qiankun的两种通信方式
qiankun官方提供的方式,适合业务划分清晰,比较简单的微前端应用,一般来说使用第一种方案就可以满足大部分的应用场景需求- 第二种是基于
redux实现的通信方式,适合需要跟踪通信状态,子应用具备独立运行能力,较为复杂的微前端应用
1. Actions通信
1.1 主应用中注册通信实例
initGlobalState(state)方法注册MicroAppStateActions实例用于通信, 该实例的返回值有三个方法:
setGlobalState: 设置globalState设置新的值时,内部将执行浅检查,如果检查到globalState发生改变则触发通知,通知所有的观察者函数onGlobalStateChange: 注册 观察者 函数 - 响应globalState变化,在globalState发生变化时触发该观察者函数offGlobalStateChange: 取消观察者函数 - 该实例不再响应globalState变化。
// mian/src/shared/actions.ts
import { initGlobalState, MicroAppStateActions } from "qiankun";
const initialState = {};
// 定义全局状态,并返回通信方法,建议在主应用使用,微应用通过 props 获取通信方法
const actions: MicroAppStateActions = initGlobalState(initialState);
export default actions;
1.2 在主应用中使用
// main/src/pages/communication/index.vue
<script lang="ts">
import { Component, Vue } from 'vue-property-decorator';
// 导入注册好的通信实例
import actions from '@/shared/actions';
@Component
export default class Communication extends Vue {
mounted() {
console.log('actions', actions)
// 注册一个观察者函数
actions.onGlobalStateChange((state, prevState) => {
console.log('主应用观察者:token改变前的值为:', prevState.token)
console.log('主应用观察者:登录状态发生变化后的token值为:', state.token)
})
}
// 注册页面上的登录按钮
async login() {
const res = await Promise.resolve({
