准备:
1:销售记录文件book_sales
2:书的描述类Sales_item.h
book_sales内容如下
0-201-70353-X 4 24.99
0-201-82470-1 4 45.39
0-201-88954-4 2 15.00
0-201-88954-4 5 12.00
0-201-88954-4 7 12.00
0-201-88954-4 2 12.00
0-399-82477-1 2 45.39
0-399-82477-1 3 45.39
0-201-78345-X 3 20.00
0-201-78345-X 2 25.00#ifndef SALESITEM_H
// we're here only if SALESITEM_H has not yet been defined
#define SALESITEM_H
// Definition of Sales_item class and related functions goes here
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class Sales_item {
// these declarations are explained section 7.2.1, p. 270
// and in chapter 14, pages 557, 558, 561
friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream&, Sales_item&);
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream&, const Sales_item&);
friend bool operator<(const Sales_item&, const Sales_item&);
friend bool
operator==(const Sales_item&, const Sales_item&);
public:
// constructors are explained in section 7.1.4, pages 262 - 265
// default constructor needed to initialize members of built-in type
Sales_item(): units_sold(0), revenue(0.0) { }
Sales_item(const std::string &book):
bookNo(book), units_sold(0), revenue(0.0) { }
Sales_item(std::istream &is) { is >> *this; }
public:
// operations on Sales_item objects
// member binary operator: left-hand operand bound to implicit this pointer
Sales_item& operator+=(const Sales_item&);
// operations on Sales_item objects
std::string isbn() const { return bookNo; }
double avg_price() const;
// private members as before
private:
std::string bookNo; // implicitly initialized to the empty string
unsigned units_sold;
double revenue;
};
// used in chapter 10
inline
bool compareIsbn(const Sales_item &lhs, const Sales_item &rhs)
{ return lhs.isbn() == rhs.isbn(); }
// nonmember binary operator: must declare a parameter for each operand
Sales_item operator+(const Sales_item&, const Sales_item&);
inline bool
operator==(const Sales_item &lhs, const Sales_item &rhs)
{
// must be made a friend of Sales_item
return lhs.units_sold == rhs.units_sold &&
lhs.revenue == rhs.revenue &&
lhs.isbn() == rhs.isbn();
}
inline bool
operator!=(const Sales_item &lhs, const Sales_item &rhs)
{
return !(lhs == rhs); // != defined in terms of operator==
}
// assumes that both objects refer to the same ISBN
Sales_item& Sales_item::operator+=(const Sales_item& rhs)
{
units_sold += rhs.units_sold;
revenue += rhs.revenue;
return *this;
}
// assumes that both objects refer to the same ISBN
Sales_item
operator+(const Sales_item& lhs, const Sales_item& rhs)
{
Sales_item ret(lhs); // copy (|lhs|) into a local object that we'll return
ret += rhs; // add in the contents of (|rhs|)
return ret; // return (|ret|) by value
}
std::istream&
operator>>(std::istream& in, Sales_item& s)
{
double price;
in >> s.bookNo >> s.units_sold >> price;
// check that the inputs succeeded
if (in)
s.revenue = s.units_sold * price;
else
s = Sales_item(); // input failed: reset object to default state
return in;
}
std::ostream&
operator<<(std::ostream& out, const Sales_item& s)
{
out << " bookNo "<< s.isbn() << " soldNum " << s.units_sold << " totalSoldMoney "
<< s.revenue << " price " << s.avg_price();
return out;
}
double Sales_item::avg_price() const
{
if (units_sold)
return revenue/units_sold;
else
return 0;
}
#endif下面开始编写代码:
hello.cc
#include <iostream>
#include "Sales_item.h"
int main()
{
Sales_item totalBook;//统计对象
if(std::cin>>totalBook){//第一次读取的值赋值给totalBook
Sales_item currBook;//当前对象
while(std::cin>>currBook)//从第二次开始,读取的值赋给currBook
{
if(totalBook.isbn()==currBook.isbn())//上一次读取的对象与当前读取的对象书本编号相等,就叠加
{
totalBook += currBook;
}else{//否则就打印上次书本统计的结果,接着又把当前读取的对象赋值给统计对象
std::cout<<totalBook<<std::endl;
totalBook = currBook;
}
}
std::cout<<totalBook<<std::endl;//打印最后统计的值
}else{
std::cerr<<"no data!!!"<<std::endl;
return -1;
}
return 0;
}逻辑类似于上一个练习,就不一一分析了。
接下来就是编译阶段
1:生成可执行程序
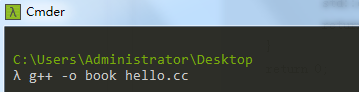
在window下会生成book.exe可执行程序
ps:上述的所有文件都在统一目录下,这点很重要,不然会报错
2:读取销售记录文件以及程序输出到文件中
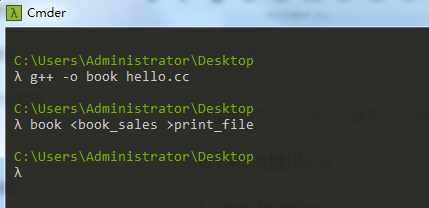
这里用到文件重定向的机制,这种机制允许我们将标准输入和标准输出与命名文件关联起来
book <book_sales >print_file
book为book.exe执行程序,<book_sales代表从book_sales读取输入,>print_file代表程序标准输出到print_file文件中
经过这一系列,在同级目录下,你会看到生成的print_file,内容如下:
bookNo 0-201-70353-X soldNum 4 totalSoldMoney 99.96 price 24.99
bookNo 0-201-82470-1 soldNum 4 totalSoldMoney 181.56 price 45.39
bookNo 0-201-88954-4 soldNum 16 totalSoldMoney 198 price 12.375
bookNo 0-399-82477-1 soldNum 5 totalSoldMoney 226.95 price 45.39
bookNo 0-201-78345-X soldNum 5 totalSoldMoney 110 price 22