文章有点长,比较啰嗦,请耐心看完!(基于Android API 25)
一、概述
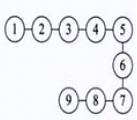
首先得明白ArrayList在数据结构中是个什么,从名字看,可以直译为“数组集合”,内部的实现八九不离十是用数组来实现的,因此在数据结构中属于线性表结构(0个或者多个元素的有限序列):数据的存储和关系
是这样:
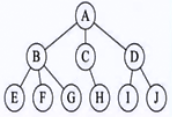
而不是这样的树形的:
ArrayList内部用到了数组来做基本的数据存储结构,那就说明是它一个连续内存块或者存储块的顺序存储结构。

这样的存储结构是优缺点是:
优点:由于是连续的内存地址存储块,对于查询一个或者多个存储内容,就很容易了,只要找到一个元素的内容a,加上每个元素所占的内存字节数c,a+c就很容易找到下一个元素,计算量小很高效。
缺点:缺点也显而易见,举个栗子。
a: 你在火车站买票,这个时候,一个漂亮的主播妹纸突然插队到你前面,你和你后面的一起排队的人是不是都得往后退一个位置,妹纸才能插入到你的位置上吧。这个时候这一队中需要挪动位置的人(也就是数组位置)是不是很多,当你和后面排队的人都后退一个位置后,妹纸的插队才算是完成了。这是不是很耗费时间。
b: 你前面的一个哥们突然不想排队走了,空出了一个位置,这时候你和后面排队的人是不是都得往前挪动一个位置,当所有人都挪动完后,这个队伍才恢复原来没有人走的情况,是不是也很耗费时间。
这优缺点要说明的是什么呢,顺序存储的线性表插入和删除的都比较耗费时间,而查询确非常的快。
二、源码解析(Android API 25)
- ArrayList的类继承关系结构

ArrayList类继承关系结构.png -
构造函数
/** * Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten. * 使用10个初始容量构造一个空的集合 */ public ArrayList() { super(); // 用一个空的数组进行初始化 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } // 来看看 elementData和EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA是什么 /** * Shared empty array instance used for empty instances. * 就是一个空数组常量,可是无参的构造的注释又说是内置了10个初始容量, * 搞不懂哪里有内置,Google的工程师注释乱写的么,逗我 */ private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; /** * The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored. * The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any * empty ArrayList with elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA will be expanded to * DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added. * ArrayList的所有元素都存储在elementData这个数组中, * 并且ArrayList的容量就是这个缓存数组的长度。 * 任何一个使用elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA初始化的空的ArrayList *(也就是用 new ArrayList()来构造一个对象的) * 在第一次调用add方法的时候,都会被扩充容量到DEFAULT_CAPACITY *(原来是在第一次调用add方法的时候用了默认的10作为ArrayList的容量, * 看来Android工程师注释不是乱写的) * * Package private to allow access from java.util.Collections. */ transient Object[] elementData;这样的设计也是体现了性能的优化:
new ArrayList()构造的时候并没有马上的扩容去申请一堆的Object[] 数据缓存堆内存,而是等到用的时候才去申请。这个性能优化的小技巧可以学习,初始化的时候尽量少开辟还暂时不用的堆内存,等到需要使用的时候再去申请。果然Android工程师都是身经百战的老司机啊,性能优化还的多看看源码好啊。/** * Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity * is negative */ public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { super(); if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; }这个构造没啥好说的,先检查初始化容量参数的合法性,别整个小于0的容量(不合法就抛出容量参数不合法异常,代码逻辑严谨),根据指定的容量初始化缓存ArrayList数据元素的数组。
/** * Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified * collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's * iterator. * 构造一个包含了参数里的集合的ArrayList * * @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null * 传进来的集合如果是null的话会抛出NullPointerException 异常 */ public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { elementData = c.toArray(); size = elementData.length; // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); }首先把传进来的collection集合转换成Object[]数组对象赋值给内部的数组缓存对象,然后初始化ArrayList的size大小,最后注释写c.toArray可能出错返回的不是Object[], 判断下如果返回的不是Object[]的类类型,就用Object[].class,复制一个Object[]类型的数组给elementData长度是size。
在使用这个构造函数初始化ArrayList的时候,需要注意的是传递的collection不是为null,比如使用的时候:
List<User> userList = null; List<LoginUser> loginUserList = null; if(null != userList) { loginUserList =new ArrayList(userList); }一定得对userList进行先行的判断,不然指不定程序在什么情况下给你来个没女朋友、没对象、没媳妇的异常报错奔溃。据腾讯Bugly报告反馈2016年Android应用奔溃最高的错误异常就是这个NullPointerException 没媳妇了,java就是这么蛋疼凡是使用前都得先做下非空判断。
-
增删改查
-
增加
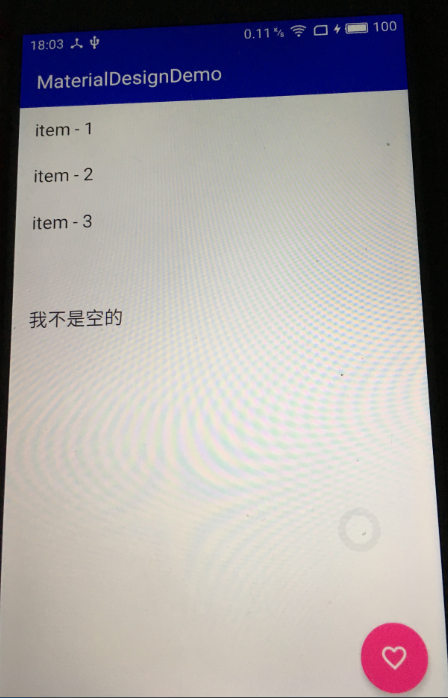
/** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * 追加一个元素到集合列表的末尾 * * @param e element to be appended to this list * @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) */ public boolean add(E e) { // 确认内部容量,并增加一次操作计数modCount ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! // 把新的元素赋值给缓存数组的size位置后size加一, elementData[size++] = e; return true; }这里需要留意的是add方法并没有判断或者抛出一次说追加进来的e元素不能为null,ArrayList是运行add一个为null的对象的,如下图:
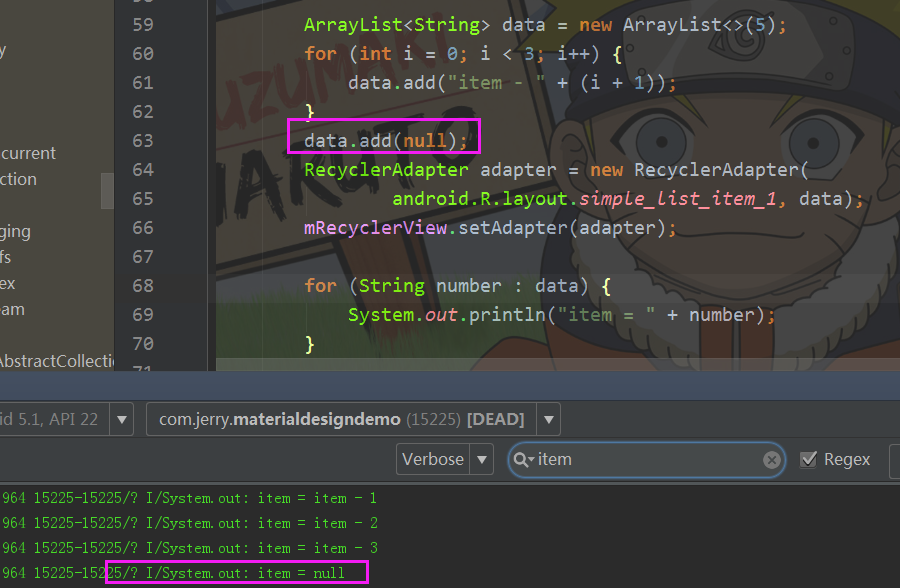
ArrayList是运行add一个为null的对象的// 确定内部的容量大小 private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { // 当使用new ArrayList()构造ArrayList对象的时候, // 在第一次add元素(这时候elementData还是一个空的缓存数组), // 此时入参数minCapacity是1,以为在调用add方法的时候size+1了 if (elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { // 就用DEFAULT_CAPACITY来作为最小的容量值10 minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } // 再一次确定明确的容量 ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); } private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { modCount++; // overflow-conscious code // minCapacity为10,此时elementData还没有元素长度是0 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); } /** * Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the * number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument. * * @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity */ private void grow(int minCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code // 从上面一路调用下来,minCapacity为10,elementData还是空的对象数组,oldCapacity为0 int oldCapacity = elementData.length; // oldCapacity 的向右位移一位就是除以2的意思,newCapacity也为0 