1. windowSoftInputMode属性的使用
Android使用windowSoftInputMode来控制Activity 的主窗口与包含屏幕软键盘的窗口的交互方式。 该属性的设置影响两个方面:
- 当 Activity 成为用户注意的焦点时软键盘的状态 — 隐藏还是可见。
- 对 Activity 主窗口所做的调整 — 是否将其尺寸调小以为软键盘腾出空间,或者当窗口部分被软键盘遮挡时是否平移其内容以使当前焦点可见。
该设置必须是下表所列的值之一,或者是一个“state...”值加上一个“adjust...”值的组合。 在任一组中设置多个值(例如,多个“state...”值)都会产生未定义结果。各值之间使用垂直条 (|) 分隔。 例如:
<activity android:windowSoftInputMode="stateVisible|adjustResize" . . .此处设置的值(“stateUnspecified”和“adjustUnspecified”除外)替换主题中设置的值。
| 值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| "stateUnspecified" | 不指定软键盘的状态(隐藏还是可见)。 将由系统选择合适的状态,或依赖主题中的设置。这是对软键盘行为的默认设置。 |
| “stateUnchanged” | 当 Activity 转至前台时保留软键盘最后所处的任何状态,无论是可见还是隐藏。 |
| “stateHidden” | 当用户选择 Activity 时 — 也就是说,当用户确实是向前导航到 Activity,而不是因离开另一 Activity 而返回时 — 隐藏软键盘。 |
| “stateAlwaysHidden” | 当 Activity 的主窗口有输入焦点时始终隐藏软键盘。 |
| “stateVisible” | 在正常的适宜情况下(当用户向前导航到 Activity 的主窗口时)显示软键盘。 |
| “stateAlwaysVisible” | 当用户选择 Activity 时 — 也就是说,当用户确实是向前导航到 Activity,而不是因离开另一 Activity 而返回时 — 显示软键盘。 |
| “adjustUnspecified” | 不指定 Activity 的主窗口是否调整尺寸以为软键盘腾出空间,或者窗口内容是否进行平移以在屏幕上显露当前焦点。 系统会根据窗口的内容是否存在任何可滚动其内容的布局视图来自动选择其中一种模式。 如果存在这样的视图,窗口将进行尺寸调整,前提是可通过滚动在较小区域内看到窗口的所有内容。这是对主窗口行为的默认设置。 |
| “adjustResize” | 始终调整 Activity 主窗口的尺寸来为屏幕上的软键盘腾出空间。 |
| “adjustPan” | 不调整 Activity 主窗口的尺寸来为软键盘腾出空间, 而是自动平移窗口的内容,使当前焦点永远不被键盘遮盖,让用户始终都能看到其输入的内容。 这通常不如尺寸调正可取,因为用户可能需要关闭软键盘以到达被遮盖的窗口部分或与这些部分进行交互。 |
系统默认值为:stateUnspecified|adjustUnspecified
上述是引用android官方文档的说明,但是这个并不能让我们理解所有内容。因此本次将具体探究这9个属性是如何影响。
1. stateUnspecified
android官方描述为:不指定软键盘的状态(隐藏还是可见)。 将由系统选择合适的状态,或依赖主题中的设置。这是对软键盘行为的默认设置。哪系统认为的合适的状态是什么样的呢?
我们采用如下布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>我们发现软键盘没有自动弹出,需要手动点击EditText后,键盘才会弹出来。
如果采用如下布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</ScrollView>
</LinearLayout>我们发现软键盘会自动弹出。这个就很奇怪了,为什么就加了一个ScrollView,难道是因为添加了ScrollView,软键盘就可以自动弹出来吗?我们看一下如下的布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</ScrollView>
</LinearLayout>运行代码可以发现,这样软键盘也会不会自动弹出来。说明软键盘自动弹出和ScrollView没有直接关系。
如果我们采用如下布局,我们发现软键盘还是会自动弹出
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="测试"
android:id="@+id/btn_test"/>
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>
</LinearLayout>如何依旧采用上述的布局,但是我们在onCreate中加上如下代码
Button button= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_test);
button.setFocusable(true);
button.setFocusableInTouchMode(true);
button.requestFocus();
button.requestFocusFromTouch();我们发现软键盘将不会自动弹出来。
现在我们总结一下,当属性设置为stateUnspecified时,系统默认时不会自动弹出软键盘,但是当界面上有滚动需求时(有ListView或ScrollView等)同时有获得焦点的输入框软键盘将自动弹出来(如果获得焦点不是输入框也不会自动弹出软键盘)。
2. stateUnspecified
这个比较简单,进入当前界面是否弹出软键盘由上一个界面决定。如果离开上一个界面,键盘是打开,那边该界面键盘就是打开;否则就是关闭的.