data: Math.floor(Math.random() * 1000)
})
const token = res.data;
// 登录成功之后,设置token
actions.setGlobalState({ token });
// 跳转 到 home 页
// this.$router.push('/');
}
}
</script>
1.3 在微应用中使用 - 以app-react项目为例
- 声明一个接收主应用actions的实例
// app-react/src/shared/actions.js
function emptyAction() {
console.warn("Current execute action is empty!");
}
class Actions {
// 默认值为空 Action
actions = {
onGlobalStateChange: emptyAction,
setGlobalState: emptyAction
};
// 设置 actions
setActions(actions) {
this.actions = actions;
}
// 映射
onGlobalStateChange(...args) {
return this.actions.onGlobalStateChange(...args);
}
// 映射
setGlobalState(...args) {
return this.actions.setGlobalState(...args);
}
}
// 创建 Action 实例
const actions = new Actions();
export default actions;
- 在
mount声明周期中,接收主应用发送的props
// app-react/src/index.js
export async function mount(props) {
console.log("ReactMicroApp mount", props);
if (props) {
// 注入 actions 实例
actions.setActions(props)
}
}
- 在微应用中使用
// app-react/src/pages/list/index.jsx
// 引入 actions
import actions from '@/shared/actions';
useEffect(() => {
// 注册观察者函数
// onGlobalStateChange 第二个参数为true,表示立即执行一次观察者函数
actions.onGlobalStateChange(state => {
const { token } = state;
if (!token) {
