这几位讲解的都不错且有图有真相。

1.简单使用,先来个超简单的案例:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
EventBus.getDefault().register(this);
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this);
}
public void eventBusPost(View view) {
EventBus.getDefault().post("event bus demo");
}
@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.MAIN,sticky = true)
public void main2Demo1(String data) {
.............................
}
}第一步:根据组件的生命周期注册[EventBus.getDefault().register(this)]和注销[EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this)]
第二步:回调方法.回调方法要求1.public类型修饰的 2.方法参数只能有一个 3.使用@Subscribe修饰
第三步: 发送事件 EventBus.getDefault().post("event");
2.EventBus中的常量说明
开始之前先来张图。定义几个词汇。
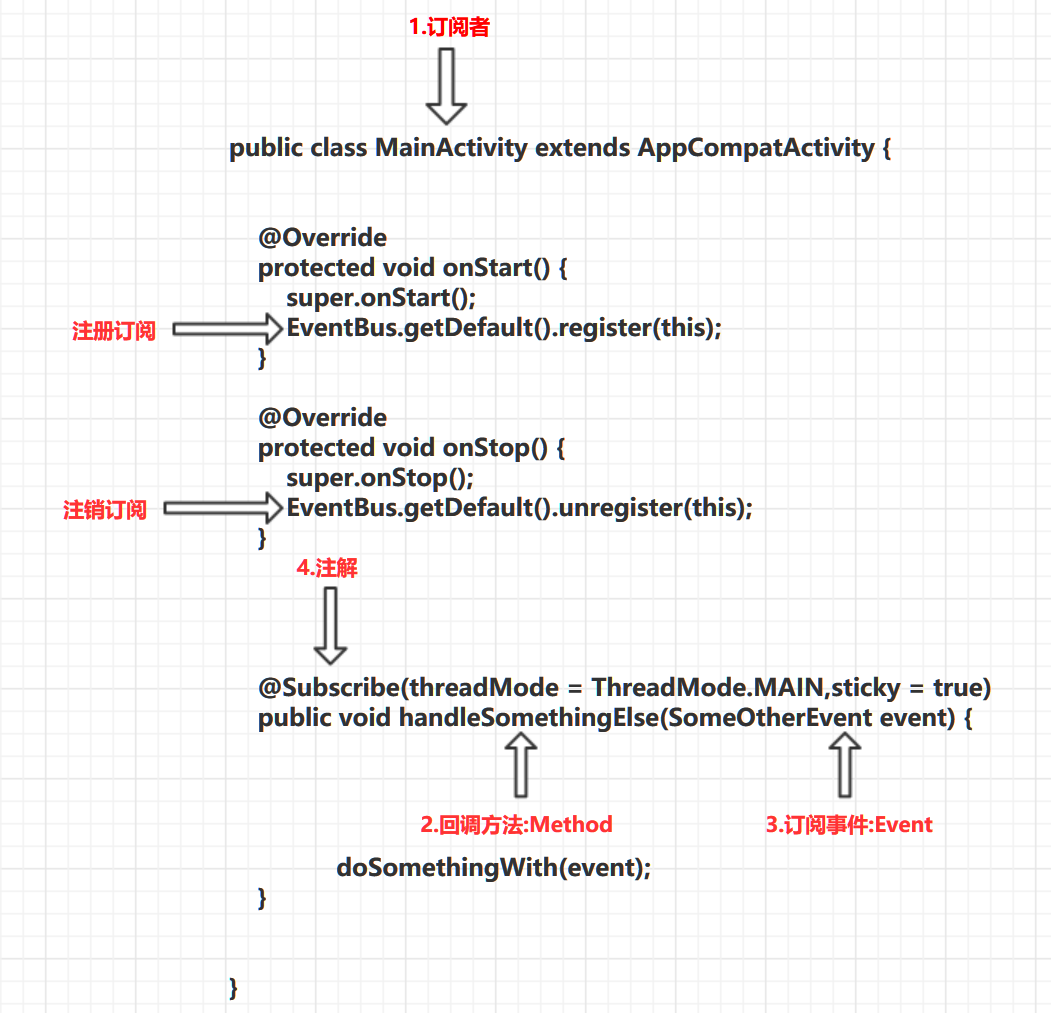
1.订阅者:EventBus中的订阅者可以是Activity|Fragment|Service。
2.回调(接收)方法:事件发送后接收的方法。在EventsBus中很粗暴,查找事件接收直接通过订阅者和回调方法名称反射调用
3.事件:所谓事件就是通过EventBus.getDefault().post(Object event)发送的数据.也就是回调方法接收的参数.