3. stateHidden
这个也比较简单,进入当前界面不管当前上一个界面或者当前界面如何,默认不显示软键盘。
4. stateAlwaysHidden
这个参数和stateHidden的区别是当我们跳转到下个界面,如果下个页面的软键盘是显示的,而我们再次回来的时候,软键盘就会隐藏起来。而设置为stateHidden,我们再次回来的时候,软键盘讲显示出来。
5. stateVisible
设置这个属性,进入这个界面时无论界面是否需要弹出软键盘,软键盘都会显示。
6. stateAlwaysVisible
这个参数和stateAlwaysVisible的区别是当我们从这个界面跳转到下个界面,从下个界面返回到这个界面是软键盘是消失的,当回到这个界面软键盘依旧可以弹出显示,而stateVisible确不会。
上述6个属性定义的是进入界面,软键盘是否显示的。下面3个属性设置的是软键盘和界面显示内容之间的显示关系。
7. adjustResize,adjustPan
我们将这两个属性放在一起讨论。为了说明这个问题,我们先看如下的布局例子
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<FrameLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="3"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_dark">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:text="这个是一个测试"
android:textSize="30sp" />
</FrameLayout>
<FrameLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="4"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_light">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:text="这个是一个测试"
android:textSize="30sp" />
</FrameLayout>
<FrameLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@android:color/white">
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center" />
</FrameLayout>
</LinearLayout>adjustResize
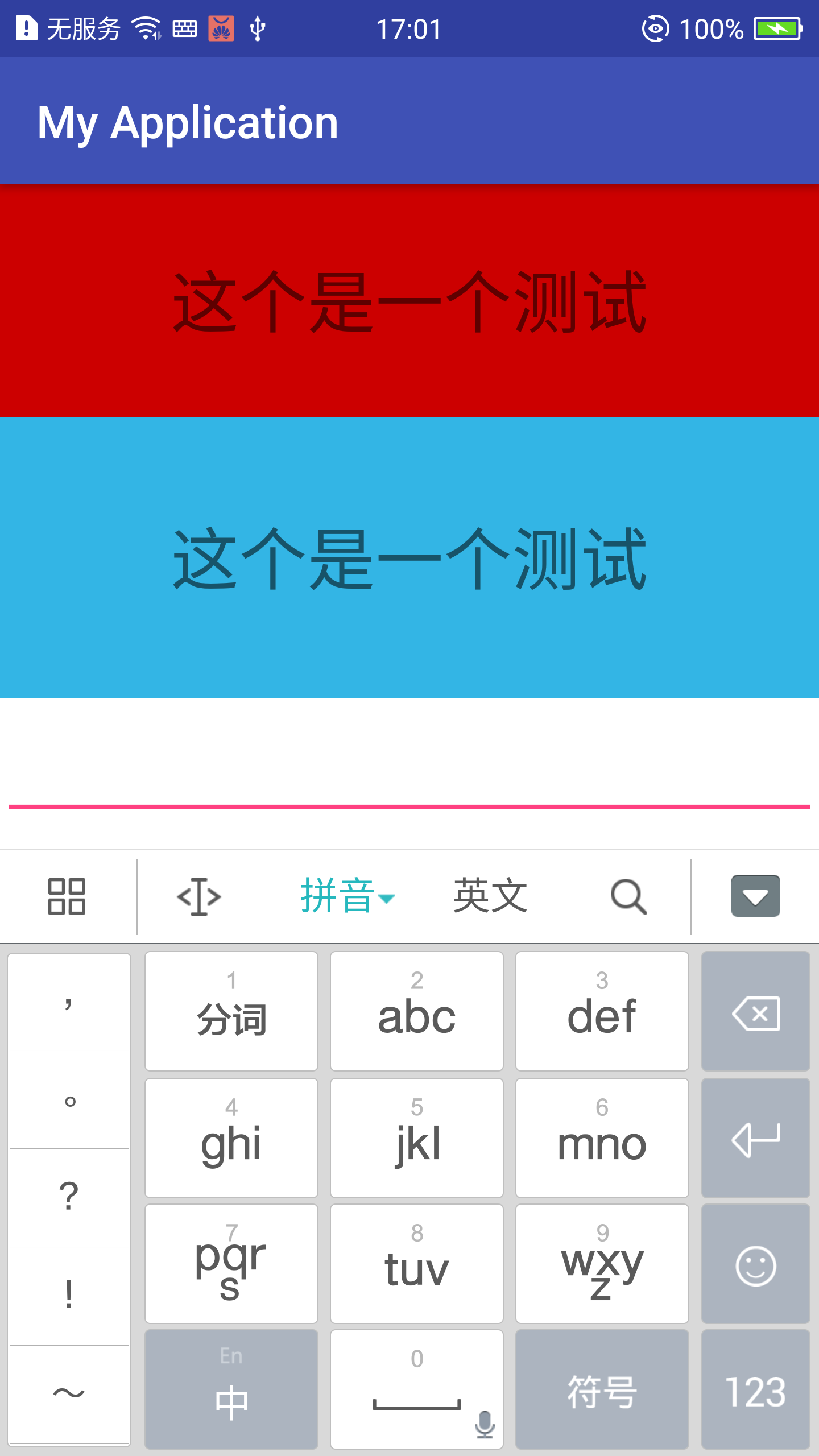
adjustPan
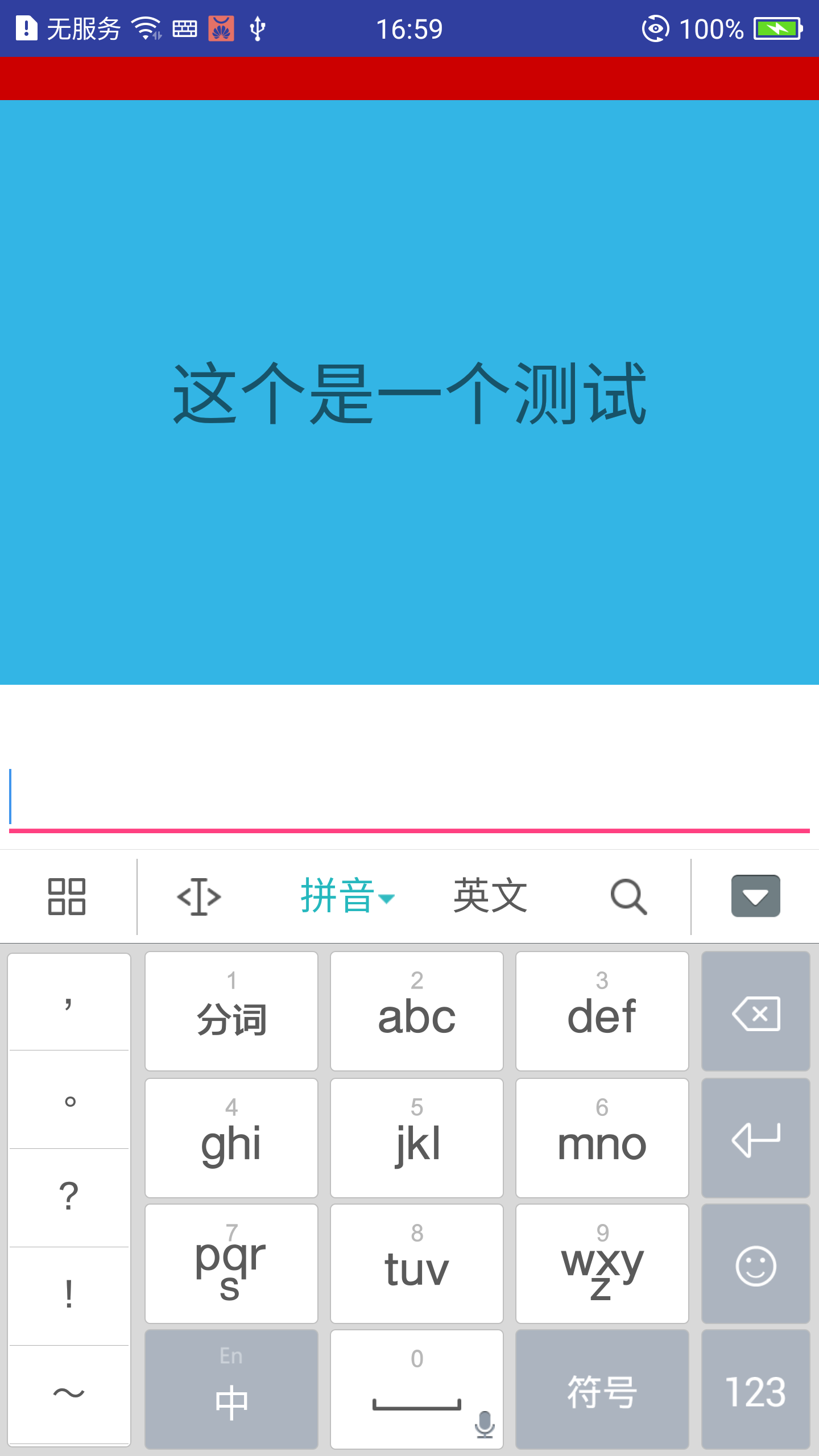
由上面两张图我们可以知道,如果设置adjustResize属性,当键盘显示时,通过对界面主窗口的大小调整(压缩等)来实现留出软键盘的大小空间;如果设置adjustPan属性,当键盘显示时,通过对界面布局的移动来保证输入框可以显示出来。
8. adjustUnspecified
这个属性是根据界面中否有可以滚动的控件来判断界面是采用adjustResize还是adjustPan来显示软键盘。如果有可以滚动的控制,那可以将其理解为adjustResize,通过压缩界面来实现.但是是有一个前提的:可通过滚动在较小区域内看到窗口的所有内容。如果没有可以滚动的控件或者不符合前提条件,则是采用adjustPan,及移动布局来实现。
