Webpack 构建策略 module 和 nomodule
前言
前端性能优化已经过了刀耕火种的年代,现在更多的优化是从代码层面,其中重中之重的当然是 JS 的优化,之前看到 React 16 加载性能优化指南这篇文章中有提到 ES2015+ 编译减少打包体积,核心就是依赖 <script type="module">的支持来分辨浏览器对 ES2015+ 代码的支持,并且可以用<script nomodule>进行优雅降级
浏览器支持
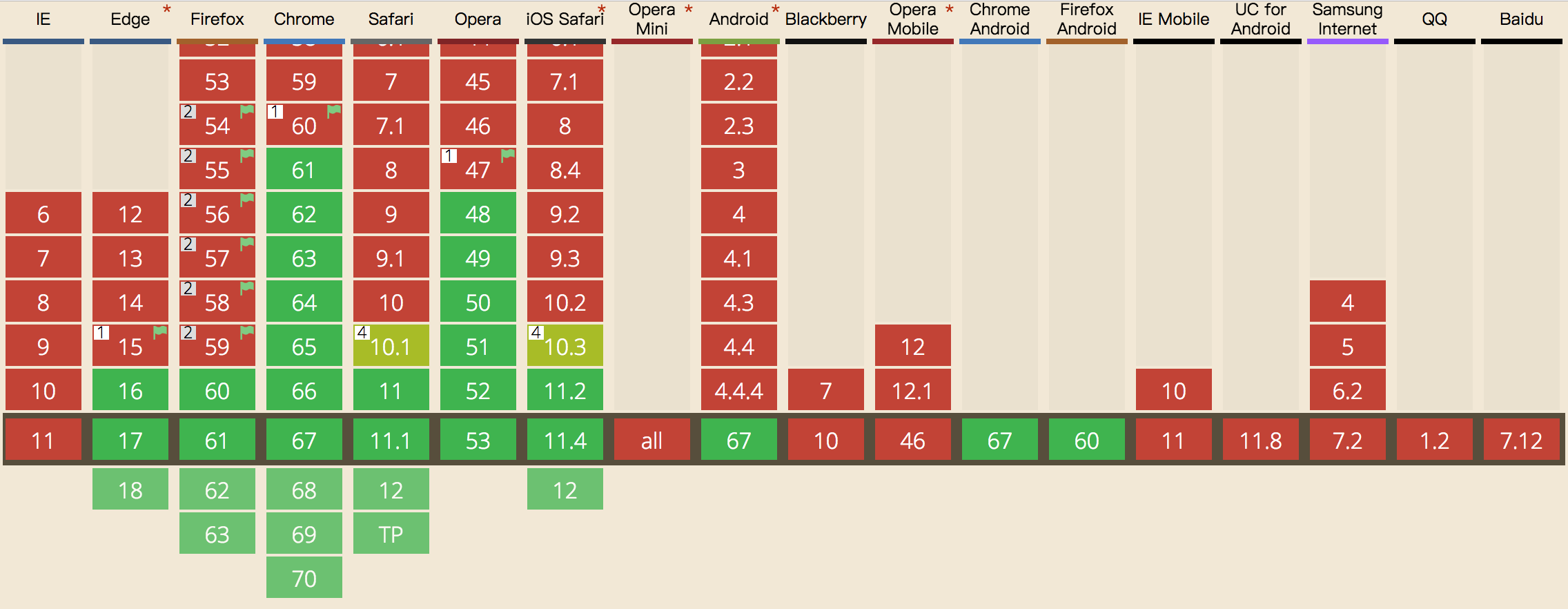
看一下 Can I use… Support tables for HTML5, CSS3, etc上面的支持情况
除了 IE 外,现在主流的现代浏览器基本上都得到了支持,尤其是 IOS 从 10.3 版本就开始支持了,这样在移动端的体验会大大增强,当然了 10.3 也会有个 BUG,大家可以看到上图的 10.3 有个 4 的标识,意思是
Does not support the nomodule attribute
不支持 nomodule 属性,这样带来的后果就是 10.3 版本的 IOS 同时执行两份 JS 文件,所以Safari 10.1 nomodule support · GitHub上面也有 hack 写法
// 这个会解决 10.3 版本同时加载 nomodule 脚本的 bug,但是仅限于外部脚本,对于内联的是没用的
// fix 的核心就是利用 document 的 beforeload 事件来阻止 nomodule 标签的脚本加载
(function() {
var check = document.createElement('script');
if (!('noModule' in check) && 'onbeforeload' in check) {
var support = false;
document.addEventListener('beforeload', function(e) {
if (e.target === check) {
support = true;
} else if (!e.target.hasAttribute('nomodule') || !support) {
return;
}
e.preventDefault();
}, true);
check.type = 'module';
check.src = '.';
document.head.appendChild(check);
check.remove();
}
}());
语法支持
module 给我们带来好处就是支持 ES6 的语法,支持且不限于
- 箭头函数
const fn = () => {
}
- Promise
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve()
}, 1000)
})
- Class
class fn {
constructor () {
this.age = 100
}
}
- Import
import { doSome } from 'util.js'
Babel
想要支持 module 和 nomodule 核心就是 Babel,利用 Babel 我们可以编译出两份文件
script type="module" src="app.js"></script>
script nomodule src="app-legacy.js"></script>
legacy 是遗产的意思,在这里面叫做老旧的意思,理解成老旧的语法
Webpack
改造下 webpack,思路就是构建两次,分别用不同的 babel 配置
// index.js
const fs = require('fs-extra')
const babelSupport = require('./babel-support')
const merge = require('webpack-merge')
const webpackConfig = require(`./build`)
handle()
async function handle() {
// 构建前清空下构建的目标目录
await fs.remove('build')
await build(
merge(webpackConfig('es2015'), {
module: {
rules: [babelSupport('es2015')]
}
})
)
await build(
