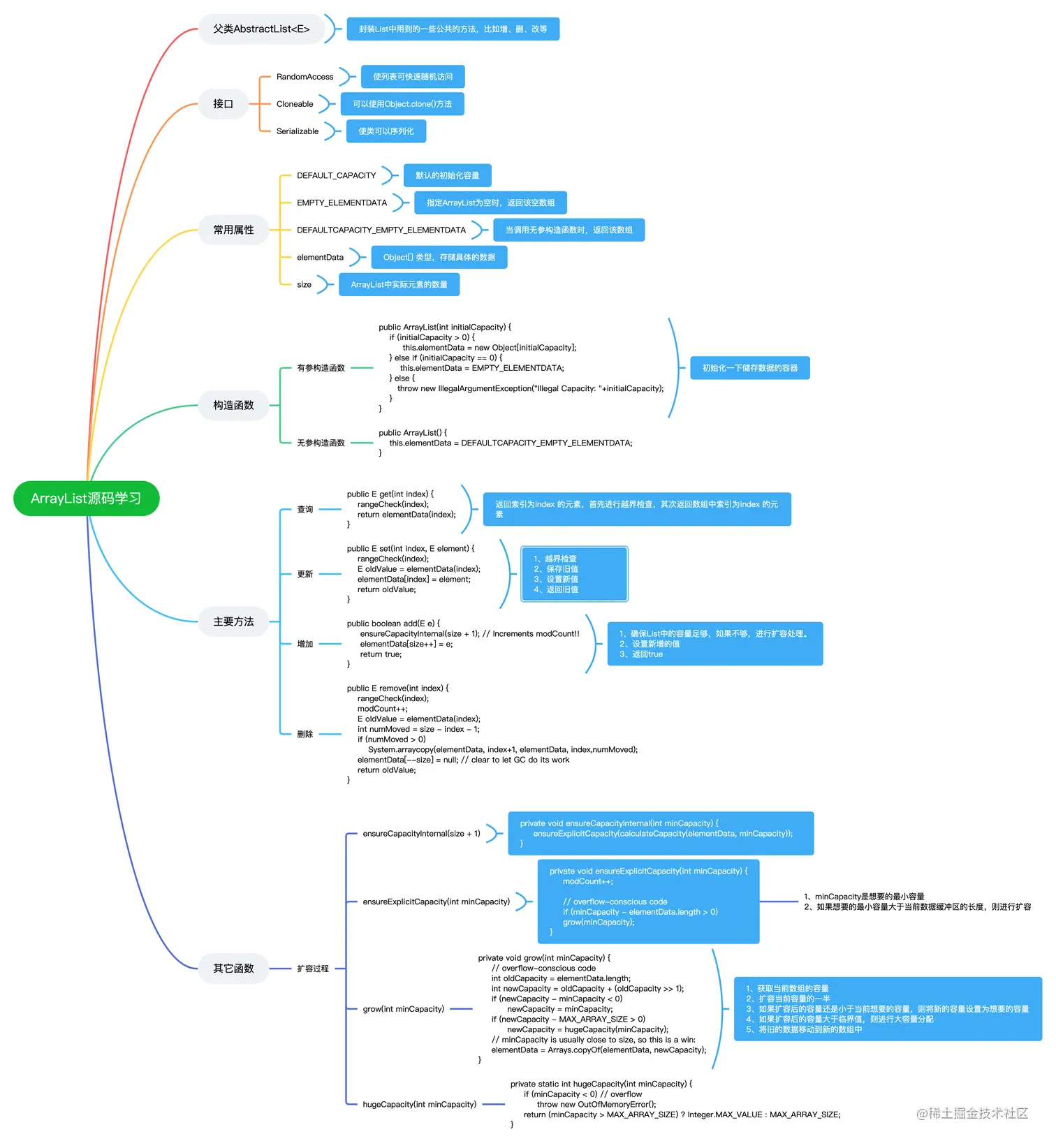
ArrayList注释版
package java.util
import java.util.function.Consumer
import java.util.function.Predicate
import java.util.function.UnaryOperator
import jdk.internal.access.SharedSecrets
/**
* 父类 AbstractList 封装了list中的一些基本的方法
* 接口 List<E> 定义了list中的一些基本方法
* 接口 RandomAccess 随机快速访问
* 接口 Cloneable 可复制
* 接口 Serializable 序列化
*/
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L
/**
* 设置默认的初始化容量
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10
/**
* 当在构造函数中传入的容量为0时 将ArrayList初始化为该对象
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}
/**
* 当使用无参构造函数初始化时,将ArrayList初始化为该对象
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}
/**
* 实际存储ArrayList元素的位置,由此可见ArrayList中采用的是数组结构
*/
transient Object[] elementData
/**
* ArrayList中实际含有的元素的数量
*/
private int size
/**
* 根据指定大小初始化一个ArrayList
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
//如果指定的大小为0,初始化对象为EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: " + initialCapacity)
}
}
/**
* 无参构造函数初始化
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
}
/**
* 基于现有的集合初始化一个新的ArrayList
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray()
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// 如果集合不为空,进行赋初值操作。
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class)
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
}
}
/**
*将ArrayList的大小调整为合适的大小
*/
public void trimToSize() {
modCount++
if (size < elementData.length) {
elementData = (size == 0)
? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
: Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size)
}
}
/**
* Increases the capacity of this {@code ArrayList} instance, if
* necessary, to ensure that it can hold at least the number of elements
* specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity > elementData.length
&& !(elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
&& minCapacity <= DEFAULT_CAPACITY)) {
modCount++
grow(minCapacity)
}
}
/**
* 允许的最大长度
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
* @throws OutOfMemoryError if minCapacity is less than zero
*/
private Object[] grow(int minCapacity) {
return elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity(minCapacity))
}
private Object[] grow() {
return grow(size + 1)
}
/**
* Returns a capacity at least as large as the given minimum capacity.
* Returns the current capacity increased by 50% if that suffices.
* Will not return a capacity greater than MAX_ARRAY_SIZE unless
* the given minimum capacity is greater than MAX_ARRAY_SIZE.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
* @throws OutOfMemoryError if minCapacity is less than zero
*/