2. 软键盘的打开和关闭
软键盘的打开和关闭主要通过InputMethodManager实现。InputMethodManager关于打开关闭软键盘的方法主要有如下几个方法。
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| hideSoftInputFromInputMethod(IBinder token, int flags) | 关闭/隐藏软键盘,让用户看不到软键盘,但是传入的token必须是是系统中token。 |
| hideSoftInputFromWindow(IBinder windowToken, int flags) | 和下面hideSoftInputFromWindow方法一样,只是resultReceiver传入的值null |
| hideSoftInputFromWindow(IBinder windowToken, int flags, ResultReceiver resultReceiver) | 关闭/隐藏软键盘,和第一个方法的区别是他传入的token是系统界面中View窗口的token |
| showSoftInput(View view, int flags, ResultReceiver resultReceiver) | 和hideSoftInputFromWindow对应 |
| showSoftInput(View view, int flags) | 同上面一个方法,但是默认的resultReceiver为null |
| showSoftInputFromInputMethod(IBinder token, int flags) | 和hideSoftInputFromInputMethod对应 |
| toggleSoftInput(int showFlags, int hideFlags) | 该方法是切换软键盘,如果软键盘打开,调用该方法软键盘关闭;反之如果软键盘关闭,那么就打开 |
| toggleSoftInputFromWindow(IBinder windowToken, int showFlags, int hideFlags) | 和上面一个方法一样,区别是传入的当前View的token |
在上述方法中我们看到需要传入相关flags,相关flags有如下几个
参数 | 说明
-------------------|---
HIDE_IMPLICIT_ONLY | 表示软键盘只有在用户未明确显示的情况才被隐藏
HIDE_NOT_ALWAYS | 表示软键盘将一致隐藏,除非调用SHOW_FORCED才会显示
SHOW_FORCED | 表示软键盘强制显示不会被关闭,除非用户明确的要关闭
SHOW_IMPLICIT | 表示软键盘接收到一个不明确的显示请求。- 我们经常看到用户传入的参数为0,不属于上述4个,那显示的是什么呢?其实如果传入的hideflag的话表示的是就是关闭软键盘,之前传入的参数不会改变,showflag的话表示的是SHOW_IMPLICIT
总结:
关闭软键盘的方法为
public void hideKeyboard(View view) {
((InputMethodManager) view.getContext().getSystemService(Context.INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE)).hideSoftInputFromWindow(
