原文:Deep Learning From Scratch III: Training Criterion - deep ideas
翻译:孙一萌
- 第一章:计算图
- 第二章:感知机
- 第三章:训练标准
- 第四章:梯度下降与反向传播
- 第五章:多层感知机
- 第六章:TensorFlow
Training criterion
现在我们学会了用线性分类器将点分类,以及计算点属于某个特定分类的概率,只要我们给权矩阵 和偏置
一个合适的值。
那么自然我们就遇到一个问题:怎样给权矩阵 和偏置
一个合适的值。在红/蓝的例子中,我们就光观察了一下训练数据,然后靠猜得到一条线,把平面上的点完美地分割成了两部分。
但一般来说,我们不想亲手去找出一条分割线,我们希望的是,把训练点提供给计算机之后,它可以自己找到一条好的分割线。
那么我们怎么评价分割线是好是坏呢?
错分率(The misclassification rate)
理想情况下,我们希望找到一条错误尽可能少的分割线。我们不知道真实的数据生成分布 是什么样的,但是对于其中的每一个点 x 及其所属的每一个分类 c(x),我们都希望使感知机分类错误的概率最小。也就是最小化
错分率:
通常情况下,我们不知道真实的数据生成分布 的情况,所以计算出错分率的确切数值是不可能的。但是我们是有一组训练点的,这些训练点里包含 x 的值和它所属的分类。
在后文中,我们会用形如 的矩阵代指一组训练点,每一行代表一个训练点,矩阵列的数目等于训练点的维数,每一列代表一个维度。
除此以外,我们把真实正确的分类情况用矩阵 表示,如果第
个训练样本拥有分类
,那么
[math]$ c_{i,j} = 1 $[/math] 。相似地,我们也用一个矩阵 代表预期的分类情况,如果第
个训练样本的预测类别是
,那么
。
最后,我们用矩阵 来表示概率,其中
表示第
个训练样本属于类别
的概率。
通过训练数据,我们能找到一个样本错分率最低的分类器:
然而我们发现,要找到错分率最低的线性分类器非常困难:随着输入数据的维度的提高,计算复杂度呈指数级增长,找到这个线性分类器显得不切实际。
就算我们找到了错分率最低的分类器,它也可能通过把类别区分得更开,使得自己更具鲁棒性以应对未知数据,即便它这么做并不会降低样本错分率。
最大似然估计
替代方法是最大似然估计,在最大似然估计中,我们尝试寻找特定的参数值,来使得概率 最大化。
此处我们引入
被称为交叉熵损失。此处我们希望把
最小化。
我们把 看成一个
Operation,那么它的输入就有:数据 、真实的分类情况
和预期概率
。
即 operation
的输出。
这样就可以计算出损失的真实数字:
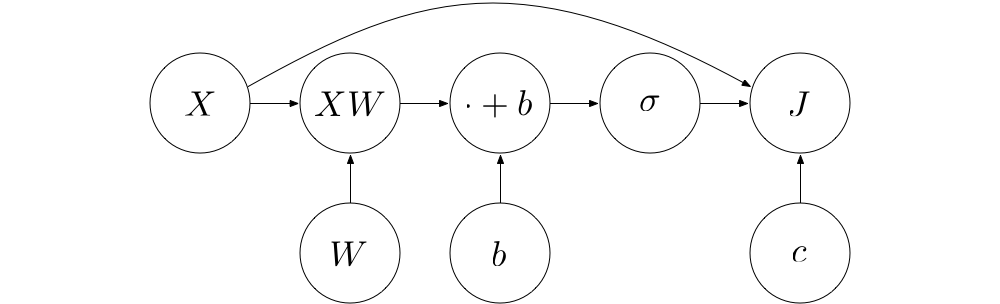
建造一个用于计算  的
的 operation
要建造用于计算 的
operaion,我们可以把多个初级一些的 operation 结合起来。首先, 可以用矩阵运算
作如下表示:
从中我们可以发现,上述的“初级一些”的 operation 有如下几种:
-
log:矩阵或者向量的,对每个元素进行的对数(log)运算
-
⊙:两个矩阵之间,对每个元素进行的乘法运算
-
:矩阵所有列的总和
-
:矩阵所有行的总和
-
−:逐元素负运算
然后我们将它们分别实现一下。
1. log
对张量(tensor)的逐元素对数运算:
class Operation:
"""Represents a graph node that performs a computation.
An `Operation` is a node in a `Graph` that takes zero or
more objects as input, and produces zero or more objects
as output.
"""
def __init__(self, input_nodes=[]):
"""Construct Operation
"""
self.input_nodes = input_nodes
# Initialize list of consumers (i.e. nodes that receive this operation's output as input)
self.consumers = []
# Append this operation to the list of consumers of all input nodes
for input_node in input_nodes:
input_node.consumers.append(self)
# Append this operation to the list of operations in the currently active default graph
_default_graph.operations.append(self)
def compute(self):
"""Computes the output of this operation.
"" Must be implemented by the particular operation.
"""
pass
class Graph:
"""Represents a computational graph
"""
def __init__(self):
"""Construct Graph"""
self.operations = []
self.placeholders = []
self.variables = []
def as_default(self):
global _default_graph
_default_graph = self
class placeholder:
"""Represents a placeholder node that has to be provided with a value
when computing the output of a computational graph
"""
def __init__(self):
"""Construct placeholder
"""
self.consumers = []
# Append this placeholder to the list of placeholders in the currently active default graph
_default_graph.placeholders.append(self)
class Variable:
"""Represents a variable (i.e. an intrinsic, changeable parameter of a computational graph).