private int newCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// 记录现有容量
int oldCapacity = elementData.length
//扩充为现有容量的150%
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1)
//如果扩充后的容量小于目标容量,
if (newCapacity - minCapacity <= 0) {
//如果初始容量为0,一定会走到这里,此时会从默认容量以及目标容量中间选取一个最大值
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity)
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError()
return minCapacity
}
//判断是否需要进行更大容量处理
return (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE <= 0)
? newCapacity
: hugeCapacity(minCapacity)
}
//处理大容量
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError()
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
? Integer.MAX_VALUE
: MAX_ARRAY_SIZE
}
/**
* 返回ArrayList中实际的元素数量
*/
public int size() {
return size
}
/**
* 是否为空
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0
}
/**
* 是否含有某个元素
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0
}
public int indexOf(Object o) {
return indexOfRange(o, 0, size)
}
//遍历操作,在在索引的允许范围内挨个比较,然后返回匹配的索引值
int indexOfRange(Object o, int start, int end) {
Object[] es = elementData
if (o == null) {
for (int i = start
if (es[i] == null) {
return i
}
}
} else {
for (int i = start
if (o.equals(es[i])) {
return i
}
}
}
return -1
}
/**
* 逆序匹配
*/
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
return lastIndexOfRange(o, 0, size)
}
//逆序匹配
int lastIndexOfRange(Object o, int start, int end) {
Object[] es = elementData
if (o == null) {
for (int i = end - 1
if (es[i] == null) {
return i
}
}
} else {
for (int i = end - 1
if (o.equals(es[i])) {
return i
}
}
}
return -1
}
/**
* 复制操作
*/
public Object clone() {
try {
ArrayList<?> v = (ArrayList<?>) super.clone()
v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size)
v.modCount = 0
return v
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError(e)
}
}
/**
* list转换为数组
*/
public Object[] toArray() {
return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size)
}
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list in proper
* sequence (from first to last element)
* array is that of the specified array. If the list fits in the
* specified array, it is returned therein. Otherwise, a new array is
* allocated with the runtime type of the specified array and the size of
* this list.
*
* <p>If the list fits in the specified array with room to spare
* (i.e., the array has more elements than the list), the element in
* the array immediately following the end of the collection is set to
* {@code null}. (This is useful in determining the length of the
* list <i>only</i> if the caller knows that the list does not contain
* any null elements.)
