List 集合
List 集合体系图
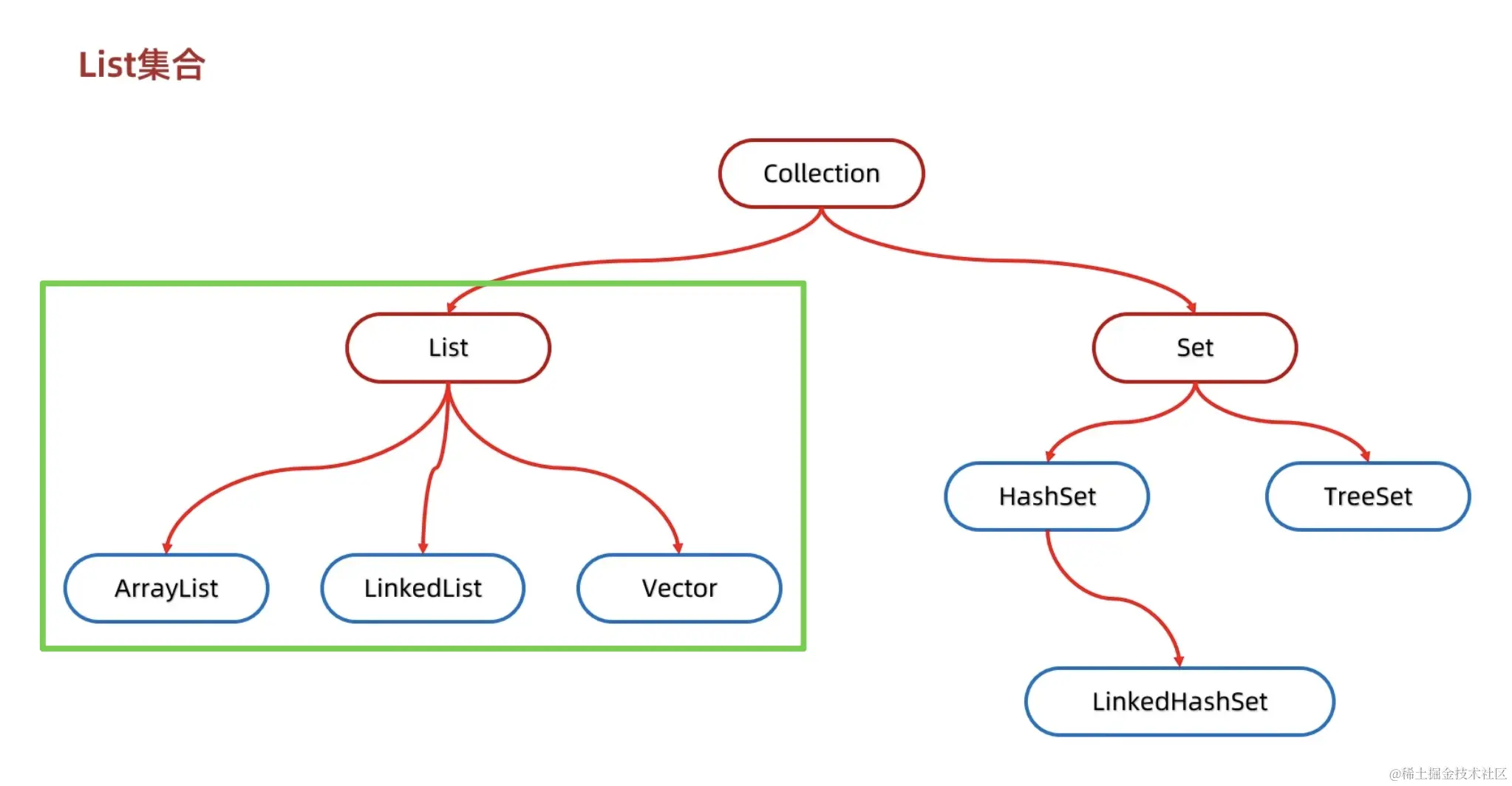
List 集合介绍
List 集合属于Collection集合体系,所以Collection中的方法在list中都适用;
List 集合特点:
1.有序:存和取的元素顺序一致;
2.有索引:可以通过索引操作元素;
3.可重复:存储的元素可以重复;
知识拓展:
ArrayList 的内容看这里:https:
LinkedList 的内容看这里:https:
Vector 的内容看这里:暂无
List 集合的特有方法
1.Collection中的方法List都继承了;
2.List集合因为有索引,所以多了很多索引操作的方法;
3.特有方法介绍
* void add(int index, E e);
* E remove(int index);
* E set(int index, E e);
* E get(int index);
4.特有方法细节
* void add(int index, E e);
细节:原来索引上的元素依次往后移。
List 遍历方式
List有5种遍历方式:
1.迭代器
2.列表迭代器
3.增强for
4.Lambda表达式
5.普通for循环(List集合有索引)
知识拓展:
Iterator 迭代器的内容看这里:https:
ListIterator 列表迭代器 的内容看这里:https:
Lambda表达式 的内容看这里:https:
List 遍历方式 代码演示:
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aaa");
list.add("bbb");
list.add("ccc");
System.out.println("1.迭代器遍历 -------------------");
Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String str = iterator.next();
System.out.println(str);
}
System.out.println("2.列表迭代器遍历 -------------------");
ListIterator<String> listIterator = list.listIterator();
while (listIterator.hasNext()) {
String str = listIterator.next();
System.out.println(str);
}
System.out.println("3.增强for遍历 -------------------");
for (String str : list) {
System.out.println(str);
}
System.out.println("4.Lambda表达式遍历 -------------------");
list.forEach(str -> System.out.println(str));
System.out.println("5.普通for循环遍历(List集合有索引)-------------------");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
String str = list.get(i);
System.out.println(str);
}
List 的5种遍历方式对比:
这个多,怎么用?
1.迭代器:在遍历过程中需要删除元素,用这个;
2.列表迭代器:在遍历过程中需要添加元素,用这个;
3.增强for:只是想遍历,用这个;
4.Lambda表达式:只是想遍历,用这个;
5.普通for循环:在遍历过程中想要操作索引,用这个;
List 集合MST
Q1.看下面代码回答问题:
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.remove(1);
请问,这时候remove方法删除的是那一条数据?为什么?
A:
这时候remove方法删除的是第二条数据,因为在List集合中有两个remove方法,
* E remove(int index);
* boolean remove(Object o);
这里需要注意,当调用方法的时候,方法出现了重载,会优先调用实参跟形参类型一致的那个方法。
所以这里调用的是操作索引的remove方法,而不是操作对象的remove方法。