一、OkHttp基本用法:
1、异步get请求
OkHttpClient okHttpClient = new OkHttpClient();
final Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("")
.build();
Call call = okHttpClient.newCall(request);
call.enqueue(new Callback() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException {
Log.d("OkHttp", "onResponse: "+response.body().toString());
}
});2、异步post请求
OkHttpClient okHttpClient = new OkHttpClient();
RequestBody requestBody = new FormBody.Builder()
.add("name","my")
.build();
final Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("")
.post(requestBody)
.build();
Call call = okHttpClient.newCall(request);
call.enqueue(new Callback() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException {
Log.d("OkHttp", "onResponse: "+response.body().toString());
}
});3、OkHttp简单封装
(1)定义回调接口
public interface ResultCallback {
//请求失败回调
void onError(Exception e);
//请求成功回调
void onResponse(Response response);
}(2)封装OkHttp
public class OkHttpEngine {
private static volatile OkHttpEngine mInstance;
private OkHttpClient mOkHttpClient;
private Handler mHandler;
public static OkHttpEngine getInstance(Context context) {
if (mInstance == null) {
synchronized (OkHttpEngine.class) {
if (mInstance == null) {
mInstance = new OkHttpEngine(context);
}
}
}
return mInstance;
}
public OkHttpEngine(Context context) {
mHandler = new Handler();
//缓存路径
File file = context.getExternalCacheDir();
//缓存大小
int cacheSize = 10 * 1024 * 1024;
mOkHttpClient = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.connectTimeout(20, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) //超时时间
.readTimeout(20, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
.writeTimeout(20, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
.addInterceptor(new HttpLoggingInterceptor()) //log日志
.cache(new Cache(file.getAbsoluteFile(), cacheSize))
.build();
}
/**
* 异步get请求
*/
public void getAsynHttp(String url, final ResultCallback callback) {
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(url)
.build();
asyncRequest(request, callback);
}
/**
* 异步post请求
*
* @param url
* @param requestMap 请求参数
* @param callback 回调接口
*/
public void postAsynHttp(String url, Map<String, String> requestMap, final ResultCallback callback) {
FormBody.Builder builder = new FormBody.Builder();
if (requestMap != null && requestMap.size() > 0) {
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : requestMap.entrySet()) {
builder.add(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(url)
.post(builder.build())
.build();
asyncRequest(request, callback);
}
public void asyncRequest(Request request, final ResultCallback callback) {
Call call = mOkHttpClient.newCall(request);
call.enqueue(new Callback() {
@Override
public void onFailure(okhttp3.Call call, final IOException e) {
if (callback != null) {
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
callback.onError(e);
}
});
}
}
@Override
public void onResponse(okhttp3.Call call, final Response response) throws IOException {
if (callback != null) {
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
callback.onResponse(response);
}
});
}
}
});
}
}二、OkHttp源码解析
1、流程图:
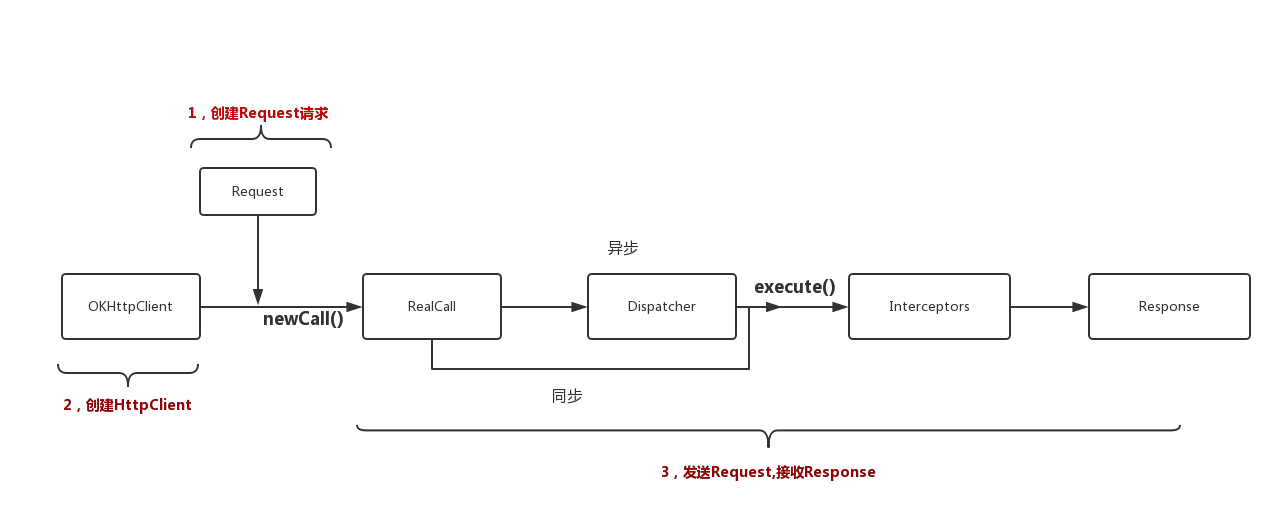
2、创建OkHttpClient:
public Builder() {
dispatcher = new Dispatcher();
protocols = DEFAULT_PROTOCOLS;
connectionSpecs = DEFAULT_CONNECTION_SPECS;
eventListenerFactory = EventListener.factory(EventListener.NONE);