message.error('未检测到登录信息!')
// 注意:微应用里面的路由跳转是在子应用内部独立运行的
history.push({
pathname: '/'
})
return;
}
// 获取用户信息
getUserInfo()
}, true)
}, [history]);
- 效果图
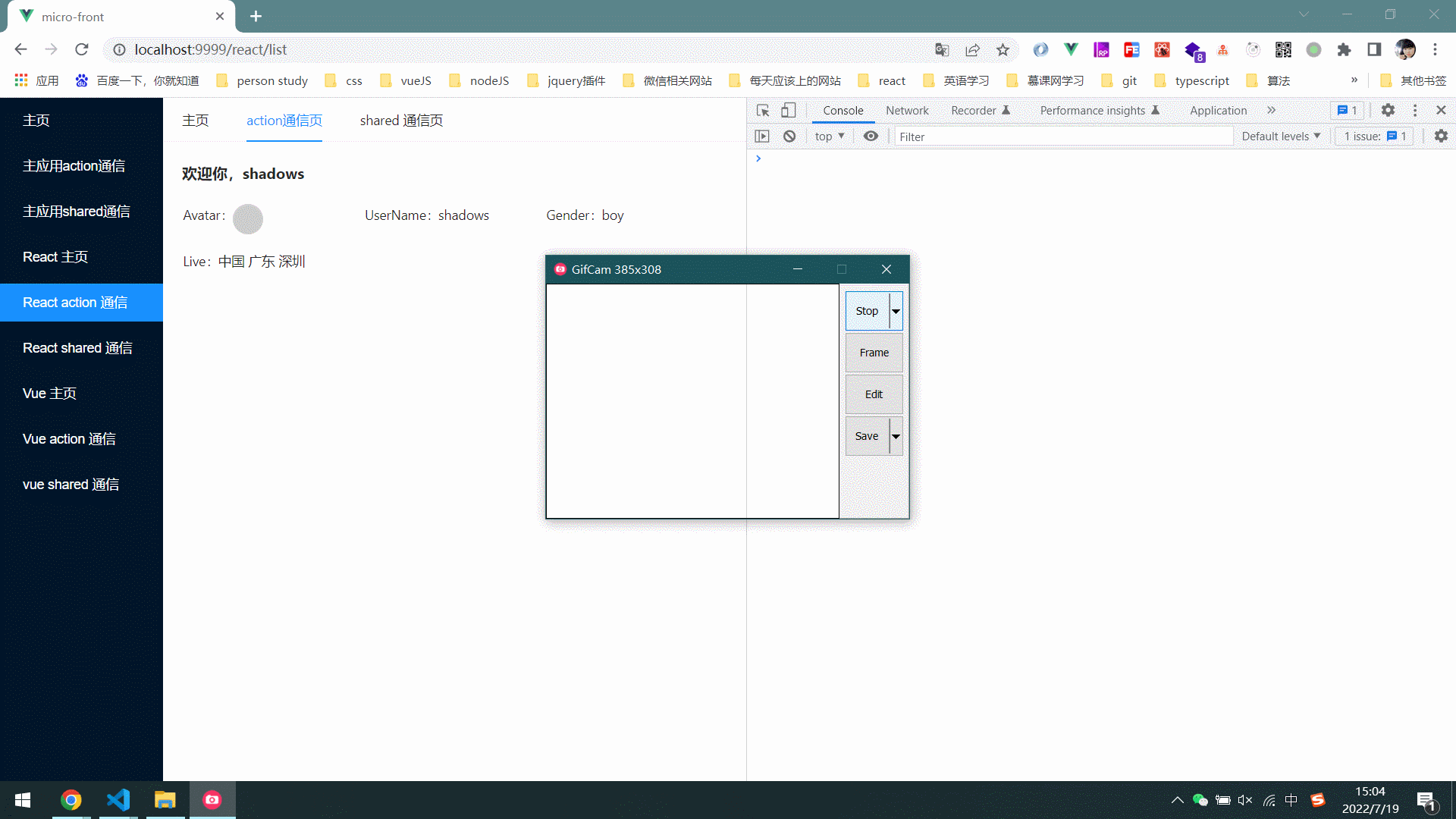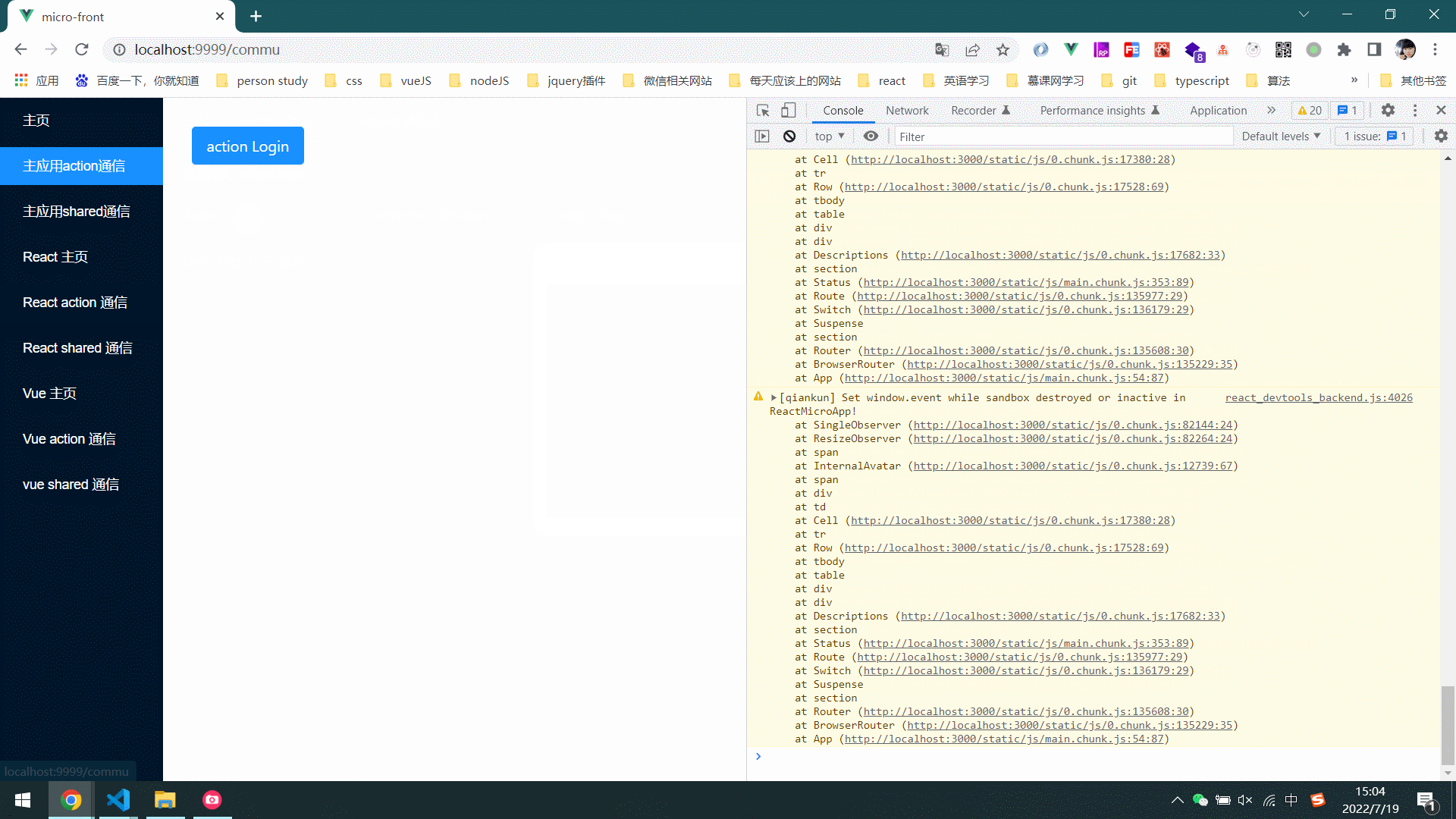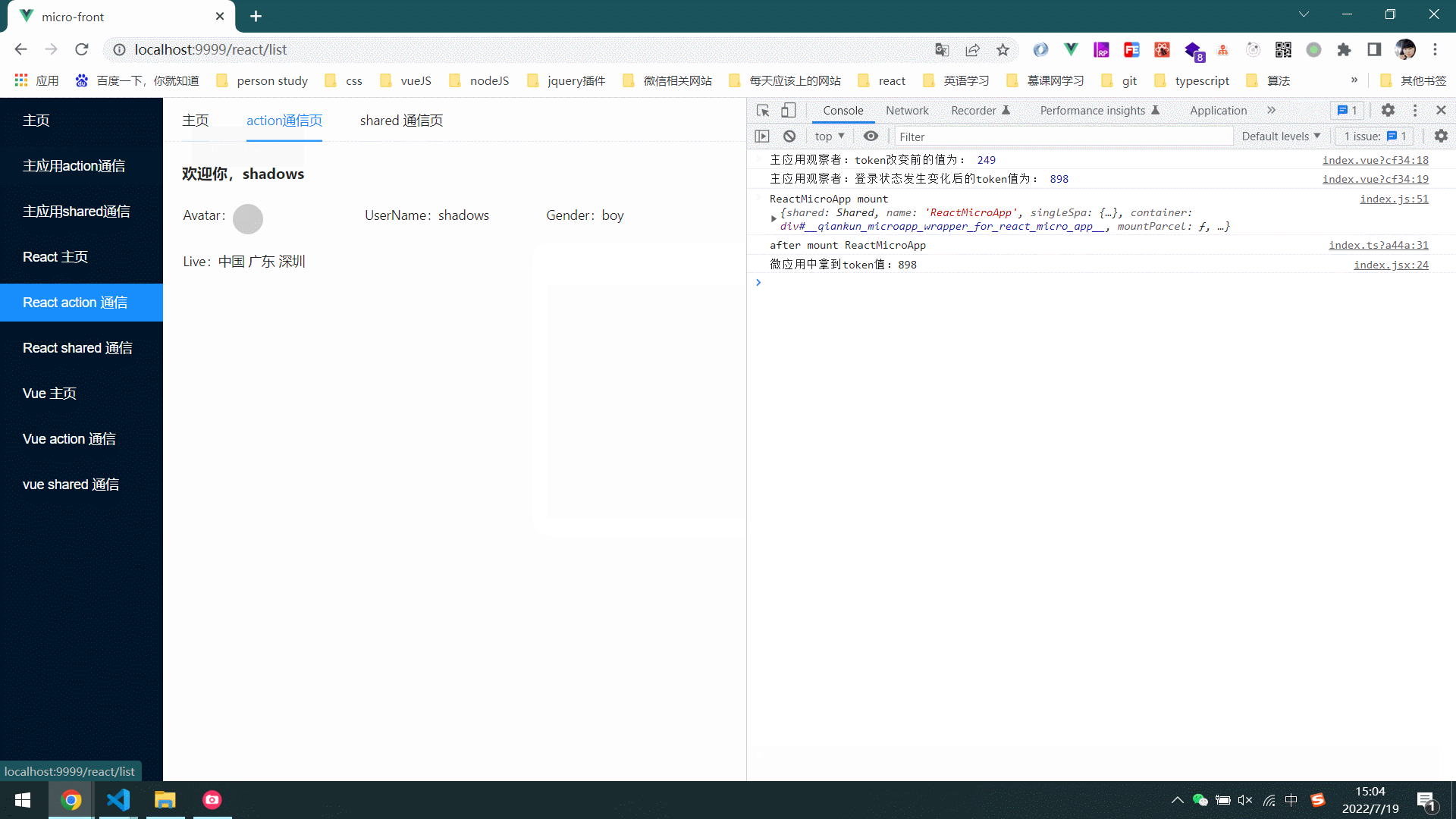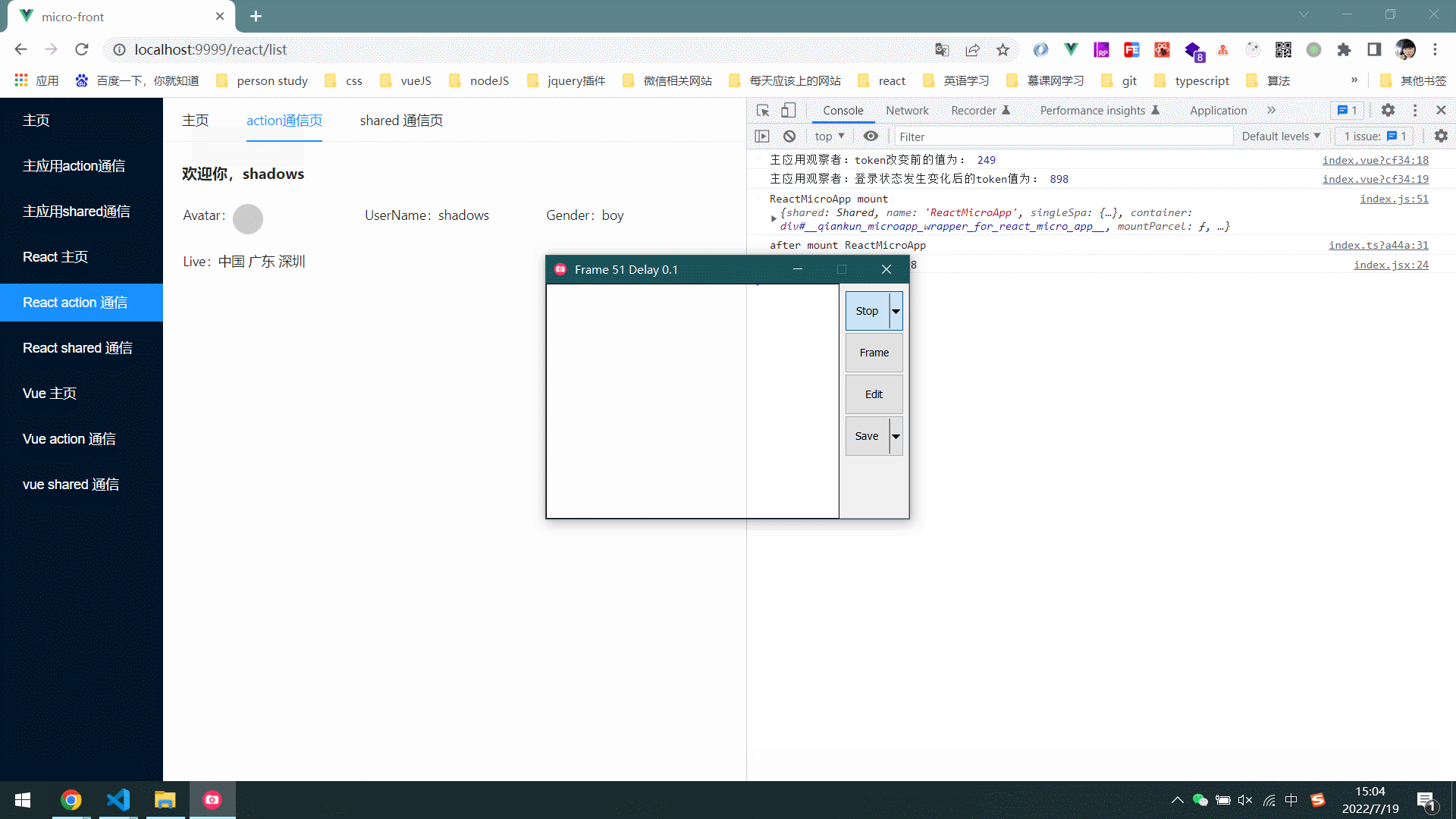
1.4 actions通信方式实现原理
1 首先是基于发布订阅模式实现的
/**
* @author dbkillerf6
* @since 2020-04-10
*/
import { cloneDeep } from 'lodash';
import type { OnGlobalStateChangeCallback, MicroAppStateActions } from './interfaces';
// 维护的全局变量
let globalState: Record<string, any> = {};
// 存储所有的依赖函数
// { [id]: callback}
const deps: Record<string, OnGlobalStateChangeCallback> = {};
// 触发全局监听
function emitGlobal(state: Record<string, any>, prevState: Record<string, any>) {
Object.keys(deps).forEach((id: string) => {
if (deps[id] instanceof Function) {
// 执行监听函数,并把前后state分别传入
deps[id](cloneDeep(state), cloneDeep(prevState));
}
});
}
export function initGlobalState(state: Record<string, any> = {}) {
if (state === globalState) {
console.warn('[qiankun] state has not changed!');
} else {
const prevGlobalState = cloneDeep(globalState);
globalState = cloneDeep(state);
emitGlobal(globalState, prevGlobalState);
}
