自定义viewGroup+ViewDragHelper: 仿探探主页卡片式滑动,层叠布局
前几天看到群里的dalao张旭童用recycleview写了一个这个效果但是我对自定义LayoutManager不熟,刚好又在学习自定义view,所以想到用自定义ViewGroup写写试试,不多说,先上效果图。
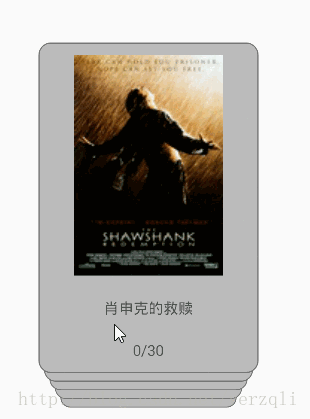
数据来自豆瓣的电影评分榜,从图上看到,我们可以滑动最顶层topview卡片,此时下面的卡片也随之变大,top-1view会变大到topview一致,下面的卡片以此类推,当topview右滑到一定距离时会删除,此时top-1view成了topview。
总的来说,分为以下几个小功能。
-
拖拽顶层view(使用工具类ViewDragHelper推荐看翔哥的这篇)和角度旋转
-
下面页面的放大和缩小
- 滑动到一定程度后删除
不多说 先上代码
public class SwipeCardView extends ViewGroup {
private static final String TAG = "SwipeCardView";
public static int TRANS_Y_GAP;
//卡片阶梯之间的宽度,单位px
private int transY = 12;
private ViewDragHelper mDragHelper;
//最顶层页面,随着手指滑动
private View topView;
//卡片中心点
private int centerX,centerY;
//手指离开屏幕的判断
private boolean isRelise;
//加载数据的adapter
private CardBaseAdapter adapter;
//可见的卡片页面
private int showCards = 3;
//随手指滑动 卡片旋转的角度
private int ROTATION = 20;
//左滑右滑判断
private boolean swipeLeft = false;
//已经删除的页面的数量
private int deleteNum;
//子view的行宽度,高度
int childWidth, childHeight;
public SwipeCardView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public SwipeCardView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public SwipeCardView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
TRANS_Y_GAP = (int) TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP, transY, context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics());
mDragHelper = ViewDragHelper.create(this, 1.0f, new ViewDragHelper.Callback() {
@Override
public boolean tryCaptureView(View child, int pointerId) {
return child == topView;
}
@Override
public int clampViewPositionHorizontal(View changedView, int left, int dx) {
if (isRelise) {
isRelise = false;
}
for (int i = 1; i < getChildCount()-1; i++) {
View view = getChildAt(i);
view.setTranslationY((childHeight*0.025f+TRANS_Y_GAP) * ( getChildCount()-1- i)
-getCenterX(changedView)*(childHeight*0.025f+TRANS_Y_GAP));
view.setScaleX(1-( getChildCount()-1-i)*0.05f + getCenterX(changedView) * 0.05f);
view.setScaleY(1-( getChildCount()-1-i)*0.05f + getCenterX(changedView) * 0.05f);
}
if (topView!=null){
if (swipeLeft){
topView.setRotation(-getCenterX(changedView) * ROTATION);
}else {
topView.setRotation(getCenterX(changedView) * ROTATION);
}
}
return left;
}
@Override
public int clampViewPositionVertical(View child, int top, int dy) {
return top;
}
@Override
public void onViewReleased(View releasedChild, float xvel, float yvel) {
// super.onViewReleased(releasedChild, xvel, yvel);
//mAutoBackView手指释放时可以自动回去
if (releasedChild.getLeft() / 2 > 300) {
if (releasedChild == topView) {
removeView(topView);
deleteNum++;
for (int i = 1; i < getChildCount()-1; i++) {
View view = getChildAt(i);
int level = getChildCount()-1-i;
view.setTranslationY((childHeight*0.025f+TRANS_Y_GAP) * (level));
view.setScaleX(1 - 0.05f * ( level));
view.setScaleY(1 - 0.05f * ( level));
}
adapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
}
} else {
isRelise = true;
mDragHelper.settleCapturedViewAt((int) (centerX-childWidth/2),(int) (centerY-childHeight/2));
