}
synchronized
- 保证原子性
- 即可修饰变量也可修饰方法
- 会阻塞线程
synchronized非静态方法
public class Test {
public synchronized void increase1() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("increase1---->" + i);
}
}
public synchronized void increase2() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("increase2---->" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Test test = new Test();
new Thread() {
public void run() {
test.increase1();
};
}.start();
new Thread() {
public void run() {
test.increase2();
};
}.start();
}
}
- 控制台输出:
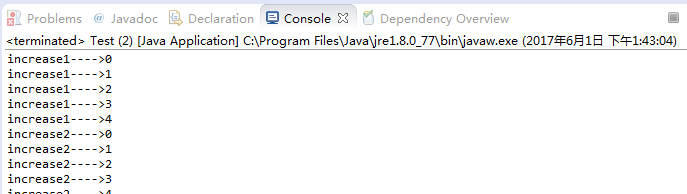
- 结论:
如果一个对象有多个synchronized方法,多个线程同时调用该对象的方法,将会同步执行,即同时只能有一个synchronized方法被调用,其他调用将被阻塞直至该方法执行完
synchronized静态方法
懒。。 直接给结论了
synchronized静态方法和非静态方法的区别在于给方法上锁的对象不一样,非静态方法是给调用的对象上锁,静态方法是给类的Class对象上锁
synchronized块
public class Test {
public void increase1() {
System.out.println("increase1----------> start");
synchronized (this) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("increase1---->" + i);
}
}
System.out.println("increase1----------> end");
}
public void increase2() {
System.out.println("increase2----------> start");
synchronized(this) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("increase2---->" + i);
}
}
System.out.println("increase2----------> end");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Test test = new Test();
new Thread() {
public void run() {
test.increase1();
};
}.start();
new Thread() {
public void run() {
test.increase2();
};
}.start();
}
}
- 控制台输出:
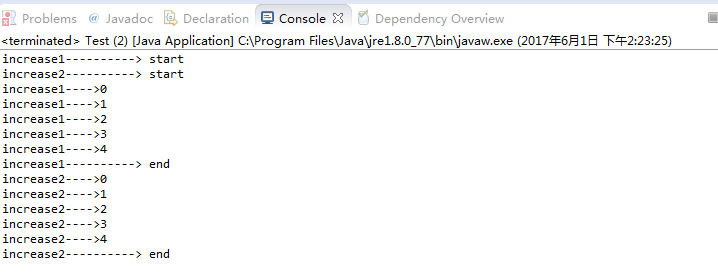
- 结论
synchronized方法是控制同时只能有一个线程执行synchronized方法;synchronized块是控制同时只能有一个线程执行synchronized块中的内容