目前大多数的APP 对于React Native 都是一个尝试阶段,用混合开发的方式,在应用中用React Native 去实现个别或则是几个页面。
首先看一下在一个App中嵌入RN页面的主要的类图以及相互之间的关系
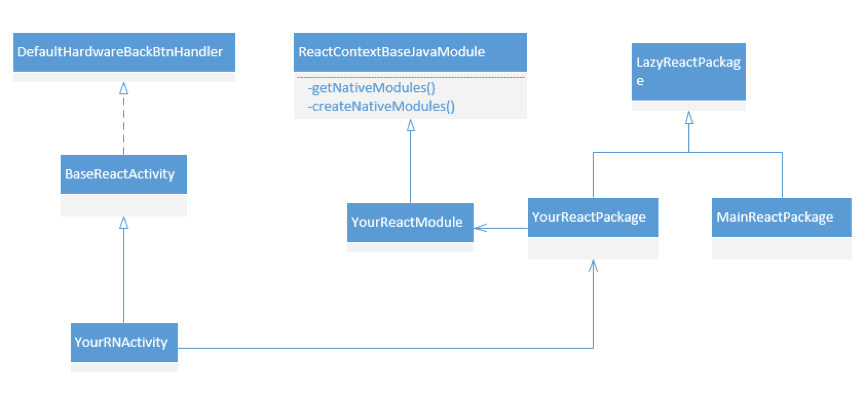
BaseReactActivity用于加载业务js bundle 文件 YourReactModule和YourReactPackage 实现Native Android 代码和 React Native页面通信。
这三个类的详细的类图 如下图所示。
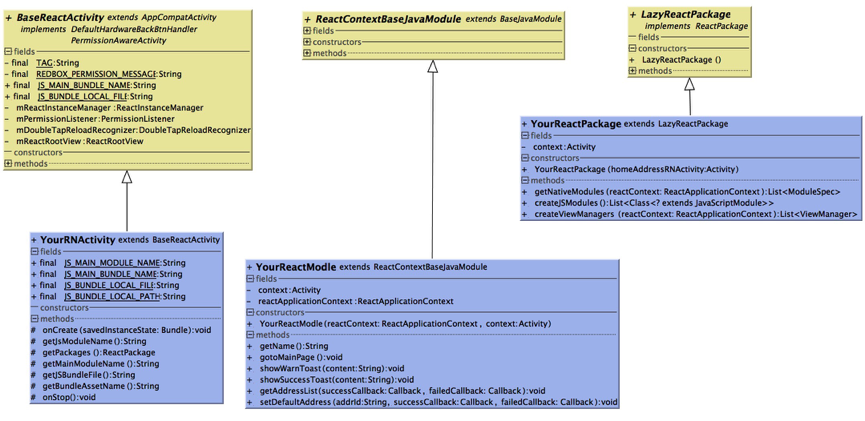
这里主要讲一下BaseActivity的实现
protected void iniReactRootView() {
ReactInstanceManager.Builder builder = ReactInstanceManager.builder()
.setApplication(getApplication())
.setJSMainModuleName(TextUtils.isEmpty(getMainModuleName()) ? JS_MAIN_BUNDLE_NAME : getMainModuleName())//bundle的名字
.setUseDeveloperSupport(BuildConfig.DEBUG)//支持debug 摇一摇 reload页面
.addPackage(new MainReactPackage())//添加RN提供的原生模块
.setInitialLifecycleState(LifecycleState.BEFORE_CREATE);
String jsBundleFile = getJSBundleFile();
File file = null;
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(jsBundleFile)) {
file = new File(jsBundleFile);
}
if (file != null && file.exists()) {
builder.setJSBundleFile(getJSBundleFile());//从手机的本地加载文件
Log.i(TAG, "load bundle from local cache");
} else {
String bundleAssetName = getBundleAssetName();
builder.setBundleAssetName(TextUtils.isEmpty(bundleAssetName) ? JS_BUNDLE_LOCAL_FILE : bundleAssetName);//从assets文件下读取加载
Log.i(TAG, "load bundle from asset");
}
if (getPackages() != null) {
builder.addPackage(getPackages());//添加自定义的通信模块
}
mReactInstanceManager = builder.build();
mReactRootView.startReactApplication(mReactInstanceManager, getJsModuleName(), null);
mDoubleTapReloadRecognizer = new DoubleTapReloadRecognizer();
}
abstract protected String getJsModuleName();
abstract protected ReactPackage getPackages();
/**
* 与modlue对应的js文件的名称
*
* @return
*/
abstract protected String getMainModuleName();
/**
* 从本地sd卡读取bundle文件
*
* @return
*/
abstract protected String getJSBundleFile();
/**
* assets 中自带的 bundle名称
*
* @return
*/
abstract protected String getBundleAssetName();
上面的代码 是ReactNative的初始化,流程 包括 设置Context,加载的bundle 文件的路径,自定义的通信模块以及相关的配置。
