python新式类模型
-
python3.x的所有类都会自动转换为一个”新式类”,不论是否有继承object对象
-
python2.x必须显式地指定类继承object父类才表示”新式类”
新式类与经典类模板
# py3.xclass Dtrees:
"""
Dtrees默认是新式类
"""
pass# py2.xclass Dtrees(object):
"""
py2.x必须显式地继承object作为父类,此时才表示是新式类
"""
passclass Dtrees:
"""
Dtrees默认是经典类
"""
pass新式类的特征
定义经典类与新式类
# newstyle.py,python环境为2.xclass Classic:
"""
python2.x默认类为经典类
由于__getatt__ 与 __getattribute__功能效果一样,这里只用__getattr__演示
"""
def __getattr__(self, method_name):
print("call Classic __getattr__,it would call built-in[%s] method " % method_name) return getattr(self.__name,method_name)class NewStyleClass(object): def __init__(self):
self.__name = "newstyle name"
"""
python2.x需要指明为新式类,python3.x默认为新式类
"""
def __getattr__(self, item):
print("call NewStyle __getattr__,it would call built-in[%s] method " %item) return getattr(self.__name,item)def test_dir():
C = Classic()
N = NewStyleClass()
print(dir(C) # 经典类内置有__getattr__方法
print(dir(N) # 新式类的内置方法继承object对象>>> python newstyle.py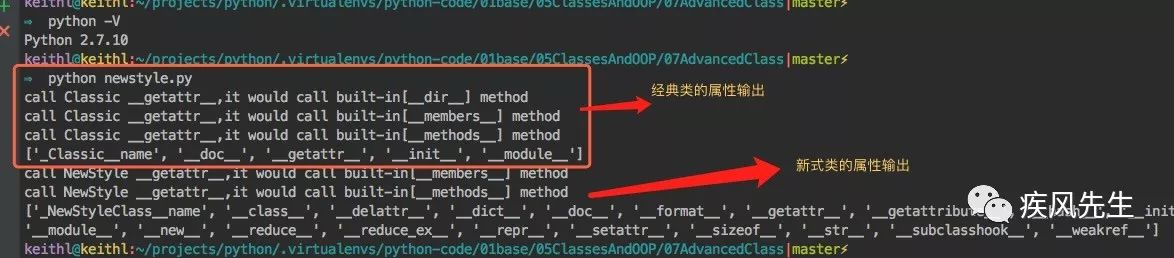
新式类中的内置属性方法的获取将以类作为搜索起点,直接跳过类的实例搜索
-
在新式类中,路由指向
__getattr__以及__getattribute__的类内置函数(__X__)直接跳过不再被拦截
# newstyle.pydef test_classis():
C = Classic()
print("python2.x classic instance built-in attributes:")
print(str(C)) # 调用str()会执行内置函数__str__,但是会先被__getattr__方法拦截,然后再调用__str__
print(C.__str__()) # 执行的输出与上述结果一样def test_new():
N = NewStyleClass()
print("python3.x classic instance built-in attributes:")
print(str(N)) # 调用str()会执行内置函数__str__,但是没有被__getattr__方法拦截
print(type(N).__str__(N)) # 必须通过类的方式调用>>> python newstyle.py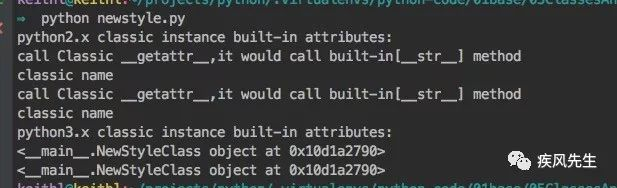
-
经典类实例添加内置操作能够正常访问使用,新式类实例则不行
# newstyle.pydef test_builtin():
C = Classic()