return getMicroAppStateActions(`global-${+new Date()}`, true);
}
- 初始化
globalState变量,为一个空对象,用来存放订阅器 - 当调用
initGlobalState方法时,会对传入的state和globalState进行比较 - 不相同时,就把全局监听函数一个个触发
- 返回一个
getMicroAppStateActions函数的返回值
2. getMicroAppStateAction函数
export function getMicroAppStateActions(id: string, isMaster?: boolean): MicroAppStateActions {
return {
/**
* onGlobalStateChange 全局依赖监听
*
* 收集 setState 时所需要触发的依赖
*
* 限制条件:每个子应用只有一个激活状态的全局监听,新监听覆盖旧监听,若只是监听部分属性,请使用 onGlobalStateChange
*
* 这么设计是为了减少全局监听滥用导致的内存爆炸
*
* 依赖数据结构为:
* {
* {id}: callback
* }
*
* @param callback 回调函数
* @param fireImmediately 是否立即执行回调函数
*/
onGlobalStateChange(callback: OnGlobalStateChangeCallback, fireImmediately?: boolean) {
if (!(callback instanceof Function)) {
console.error('[qiankun] callback must be function!');
return;
}
if (deps[id]) {
console.warn(`[qiankun] '${id}' global listener already exists before this, new listener will overwrite it.`);
}
deps[id] = callback;
if (fireImmediately) {
const cloneState = cloneDeep(globalState);
callback(cloneState, cloneState);
}
},
/**
* setGlobalState 更新 store 数据
*
* 1. 对输入 state 的第一层属性做校验,只有初始化时声明过的第一层(bucket)属性才会被更改
* 2. 修改 store 并触发全局监听
*
* @param state
*/
setGlobalState(state: Record<string, any> = {}) {