invalidate();
}
}
@Override
public void onViewPositionChanged(View changedView, int left, int top, int dx,
int dy) {
super.onViewPositionChanged(changedView, left, top, dx, dy);
//当手指松开后对顶层卡片进行移动
if (changedView == topView && isRelise) {
for (int i = 1; i < getChildCount()-1; i++) {
View view = getChildAt(i);
int level = getChildCount()-1-i;
view.setTranslationY((childHeight*0.025f+TRANS_Y_GAP) * ( level)-
getCenterX(changedView)*(childHeight*0.025f+TRANS_Y_GAP));
view.setScaleX(1-(level)*0.05f + getCenterX(changedView) * 0.05f);
view.setScaleY(1-(level)*0.05f + getCenterX(changedView) * 0.05f);
}
if (topView!=null){
//根据角度来对卡片旋转角度进行测算
if (swipeLeft){
topView.setRotation(-getCenterX(changedView) * ROTATION);
}else {
topView.setRotation(getCenterX(changedView) * ROTATION);
}
}
}
}
}
);
mDragHelper.setEdgeTrackingEnabled(ViewDragHelper.EDGE_LEFT);
}
private float getCenterX(View child) {
if (child.getWidth() / 2 + child.getX() - centerX<0){
swipeLeft = true;
}else {
swipeLeft = false;
}
float width = Math.abs(child.getWidth() / 2 + child.getX() - centerX);
if (width > centerX) {
width = centerX;
}
return width / centerX;
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
centerX = widthSize / 2;
centerY = heightSize/2;
measureChildren( widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//子view
View child = null;
//获取子view的margin值
MarginLayoutParams params = null;
if (getChildCount()>0){
child = getChildAt(0);
//这里我就是用第一个页面的大小来当做长款,因为后面不可能比他大了
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
params = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin;
childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin;
}
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, heightSize);
}
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
if (mDragHelper.continueSettling(true)) {
invalidate();
}
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean b, int i, int i1, int i2, int i3) {
topView = getChildAt(getChildCount()-1);
int level = getChildCount() - 1;
View view;
if (getChildCount() > 1) {
for (int j = 0; j<=getChildCount() -1; j++) {
view = getChildAt(j);
view.layout((int) (centerX-childWidth/2),(int) (centerY-childHeight/2),
(int) (centerX+childWidth/2), (int) (centerY+childHeight/2));
view.setTranslationY((childHeight*0.025f+TRANS_Y_GAP) * (level - 1));
view.setScaleX(1 - 0.05f * (level - 1));
view.setScaleY(1 - 0.05f * (level - 1));
//这里说明下,虽然你可见的是4张卡片,但是其实加载了5行,第五张和第四章重叠,这么做是为了滑动顶部view
// 时第四张卡片滑动时可以显示,所以这里第四张和第五张卡片的位置是一样的。
if (j!=0){
level--;
}
}
}else if (getChildCount() > 0) {
view = getChildAt(0);
view.layout((int) (centerX-childWidth/2),(int) (centerY-childHeight/2),
(int) (centerX+childWidth/2), (int) (centerY+childHeight/2));
}
}
public void setAdapter(@NonNull CardBaseAdapter adapter) {
if (adapter == null) throw new NullPointerException("Adapter不能为空");
this.adapter = adapter;
//初始化数据 你需要显示几个页面
changeViews();
adapter.registerDataSetObserver(new DataSetObserver() {
@Override
public void onChanged() {