"""
def __init__(self, initial_value=None):
"""Construct Variable
Args:
initial_value: The initial value of this variable
"""
self.value = initial_value
self.consumers = []
# Append this variable to the list of variables in the currently active default graph
_default_graph.variables.append(self)
class add(Operation):
"""Returns x + y element-wise.
"""
def __init__(self, x, y):
"""Construct add
Args:
x: First summand node
y: Second summand node
"""
super().__init__([x, y])
def compute(self, x_value, y_value):
"""Compute the output of the add operation
Args:
x_value: First summand value
y_value: Second summand value
"""
return x_value + y_value
class matmul(Operation):
"""Multiplies matrix a by matrix b, producing a * b.
"""
def __init__(self, a, b):
"""Construct matmul
Args:
a: First matrix
b: Second matrix
"""
super().__init__([a, b])
def compute(self, a_value, b_value):
"""Compute the output of the matmul operation
Args:
a_value: First matrix value
b_value: Second matrix value
"""
return a_value.dot(b_value)
class Session:
"""Represents a particular execution of a computational graph.
"""
def run(self, operation, feed_dict={}):
"""Computes the output of an operation
Args:
operation: The operation whose output we'd like to compute.
feed_dict: A dictionary that maps placeholders to values for this session
"""
# Perform a post-order traversal of the graph to bring the nodes into the right order
nodes_postorder = traverse_postorder(operation)
# Iterate all nodes to determine their value
for node in nodes_postorder:
if type(node) == placeholder:
# Set the node value to the placeholder value from feed_dict
node.output = feed_dict[node]
elif type(node) == Variable:
# Set the node value to the variable's value attribute
node.output = node.value
else: # Operation
# Get the input values for this operation from node_values
node.inputs = [input_node.output for input_node in node.input_nodes]
# Compute the output of this operation
node.output = node.compute(*node.inputs)
# Convert lists to numpy arrays
if type(node.output) == list:
node.output = np.array(node.output)
# Return the requested node value
return operation.output
def traverse_postorder(operation):
"""Performs a post-order traversal, returning a list of nodes
in the order in which they have to be computed
Args:
operation: The operation to start traversal at
"""
nodes_postorder = []
def recurse(node):
if isinstance(node, Operation):
for input_node in node.input_nodes:
recurse(input_node)
nodes_postorder.append(node)
recurse(operation)
return nodes_postorder
class softmax(Operation):
"""返回 a 的 softmax 函数结果.
"""
def __init__(self, a):
"""构造 softmax
参数列表:
a: 输入节点
"""
super().__init__([a])
def compute(self, a_value):
"""计算 softmax operation 的输出值
参数列表:
a_value: 输入值
"""
return np.exp(a_value) / np.sum(np.exp(a_value), axis=1)[:, None]
class log(Operation):
""" 对每一个元素进行对数运算
"""
def __init__(self, x):
""" 构造 log
参数列表:
x: 输入节点
"""
super().__init__([x])
def compute(self, x_value):
""" 计算对数 operation 的输出
参数列表:
x_value: 输入值
"""
return np.log(x_value)
2. 乘法 / ⊙
对两个同样形状的张量的逐元素乘法运算
class multiply(Operation):
""" 对每一个元素,返回 x * y 的值
"""
def __init__(self, x, y):
""" 构造乘法
参数列表:
x: 第一个乘数的输入节点
y: 第二个乘数的输入节点
"""
super().__init__([x, y])
def compute(self, x_value, y_value):
""" 计算乘法 operation 的输出
Args:
x_value: 第一个乘数的值
y_value: 第二个乘数的值
"""
return x_value * y_value
3. reduce_sum
为了在单个 operation 里计算多种总和(比如所有行的总和、所有列的总和等等),我们指定一个值 axis,如果 axis = 0 就表示计算行的总和,axis = 1 表示计算列的总和,等等等等。Numpy 就是这样实现的。
class reduce_sum(Operation):
""" 计算张量中元素延某一或某些维度的总和
"""
def __init__(self, A, axis=None):
""" 构造 reduce_sum
参数列表:
A: 要进行 reduce 运算的张量
axis: 需要 reduce 的维度,如果 `None`(即缺省值),则延所有维度 reduce
"""
super().__init__([A])
self.axis = axis
def compute(self, A_value):
""" 计算 reduce_sum operation 的输出值
参数列表:
A_value: 输入的张量值
"""
return np.sum(A_value, self.axis)
4. 负运算
对张量的每个元素进行负运算:
class negative(Operation):
""" 逐元素计算负数
"""
def __init__(self, x):
""" 构造负运算
参数列表:
x: 输入节点
"""
super().__init__([x])
def compute(self, x_value):
""" 计算负运算 operation 的输出
参数列表:
x_value: 输入值
"""
return -x_value
5. 结合这些 operation
用上述这些 operation,我们现在可以把 J 的运算写成如下形式:
J = negative(reduce_sum(reduce_sum(multiply(c, log(p)), axis=1)))
### 举例 现在我们来计算一下红/蓝 perceptron 的损失
import numpy as np
red_points = np.random.randn(50, 2) - 2*np.ones((50, 2))
blue_points = np.random.randn(50, 2) + 2*np.ones((50, 2))
# 创建一个新的 graph
Graph().as_default()
X = placeholder()
c = placeholder()
W = Variable([
[1, -1],
[1, -1]
])
b = Variable([0, 0])
p = softmax(add(matmul(X, W), b))
# 交叉熵损失
J = negative(reduce_sum(reduce_sum(multiply(c, log(p)), axis=1)))
session = Session()
print(session.run(J, {
X: np.concatenate((blue_points, red_points)),
c:
[[1, 0]] * len(blue_points)
+ [[0, 1]] * len(red_points)
}))
如果你有什么疑问,尽管在评论区提出。