一、基础知识
1.Android 进程优先级
1.1 进程优先级等级一般分法
- Activte process
- Visible Process
- Service process
- Background process
- Empty process
1.2 进程优先级号
static final int UNKNOWN_ADJ = 16;
static final int CACHED_APP_MAX_ADJ = 15;
static final int CACHED_APP_MIN_ADJ = 9;
static final int SERVICE_B_ADJ = 8;
static final int PREVIOUS_APP_ADJ = 7;
static final int HOME_APP_ADJ = 6;
static final int SERVICE_ADJ = 5;
static final int HEAVY_WEIGHT_APP_ADJ = 4;
static final int BACKUP_APP_ADJ = 3;
static final int PERCEPTIBLE_APP_ADJ = 2;
static final int VISIBLE_APP_ADJ = 1;
static final int FOREGROUND_APP_ADJ = 0;
static final int PERSISTENT_SERVICE_ADJ = -11;
static final int PERSISTENT_PROC_ADJ = -12;
static final int SYSTEM_ADJ = -16;
static final int NATIVE_ADJ = -17;
2. Android Low Memory Killer
Android系统内存不足时,系统会杀掉一部分进程以释放空间,谁生谁死的这个生死大权就是由LMK所决定的,这就是Android系统中的Low Memory Killer,其基于Linux的OOM机制,其阈值定义如下面所示的lowmemorykiller文件中,当然也可以通过系统的init.rc实现自定义。 lowmemorykiller.c
static uint32_t lowmem_debug_level = 1;
static int lowmem_adj[6] = {
0,
1,
6,
12,
};
static int lowmem_adj_size = 4;
static int lowmem_minfree[6] = {
3 * 512,
2 * 1024,
4 * 1024,
16 * 1024,
};
static int lowmem_minfree_size = 4;
① 在Low Memory Killer中通过进程的oom_adj与占用内存的大小决定要杀死的进程,oom_adj值越小越不容易被杀死。其中,lowmem_minfree是杀进程的时机,谁被杀,则取决于lowmem_adj,具体值得含义参考上面 Android进程优先级 所述.
② 在init.rc中定义了init进程(系统进程)的oom_adj为-16,其不可能会被杀死(init的PID是1),而前台进程是0(这里的前台进程是指用户正在使用的Activity所在的进程),用户按Home键回到桌面时的优先级是6,普通的Service的进程是8. init.rc
# Set init and its forked children's oom_adj.
write /proc/1/oom_adj -16
关于Low Memory Killer的具体实现原理可参考Ref-2.
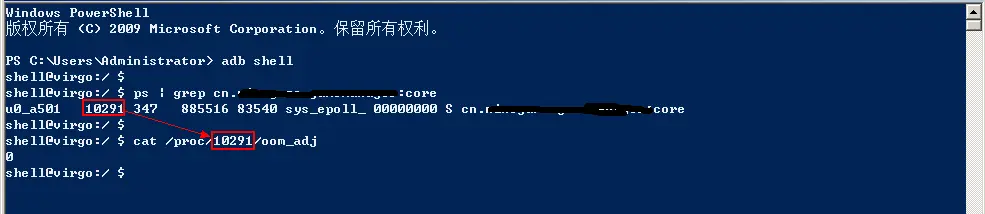
3. 查看某个App的进程
步骤(手机与PC连接)