getMore();
}
@Override
public void onInvalidated() {
getMore();
}
});
}
public void getMore() {
if (getChildCount()+deleteNum<adapter.getCount()){
View view = adapter.getView(getChildCount()+deleteNum,
getChildAt(getChildCount()),this);
//后面加载进来数据都放在最底层
addView(view,0);
}
}
private void changeViews() {
View view = null;
/**
* showCards 是你需要显示几张卡片,showCards-j是为了排列顺序
* viewgroup是最先加进来的view是在最底层的,所以我为了让第一个加进来的放在最上层,用了这个
* 举个栗子:显示3张页面 showCards = 3,先加载第四个页面(因为最底层还要有一个你看不到的页面)放在最底层,
* 到最后j=3时 加载第一张页面数据,同时将它显示优先级设为最高addView(view,j);
* deleteNum是你右滑删掉的页面数量
*/
for (int j = 0; j <=showCards; j++) {
if (j+deleteNum<adapter.getCount()){
view = adapter.getView(showCards-j, getChildAt(j),this);
addView(view,j);
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean onInterceptHoverEvent(MotionEvent event) {
return mDragHelper.shouldInterceptTouchEvent(event);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
mDragHelper.processTouchEvent(event);
return true;
}
@Override
public ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(),attrs);
}
public SwipeCardView setShowCards(int showCards) {
this.showCards = showCards;
return this;
}
public SwipeCardView setTransY(int transY) {
this.transY = transY;
return this;
}
}
下面对最重要的onlayout代码分析一下,其他滑动的算法和这个基本一致
topView = getChildAt(getChildCount()-1);
int level = getChildCount() - 1;
View view;
if (getChildCount() > 1) {
for (int j = 0; j<=getChildCount() -1; j++) {
view = getChildAt(j);
view.layout((int) (centerX-childWidth/2),(int) (centerY-childHeight/2),
(int) (centerX+childWidth/2), (int) (centerY+childHeight/2));
view.setTranslationY((childHeight*0.025f+TRANS_Y_GAP) * (level - 1));
view.setScaleX(1 - 0.05f * (level - 1));
view.setScaleY(1 - 0.05f * (level - 1));
if (j!=0){
level--;
}
}
}else if (getChildCount() > 0) {
view = getChildAt(0);
view.layout((int) (centerX-childWidth/2),(int) (centerY-childHeight/2),
(int) (centerX+childWidth/2), (int) (centerY+childHeight/2));
} 。如图showCards是可见卡片数量,TRANS_Y_GAP是下端露出的宽度,这里是对下面这一块进行计算,方便下面的layout。
。如图showCards是可见卡片数量,TRANS_Y_GAP是下端露出的宽度,这里是对下面这一块进行计算,方便下面的layout。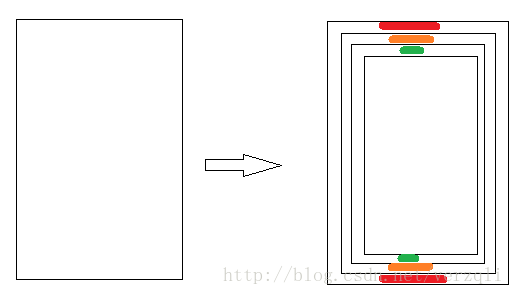 这里我先将这些卡片layout为屏幕的中点,然后对他们进行缩放,代码中0.05f就是缩放比例,第一层缩放0.05,第二层0.10,第三层0.15,以此类推,上图中颜色标注的就是两个缩放区域,他们分别是0.05f的一半,后面代码中可以看到。
这里我先将这些卡片layout为屏幕的中点,然后对他们进行缩放,代码中0.05f就是缩放比例,第一层缩放0.05,第二层0.10,第三层0.15,以此类推,上图中颜色标注的就是两个缩放区域,他们分别是0.05f的一半,后面代码中可以看到。view.setTranslationY((childHeight*0.025f+TRANS_Y_GAP) * (level - 1));- 当layout好他们的位置之后就可以对他们进行位移。childHeight*0.025f位移的就是上图颜色块的距离然后再加上卡片间隔距离TRANS_Y_GAP再乘以他们的阶次,就完成整个的布局了。
- 后面clampViewPositionHorizontal,onViewReleased和onViewPositionChanged方法的算法和这个类似。大致的注释在代码中已经写了,又不懂的可以留言我。
- 先去学习下ViewDragHelper再来看比较好
- 文中的adapter是我自己写的一个自定义adapter,这里我就不列了,想要的自己可以去下载。
- 如果你对卡片大小不满意 ,可以自己去设置,就那个0.05f,这里忘了给他设置成全局变量了,点击事件我也没加了,你们有需要的可以自己加,实在不会评论我,我发给你,其实也不难。
- 在这里我设了两个外部可以控制的变量,卡片可见数量和卡片间隔距离,在外部这样调用就可以了
swipeCards.setShowCards(5)
.setTransY(50)
.setAdapter(new CardBaseAdapter(this,subjectsList));
很久没写博客了,都不怎么会写了,也不怎么会去表达了。暂时就想到这么多,又是想法可以留言我,我一定会看的,恩 就这么多了。