前段时间在了解分布式,发现firefoxbug在博客中写的这篇《一致性hash在分布式系统中的应用》对这个问题说明得比较清晰易懂,本文主要是自己的理解和实践。
在后端一般会遇到这样的场景:随着应用系统的访问量或者DB/文件存储系统的数据量增大,系统由于负载增大而出现响应延迟甚至down掉的情况。为了解决这个问题,往往会对系统采用垂直扩展和水平扩展的架构设计,而分布式系统正是水平扩展架构的一种应用实践。
1 分布式系统要求
分布式设计的初衷就是为了解决单一服务端负载过大的问题,所以在对系统做水平扩展后,数据要尽量均匀地分布在每台服务器节点的上(即不会出现热点数据节点)。其次,如果后期需要扩容或者某一节点发生故障需要从集群中剔除,那么处理后的分布式系统应该做到对已存储的数据影响最小,降低数据迁移的成本和风险。
2 解决方法
由于机器的数量不可能是无限的,所以水平扩展的时候,要考虑把无限的数据通过一定的算法平衡、有序、易扩展地分布在这些机器上。
常见的做法是利用把要处理的数据进行编号,然后对机器的数据进行取模运算。例如,假设有10个数据(编号为0~9),机器数量为3(编号为0~2),那么每个数据编号对机器数3取模后,0号机器存放了编号为0,3,6,9的数据;1号机器存了编号为1,4,7的数据;2号机器存放了编号为2,5,8的数据。
取模算法比较简单,但是当某个服务器节点出现故障或者新增节点后,需要对已有数据作大量的迁移。在memcached分布式原理中介绍了Consistent Hashing算法,它能较好地解决这个问题。
3 一致性哈希算法原理
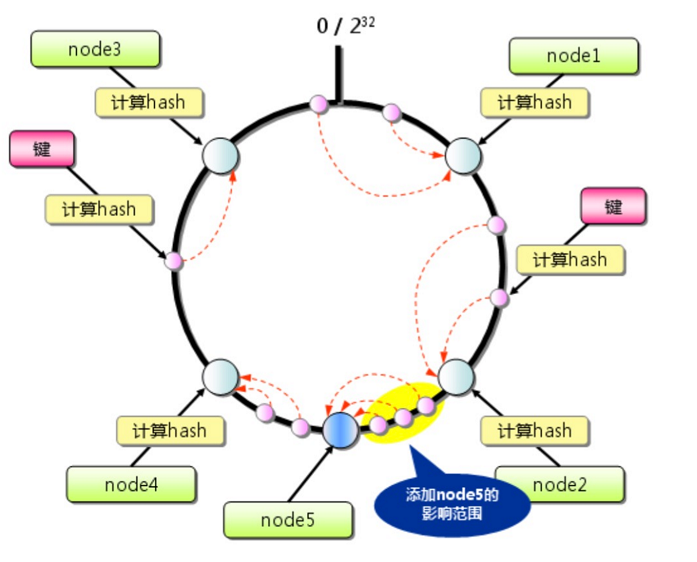
如上图所示,memcached分布式提供的哈希算法的主要处理流程如下:
1、使用算法求出每个memcached服务器节点(ip地址)的哈希值x,并将其分配到0~2^32的圆上(值域);
2、用同样的方法求出存储数据键的哈希值y,并映射到圆上。
3、按顺时针方向查找第1个比y大的x,那么y就分布在x前面那个节点上。
4 示例程序
在firefoxbug的原文中提供了python2的示例程序,这里改成了python3。注意,程序中对这4台机器都使用了虚拟节点(replicas),它可以增加数据分布的均匀性。
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
'''
FileName: consistenthashdistributed1.sh
Description: 分布式系统:一致性hash算法的应用
Simple Usage: python consistenthashdistributed1.py [numbers of replicate]
Reference: http://www.firefoxbug.com/index.php/archives/2791/
(c) 2018.02.17 vfhky https://typecodes.com/python/consistenthashdistributed1.html
'''
import sys
import hashlib
CONTENT = """Consistent hashing is a special kind of hashing such that when a hash table is resized and consistent hashing is used, only K/n keys need to be remapped on average, where K is the number of keys, and n is the number of slots. In contrast, in most traditional hash tables, a change in the number of array slots causes nearly all keys to be remapped."""
# 所有机器列表
SERVERS = [
"192.168.1.1",
"192.168.2.2",
"192.168.3.3",
"192.168.4.4"
]
class HashRing(object):
"""Constructs.
"""
def __init__(self, nodes=None, replicas=3):
"""Manages a hash ring.
`nodes` is a list of objects that have a proper __str__ representation.
`replicas` indicates how many virtual points should be used pr. node,
replicas are required to improve the distribution.
"""
self.replicas = replicas
self.ring = dict()
self._sorted_keys = []
if nodes:
for node in nodes:
self.add_node(node)
def add_node(self, node):
"""Adds a `node` to the hash ring (including a number of replicas).
"""
for i in range(0, self.replicas):
key = self.gen_key('%s:%s' % (node, i))
self.ring[key] = node
# print("key=[%s]=[%s]." %(key, node))
self._sorted_keys.append(key)
self._sorted_keys.sort()
#print("%s" %(self._sorted_keys))
def remove_node(self, node):
"""Removes `node` from the hash ring and its replicas.
"""
for i in range(0, self.replicas):
key = self.gen_key('%s:%s' % (node, i))
del self.ring[key]
self._sorted_keys.remove(key)
def get_node(self, string_key):
"""Given a string key a corresponding node in the hash ring is returned.
If the hash ring is empty, `None` is returned.
"""
return self.get_node_pos(string_key)[0]
def get_node_pos(self, string_key):
"""Given a string key a corresponding node in the hash ring is returned
along with it's position in the ring.
If the hash ring is empty, (`None`, `None`) is returned.
"""
if not self.ring:
return None, None
key = self.gen_key(string_key)
nodes = self._sorted_keys
nodes_num = len(nodes)
for i in range(0, nodes_num):
node = nodes[i]
if key <= node:
return self.ring[node], i
# 对于key>node节点key的,全部落在第1个key对应的节点(192.168.1.4)上,这样就形成了1个闭环。
print("[%s:%s] string_key=[%s] key=[%s] node=[%s] self.ring[nodes[0]]=[%s].\n" %(__file__, sys._getframe().f_lineno, string_key, key, node, self.ring[nodes[0]]))
return self.ring[nodes[0]], 0
def gen_key(self, key):
"""Given a string key it returns a long value,
this long value represents a place on the hash ring.
md5 is currently used because it mixes well.
"""
m = hashlib.md5()
m.update(key.encode('utf-8'))
return m.hexdigest()
def consistent_hash(replicas):
'''docstring'''
# 模拟初始化每天机器的db
database = {}
for s in SERVERS:
database[s] = []
hr = HashRing(SERVERS,replicas)
for w in CONTENT.split():
database[hr.get_node(w)].append(w)
# 打印所有的节点下面的数据
for node in database:
print("[%s]=[%s].\n" %(node, database[node]))
if __name__ == '__main__':
'''docstring'''
replicas = 3
if len(sys.argv) > 1:
replicas = long(sys.argv[1])
if( replicas < 3 or replicas > 100000 ):
print( "Rreplicas should lower than 100000." )
sys.exit()
consistent_hash(replicas)
5 测试
上面程序在查找落地节点时,采用的是遍历整个hash圈上的值,所以虚拟节点不宜过大,否则会出现查找时间过长的问题。如下图所示,BZ在自己的单核1G内存的虚拟机中测试,发现4个节点如果都有10000个虚拟节点时在速度和均衡性方面都是不错的。