散列表
先到wiki 看看散列表(Hash table)的原理描述。
散列表(Hash table,也叫哈希表),是根据键(Key)而直接访问在内存存储位置的数据结构。也就是说,它通过计算一个关于键值的函数,将所需查询的数据映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,这加快了查找速度。这个映射函数称做散列函数,存放记录的数组称做散列表。
两个重点
- 构造散列函数
- 处理冲突
HashMap
HashMap就是基于散列表的原理来实现的,看源码,获知有哪些数据结构组成了HashMap。
-
散列表,是一个数组,其长度为2的次方。
/** * The table, resized as necessary. Length MUST Always be a power of two. */ transient HashMapEntry[] table = (HashMapEntry[]) EMPTY_TABLE; /** * */ -
再看散列表中存放的元素HashMapEntry。
static class HashMapEntry implements Map.Entry { final K key; V value; HashMapEntry next; int hash; } /** * */
其中包含的成员变量HashMapEntry next是一个单链表的设计,所以HashMap处理冲突的方法是单独链表法。其他细节看源码吧。
LinkedHashMap
继承于HashMap,与HashMap不同的是其数组中存放的元素是LinkedHashMapEntry,总体上说是比HashMap多了一个双向链表的数据结构。
-
双向链表表头
public class LinkedHashMap extends HashMap implements Map { /** * The head of the doubly linked list. */ private transient LinkedHashMapEntry header; } -
散列表中存放的元素是
LinkedHashMapEntry,继承于HashMapEntry,多了两个成员变量。
private static class LinkedHashMapEntry extends HashMapEntry { // These fields comprise the doubly linked list used for iteration. LinkedHashMapEntry before, after; }
before,after组成了一个双向链表,一个双向循环链表。这个链表串联了散列表中的所有元素,组成了一个有序列表。
LinkedHashMap利用双向链表实现了按访问元素来排序或按插入元素来排序。
总结:LinkedHashMap完全拥有HashMap的行为、属性,只是多了一个链表,多了些行为、属性。若设置了按访问元素来排序(accessOrder == true),则每次get(Object key)操作都会让该元素置于表头header.before。插入操作会忽略accessOrder,插入新元素时都会置于表头,插入旧元素(即key已存在)则不会改变排序顺序。
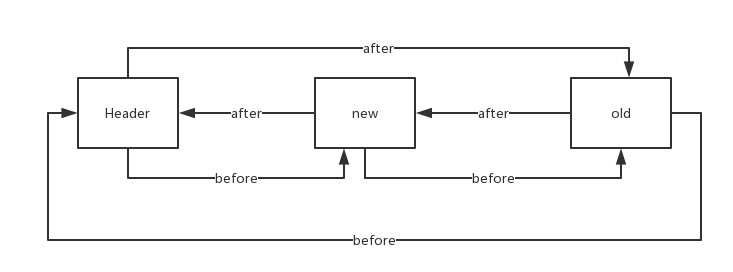
根据下面代码演绎出图示,existingEntry都是指Header元素,代码中都是这么用的:e.addBefore(header);
private void addBefore(LinkedHashMapEntry existingEntry) {
after = existingEntry;
before = existingEntry.before;
before.after = this;
after.before = this;
}看图,哪里是表头哪里是表尾呢。我说的表头是指靠近Header的。
LruCache
LruCache的源码很少很简单。用的数据结构是LinkedHashMap,按访问元素来排序。最近最少使用的元素在表尾(eldest = header.after,header.after指向表尾)。
public class LruCache {
private final LinkedHashMap map;
public LruCache(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize );
}
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.map = new LinkedHashMap(0, 0.75f, true);
}
/**
* Remove the eldest entries until the total of remaining entries is at or
* below the requested size.
*
* @param maxSize the maximum size of the cache before returning. May be -1
* to evict even 0-sized elements.
*/
public void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
while (true) {
K key;
V value;
synchronized (this) {
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName()
+ ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
if (size <= maxSize) {
break;
}
Map.Entry toEvict = map.eldest();
if (toEvict == null) {
break;
}
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
map.remove(key);
size -= safeSizeOf(key, value);
evictionCount++;
}
entryRemoved(true, key, value, null);
}
}不能直接使用LruCache,必须要重写它的protected int sizeOf(K key, V value)方法。