持续创作,加速成长!这是我参与「掘金日新计划 · 6 月更文挑战」的第2天,点击查看活动详情。
本文学习一个同步、阻塞、有界、循环队列------ArrayBlockingQueue。
简介
ArrayBlockingQueue虽不是一个常用的同步队列,但对于后面对于其他同步容器的理解是有益处的。-
-
其内部维护了一个对象数组用于存储数据
-
通过两个int值:takeIndex、putIndex来记录获取和存放元素的下标
-
使用ReenTrantLock来实现同步。默认非公平锁,可自定义公平锁。
-
使用两个Condition:notEmpty、notFull。分别来处理
①当数组长度为空时,进行获取元素操作的线程加入等待队列
②当数组满了,进行添加元素操作加入等待队列
属性
//使用对象数组保存元素
final Object[] items;
//items index for next take, poll, peek or remove
//下一个执行 take, poll, peek or remove操作元素的下标
int takeIndex;
// items index for next put, offer, or add
//下一个执行put, offer, or add 操作的元素下标
int putIndex;
//队列元素个数
int count;
//重入锁,默认非公平
final ReentrantLock lock;
//当数组为空时,执行获取元素操作的线程进入等待队列
private final Condition notEmpty;
//当数组满了时,执行添加元素操作的线程进入等待队列
private final Condition notFull;
构造器
ArrayBlockingQueue的三个构造器都是有初始容量的,并且没有扩容操作,所以说是
有界的。
//自定义队列容量(对象数组长度)
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this(capacity, false);
}
//自定义队列容量(对象数组长度),自定义是否为公平锁
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) {
if (capacity <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.items = new Object[capacity];
lock = new ReentrantLock(fair);
notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
notFull = lock.newCondition();
}
//自定义队列容量(对象数组长度),自定义是否为公平锁,并初始化对象数组
//会报出数组下标溢出异常
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair,
Collection<? extends E> c) {
this(capacity, fair);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int i = 0;
try {
for (E e : c) {
checkNotNull(e);
items[i++] = e;
}
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
count = i;
putIndex = (i == capacity) ? 0 : i;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
基本状态的方法
//获取队列元素个数
public int size();
//获取队列剩余容量
public int remainingCapacity();
//队列是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(Object o);
//清除队列。
public void clear();
================以下方法不提供外部使用===============
//获取对应下标 元素
E itemAt(int i);
//移除对应下标 元素
void removeAt(final int removeIndex);
clear方法会将队列内元素置为null,takeIndex指向putindex(相当于初始化时两个都是0),当队列size没有达到数组长度时,putindex已经移动到items.length-1处,此刻putIndex会置为0,也就是循环队列。
添加元素
- add()方法
会调用offer方法,添加失败会抛出异常。
- offer
添加失败返回false。添加成功返回true,移动putIndex
- put方法
- 获取的是可响应中断锁。
- 如果队列满了,当前线程就会加入等待队列。
- 存在一个超时时间重载
//调用 offer(E e)方法
//这个add方法是AbstractQueue定义的,如果offer失败(返回false),抛出异常
public boolean add(E e)
public boolean offer(E e)
//①put失败会加入等待队列。②可响应中断
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException
//添加超时时间,达到时间返回false
public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
获取元素
-
peek()
获取takeIndex下标对应元素。队列为空返回null。不会修改takeIndex。 AbstractQueue定义的element()方法会调用peek()
-
poll()
获取takeIndex下标对应元素。队列为空返回null。
会修改takeIndex。
并会唤醒notFull等待队列下的一个线程。
存在一个超时重载。重载方法,队列为空会加入notEmpty等待队列。
-
take()
