一、基本数据处理:字符串和数字
1.1 ASCII 码范围
大写字母(即 A 到 Z)为 65 到 90
小写字母为 97 到 122
数字 0~9 为 48 到 57
空格的 ASCII 码为 32,换行符的 ASCII 码为 10
函数 string.charCodeAt() 取字符的 ASCII 码
1.2 字符串拼接
// 简单拼接
wordOnlyText += letter
// 数组拼接
arrStr = arr.join('')
// 格式化 ${}
const name = 'Will Wen Gunn'
const level = 'Gold'
const message = `
Hello, ${name}.
Here is Turing Airline, you are the ${level} member of our Privilege Club.`
1.3 大小写字母转换
将 ASCII 码转换为对应字符 String.fromCharCode(code)
// 大写转小写
if (asciiCode >= 65 && asciiCode <= 90) {
lowerCaseText += String.fromCharCode(asciiCode + 32)
}
// 转大写 string.toLowerCase()
const lowerCaseText = wordOnlyText.toLowerCase()
1.4 字符串切分
数据清洗和分割
// 切分 string.split(separator)
const words = lowerCaseText.split(' ')
// 正则
const originalText = 'Hey dude, how is it going?'
const words = originalText.toLowerCase().match(/\w+/g)
// Output: [ 'hey', 'dude', 'how', 'is', 'it', 'going' ]
链式
正则更灵活
1.5 数字运算
幂运算 Math.pow(base, exponent)
对数运算 Math.log(x)
function getBaseLog(base, x) {
return Math.log(x) / Math.log(base)
}
console.log(getBaseLog(2, 1024)) //=> 10
二、基本数据处理:对象
2.1 对象例子
const prefix = 'MK'
const sourceVersion = 1
const latestVersion = 47
const ironMan = {
[prefix + sourceVersion]: '2008',
[prefix + latestVersion]: '2017'
}
console.log(ironMan.MK47) //=> 2017...
在 { [<expression>]: value } 中的 expression 为一个表达式
key甚至数字(只要为固定值),value可以是函数
2.2 对象读取
对象的读取方式(不同于pyhton的字典)
1、
<obj>.<key>(常用)
2、obj[key]
目标属性键为**数字、包含英文字母和下划线以外的字符串甚至是 Symbol 对象**的时候,用obj[key]
const obj = {
1: 2, // 数字
'a b c': 'd e f', //空格
[Symbol.for('foo')]: 'bar'
}
console.log(obj[1]) //=> 2; 像数组的引用
console.log(obj['a b c']) //=> d e f
console.log(obj[Symbol.for('foo')]) //=> bar...
2.3修改属性
const obj = {}
obj.foo = 'bar'
obj[1] = 2 // 像数组的引用
三、基本数据处理:数组
3.1 数组的操作
3.1.1 变异方法 (mutation method)
1、删除第一项:
shift() 返回删除结果
2、删除最后一项:
pop() 返回删除结果
3、在最后增加,可以push多个:
push() 结果返回数组的长度
4、在最前增加,可以连续序列:
unshift(1,2,3) 结果返回数组的长度
5、在中间插入
splice(index, 0, 'a', 'b', 'c') // 在index的位置插入,下标[index, end]都后退
6、删除:
splice(index, 1) 截取从下标index开始的1个元素,返回结果的内容
7、替换:
splice(1, 1, {id: "333", text: "Dell"}) // 取一个,并替换
8、增加:
splice(0, 0, 'a') //下标0开始的第0个元素,就是将a插在下标0前
splice(6, 2, 'a', 'b') //6为末尾,在末尾增加2个
9、排序:
l.sort()
10、倒序:
l.reverse() 返回整个倒序后的对象
----
splice本质上是对数组做截取 array.splice(start, deleteCount, element1[, ...[, elementN]])
如果超过2个参数,其含义:
先取,后塞;
取不到,就相当于增加了;
取到了,就当替换
let l = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
l.splice(2) // 返回下标[2, end]的数组截取,l为剩下的[0, 2)
l.splice(2,4) // 截取范围[2, 5]4个数; Output:[ 3, 4, 5, 6 ];l为剩下的[ 1, 2, 7, 8, 9 ]
3.1.2 非变异方法 (non-mutating method)
不会改变原始数组,但总是 返回一个新数组
// 过滤(或查找)
l.filter(x => x > 2)
// 拼接
l1.concat(l2)
// 截取
l.slice(6) // 从下标6开始,[6, end]
l.slice(6, 11) // 下标[6, 11)的范围
3.2 自定义封装数组操作
封装好 append、prepend 和 insert 函数
const arrayUtils = {
append(array, ...elements) {
array.push(...elements)
return array
},
prepend(array, ...elements) {
array.unshift(...elements)
return array
},
insert(array, index, ...elements) {
array.splice(index, 0, ...elements)
return array
},
remove(array, index) {
array.splice(index, 1)
return array
}
}
// 使用
const array = []