主要关注一下 setJSBundleFile()这个方法,这个方法非常的重要,通过这个方法RN 可以从手机的sd卡读取文件并且加载显示,这是热跟新实现的基础。举个例子,我们可以将最新的RNbundle 文件下载的本地 然后替换掉老的版本,在页面初始化的时候 加载最新的bundle,这样就实现了无需发版 就可以更新页面。
当然这不是今天要讲的重点。 以上所说的都是一些RN的基础知识,当我们将RN运用到实际的项目中的时候发现了很多问题。其中最大的一个问题就是页面加载速度缓慢,bundle 文件过于臃肿。
接下来就探讨一下如何解决这个问题。
首先我们可以通过 React Native的打包命令 打包一个最基础的显示 helloworld的index.android.js。
打包命令:react-native bundle --platform android --dev false --entry-file index.android.js --bundle-output app/src/main/assets/index.android.bundle
index.android.js的源码:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import{
AppRegistry,
View,
Text,
DeviceEventEmitter,
} from 'react-native';
var TestModule = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text style={styles.welcome}>
hello world
</Text>
</View>
);
}
});
var styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
backgroundColor: '#F5FCFF',
},
welcome: {
fontSize: 20,
textAlign: 'center',
margin: 10,
},
instructions: {
textAlign: 'center',
color: '#333333',
marginBottom: 5,
},
});
AppRegistry.registerComponent('TestModule', () => TestModule);
的打出的业务bundle文件如下图所示
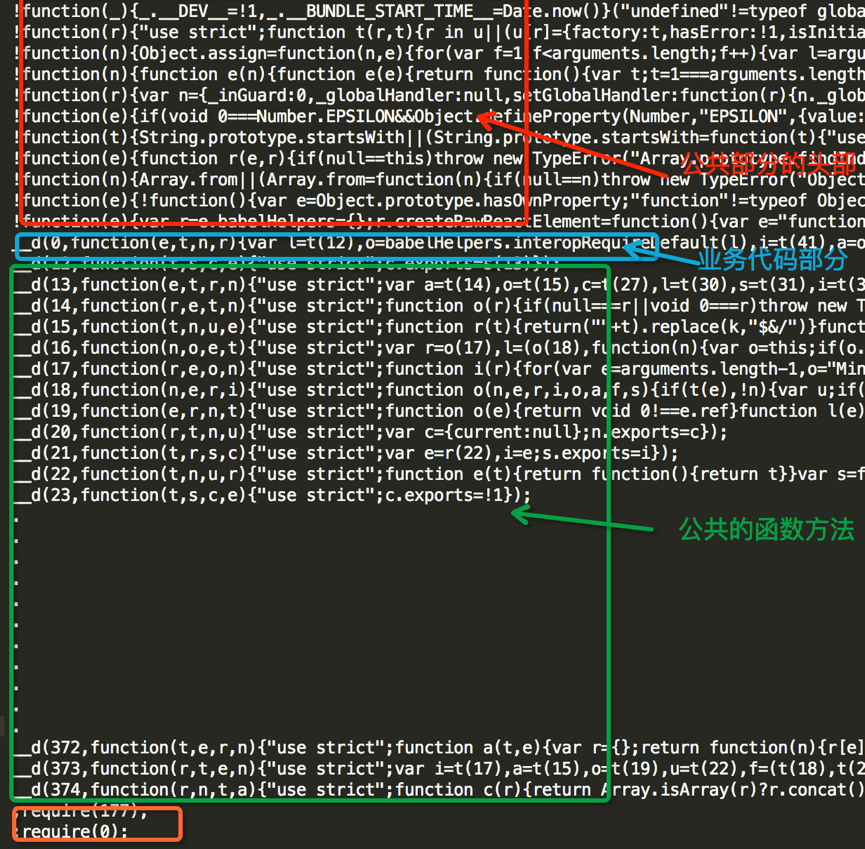 仅仅只是一个普通的helloworld文件打开之后就是密密麻麻的大概有400行,然后找个bundle 文件的大小将近有530k,其实仅仅看这个一个文件是看不什么东西的,当你尝试着多打几个bundle包,你会惊奇的发现,打出的bundle包里有绝大部分的内容都是相同的,只有这一行
仅仅只是一个普通的helloworld文件打开之后就是密密麻麻的大概有400行,然后找个bundle 文件的大小将近有530k,其实仅仅看这个一个文件是看不什么东西的,当你尝试着多打几个bundle包,你会惊奇的发现,打出的bundle包里有绝大部分的内容都是相同的,只有这一行
__d(0,function(e,t,n,r){var l=t(12),o=babelHelpers.interopRequi…….不同
而仔细的观察你会发现 这一行其实就是把你的index.android.js文件进行了简单的压缩和转换,代表的就是当前业务bundle 的代码。如图中蓝圈里标示的。
于是如下图中的四个圈:
红圈 公共的头部部分。
篮圈 js业务代码
绿圈 公共的js方法
橙圈 业务的入口
有了以上的分析以后,我们至少解决了一个问题,那就是 ReactNative 业务bundle臃肿的问题,
使用Reactnative bundle打包后将公共的部分抽离出来,生成一个Common.js,即上图中的红圈绿圈橙圈部分 将业务bundle 的生成一个单独的不module.js文件即上图中的绿圈部分。在需要加载相应的ReactNative页面的时候 将 Common.js和业务的module.js 生成完整的bundle.js存储到本地,然后通过geJsbundleFile()方法从本地加载。
可参考demo 其、github地址 :github.com/pukaicom/Re…
dem中用到了bsdiff增量合成方法。该方法的实现参考:my.oschina.net/liucundong/…
这只是解决了部分问题,但是并没有解决ReactNative 页面加载缓慢的问题,通过上面的分析可以知道,如果按照合成的bundle 的方案,在加载每一个RN页面的时候其实 重复加载了大量的文件内容,读取文件到内存是一个耗费时间的过程,如果每个页面都重复读取的话,效率和用户体验明显是不好的,那能不能避免重复读取重复的文件呢,当然是可以的。