C.__add__ = lambda x:x+2 # 为类实例添加内置属性方法
print(C+2)
N = NewStyleClass()
N.__add__ = lambda x: x + 2
print(N + 2) # unsupported operand type(s) for +: 'NewStyleClass' and 'int',类中没有定义__add__>>> python newstyle.py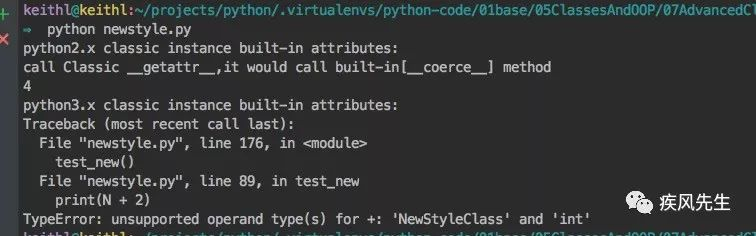
类模型的变更
-
classes are types,类都是type的一个实例
# newstyle.pydef test_model_change():
C = Classic()
print(type(C))
print(C.__class__)
N = NewStyleClass()
print(type(N))
print(N.__class__)>>> python newstyle.py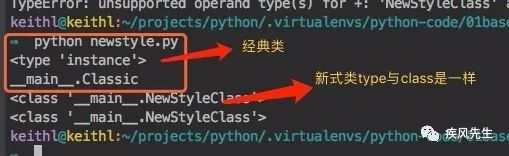
-
types are classes,type都是类的一个实例
# newstyle.py ...class D:passclass NClass(object):passdef test_model_change2():
C1 = Classic()
C2 = D()
print(type(C1) == type(C2)) # 经典类中的所有实例都拥有相同的type
N1 = NewStyleClass()
N2 = NClass()
print(type(N1) == type(N2)) # 新式类:type is class,class is type>>> python newstyle.py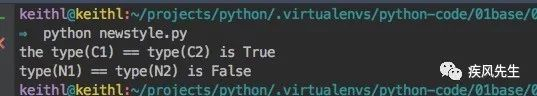
所有的类都继承object,object是处于顶级的基类
-
类实例对象的type是class,class的type是type,type的type是type
# newstyle.py def test_class():
print(type("str class"))
print(type(str))
print(type(type))>>> python newstyle.py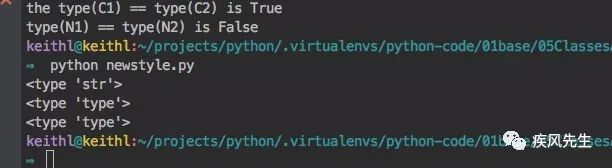
-
所有的新式类拥有来自基类object的属性
# newstyle.py def test_inherit():
print(Classic.__bases__)
print(dir(Classic))
print(NewStyleClass.__bases__)
print(dir(object))
print(dir(NewStyleClass))>>> python newstyle.py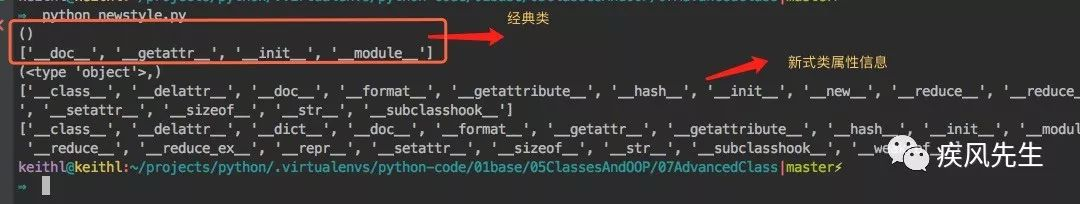
继承树搜索在以同一个基类的基础下将以广度优先的方式进行遍历
-
拥有一个相同的顶层类
# newstyle.py class A1(object):attr = 1class B(A1):passclass C(A1):attr = 4class D2(B,C):passdef test_search():
d = D2()
print(d.attr) # 经典类搜索:深度优先,即 D2 -- B --- A1 --- C,新式类:即D2 --- B --- C --- A1
print(D2.__mro__) # 列出D的遍历搜索方式,只有在新式类中生效并且只有属于同一个类下的才会走广度优先if __name__ == '__main__':