- adb shell
- ps | grep 进程名
- cat /proc/pid/oom_adj //其中pid是上述grep得到的进程号
4. Android账号和同步机制
属于Android中较偏冷的知识,具体参考 Ref 3 /4 /5
二、现有方法
1. 网络连接保活方法
A. GCM B. 公共的第三方push通道(信鸽等) C. 自身跟服务器通过轮询,或者长连接 具体实现请参考 微信架构师杨干荣的”微信Android客户端后台保活经验分享” (Ref-1).
2. 双service 提高进程优先级
思路:(API level > 18 )
- 应用启动时启动一个假的Service(FakeService), startForeground(),传一个空的Notification
- 启动真正的Service(AlwaysLiveService),startForeground(),注意必须相同Notification ID
- FakeService stopForeground()
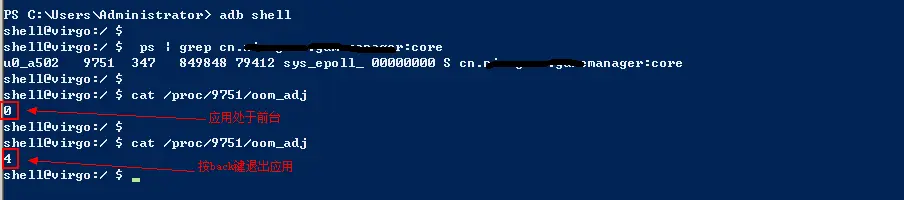
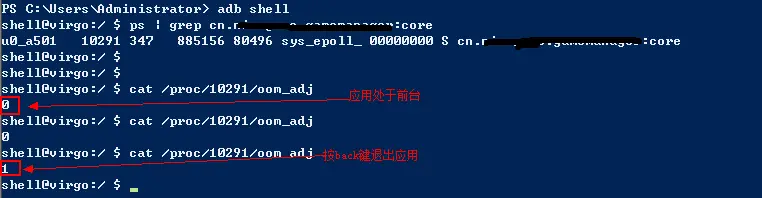
效果:通过adb查看,运行在后台的服务其进程号变成了1(优先级仅次于前台进程)
风险:Android系统前台service的一个漏洞,可能在6.0以上系统中修复
实现:核心代码如下 AlwaysLiveService 常驻内存服务
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
startForeground(R.id.notify, new Notification());
startService(new Intent(this, FakeService.class));
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
FakeService 临时服务
public class FakeService extends Service {
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
startForeground(R.id.notify, new Notification());
stopSelf();
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
stopForeground(true);
super.onDestroy();
}
}
3. 守护进程及时拉起
AlarmReceiver, ConnectReceiver,BootReceiver等
三、新方法(AccountSyncAdapter)
1. 思路:
利用Android系统提供的账号和同步机制实现
2. 效果:
- 通过adb查看,运行在后台的服务其进程号变成了1(优先级仅次于前台进程),能提高进程优先级,对比如下图
3. 风险:
- SyncAdapter时间进度不高,往往会因为手机处于休眠状态,而时间往后调整,同步间隔最低为1分钟
- 用户可以单独停止或者删除,有些手机账号默认是不同步的,需要手动开启
4. 实现:核心代码如下
4.1 建立数据同步系统(ContentProvider) 通过一个ContentProvider用来作数据同步,由于并没有实际数据同步,所以此处就直接建立一个空的ContentProvider即可
public class XXAccountProvider extends ContentProvider {
public static final String AUTHORITY = "包名.provider";
public static final String CONTENT_URI_BASE = "content://" + AUTHORITY;
public static final String TABLE_NAME = "data";
public static final Uri CONTENT_URI = Uri.parse(CONTENT_URI_BASE + "/" + TABLE_NAME);
@Override
public boolean onCreate() {
return true;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public Cursor query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String selection, String[] selectionArgs, String sortOrder) {
return null;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public String getType(Uri uri) {
return new String();
}
@Nullable
@Override
public Uri insert(Uri uri, ContentValues values) {
return null;
}
@Override
public int delete(Uri uri, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int update(Uri uri, ContentValues values, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) {
return 0;
}
}
然后再Manifest中声明
4.2 建立Sync系统 (SyncAdapter) 通过实现SyncAdapter这个系统服务后, 利用系统的定时器对程序数据ContentProvider进行更新,具体步骤为:
public class XXSyncService extends Service {
private static final Object sSyncAdapterLock = new Object();
private static XXSyncAdapter sSyncAdapter = null;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
synchronized (sSyncAdapterLock) {
if (sSyncAdapter == null) {
sSyncAdapter = new XXSyncAdapter(getApplicationContext(), true);
}
}
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return sSyncAdapter.getSyncAdapterBinder();
}
static class XXSyncAdapter extends AbstractThreadedSyncAdapter {
public XXSyncAdapter(Context context, boolean autoInitialize) {
super(context, autoInitialize);
}
@Override
public void onPerformSync(Account account, Bundle extras, String authority, ContentProviderClient provider, SyncResult syncResult) {
getContext().getContentResolver().notifyChange(XXAccountProvider.CONTENT_URI, null, false);
}
}
}
其中sync_adapter为:
参数说明:
android:contentAuthority 指定要同步的ContentProvider在其AndroidManifest.xml文件中有个android:authorities属性。 android:accountType 表示进行同步的账号的类型。 android:userVisible 设置是否在“设置”中显示 android:supportsUploading 设置是否必须notifyChange通知才能同步 android:allowParallelSyncs 是否支持多账号同时同步 android:isAlwaysSyncable 设置所有账号的isSyncable为1 android:syncAdapterSettingsAction 指定一个可以设置同步的activity的Action。
- 账户调用Sync服务 首先配置好Account(第三步),然后再通过ContentProvider实现 手动更新
public void triggerRefresh() {
Bundle b = new Bundle();
b.putBoolean(ContentResolver.SYNC_EXTRAS_MANUAL, true);
b.putBoolean(ContentResolver.SYNC_EXTRAS_EXPEDITED, true);
ContentResolver.requestSync(
account,
CONTENT_AUTHORITY,
b);
}
添加账号
Account account = AccountService.GetAccount();
AccountManager accountManager = (AccountManager) context.getSystemService(Context.ACCOUNT_SERVICE);
accountManager.addAccountExplicitly(...)