merge(webpackConfig('legacy'), {
module: {
rules: [babelSupport('legacy')]
}
})
)
}
async function build(webpackConfig) {
const compiler = webpack(webpackConfig)
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
compiler.run((err, status) => {
if (err) {
reject()
throw err
}
resolve()
})
})
}
利用 webpack-merge 我们可以轻松的得到想要的 webpack 配置,上面的代码可以看到我们在 handle 中 build 了两次,一次是 ES2015+ 的,一次是 legacy,接下来看下 build 的配置
// build.js
// base 是基础的配置
// 根据 target 我们构建出不同的文件名
module.exports = target => {
const isLegacy = target === 'legacy'
return merge(base, {
output: {
...
filename: isLegacy
? 'js/[name]-legacy.[chunkhash].js'
: 'js/[name].[chunkhash].js',
chunkFilename: isLegacy
? 'js/[name]-legacy.[chunkhash].js'
: 'js/[name].[chunkhash].js'
},
plugins: [
// 这里要对 HtmlWebpackPlugin 处理下,template 指的是源文件,构建两次,第一次构建的是 ES2015+,所以我们直接用 src 目录下的模板即可,第二次构建的 legacy 的,我们直接用构建目标目录的的模板就好了,这样构建完成后模板中会同时有两份文件
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: isLegacy ? 'build/index.html' : 'src/index.html',
filename: 'index.html',
inject: 'body'
})
]
})
}
再来看下 babel 的动态配置
// babel-support.js
// 使用 babel 7 我们可以轻松的构建
// babel 7 的 preset-env 有个 esmodules 支持可以让我们直接编译到 ES2015+ 的语法,如果你使用的是 babel 6 的话那么可以自己去写对应的 browserlist
module.exports = target => {
const targets =
target === 'es2015'
? { esmodules: true }
: { browsers: ['ios >= 7', 'android >= 4.4'] }
return {
test: /\.js[x]?$/,
loader: 'babel-loader?cacheDirectory',
options: {
presets: [
[
'@babel/preset-env',
{
debug: false,
modules: false,
useBuiltIns: 'usage',
targets
}
],
[
'@babel/preset-stage-2',
{
decoratorsLegacy: true
}
]
]
}
}
}
这样构建出来的文件就会根据不同的 targets 实现不同的语法,接下来再来处理下模板中的 module 和 nomodule 属性,写个 HtmlWebpackPlugin 插件
// 把 IOS 10.3 的 fix 代码单独拎出来
const safariFix = `!function(){var e=document,t=e.createElement("script");if(!("noModule"in t)&&"onbeforeload"in t){var n=!1;e.addEventListener("beforeload",function(e){if(e.target===t)n=!0;else if(!e.target.hasAttribute("nomodule")||!n)return;e.preventDefault()},!0),t.type="module",t.src=".",e.head.appendChild(t),t.remove()}}();`