test_search()>>> python newstyle.py # 经典类和新式类的输出结果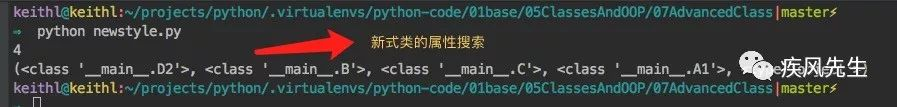
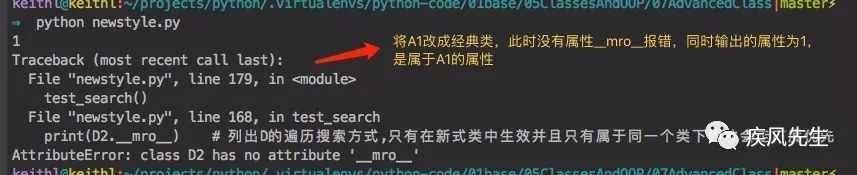
可以参考先前的python面向对象编程(1)中提到的属性继承搜索
-
顶层基类不是相同一个
# newstyle.pyclass A1(object):attr = 1class A2(object):attr = 2class B(A1):passclass C(A2):attr = 4class T(A2):passclass D2(B,T,C):passdef test_search():
d = D2()
print(d.attr)
print(D2.__mro__) >>> python newstyle.py # 新式类的输出结果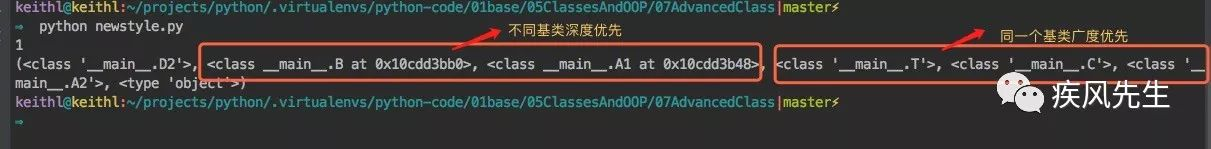
新式类的扩展
使用
__slots__槽来存储实例对象的属性名称
-
1.定义:assigning a sequence of string attribute names,用一个序列存储字符串属性名称
-
2.作用:
-
1)避免随意添加类的实例属性,只能通过槽指定的属性来做设置和访问
-
2)可以优化内存的使用和加快程序执行的速度
-
3.声明:
-
1)通过内置属性
__slots__变量来定义 -
2)必须定义在类顶部的语句中
-
4.注意点:
-
必须为槽定义的属性名称进行分配值,如果没有分配而进行访问将会报错,即AttributeError
-
5.代码测试
# newstyle_extend.pyclass MyObject(object):
"""
定义属性槽,类实例只能使用下面的属性来进设置和访问,试图设置或者访问不在槽定义的会报错
"""
__slots__ = ['age','name','job']def test_slots():
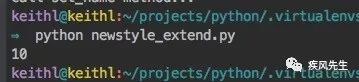
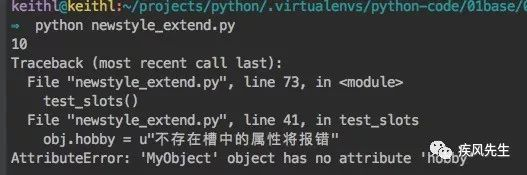
obj = MyObject() # print(obj.age) # 未分配但尝试访问报错
obj.age = 10
print(obj.age) # obj.hobby = u"不存在槽中的属性将报错">>> python newstyle_extend.py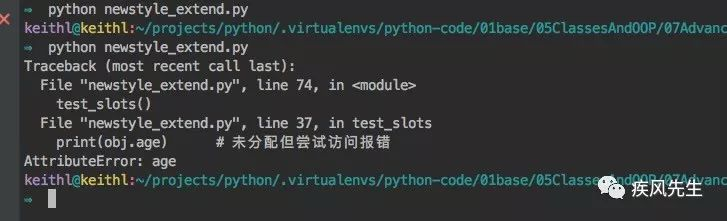
-
6.槽与命名空间字典
-
__slots__会排除实例字典属性,除非字典属性会显式地定义在槽中 -
一旦我们需要定义槽以外的属性存储在命名空间字典的时候,需要在槽里面添加一个属性,即
__dict__
# newstyle_extend.pyclass MyObject(object):
"""
定义属性槽,类实例只能使用下面的属性来进设置和访问,试图设置或者访问不在槽定义的会报错
"""
__slots__ = ['age','name','job','__dict__']def test_slots():
obj = MyObject() # 这里用unicode,打印输出的时候是以unicode的形式输出
obj.hobby = u"不存在槽中的hobby属性将存储在命名空间字典中"
print(obj.__dict__)>>> python newstyle_extend.py
-
7.在继承树中使用槽,子类将继承父类的槽属性取并集操作