if (state === globalState) {
console.warn('[qiankun] state has not changed!');
return false;
}
const changeKeys: string[] = [];
const prevGlobalState = cloneDeep(globalState);
globalState = cloneDeep(
Object.keys(state).reduce((_globalState, changeKey) => {
if (isMaster || _globalState.hasOwnProperty(changeKey)) {
changeKeys.push(changeKey);
return Object.assign(_globalState, { [changeKey]: state[changeKey] });
}
console.warn(`[qiankun] '${changeKey}' not declared when init state!`);
return _globalState;
}, globalState),
);
if (changeKeys.length === 0) {
console.warn('[qiankun] state has not changed!');
return false;
}
emitGlobal(globalState, prevGlobalState);
return true;
},
// 注销该应用下的依赖
offGlobalStateChange() {
delete deps[id];
return true;
},
};
}
3. 如何传给微应用的props
// 1. 在qiankun里面唯一id
// window.__app_instance_name_map__[appName] 是 number 类型, 每注册一次对应的微应用会加1
appInstanceId =`${appName}_${window.__app_instance_name_map__[appName]}`
// 2. 获取actions
const { onGlobalStateChange, setGlobalState, offGlobalStateChange }: Record<string, CallableFunction> =
getMicroAppStateActions(appInstanceId);
// 3. 把qiankun生成生命周期传递给 single-spa
async (props) => mount({ ...props, container: appWrapperGetter(), setGlobalState, onGlobalStateChange }),