可以将公共的部分预先读取到Activity,然后在需要加载某个页面的时候,通过ReactNative的 RCTDeviceEventEmitter机制,发送消息到当前的RN 页面,然后通过require方法 加载需要展现的modle的js文件 然后展示。我们先看一下文件的目录结构
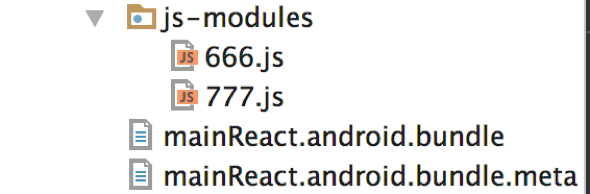
666.js 和777.js代表的是业务的id,里面的内容如下:

其实就是前面提到的 __d(0,function………………..方法
只不过 将里面的内容改成了和文件名一样的数字,666.js改为了__d(666,function。。。。777.js改为了__d(777,function…… 这一步很重要,因为一会儿要通过这个id在主页面mainReact.android.js中通过require(id)方法 将该部分的业务bundle 读取到内存。
看一下MainReact.android.js的代码:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import{
AppRegistry,
View,
Text,
DeviceEventEmitter,
} from 'react-native';
class startComponent extends Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state = {
content:null,showModule:false
};
DeviceEventEmitter.addListener("test", (result) => {
let mainComponent = require(result.name);
this.setState({
content:mainComponent,
showModule:true
})
});
}
render(){
let _content = null;
if(this.state.content){
_content = React.createElement(this.state.content,this.props);
return _content;
}else{
return (<Text>I am the MainPage</Text>)
}
}
}
AppRegistry.registerComponent('mainRNModule', () => startComponent);
通DeviceEventEmitter 监听页面跳转的信号,将当前需要加载的页面id放到result.name中,然后通过require获取当前的component 然后 通过render展示在当前的页面上。
在Native 原生中发送 Emitter消息的代码如下
public void gotoMainPage() {
//发送事件
WritableMap params = Arguments.createMap();
params.putInt("name", 666);
reactApplicationContext
.getJSModule(DeviceEventManagerModule.RCTDeviceEventEmitter.class)
.emit("test", params);
}
当需要切换当前activity展示的业务bundle页面时 直接通过 emit发送消息到主页面,主页面接收到需要展示的bundle 页面的id时通过require将该文件读取到内存并且展示。
需要注意的是由于每次展示的其实是 mainReact.android.js 页面。所以只需要在
改文件中添加这句话即可。
AppRegistry.registerComponent('mainRNModule', () => startComponent);
其它的业务bundle文件则 只需要将当前文件定义为可以应用的一个component即可:在文件的末尾 将AppRegistry……… 替换为下面的代码。
module.exports = FamilyAddressComponent;
具体的参见demo:github.com/pukaicom/re…
相关的引用:
http://reactnative.cn/docs/0.30/integration-with-existing-apps.html#content
https://my.oschina.net/liucundong/blog/160436