class ModuleHtmlPlugin {
constructor(isModule) {
this.isModule = isModule
}
apply(compiler) {
const id = 'ModuleHtmlPlugin'
// 利用 webpack 的核心事件 tap
compiler.hooks.compilation.tap(id, compilation => {
// 在 htmlWebpackPlugin 拿到资源的时候我们处理下
compilation.hooks.htmlWebpackPluginAlterAssetTags.tapAsync(
id,
(data, cb) => {
data.body.forEach(tag => {
//遍历下资源,把 script 中的 ES2015+ 和 legacy 的处理开
if (tag.tagName === 'script') {
// 给 legacy 的资源加上 nomodule 属性,反之加上 type="module" 的属性
if (/-legacy./.test(tag.attributes.src)) {
delete tag.attributes.type
tag.attributes.nomodule = ''
} else {
tag.attributes.type = 'module'
}
}
//在这一步加上 10.3 的 fix,很简单,就是往资源的数组里面的 push 一个资源对象
if (this.isModule) {
// inject Safari 10 nomdoule fix
data.body.push({
tagName: 'script',
closeTag: true,
innerHTML: safariFix
})
}
})
cb(null, data)
}
)
// 在 htmlWebpackPlugin 处理好模板的时候我们再处理下,把页面上 <script nomudule=""> 处理成 <script nomudule>,正则全局处理下
compilation.hooks.htmlWebpackPluginAfterHtmlProcessing.tap(id, data => {
data.html = data.html.replace(/\snomodule="">/g, ' nomodule>')
})
})
}
}
module.exports = ModuleHtmlPlugin
构建后出现两份 js 文件,用最新的 Chrome 跑一下运行正常,并且体积优化相比 legacy 减少 30%-50%,但更多的期待是浏览器对新语法的性能优化
后记
module 和 nomodule 虽然早已经不是2018年的技术点了,但是对于前端的性能优化也是开了一扇窗,但是也会遇到一些问题
下载两份
实测低版本的 Firefox 会下载两份 js 文件,但是只会执行一份,感兴趣的可以测试下其他的其他的浏览器,测试连接
Deploying ES2015+ Code in Production Today — Philip Walton
Import 路径
只支持显示的绝对和相对路径
// 支持
import { doSome } from '../utils.js'
import { doSome } from './utils.js'
// 不支持
import { doSome } from 'utils.js'
Defer
module 的脚本默认会像 <script defer> 一样加载,所以如果出现 JS 报错可以看下是不是在文档加载完成前就使用了文档的元素
CROS 跨域限制
// 不会执行 <script type="module" src="https://disanfang.com/cdn/react.js"></script>
凭证-credentials
这个是在 vue-cli 的 Modern mode failing to load module when under HTTP Basic Auth use credentials · Issue #1656 · vuejs/vue-cli · GitHub看到的,已经被 fix 掉了,具体的可以看下这个 issues
总得来说性能的提升结合公司的实际使用情况,尽可能的在构建层面解决掉,这样可以二分之一劳永逸