EventBus源码中的常量
private static final EventBusBuilder DEFAULT_BUILDER = new EventBusBuilder();
private static final Map<Class<?>, List<Class<?>>> eventTypesCache = new HashMap<>();
private final Map<Class<?>, CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription>> subscriptionsByEventType;
private final Map<Object, List<Class<?>>> typesBySubscriber;
private final Map<Class<?>, Object> stickyEvents;
private final ThreadLocal<PostingThreadState> currentPostingThreadState = new ThreadLocal<PostingThreadState>() {
@Override
protected PostingThreadState initialValue() {
return new PostingThreadState();
}
};- DEFAULT_BUILDER :EventBus默认使用的build。也可以使用自己的build
- eventTypesCache:Map类的数据集合。key是事件的class,value是当前事件class所有实现的接口类的集合。
private static List<Class<?>> lookupAllEventTypes(Class<?> eventClass) { synchronized (eventTypesCache) { List<Class<?>> eventTypes = eventTypesCache.get(eventClass); if (eventTypes == null) { eventTypes = new ArrayList<>(); Class<?> clazz = eventClass; while (clazz != null) { eventTypes.add(clazz); addInterfaces(eventTypes, clazz.getInterfaces()); clazz = clazz.getSuperclass(); } eventTypesCache.put(eventClass, eventTypes); } return eventTypes; } } Map<Class<?>, CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription>> subscriptionsByEventType:Map类的数据集合。key是事件的class , value是CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> 的集合类型.value为什么是集合类型?简单讲,同一个事件类型可能对应着多个订阅者的多个回调方法。例如:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onStart() { super.onStart(); EventBus.getDefault().register(this); } @Override protected void onStop() { super.onStop(); EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this); } @Subscribe public void receive1(String data) { ....... } @Subscribe public void receive2(String data) { ...... } @Subscribe public void receive3(String data) { ...... } @Subscribe public void receive4(String data) { ...... } } public class Main2Activity extends AppCompatActivity { ............. @Subscribe public void receive1(String data) { ....... } @Subscribe public void receive2(String data) { ...... } }可以看到在MainActivity中,事件是string类型的有4个回调方法.在Main2Activity中,事件是string类型的有2个回调方法.
Subscription是什么?
final class Subscription { //订阅者 final Object subscriber; //回调方法 final SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod; volatile boolean active; Subscription(Object subscriber, SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod) { this.subscriber = subscriber; this.subscriberMethod = subscriberMethod; active = true; } @Override public boolean equals(Object other) { //比较是否是同一个订阅和是否是同一个方法.来判定是否是同一个订阅者 if (other instanceof Subscription) { Subscription otherSubscription = (Subscription) other; return subscriber == otherSubscription.subscriber && subscriberMethod.equals(otherSubscription.subscriberMethod); } else { return false; } } @Override public int hashCode() { return subscriber.hashCode() + subscriberMethod.methodString.hashCode(); } }其实Subscription很简单就是对订阅者(Activity|Fragment|Service)和订阅者中的回调方法进行封装。再来看看SubscriberMethod
public class SubscriberMethod { //回调方法 final Method method; //线程模式 final ThreadMode threadMode; //事件class类型 final Class<?> eventType; //方法优先级 final int priority; //是否是粘性事件 final boolean sticky; //方法比较使用,类名称#方法名称(事件class名称 组合而成 String methodString; public SubscriberMethod(Method method, Class<?> eventType, ThreadMode threadMode, int priority, boolean sticky) { this.method = method; this.threadMode = threadMode; this.eventType = eventType; this.priority = priority; this.sticky = sticky; } @Override public boolean equals(Object other) { if (other == this) { return true; } else if (other instanceof SubscriberMethod) { checkMethodString(); SubscriberMethod otherSubscriberMethod = (SubscriberMethod)other; otherSubscriberMethod.checkMethodString(); return methodString.equals(otherSubscriberMethod.methodString); } else { return false; } } private synchronized void checkMethodString() { if (methodString == null) { StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(64); builder.append(method.getDeclaringClass().getName()); builder.append('#').append(method.getName()); builder.append('(').append(eventType.getName()); methodString = builder.toString(); } } @Override public int hashCode() { return method.hashCode(); } }SubscriberMethod是对回调的方法进行了封装.包含反射的Method、threadMode回调方法线程类型、eventType事件class类型、priority方法优先级、sticky是否是粘性事件。
- Map<Object, List<Class<?>>> typesBySubscriber,key是订阅者,value是当前订阅者回调方法对应的事件的 class类型集合。在注册EventBus#register()会将订阅者和回调方法一一添加进去。在注销EventBus#unregister()时会将订阅者的方法集合全部移除。
- Map<Class<?>, Object> stickyEvents。粘性事件的集合。key是事件的class,value是事件对象。EventBus的粘性事件原理很简单。就是在注册时就去stickyEvents集合中判断当前注册的方法是粘性方法的事件(回调参数类型)是否包含,如果存在就直接调用回调方法.
