MVP介绍
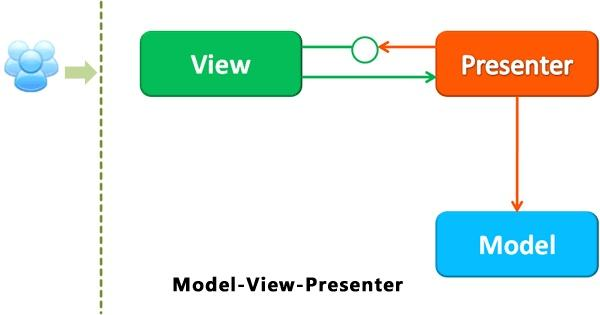
- MVP 即Model-View-Presenter
- Model:这一层主要是处理具体的业务逻辑
- View:View主要负责UI层数据展示,用户交互,和MVC里边的View含义基本一直,Activity、Fragment和xml,都属于View层,一般负责加载UI,具体的操作由其持有的Prosenter去处理。
- Presenter:连接Model层和View层,View层的指令经由Presenter发给Model层去处理,然后再将Model处理完的东西反馈给View,
MVP有什么优点?
可以更好的将业务逻辑和UI剥离开,松散耦合,Activity和Fragment的View层只负责UI的展示,其他无关的东西全都交由Presenter完成。
MVP模式的代码实现
View interface主要是为了给Presenter提供更新UI的方法
/**
* Created with Android Studio.
*
* @author Kimger
* @email kimger@onetos.cc
* @date 2018-7-12 20:04
*/
public interface MvpView {
void showLoading();
void hideLoading();
void showData(String data);
void showFailureMessage(String msg);
void showErrorMessage(String msg);
}
Callback 主要是为了把Model处理完的数据和事件回调给Presenter,然后由Presenter去通知UI更新
/**
* Created with Android Studio.
*
* @author Kimger
* @email kimger@onetos.cc
* @date 2018-7-12 20:00
*/
public interface MvpCallback {
void onSuccess(String data);
void onFail(String failMsg);
void onError(String errorMsg);
void onComplete();
}
Model处理具体的数据操作,比如查询数据库,网络请求等...
/**
* Created with Android Studio.
*
* @author Kimger
* @email kimger@onetos.cc
* @date 2018-7-12 20:01
*/
public class MvpModel {
/**
* 模拟获取网络接口数据
* @param param 请求参数
* @param callback 数据回调结构
*/
public static void TestHttp(final String param, final MvpCallback callback){
new Handler().postDelayed(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if ("success".equals(param)){
callback.onSuccess("请求的网络数据成功!!");
return;
}else if ("fail".equals(param)){
callback.onFail("请求的网络数据失败!!");
return;
}else if ("error".equals(param)){
callback.onError("错误!!");
return;
}
callback.onComplete();
}
},5000);
}
}
Presetner负责沟通View和Model,完成Model数据向View的更新,以及View的命令向Model的执行
/**
* Created with Android Studio.
*
* @author Kimger
* @email kimger@onetos.cc
* @date 2018-7-12 20:06
*/
public class MvpPresenter {
private MvpView mView;
public MvpPresenter(MvpView view) {
mView = view;
}
public void getData(String params){
//显示正在加载进度条
mView.showLoading();
//调用Model请求数据
MvpModel.TestHttp(params, new MvpCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(String data) {
mView.showData(data);
mView.hideLoading();
}
@Override
public void onFail(String msg) {
mView.showFailureMessage(msg);
mView.hideLoading();
}
@Override
public void onError(String msg) {
mView.showErrorMessage(msg);
mView.hideLoading();
}
@Override
public void onComplete() {
mView.hideLoading();
}
});
}
}
然后是Acitivity的相关操作,也就是实际UI层操作,这里需要去实现之前定义的MVPView的接口,方便Presetner去通知View层的UI更新操作
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements MvpView{
private PopupWindow mPopupWindow;
private TextView text;
private MvpPresenter mMvpPresenter;
private AnimationDrawable mDrawable;
private View mPopView;
private ImageView mImageView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
text = findViewById(R.id.text);
mPopupWindow = new PopupWindow(this);
mPopView = LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.pop_view, null);
mPopupWindow.setContentView(mPopView);
mImageView = mPopView.findViewById(R.id.imageView);
mDrawable = (AnimationDrawable) mImageView.getDrawable();
mMvpPresenter = new MvpPresenter(this);
}
public void getData(View view){
mMvpPresenter.getData("success");
}
public void getDataForFailure(View view){
mMvpPresenter.getData("fail");
}
public void getDataForError(View view){
mMvpPresenter.getData("error");
}
@Override
public void showLoading() {
if (mPopupWindow != null) {
mPopupWindow.showAtLocation(getWindow().getDecorView(), Gravity.TOP|Gravity.LEFT,getScreenWidth(this)
/2-50,
getScreenHeight(this)/2);
mDrawable.start();
}
}
@Override
public void hideLoading() {
if (mPopupWindow != null) {
mDrawable.stop();
mPopupWindow.dismiss();
}
}
@Override
public void showData(String data) {
text.setText(data);
}
@Override
public void showFailureMessage(String msg) {
Toast.makeText(this, msg, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
text.setText(msg);
}
@Override
public void showErrorMessage(String msg) {
Toast.makeText(this, "网络请求出现异常", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
text.setText("网络请求出现异常");
}
/**
* 获取屏幕高度(px)
*/
public static int getScreenHeight(Context context) {
DisplayMetrics displayMetrics = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics();
return displayMetrics.heightPixels;
}
/**
* 获取屏幕宽度(px)
*/
public static int getScreenWidth(Context context) {
DisplayMetrics displayMetrics = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics();
return displayMetrics.widthPixels;
}
}
acitivity 的layout文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="操作执行结果"/>
<LinearLayout
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<Button
android:onClick="getData"
android:text="获取网络数据成功"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button
android:onClick="getDataForFailure"
android:text="获取数据失败"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button
android:text="获取数据异常"
android:onClick="getDataForError"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>