同步周期设置
ContentResolver.setIsSyncable(account, CONTENT_AUTHORITY, 1);
ContentResolver.setSyncAutomatically(account, CONTENT_AUTHORITY, true);
ContentResolver.addPeriodicSync(account, CONTENT_AUTHORITY, new Bundle(), SYNC_FREQUENCY);
4.3 建立账号系统 (Account Authenticator) 通过建立Account账号,并关联SyncAdapter服务实现同步
public class XXAuthService extends Service {
private XXAuthenticator mAuthenticator;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
mAuthenticator = new XXAuthenticator(this);
}
private XXAuthenticator getAuthenticator() {
if (mAuthenticator == null)
mAuthenticator = new XXAuthenticator(this);
return mAuthenticator;
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return getAuthenticator().getIBinder();
}
class XXAuthenticator extends AbstractAccountAuthenticator {
private final Context context;
private AccountManager accountManager;
public XXAuthenticator(Context context) {
super(context);
this.context = context;
accountManager = AccountManager.get(context);
}
@Override
public Bundle addAccount(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, String accountType, String authTokenType, String[] requiredFeatures, Bundle options) throws NetworkErrorException {
final Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
final Intent intent = new Intent(context, AuthActivity.class);
intent.putExtra(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_AUTHENTICATOR_RESPONSE, response);
bundle.putParcelable(AccountManager.KEY_INTENT, intent);
return bundle;
}
@Override
public Bundle getAuthToken(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, Account account, String authTokenType, Bundle options) throws NetworkErrorException {
String authToken = accountManager.peekAuthToken(account, getString(R.string.account_token_type));
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(authToken)) {
final String password = accountManager.getPassword(account);
if (password != null) {
authToken = account.name + password;
}
}
final Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(authToken)) {
bundle.putString(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_NAME, account.name);
bundle.putString(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_TYPE, account.type);
bundle.putString(AccountManager.KEY_AUTHTOKEN, authToken);
return bundle;
}
final Intent intent = new Intent(context, AuthActivity.class);
intent.putExtra(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_AUTHENTICATOR_RESPONSE, response);
intent.putExtra(AuthActivity.ARG_ACCOUNT_NAME, account.name);
bundle.putParcelable(AccountManager.KEY_INTENT, intent);
return bundle;
}
@Override
public String getAuthTokenLabel(String authTokenType) {
return null;
}
@Override
public Bundle editProperties(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, String accountType) {
return null;
}
@Override
public Bundle confirmCredentials(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, Account account, Bundle options) throws NetworkErrorException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Bundle updateCredentials(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, Account account, String authTokenType, Bundle options) throws NetworkErrorException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Bundle hasFeatures(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, Account account, String[] features) throws NetworkErrorException {
return null;
}
}
}
其中authenticator为:
Refs
版权声明
SkySeraph by SkySeraph is licensed under a Creative Commons BY-NC-ND 4.0 International License. 由Bob创作并维护的SkySeraph博客采用创作共用保留署名-非商业-禁止演绎4.0国际许可证. 本文首发于SkySeraph博客( skyseraph.com ),版权归作者所有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。微信扫码打赏SkySeraph

如果您愿意捐助其它金额请戳我~~,扫码支付宝/微信
本文永久链接:skyseraph.com/2016/06/19/…