// 4. 在 single-spa里面使用getProps获取传过来的自定义参数customProps 最后给我们子应用的钩子函数使用
app.loadApp(getProps(app));
const result = assign({}, customProps, {
name,
mountParcel: mountParcel.bind(appOrParcel),
singleSpa,
});
2. Shared通信
主应用基于redux维护一个状态池,通过shared实例暴露一些方法给子应用使用。同时,子应用需要单独维护一份shared实例,在独立运行时使用自身的shared实例,在嵌入主应用时使用主应用的shared实例,这样就可以保证在使用和表现上一致。
2.1 主应用中定义store
// main/src/shared/store.ts
import { createStore } from "redux";
export type State = {
token?: string;
};
type Action = {
type: string;
payload: any;
};
const reducer = (state: State = {}, action: Action): State => {
switch (action.type) {
default:
return state;
// 设置 Token
case "SET_TOKEN":
return {
...state,
token: action.payload,
};
}
};
const store = createStore<State, Action, unknown, unknown>(reducer);
export default store;
2.2 主应用中暴露一些方法
// main/src/shared/index.ts
import store from "./store";
class Shared {
/**
* 获取 Token
*/
public getToken(): string {
const state = store.getState();
return state.token || "";
}
/**
* 设置 Token
*/
public setToken(token: string): void {
// 将 token 的值记录在 store 中
store.dispatch({
type: "SET_TOKEN",
payload: token
});
}
}
const shared = new Shared();