proxySelector = ProxySelector.getDefault();
cookieJar = CookieJar.NO_COOKIES;
socketFactory = SocketFactory.getDefault();
hostnameVerifier = OkHostnameVerifier.INSTANCE;
certificatePinner = CertificatePinner.DEFAULT;
proxyAuthenticator = Authenticator.NONE;
authenticator = Authenticator.NONE;
connectionPool = new ConnectionPool();
dns = Dns.SYSTEM;
followSslRedirects = true;
followRedirects = true;
retryOnConnectionFailure = true;
connectTimeout = 10_000;
readTimeout = 10_000;
writeTimeout = 10_000;
pingInterval = 0;
}3、创建Request:
public final class Request {
final HttpUrl url;
final String method;
final Headers headers;
final @Nullable RequestBody body;
final Object tag;
...Request类封装了请求报文信息:请求的Url地址、请求的方法(如GET、POST等)、各种请求头(如Content-Type、Cookie)以及可选的请求体。一般通过内部类Request.Builder的链式调用生成Request对象。
4、创建RealCall对象:
(1)Call接口:
public interface Call extends Cloneable {
//返回当前Call的request对象
Request request();
//同步请求
Response execute() throws IOException;
//异步请求
void enqueue(Callback responseCallback);
//取消请求
void cancel();
//是否执行过
boolean isExecuted();
//是否取消请求
boolean isCanceled();
interface Factory {
okhttp3.Call newCall(Request request);
}
}Call是一个接口,主要定义了进行请求和取消请求等的方法 。内部有一个newCall方法,传入一个Request返回一个Call。
(2)RealCall对象:
final class RealCall implements Call {
final OkHttpClient client;
final RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor retryAndFollowUpInterceptor;
private EventListener eventListener;
final Request originalRequest;
final boolean forWebSocket;
// Guarded by this.
private boolean executed;
...
static okhttp3.RealCall newRealCall(OkHttpClient client, Request originalRequest, boolean forWebSocket) {
// Safely publish the Call instance to the EventListener.
okhttp3.RealCall call = new okhttp3.RealCall(client, originalRequest, forWebSocket);
call.eventListener = client.eventListenerFactory().create(call);
return call;
}
}RealCall发起请求的真正类,实现了Call接口
(3)创建RealCall:
@Override public Call newCall(Request request) {
return RealCall.newRealCall(this, request, false);
}通过调用OkHttpClient newCall方法创建,内部是通过RealCall的newRealCall方法
5、进行异步请求:
(1) Realcall的enqueue方法:
@Override public void enqueue(Callback responseCallback) {
synchronized (this) {
if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");
executed = true;
}
captureCallStackTrace();
eventListener.callStart(this);
client.dispatcher().enqueue(new AsyncCall(responseCallback));
}client.dispatcher返回的是Dispatcher,最终调用了Dispatcher的enqueue方法
(2)Dispatcher任务调度:
public final class Dispatcher {
//最大并发请求数64
private int maxRequests = 64;
//每个主机的最大请求数
private int maxRequestsPerHost = 5;
private @Nullable
Runnable idleCallback;
//消费者线程池
private @Nullable
ExecutorService executorService;
//将会开始的异步任务队列
private final Deque<RealCall.AsyncCall> readyAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
//正在进行的异步任务队列
private final Deque<RealCall.AsyncCall> runningAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
//正在运行的同步任务队列
private final Deque<RealCall> runningSyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
public Dispatcher(ExecutorService executorService) {
this.executorService = executorService;
}
public Dispatcher() {
}
public synchronized ExecutorService executorService() {
if (executorService == null) {
executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(), Util.threadFactory("OkHttp Dispatcher", false));
}
return executorService;
}
...
