关注我,每天都有优质技术文章推送,工作,学习累了的时候放松一下自己。
本篇文章同步微信公众号
欢迎大家关注我的微信公众号:「醉翁猫咪」

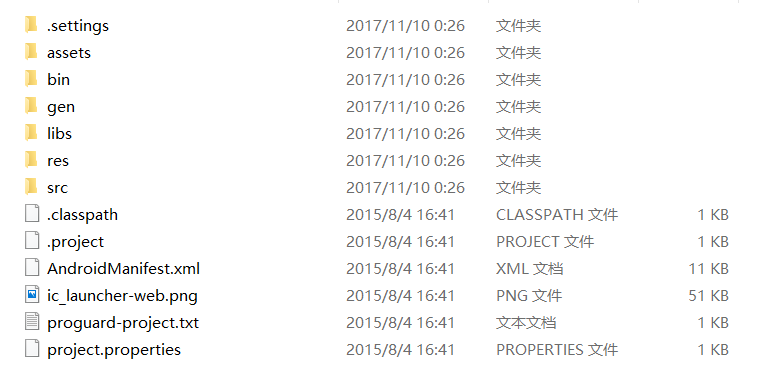
bin目录:在bin目录下存放的是可执行的相关文件,这个目录为空时,代表项目没有进行执行,不为空时,就会在该目录下产生可执行文件。
gen目录:在该目录下的文件只有读模式,不能进行修改。
libs目录:在该目录下存放的是相关的导入包,文件以.jar结尾。
res目录:在该目录下存放了这些文件,比如图片资源文件,布局资源文件,菜单文件等等。对于layout文件,主要.xml格式文件,界面效果文件。
proguard-project.txt文件:该文件时混淆代码的脚本配置文件。
project.properties文件:该文件时项目的配置文件信息。
应用程序分析
我们来讲讲我们常见:string.xml文件,该文件放在res/values目录中,该文件中可以看到string元素,我们来看看这个:Hello world!,那么我们在代码中如何使用该代码,就需要使用字符串资源的ID和getString()方法来获取。
闲谈“@+id”和“@id”的区别
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@drawable/launch_bg"
tools:context=".SplashActivity" >
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progressBar1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_splash_version"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_below="@+id/progressBar1"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:shadowColor="#ffff00"
android:textColor="#A2A2A2"
android:shadowDx="1"
android:shadowDy="1"
android:shadowRadius="2"
android:text="版本号:1.0"
android:textSize="16sp" />
</RelativeLayout>
“@+id/”这个表示在R文件中生成一个资源id,而后面的变量名,就随便取了,但是也不能够太随便了,尽量见名知意的好。“@+id/”只能在R.java中生成一次,如果这个变量的值已经存在了,就不会再生成。
“@id”这个是一旦建立好资源id文件,就引用该定义好的id。
闲谈单位问题
对于px,nm,in,pt,dp,sp等等,是不很乱呢?
px像素,dp与密度无关的像素,1dp=1px,之间的换算也可能改变,mm毫米,in英寸,pt榜,我们常用的sp,用于字体显示大小。
AndroidManifest.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.jack.myapplication">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUN
CHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
build.gradle(Module:app)
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
android {
compileSdkVersion 26
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.example.jack.myapplication"
minSdkVersion 19 //表示Android SDK的最低版本
targetSdkVersion 26 //表示应用程序的目标版本
versionCode 1 //表示应用程序的相应版本
versionName "1.0" //版本信息
testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
}
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
implementation 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:26.1.0'
implementation 'com.android.support.constraint:constraint-layout:1.0.2'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.12'
androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test:runner:1.0.1'
androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.0.1'
}
应用程序权限
网络权限:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET">
</uses-permission>
权限是放在AndroidManifest.xml中声明的。
如果觉得不错,可以分享哦,你的鼓励是我最大的进步!