export default shared;
2.3 主应用中使用
// main/src/pages/login/index.vue
import { Component, Vue } from "vue-property-decorator";
import shared from "@/shared";
@Component
export default class Login extends Vue {
// 页面上注册的登录按钮事件方法
async login() {
const result = await ApiLogin();
const token = result.data;
// 使用 shared 的 setToken 记录 token
shared.setToken(token);
this.$router.push("/");
}
}
2.4 微应用中使用 - 以app-react项目为例
1. 在主应用注册微应用apps中传入props
// main/src/micro/apps.ts
import shared from "@/shared"
const apps = [
/**
* name: 微应用名称 - 具有唯一性
* entry: 微应用入口 - 通过该地址加载微应用,这里我们使用 config 配置
* container: 微应用挂载节点 - 微应用加载完成后将挂载在该节点上
* activeRule: 微应用触发的路由规则 - 触发路由规则后将加载该微应用
*/
{
name: "ReactMicroApp",
entry: REACT_MICRO_APP,
container: "#frame",
activeRule: "/react",
// 通过 props 将shared 传递给子应用
props: {
shared
}
},
]
2. 定义一个接收主应用通信的实例
// app-react/src/shared/index.js
// 子应用自身的 shared ,子应用独立运行时将使用该 shared ,子应用的 shared 使用 localStorage 来操作 token
class Shared {
/**
* 获取 Token
*/
getToken() {
// 子应用独立运行时,在 localStorage 中获取 token
return localStorage.getItem("token") || "";
}
/**
* 设置 Token
*/
setToken(token) {
// 子应用独立运行时,在 localStorage 中设置 token
localStorage.setItem("token", token);
}
}
// 用于管理 shared ,例如重载 shared 实例、获取 shared实例