}可以在构造函数中传入自定义线程池
(3)调用enqueue方法:
synchronized void enqueue(AsyncCall call) {
if (runningAsyncCalls.size() < maxRequests && runningCallsForHost(call) < maxRequestsPerHost) {
runningAsyncCalls.add(call);
executorService().execute(call);
} else {
readyAsyncCalls.add(call);
}
}请求队列请求数小于64,正在运行请求主机数小于5,将请求加入正在运行的队列并在线程池中执行。否则加入准备队列。(传入的参数为AsyncCall类型对象)
(4)调用AsyncCall的execute方法
final class AsyncCall extends NamedRunnableAsyncCall为RealCall内部类,继承了NamedRunnable,也是一个Runnable实现类
@Override protected void execute() {
boolean signalledCallback = false;
try {
//返回request
Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
if (retryAndFollowUpInterceptor.isCanceled()) {
signalledCallback = true;
//请求失败回调
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, new IOException("Canceled"));
} else {
signalledCallback = true;
//请求成功回调
responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
if (signalledCallback) {
// Do not signal the callback twice!
Platform.get().log(INFO, "Callback failure for " + toLoggableString(), e);
} else {
eventListener.callFailed(RealCall.this, e);
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, e);
}
} finally {
//完成操作后,调用Dispatcher的finished方法
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
}(5)调用Dispatcher的finished方法:
finished内部调用了promoteCalls方法
private void promoteCalls() {
if (runningAsyncCalls.size() >= maxRequests) return; // Already running max capacity.
if (readyAsyncCalls.isEmpty()) return; // No ready calls to promote.
for (Iterator<AsyncCall> i = readyAsyncCalls.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
AsyncCall call = i.next();
if (runningCallsForHost(call) < maxRequestsPerHost) {
i.remove();
runningAsyncCalls.add(call);
executorService().execute(call);
}
if (runningAsyncCalls.size() >= maxRequests) return; // Reached max capacity.
}
}进行迭代下个请求,在准备队列移除并加入到正在运行的队列,并执行线程池。
(6)请求是通过调用getResponseWithInterceptorChain,返回Response
Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException {
// Build a full stack of interceptors.
List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors());
interceptors.add(retryAndFollowUpInterceptor);
interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar()));
interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache()));
interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client));
if (!forWebSocket) {
interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors());
}
interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket));
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, null, null, null, 0,
originalRequest, this, eventListener, client.connectTimeoutMillis(),
client.readTimeoutMillis(), client.writeTimeoutMillis());
return chain.proceed(originalRequest);
}创建拦截器集合,并添加自定义拦截器、失败重连、缓存等拦截器。创建RealInterceptorChain对象,并调用proceed方法
@Override public Response proceed(Request request) throws IOException {
return proceed(request, streamAllocation, httpCodec, connection);
}
public Response proceed(Request request, StreamAllocation streamAllocation, HttpCodec httpCodec,
RealConnection connection) throws IOException {
if (index >= interceptors.size()) throw new AssertionError();
calls++;
...
// Call the next interceptor in the chain.
RealInterceptorChain next = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, streamAllocation, httpCodec,
connection, index + 1, request, call, eventListener, connectTimeout, readTimeout,
writeTimeout);
Interceptor interceptor = interceptors.get(index);
Response response = interceptor.intercept(next);
...
return response;
}
}创建一个新的RealInterceptorChain用于把Request传递给下一个Interceptor去处理 ,最终以链式调用的方式完成所有拦截器的处理工作,最终返回Response对象。
6、进行同步请求:
调用RealCall的execute方法:
@Override public Response execute() throws IOException {
synchronized (this) {
if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");
executed = true;
}
captureCallStackTrace();
eventListener.callStart(this);
try {
client.dispatcher().executed(this);
Response result = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
if (result == null) throw new IOException("Canceled");
return result;
} catch (IOException e) {
eventListener.callFailed(this, e);
throw e;
} finally {
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}直接调用了Diapatcher的executed方法,将RealCall加入正在运行的同步任务队列中
synchronized void executed(RealCall call) {
runningSyncCalls.add(call);
}然后通过调用getResponseWithInterceptorChain方法,通过拦截器处理后返回Response对象。
最终调用finished方法,开始下一个任务请求工作。