view.getWindowToken(), InputMethodManager.HIDE_NOT_ALWAYS);
}打开关键盘的方法为
public void OpenKeyboard(View view) {
((InputMethodManager) view.getContext().getSystemService(Context.INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE)).toggleSoftInput(InputMethodManager.SHOW_IMPLICIT, InputMethodManager.HIDE_NOT_ALWAYS);
}3. 监听软键盘的打开和关闭
3.1 常规方法
监听软键盘的打开和关闭最常规的方法是监听View的层次结构,这个View的层次结构的发生全局性的事件如布局发生变化等我们可以通过调用getViewTreeObserver监听到布局的变化。代码实例如下:
view.getViewTreeObserver().addOnGlobalLayoutListener(new ViewTreeObserver.OnGlobalLayoutListener() {
@Override
public void onGlobalLayout() {
// 虚拟键的高度
int navigationBarHeight = 0;
int resourceId = activityRootView.getContext().getResources().getIdentifier("navigation_bar_height", "dimen", "android");
//判断是否有虚拟键
if (resourceId > 0 && checkDeviceHasNavigationBar(activityRootView.getContext())) {
navigationBarHeight = activityRootView.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(resourceId);
}
// status bar的高度
int statusBarHeight = 0;
resourceId = activityRootView.getContext().getResources().getIdentifier("status_bar_height", "dimen", "android");
if (resourceId > 0) {
statusBarHeight = activityRootView.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(resourceId);
}
// 获得app的显示大小信息
Rect rect = new Rect();
((Activity)activityRootView.getContext()).getWindow().getDecorView().getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame(rect);
//获得软键盘的大小:屏幕高度-(status bar的高度+虚拟键的高度+app的显示高度)