获取takeIndex下标对应元素。
会修改takeIndex。
并会唤醒notFull等待队列下的一个线程。
队列为空会加入notEmpty等待队列。
public E take() throws InterruptedException
public E poll()
public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException
public E peek()
严格意义上来讲上面三个方法只有peek()方法才是存粹获取队列元素,其余两个类似出队操作。
移除元素
会首先找到首个匹配元素的下标,调用removeAt(index)方法。
- 如果被移除元素下标为takeIndex的话,直接将iteams[++takeIndex] = null
- 否则会以覆盖的形式移除元素(类似于ArrayCopy)
public boolean remove(Object o)
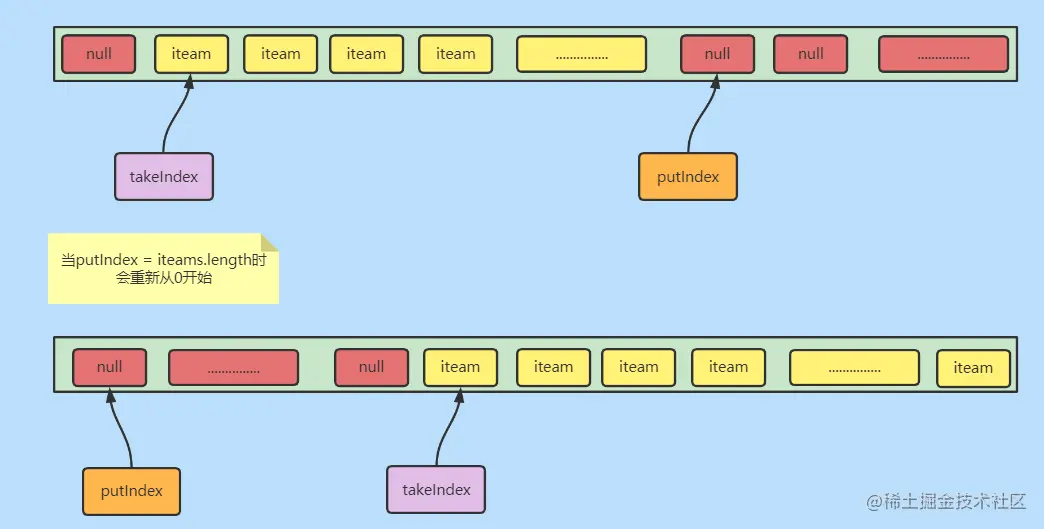
简单结构
其实可以把它想象成一个环。这也是为什么说他是循环队列的原因。
遍历方法
有10个勒,其实分类一下还是好理解的。
collection接口下的集合遍历方法就有:
- 增强for循环
- 转数组普通for循环
- Collection接口的stream的foreach
- Iterable接口的foreach
- 迭代器 hasNext 和 next 队列的出队操作
- take(会等待) & poll(不等待,为空返回nunll) &poll的超时重载(也会等待)
- 分离器
public class ArrayBlockForeach {
@Test
public void testForeach() throws InterruptedException {
/**
* queue 是 collection的子接口
*/
final StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
ArrayBlockingQueue<Object> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Object>(20);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
queue.add(i);
}
System.out.println("=======增强for循环========");
for (Object obj : queue) {
sb.append(obj + ", ");
}
mySout(sb);
System.out.println("=======Collectio stream api========");
queue.stream().forEach((obj) -> {
sb.append(obj + ", ");
});
mySout(sb);
System.out.println("=======Iterable foreach========");
queue.forEach((obj) -> {
sb.append(obj + ", ");
});
mySout(sb);
System.out.println("=======迭代器========");
Iterator<Object> iterator = queue.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
sb.append(iterator.next() + ", ");
}
mySout(sb);
System.out.println("=======toArray 转数组foreach========");
Object[] objects = queue.toArray();
for (int i = 0; i < objects.length; i++) {
sb.append(objects[i] + ", ");
}
mySout(sb);
//System.out.println("=======take========");
//int size = queue.size();
//while (size-- > 0) {
// sb.append(queue.take() + ", ");
//}
//mySout(sb);
//System.out.println("=======poll 不会await========");
//Object poll = null;
//while ((poll = queue.poll()) != null) {
// sb.append(poll+", ");
//}
//mySout(sb);
//System.out.println("=======分离器1========");
//Spliterator<Object> spliterator = queue.spliterator();
//while (spliterator.tryAdvance((obj) ->
// sb.append(obj + ", ")
//)) ;
//mySout(sb);
System.out.println("=======分离器2========");
Spliterator<Object> spliterator2 = queue.spliterator();
spliterator2.forEachRemaining((obj) -> sb.append(obj + ", "));
mySout(sb);
}
public void mySout(StringBuffer sb) {
StringBuffer sbTemp = new StringBuffer("{");
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.lastIndexOf(","));
sb.append("}");
sbTemp.append(sb);
System.out.println(sbTemp.toString());
sb.delete(0, sb.length());
}
}