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); // 0 - 10 < 0成立 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) // newCapacity为10 newCapacity = minCapacity; // MAX_ARRAY_SIZE是个啥玩意,请看下面解释 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) // 当想要申请的数组容量大小超过了最大的虚拟机允许的大小, // 就会重新计算出合适的 newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: // 很显然这里我们没有超过,通常情况下minCapacity是比较接近size值的, // 那么接下来就是真正的给elementData缓存数组扩容, // Arrays.copyOf返回了一个复制好原来elementData内容的新的数组对象给elementData, // 对于我们这样从上门一直调用下来的情况elementData只是扩充了容量elementData.length变成了10, // 但是这个数组里面目前还没有元素,ArrayList的属性size还是为0, // 扩容完成后,我们再回过头来看上面add(E e)方法中: // elementData[size++] = e就很容易理解了, // 此处e只是添加到了elementData数组的第0个位置, // 然后size+1变成1,ArrayList.size()是1, // 表示里面真实的元素有1个,而非里面数组的长度是1。 // 所以ArrayList的size和容量不一定是一样的,是不同的概念。 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] original, int newLength) { return (T[]) copyOf(original, newLength, original.getClass()); } public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) { // newType我们就是Object[]的类类型,于是重新实例化了一个Object[]数组对象 T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class) ? (T[]) new Object[newLength] : (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength); // 并把传递进来的original就是elementData复制到新创建的copy数组对象里, // 这是一个jni的本地接口,因为数组的复制计算性能耗费高, // 所以Android工程师就采用了jni底层c/c++来更高效的执行复制操作, // 最后返回复制好的新创建的数组对象 System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0, Math.min(original.length, newLength)); return copy; } // 处理巨大容量的问题 private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { // 当前最小的容量小于0就抛出内存溢出错误 if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow throw new OutOfMemoryError(); // 否则如果超过虚拟机允许的最大的数组大小, // 就使用Integer的最大值,反正使用Array的最大的值 return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; } /** * The maximum size of array to allocate. * Some VMs reserve some header words in an array. * Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in * OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit * Integer的最大值减去8 = 2147483647 - 8 = 2147483639 * 这是数组能够申请最大的大小,如果试图申请比这个还要大的大小, * 就会超过VM虚拟机的限制而抛出内存溢出的错误OutOfMemoryError */ private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; -
删除