int keyboardHeight = ((Activity) activityRootView.getContext()).getWindow().getDecorView().getRootView().getHeight() - (statusBarHeight + navigationBarHeight + rect.height());
if (keyboardHeight>100 && !isSoftKeyboardOpened) {
isSoftKeyboardOpened = true;
notifyOnSoftKeyboardOpened(keyboardHeight);
Log.d(TAG, "keyboard has been opened");
} else if(keyboardHeight <100 && isSoftKeyboardOpened){
isSoftKeyboardOpened = false;
notifyOnSoftKeyboardClosed();
Log.d(TAG, "keyboard has been closed");
}
}
} )status bar是否存在其实也需要判断,但是因为app本身可以判断当前界面是否显示status的高度,所以上述代码默认status显示。
3.2 重写根布局的onMeasure
该方法使用于windowSoftInputMode被设置为adjustResize。如上文所致,adjustResize是采用压缩界面布局来实现软键盘可以正常显示。具体代码如下
public class KeyBoardFrameLayout extends FrameLayout {
public KeyBoardFrameLayout(@NonNull Context context) {
super(context);
}
public KeyBoardFrameLayout(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public KeyBoardFrameLayout(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, @AttrRes int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
final int proposedheight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
final int actualHeight = getHeight();
int keyboardHeight = actualHeight - proposedheight;
if (keyboardHeight > 100) {
notifyOnSoftKeyboardOpened(keyboardHeight);
} else if (keyboardHeight < -100) {
notifyOnSoftKeyboardClosed();
}
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}对比上述两种方法:
- 第一种方法的优点是不管windowSoftInputMode被设置为什么,都可以实现软键盘的开关键盘;第二种需要将上述的布局作为界面的根布局才能实现监听
- 第一种方法的缺点是事后监听,已当onLayout之后才会拿到监听,这个导致界面容易出现闪屏的情况;而第二种方法是在界面onLayout之前就拿到了监听,因此不会出现闪屏的情况。