arrayUtils.append(array, 3) // 末端添加元素 3
arrayUtils.prepend(array, 1) // 首端添加元素 1
arrayUtils.insert(array, 1, 2) // 在位置 1 添加元素 2
arrayUtils.remove(array, 1)
3.3 数组的转换和聚合
进行数据转换的 map 和用于聚合数据的 reduce
3.3.1 转换 map
将一个数组中的内容,以一定的方式规律地转换为另一个数组内容。
const array = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ]
const addedArray = array.map(x+ => x + 2)
3.3.2 转换 reduce
const array = [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ]
const sumResult = array.reduce((left, right) => left + right)
3.3.3 封装
const array = [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ]
// 求和公式
function sum(array) {
return array.reduce(function(left, right) {
return left + right
})
}
// 求积公式
function multi(array) {
return array.reduce(function(left, right) {
return left * right
})
}
console.log(sum(array)) //=> 10
console.log(multi(array)) //=> 24
进一步抽象化封装 函数式编程 (回调)
const array = [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ]
function reduceFn(callback) {
return function(array) {
return array.reduce(callback)
}
}
const sum = reduceFn(function(left, right) {
return left + right
})
const multi = reduceFn(function(left, right) {
return left * right
})
console.log(sum(array)) //=> 10
console.log(multi(array)) //=> 24
3.4 Lodash 工具库
_.sum([ 1, 2, 3, 4 ]) // 求和
四、基本数据处理:基本统计
数列的数学特征值:平均、众数 等
4.1 平均值
平均值_.mean([ 1, 2, 3, 4 ])
// 应用: 求年龄的平均值
// Map & Reduce的结合
const crew = [
{
name: 'Peter',
gender: 'male',
level: 'Product Manager',
age: 32
},
{
name: 'Ben',
gender: 'male',
level: 'Senior Developer',
age: 28
},...
]
const ages = _.map(crew, function(person) {
return person.age
})
const meanAge = _.mean(ages)
// 或者
const meanAge = _.meanBy(crew, 'age')
// 或者
const meanAge = _.meanBy(crew, function(person) {
return person.age
})
4.2 统计 reduceByKey
"hello" -> [ "hello", 1 ]
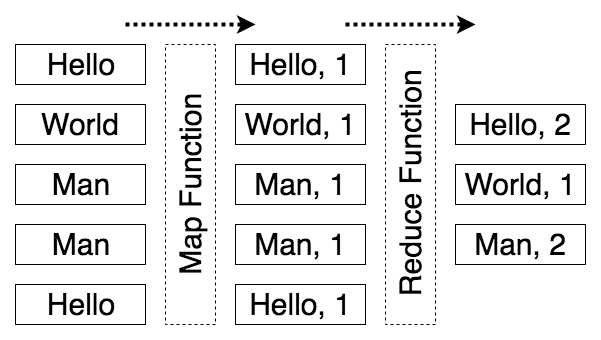
// 自定义reduceByKey
_.reduceByKey = function(tuples, reduceCallback) {
const grouped = _.groupBy(tuples, function(tuple) {
return tuple[0]
}) // { copy: [ [ 'copy', 1 ], [ 'copy', 1 ] ]...}
return _.toPairs(_.mapValues(grouped, function(tuples) {
return _.chain(tuples)
.map(function(tuple) {
return tuple[1]
})
.reduce(reduceCallback)
.value()
}))
}
// 数据来源 & map处理
const originalText = 'Permission is hereby granted, ...'
const words = originalText.toLowerCase().match(/\w+/g)
const tuples = words.map(function(word) {
return [ word, 1 ]
})
// 处理
const wordCountResult = _.reduceByKey(tuples, function(left, right) {
return left + right
})
console.log(wordCountResult) //=> [["permission", 2], ["is", 4], ["hereby", 1], ["granted", 1], ["free", 1], …]...
4.3 排序
const sorted = wordCountResult.sort(function(leftTuple, rightTuple) {
return rightTuple[1] - leftTuple[1] //比较第2个参数
})
console.log(sorted) //=> [["the", 14], ["or", 9], ["software", 9], ["of", 8], ["to", 8], …]...
4.4 裁剪
基于已排序的数组
// 取最前的
const top5 = sorted.slice(0, 5)
// 或者
const top5 = _.take(sorted, 5).map(function(tuple) {
return tuple[0]
}) //=> ["the", "software", "or", "to", "of"]...
// 取最小的(最后的)
const minimal5 = _.takeRight(sorted, 5) //=> [["from", 1], ["out", 1], ["connection", 1], ["with", 1], ["above", 1]]...