/** * Removes the element at the specified position in this list. * Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their * indices). * * @param index the index of the element to be removed * @return the element that was removed from the list * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E remove(int index) { // 检查下需要删除的index会不会超过size大小, // 超过了虽然不一定会超出elementData的数组下标大小, // 当是木有元素内容啊,没有意义, // 而且数组删除内容是要移动元素位置的,容易出现问题,所以抛出了一个下标越界异常 if (index >= size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); // 操作计数加一 modCount++; // 临时缓存下要被删除的元素对象 E oldValue = (E) elementData[index]; // 表示删除一个元素数组需要移动的个数 int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); // 缓存数组size-1的位置的引用置空,交给GC来管理内存 elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work // 返回被删除的元素对象 return oldValue; }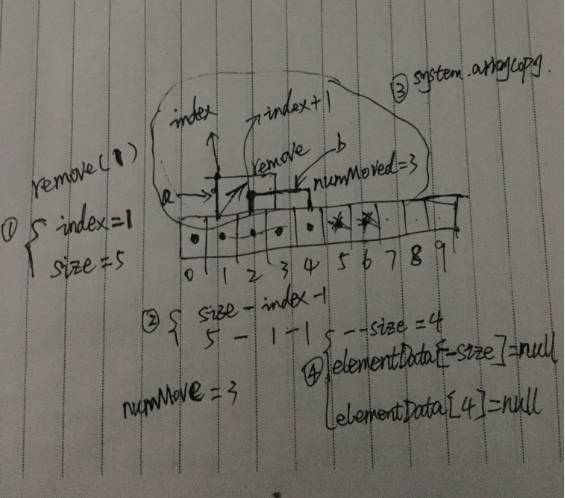
具体的删除操作.png
(画的这么丑也好意思贴出来,真是表脸),
①、调用remove(1)方法时,index为1,如图假设我们ArrayList的容量是10,元素有5个即size为5。
②、计算后,numMove为3。
③、通过System.arraycopy来copy移动elementData数组,b为需要移动的元素,移动到a(也就是覆盖了index为1的值)。
④、元素少了一个size减一,移动后elementData[4]的元素就没用了腾出来了,置为null后交给GC去处理内存。
最后返回被删除的旧元素对象。注意事项:从上面可以看出,调用remove方法的时候,size是变动的,所以一下边遍历边删除就会出现问题:

边遍历边删除.png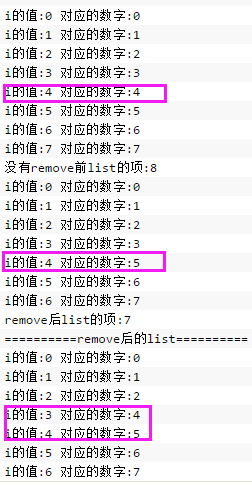
执行结果
对应的值错乱了。解决方案:改用迭代器来删除。
-
// 删除集合中的指定的一个元素
public boolean remove(Object o) {
// 当指定的元素为null时
if (o == null) {
// 遍历查找,如果相等就删除,然后终止查找
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
// 遍历查找,如果相等就删除,然后终止查找
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}从上面源码可以看出,这个remove方法只是删除遍历的时候第一个与入参对象相等的元素,如下图所示:
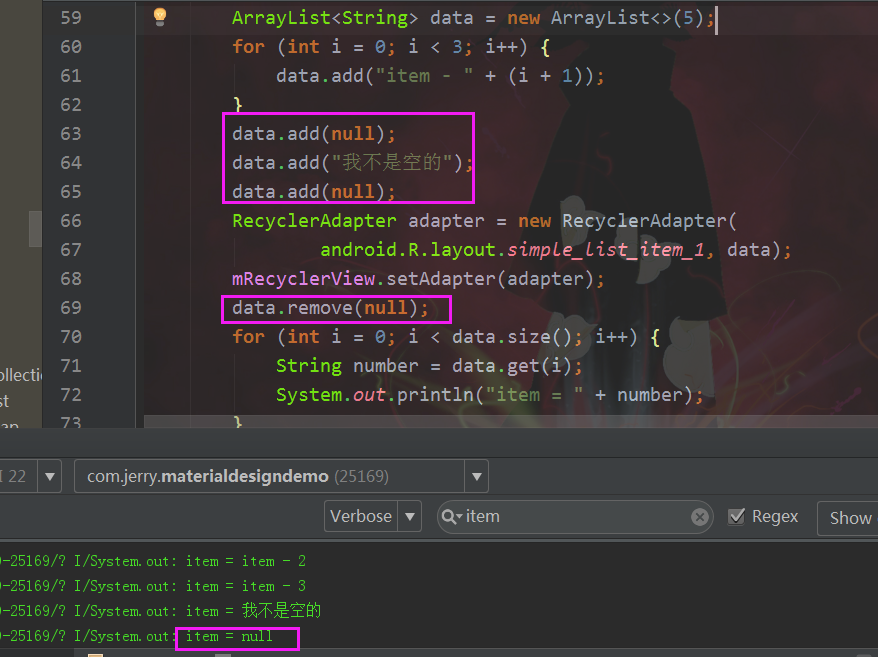
注意事项:add了null的元素后,RecyclerView出现了空白项item的问题,所以数据在设置到适配器前得做非空检查
add了null后.png
public void clear() {
modCount++;
// clear to let GC do its work
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
size = 0;
}clear方法就很简单了,把遍历把缓存数组中有元素部分遍历置空,size也为0后交给GC处理。
-
修改
public E set(int index, E element) { if (index >= size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); // 保存修改前旧的元素对象 E oldValue = (E) elementData[index]; // 直接赋值修改index下标对应的缓存数组里的元素 elementData[index] = element; // 返回修改前旧的元素对象 return oldValue; }-
查询
/** * Returns the element at the specified position in this list. * 返回指定位置的列表元素 * * @param index index of the element to return 指定的位置 * @return the element at the specified position in this list * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 下标边界值异常 */ public E get(int index) { if (index >= size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); // 很简单直接获取缓存数组对应下标的元素对象 return (E) elementData[index]; }通常我们查询遍历ArrayList的时候还会用到迭代器:
Iterator<String> iterator = dataList.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ String item = iterator.next(); System.out.println("item_iterator = " + item); }来看看内部的实现:
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { // The "limit" of this iterator. This is the size of the list at the time the // iterator was created. Adding & removing elements will invalidate the iteration // anyway (and cause next() to throw) so saving this value will guarantee that the // value of hasNext() remains stable and won't flap between true and false when elements // are added and removed from the list. protected int limit = ArrayList.this.size; // 游标值表示下一个元素的index下标 int cursor; // index of next element to return // 表示当前遍历到了哪一个元素的index下标,如果没有了就为-1 int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such // 操作计数器 int expectedModCount = modCount; public boolean hasNext() { // 如果下一个index小于当前具体的元素个数(初始值是集合的size,使用迭代器来add、remove元素的时候会被修改)表示集合中还有下一个元素返回true,否则为false return cursor < limit; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E next() { // 操作计数器不相等,抛出并发修改值异常(ArrayList是一个线程不安全的线性表, // 不同线程都操作一个ArrayList对象会出现线程同步问题) if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); // 临时存储游标值 int i = cursor; // 如果游标值大于等于现有的元素个数,抛出没有此元素异常 if (i >= limit) throw new NoSuchElementException(); // 赋值给一个新的Object数组对象,避免全局的elementData被修改 Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); // 游标值加一,便于下一次迭代器遍历使用 cursor = i + 1; // 取出当前元素对象返回 return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; } public void remove() { if (lastRet < 0) throw new IllegalStateException(); if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); try { // 使用ArrayList的remove方法删除当前遍历位置的元素 ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet); // 回退当前的游标值 cursor = lastRet; // 当前遍历的元素已经被删除了index不存在则为-1 lastRet = -1; expectedModCount = modCount; // 集合可被遍历的元素个数值减一 limit--; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { // 删除元素的时候,当前遍历的元素大于等于集合的size则抛出异常, // 不过这里不太明白,为什么是抛出并发修改异常, // 估计是只有不同线程同时在做remove, // 或者add操作的时候由于size的变动而导致lastRet>=size的情况, // maybe暂且这么理解吧,希望有知道的小伙伴们告知留言 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } }
-
三、总结
- ArrayList是线性表中的顺序存储结构的顺序表,因为内部维护的是一个数组,数组是一个拥有连续存储地址的存储块。
- ArrayList因为内部维护的是一个数组,查询和修改的效率很高,但是插入添加和删除的效率比较低,特别是数据量大的情况下必较明显。
- 在使用普通的for循环遍历ArrayList的时候删除其中的元素容易出现数据删除错乱问题,改用Iterator迭代器能够很好的解决这个问题。
- ArrayList在添加元素的时候是允许加入null元素的,为了避免后续使用数据时出现NullPointerException的异常,请先对要添加的元素做非空判断。
- ArrayList从上面的源码分析可以看出,它可以添加重复的元素对象,所以在添加对象的时候做好相等对象的判断。
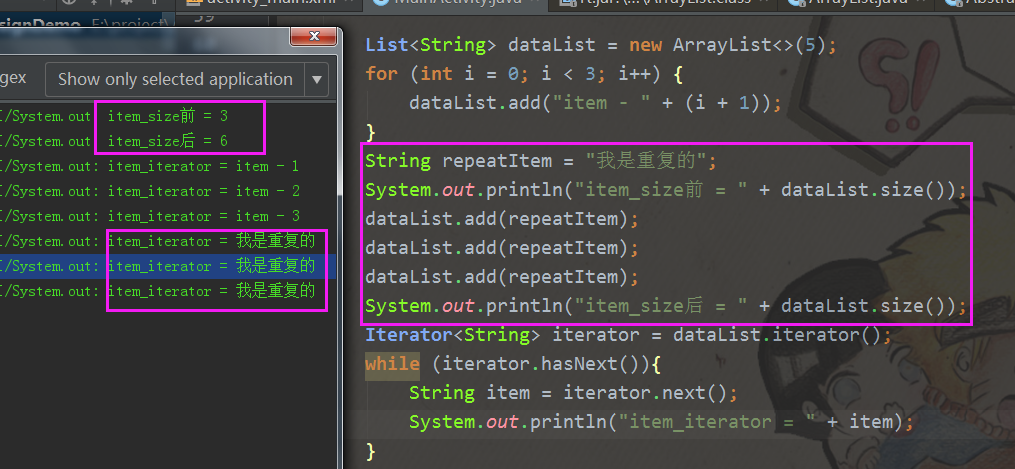
添加重复元素对象.png - 从上面源码可以看出,ArrayList的size和真实申请的堆内存对象容量不同,所以在使用的时候控制好ArrayList的容量使用也是很好的性能优化手段。
- ArrayList的是线程不安全的,在多线程环境下需要注意对象数据同步问题。