- ThreadLocal<PostingThreadState> currentPostingThreadState。保证当前线程中只有一个实例。这个常量的主要作用是将发送的事件加入队列。
public void post(Object event) { PostingThreadState postingState = currentPostingThreadState.get(); List<Object> eventQueue = postingState.eventQueue; //在这里将事件加入队列 eventQueue.add(event); if (!postingState.isPosting) { postingState.isMainThread = isMainThread(); postingState.isPosting = true; if (postingState.canceled) { throw new EventBusException("Internal error. Abort state was not reset"); } try { while (!eventQueue.isEmpty()) { //循环发送事件,每次移除一个事件。直到事件集合为空 postSingleEvent(eventQueue.remove(0), postingState); } } finally { postingState.isPosting = false; postingState.isMainThread = false; } } }
3.SubscriberMethodFinder中的常量
private static final Map<Class<?>, List<SubscriberMethod>> METHOD_CACHE = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static final int POOL_SIZE = 4;
private static final FindState[] FIND_STATE_POOL = new FindState[POOL_SIZE];- METHOD_CACHE。这个很好理解就是方法缓存。key是订阅者的class类型,value是集合类型,集合泛型是SubscriberMethod(这个类前面讲过了)。作用是在查找订阅者中的回调方法的时候,先根据订阅者class判断METHOD_CACHE中是否已经有SubscriberMethod集合。这样可以快速找到,避免再次查找。
- FIND_STATE_POOL。是FindState类型的数组。FindState是SubscriberMethodFinder的内部静态类。FIND_STATE_POOL的作用是快速提供一个FindState对象。
static class FindState { final List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = new ArrayList<>(); final Map<Class, Object> anyMethodByEventType = new HashMap<>(); final Map<String, Class> subscriberClassByMethodKey = new HashMap<>(); final StringBuilder methodKeyBuilder = new StringBuilder(128); Class<?> subscriberClass; Class<?> clazz; boolean skipSuperClasses; SubscriberInfo subscriberInfo; void initForSubscriber(Class<?> subscriberClass) { this.subscriberClass = clazz = subscriberClass; skipSuperClasses = false; subscriberInfo = null; } void recycle() { subscriberMethods.clear(); anyMethodByEventType.clear(); subscriberClassByMethodKey.clear(); methodKeyBuilder.setLength(0); subscriberClass = null; clazz = null; skipSuperClasses = false; subscriberInfo = null; } ...........省略.......... }FindState的主要作用是,将SubscriberMethodFinder反射订阅者的回调方法保存在FindState的subscriberMethods中。还有一个作用1.是判断在同一个类中是否存在回调方法名称形同且参数类型相同(怎么可能嘛!),2.如果在有继承关系的订阅者类中子类是否覆写了父类中的订阅回调方法,如果覆写了就用只会保存子类覆写的方法.

是不是看完(怎么可能看完呢!)觉得越来越迷糊了,那就对了.一定要先看看推荐的几位的文章.