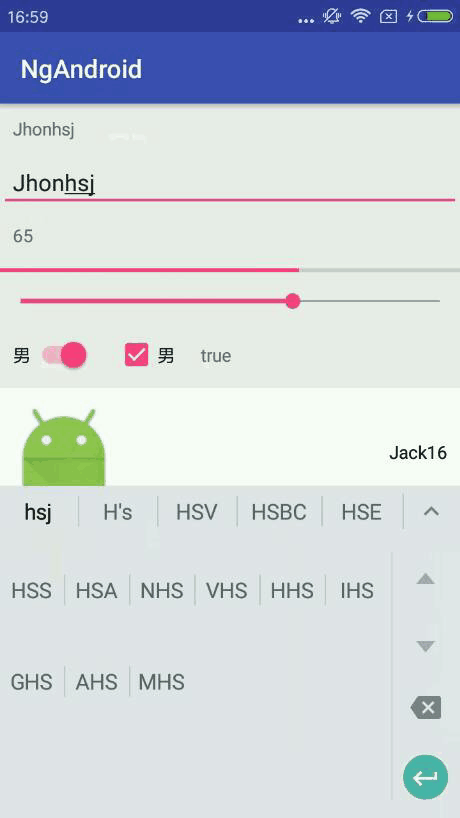
先上一张完成的效果图:
> GitHub地址:github.com/superyoyo/A…
完成这么多的UI操作,其实指需要很少的代码,现在附上全部关键代码。
首先是布局文件:activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
xmlns:ng="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/activity_main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/ll_container"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:tag="ng:user:name"
android:text="Hello World!" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="userName"
android:padding="10dp"
android:tag="ng:user:name" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:tag="ng:user:age" />
<ProgressBar
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
style="@style/Base.Widget.AppCompat.ProgressBar.Horizontal"
android:progress="10"
android:tag="ng:user:age"/>
<SeekBar
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:progress="0"
android:tag="ng:user:age"/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Switch
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="男"
android:tag="ng:user:isMale"
android:layout_margin="10dp"/>
<CheckBox
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:tag="ng:user:isMale"
android:text="男"
android:layout_margin="10dp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:tag="ng:user:isMale"
android:text="Hello World!" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/rv_list"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:tag="nglist:user:list">
<com.autonavi.jacklee.ngandroid.angular.view.NgItemView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:tag="ng:student"
ng:ngRecyclerViewItemList="@layout/item_student" />
<com.autonavi.jacklee.ngandroid.angular.view.NgItemView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:tag="ng:title"
ng:ngRecyclerViewItemList="@layout/item_tag" />
<com.autonavi.jacklee.ngandroid.angular.view.NgItemView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:tag="ng:content"
ng:ngRecyclerViewItemList="@layout/item_content" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
其中java代码部分如下:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements CommonAdapter.CommonAdapterInterface{
private NgGo ngGo;
private NgModel ngUser;
private List list;
private LinearLayout ll_container;
private Handler handler = new
Handler(){
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
if((int)ngUser.getValue("age") >= 100){
ngUser.addParams("age", 0 );
}else{
ngUser.addParams("age", ((int)ngUser.getValue("age")) + 2 );
}
NgModel user = ((List<NgModel>)ngUser.getValue("list")).get(0);
user.addParams("name", "Jack" + ((int)ngUser.getValue("age")));
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
ll_container = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.ll_container);
ngGo = new NgGo(ll_container);
ngUser = new NgModel("user");
ngGo.addNgModel(ngUser);
ngGo.start();
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
initNgGo();
}
private void initNgGo(){
ngUser.addParams("name", "Jhon");
ngUser.addParams("sex", "nan");
ngUser.addParams("age", 14);
ngUser.addParams("isMale", false);
list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i<10; i++){
if(i%3 == 0){
NgModel ngUser = new NgModel("student");
ngUser.addParams("name", "Jack" + i);
list.add(ngUser);
}else if(i%3 == 1){
NgModel ngUser = new NgModel("title");
ngUser.addParams("name", "title" + i);
list.add(ngUser);
}else{
NgModel ngUser = new NgModel("content");
ngUser.addParams("name", "Content" + i);
list.add(ngUser);
}
}
ngUser.addParams("list", list);
Message msg = Message.obtain();
handler.sendMessageDelayed(msg, 1000);
CommonAdapter adapter = ngGo.getRecyclerAdapter(R.id.rv_list);
adapter.setCommonAdapterInterface(this);
}
@Override
public void handleItem(int id, CommonAdapter.CommonHolder holder, final int position) {
switch (id){
case R.id.rv_list:
if(list.get(position).getTag().equals("student")){
holder.getView(R.id.iv_head).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
}
});
}
holder.getItemView().setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), position + "_item", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
break;
}
}
}
以上就是所有代码,是不是感觉代码很少?哈哈哈
现在开始介绍AngularAndroid
一 需要记住的几个对象
- NgGo:这个是AngularAndroid渲染的具体执行者
- NgModel:这个是数据绑定中的绑定对象,只要它的属性值产生了变化,那么只要绑定在它身上的View就会做出相应的改变
- CommonAdapter:这个是RecyclerView的通用适配器
- NgItemView:这个是RecyclerView的Item,NgGo在监测到LinearLayout的tag中以nglist开头,会自动将LinearLayout转为RecyclerView,LinearLayout有多少个NgItemView,RecyclerView就有多少种item类型。
二 使用步骤
1.初始化NgGo对象 NgGo ngg = new NgGo(View parent);
parent这个view对象,类似与angularjs中的控制域,可能一个页面中有不同的逻辑部分,这个时候,需要多个逻辑对象,这样的话,每个逻辑操作对象都对应一个控制域。一般这样的情况比较少。
2.初始化NgModel对象 NgModel user = new NgModel("user");
其中“user”这个参数,对应xml中"ng:user:name"的user,也就是NgModel需要指定对象名字。
3.将NgModel添加到NgGo中,交给NgGo去控制 ngg.addNgModel(user);
4.NgGo开始渲染 ngg.start();
至此,数据绑定完成,现在尝试改变user的属性值:user.addParams("name", "Jhon");
然后运行程序,是不是发现只要xml中tag为"ng:user:name"的view都显示"Jhon"?
因为是双向绑定,所以,当view的文本发生改变时,对应的NgModel的相应属性也会发生变化。倘若Editext和TextView的tag都设置为"ng:user:name"时,会发现,TextView的值是跟着EditText的值动态改变的。
有人会问这有什么用?现在举例一个最简单的场景:
现在要做一个登录页面:
原始做法:
1.实例化帐号和密码两个EditText
3.点击登录时,判断EditText的输入值是否符合规定。
现在的做法:
1.点击登录时,判断user对象的帐号(account)和密码(password)是否符合规定
有木有发现,全程不用关注View对象,只需要关注具体的逻辑对象User,思维不用来回切