class SharedModule {
static shared = new Shared();
/**
* 重载 shared
*/
static overloadShared(shared) {
SharedModule.shared = shared;
}
/**
* 获取 shared 实例
*/
static getShared() {
return SharedModule.shared;
}
}
export default SharedModule;
3. 在mount生命周期函数中引入从主应用传过来的通信参数
export async function mount(props) {
console.log("ReactMicroApp mount", props);
// 当传入的 shared 不为空时,则重载子应用的 shared
// 当传入的 shared 为空时,使用自身的 shared
const { shared = SharedModule.getShared() } = props;
SharedModule.overloadShared(shared);
}
4. 在微应用中使用
// app-react/src/pages/communication/index.jsx
import SharedModule from "../../shared";
import React, { useEffect } from "react"
import { Button } from "antd"
import { useHistory } from "react-router-dom"
export default () => {
const history = useHistory()
useEffect(() => {
// 获取 shared 实例对象
const shared = SharedModule.getShared()
// 获取实例下对应的方法
const token = shared.getToken()
if (!token) {
history.push("/")
}
console.log("我是通过shared通信获取的token:", token)
}, [history])
return (
<div>
<Button >我是shared通信</Button>
</div>
)
}
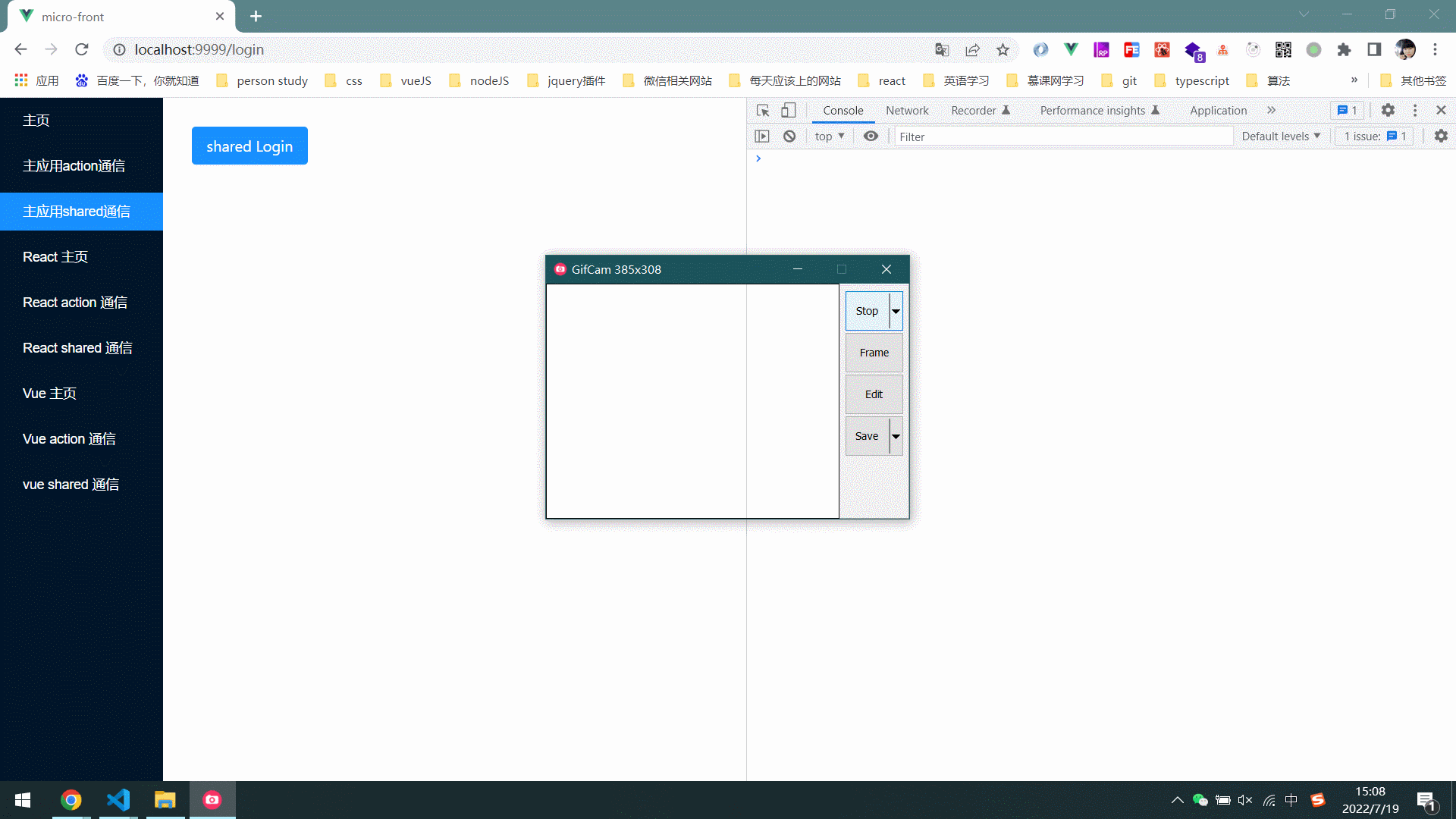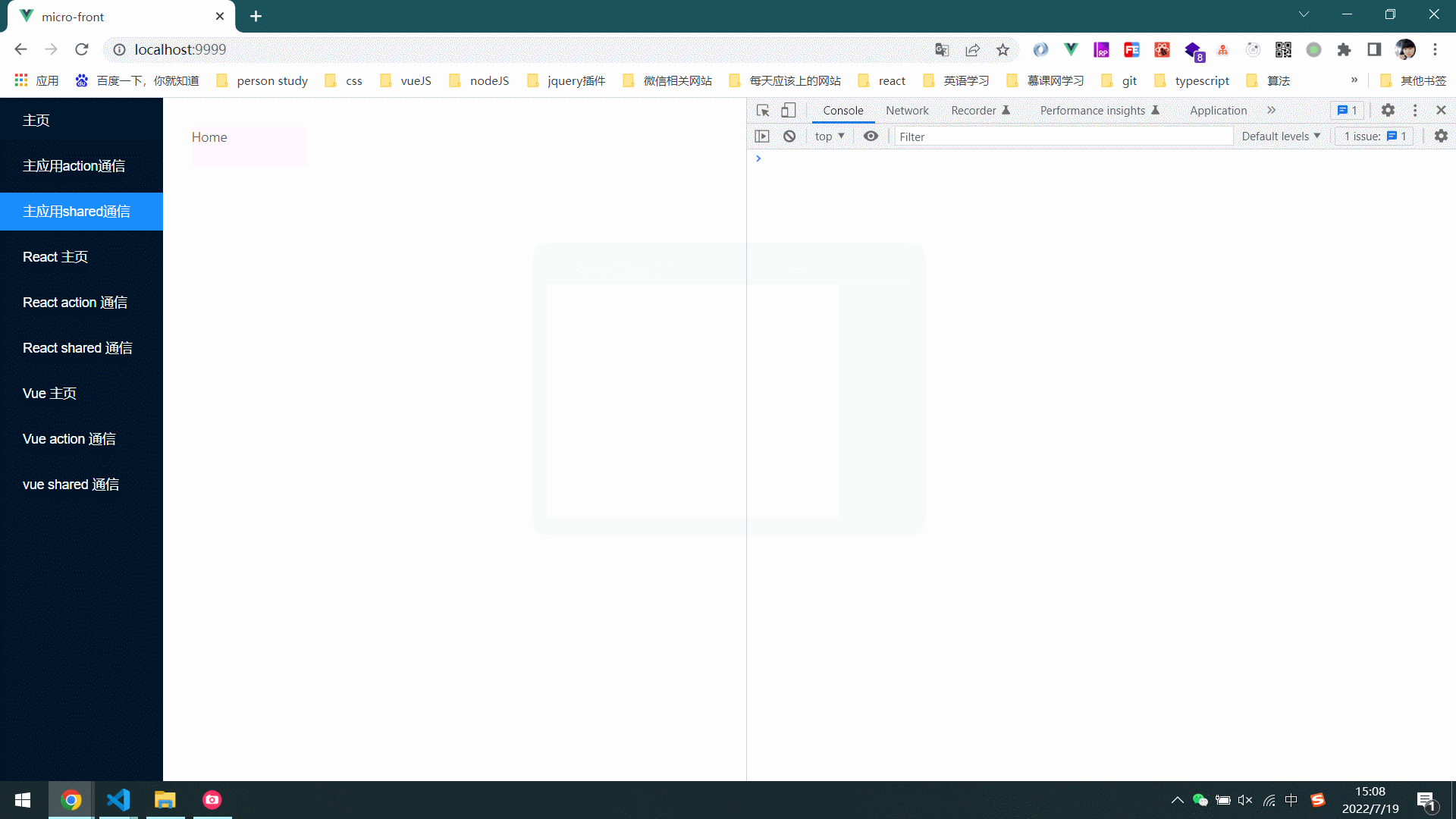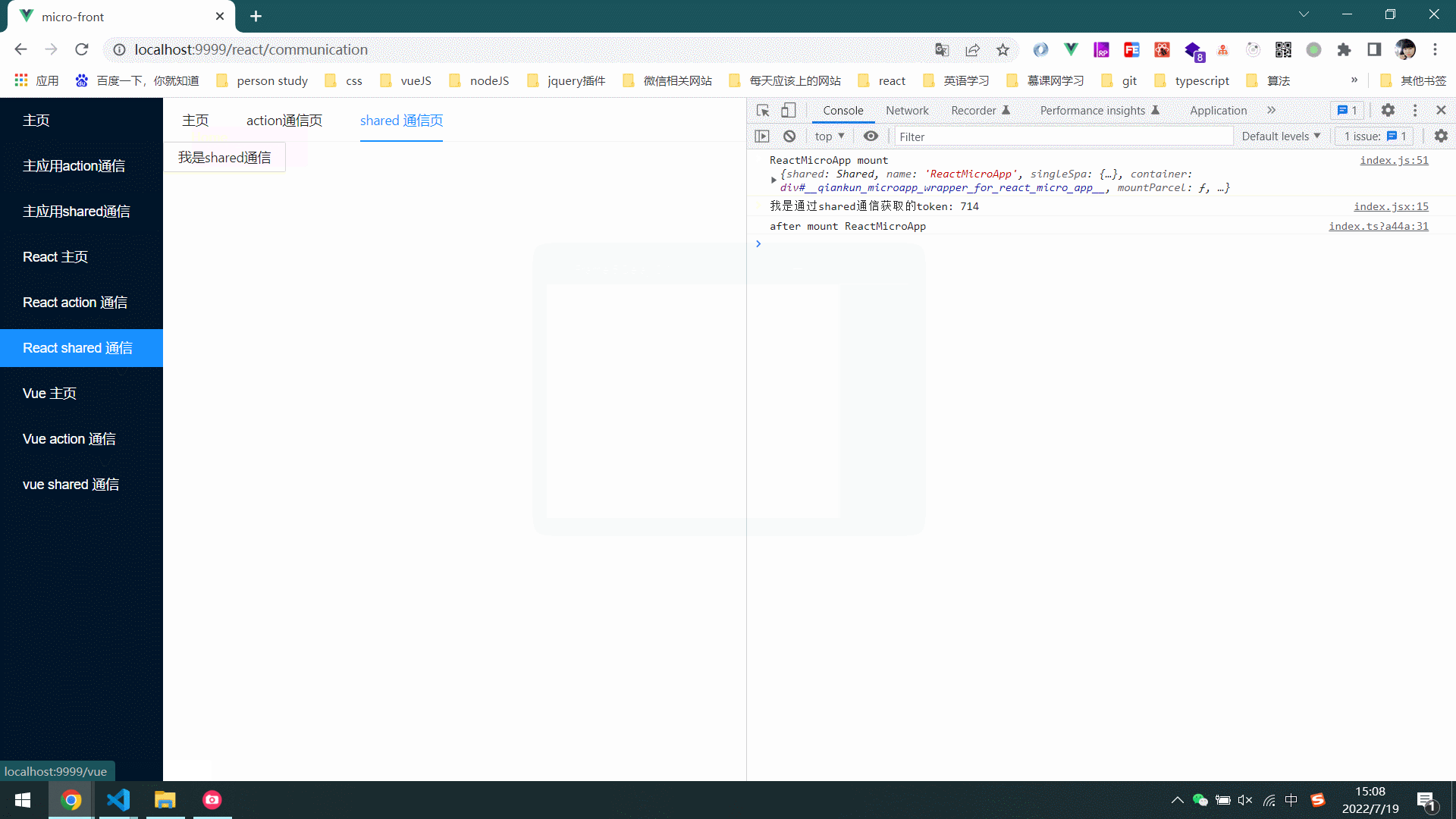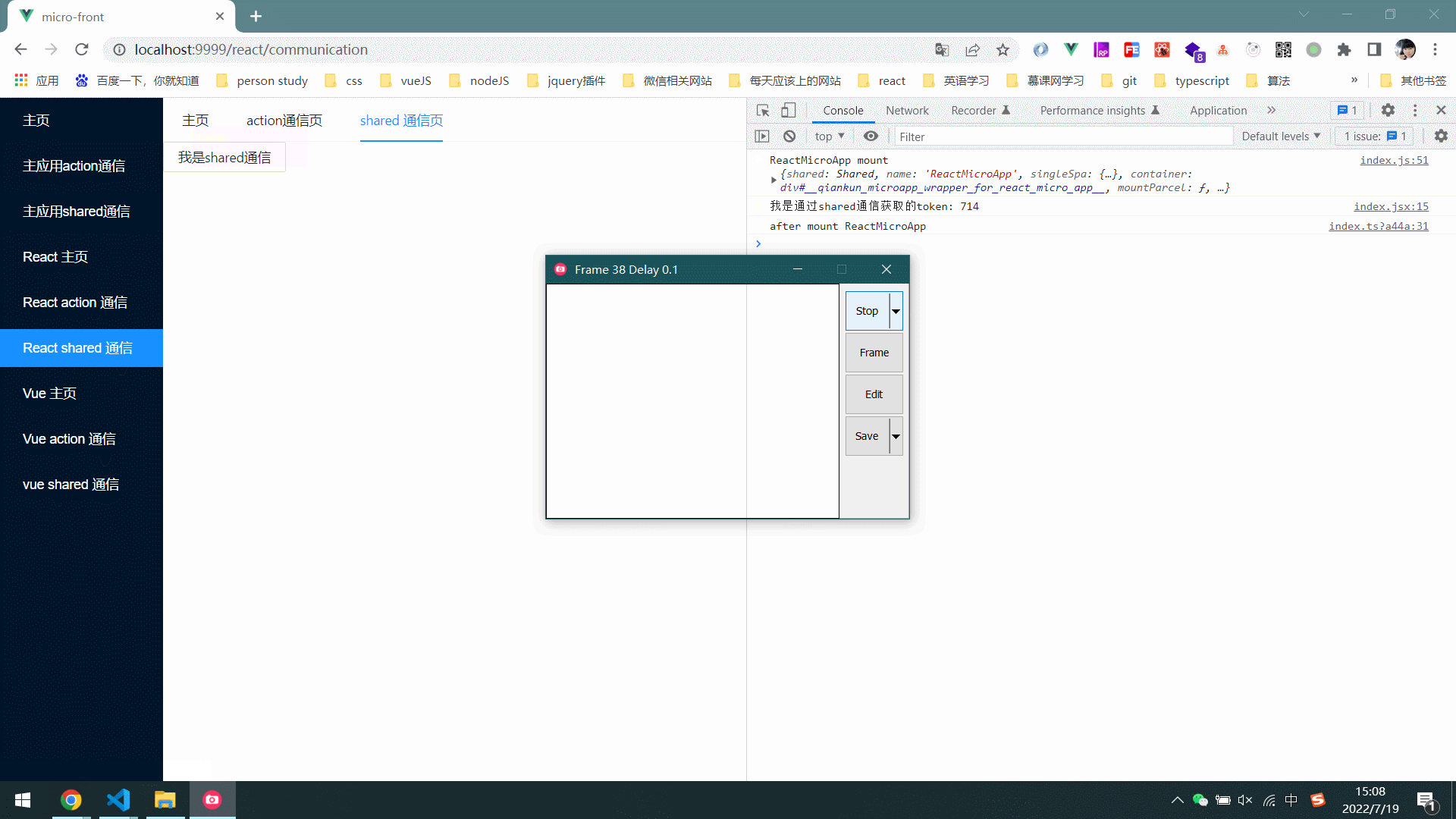
5.效果图