


1.设计线程安全的类
设计普通的类:
public class Counter {
private long value = 0;
public long getValue() {
return value;
}
public long increment() {
if (value == Long.MAX_VALUE) {
throw new IllegalStateException("counter overflow");
}
return ++ value;
}
}
线程安全的类

public class SimpleThread extends Thread {
Counter counter = new Counter();
SimpleLock lock = SimpleLock.getInstance();
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
counter.increment();
}
}
// @Override
// public void run() {
// counter.increment();
// }
}


1.对象状态组成:

见下文。。。
3.并发访问策略:
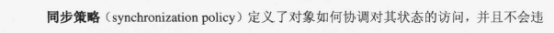

1.1收集同步需求

状态空间:变量类型限制?
不可变约束:语法规则与业务规则?
1.2状态依赖操作

1.3状态所有权


2.组合对象分类:
2.1 简单示例
监视器模式:
**
* Java监视器模式 简单线程安全的计数器
*/
public final class Counter_ThreadSafeSimple {
private long value = 0;
public synchronized long getValue() {
return value;
}
public synchronized long increment() {
if (value == Long.MAX_VALUE) {
throw new IllegalStateException("counter overflow");
}
return ++ value;
}
}
/**
* 非线程安全的计数器
*/
public final class Counter_NotThreadSafe {
private long value = 0;
public long getValue() {
return value;
}
public long increment() {
if (value == Long.MAX_VALUE) {
throw new IllegalStateException("counter overflow");
}
return ++ value;
}
}
**
* 实例限制线程安全的计数器
*/
public final class Counter_ThreadSafeWrapper {
private Counter_NotThreadSafe counter;
public Counter_ThreadSafeWrapper () {
counter = new Counter_NotThreadSafe();
}
public synchronized long getValue() {
return counter.getValue();
}
public synchronized long increment() {
return counter.increment();
}
}
**
* 委托线程安全的计数器
*/
public final class Counter_DelegateThreadSafe {
private AtomicLong value = new AtomicLong(0);
public long getValue() {
return value.longValue();
}
public long increment() {
return value.incrementAndGet();
}
}
2.2实战注意
1)使用私有锁:











3.向已有的线程安全类添加功能



4.同步策略的文档化