# newstyle_extend.pyclass D(object):
__slots__ = ['a','b']class E(object):
__slots__ = ['c', 'd']class M(E):
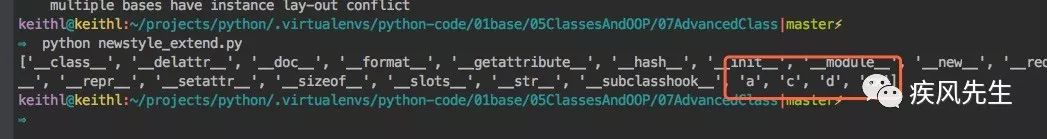
__slots__ = ['xx','a'] # 子类使用槽的时候,只能继承一个父类,否则报multiple bases have instance lay-out conflictdef test_inherhit_class():
m = M()
print(dir(m))>>> python newstyle_extend.py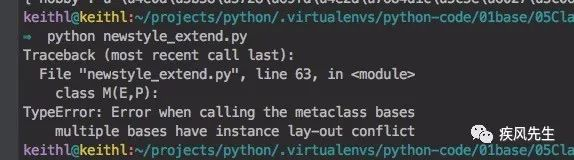
属性访问器
-
使用property函数来获取属性,其格式为:property(get,set,del,doc),即包含了获取、设置、删除以及文档属性的操作
# property.pyclass PropertyObject(object):
def get_name(self):
print("call get_name method...") return "keithl"
def set_name(self, value):
print("call set_name method for value[%s]..." % value)
self.__name = value
name = property(fget = get_name,fset = set_name)def test_property():
po = PropertyObject()
print(po.name)
po.name = "xiaokun"if __name__ == '__main__':
test_property()>>> python property.py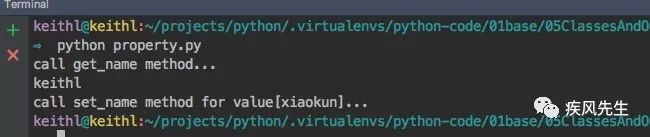
-
使用装饰器代替上述的属性设置
# property.pyclass PropertyObject(object):
@property
def name(self):
print("call get_name method...") return "keithl"
@name.setter
def name(self,value):
print("call set_name method value[%s]..." % value)
self.__name = value ... 测试代码省略 >>> python property.py
属性工具:
__getattribute__和描述符
在前面详细说明了属性获取与重载运算符的关系,不熟悉的同学可以参考下python面向对象编程(5)
-
新式类中的
__getattribute__方法会拦截所有属性获取的操作,包括上述属性定义的操作 -
使用类的描述符
__get__&__set__
# property.pyclass NameDescriptor(object):
def __get__(self, instance, owner):return "get_keithl"
def __set__(self, instance, value):instance._name="set_"+valueclass descriptors(object):
name = NameDescriptor()def test_name_desc():
nd = descriptors()
print(nd.name)
nd.name = "keithl"
print(nd.name)
print(nd._name)>>> python property.py
如有收获,欢迎转发~