*
* @param a the array into which the elements of the list are to
* be stored, if it is big enough
* same runtime type is allocated for this purpose.
* @return an array containing the elements of the list
* @throws ArrayStoreException if the runtime type of the specified array
* is not a supertype of the runtime type of every element in
* this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified array is null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
if (a.length < size)
// Make a new array of a's runtime type, but my contents:
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, a.getClass())
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, size)
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null
return a
}
// 查询操作辅助方法
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index]
}
// 查询操作辅助方法
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static <E> E elementAt(Object[] es, int index) {
return (E) es[index]
}
/**
* 查询操作,返回给定索引值出的元素
*/
public E get(int index) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size)
return elementData(index)
}
/**
* 更新操作,更新给定索引处的元素值
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size)
E oldValue = elementData(index)
elementData[index] = element
return oldValue
}
/**
* 新增操作,在给定的索引处新增元素值
*/
private void add(E e, Object[] elementData, int s) {
if (s == elementData.length)
elementData = grow()
elementData[s] = e
size = s + 1
}
/**
* 新增操作,在列表最后新增元素值
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
modCount++
add(e, elementData, size)
return true
}
/**
* 新增操作,在给定的索引处添加元素
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index)
modCount++
final int s
Object[] elementData
if ((s = size) == (elementData = this.elementData).length)
elementData = grow()
System.arraycopy(elementData, index,
elementData, index + 1,
s - index)
elementData[index] = element
size = s + 1
}
/**
* 删除操作,删除指定索引处的元素,入参为索引值
*/
public E remove(int index) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size)
final Object[] es = elementData
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E oldValue = (E) es[index]
fastRemove(es, index)
return oldValue
}
/**
* 删除操作,删除指定的元素,入参为想要删除的元素
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
final Object[] es = elementData
final int size = this.size
int i = 0
found: {
if (o == null) {
for (
if (es[i] == null)
break found
} else {
for (
if (o.equals(es[i]))
break found
}
return false
}
fastRemove(es, i)
return true
}
/**
* Private remove method that skips bounds checking and does not
* return the value removed.
*/
private void fastRemove(Object[] es, int i) {
modCount++
final int newSize
if ((newSize = size - 1) > i)
System.arraycopy(es, i + 1, es, i, newSize - i)
es[size = newSize] = null
}
/**
* 删除操作,清除所有元素
*/
public void clear() {
modCount++
final Object[] es = elementData
for (int to = size, i = size = 0
es[i] = null
}
/**
* 新增操作,将一个集合添加到该ArrayList中,入参为集合
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray()
modCount++
int numNew = a.length
if (numNew == 0)
return false
Object[] elementData
final int s
if (numNew > (elementData = this.elementData).length - (s = size))
elementData = grow(s + numNew)
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, s, numNew)
size = s + numNew
return true
}
/**
* 新增操作,将一个集合添加到ArrayList中指定的位置处,入参为索引以及被插入的集合
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index)
Object[] a = c.toArray()
modCount++
int numNew = a.length
if (numNew == 0)
return false
Object[] elementData
final int s
if (numNew > (elementData = this.elementData).length - (s = size))
elementData = grow(s + numNew)
int numMoved = s - index
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index,
elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved)
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew)
size = s + numNew
return true
}
/** 删除指定索引范围内的元素 */
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
if (fromIndex > toIndex) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
outOfBoundsMsg(fromIndex, toIndex))
}
modCount++
shiftTailOverGap(elementData, fromIndex, toIndex)
}
/** 数组元素移动覆盖,多余重复元素置位null */
private void shiftTailOverGap(Object[] es, int lo, int hi) {
System.arraycopy(es, hi, es, lo, size - hi)
for (int to = size, i = (size -= hi - lo)
es[i] = null
}
/**
* 辅助方法, 索引范围检查
*/
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index))
}
/**
* 辅助方法,错误提示信息
*/
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size
}
/**
* 辅助方法,错误提示信息
*/
private static String outOfBoundsMsg(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return "From Index: " + fromIndex + " > To Index: " + toIndex
}
/**
*移除指定集合中的所有元素
*/
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
return batchRemove(c, false, 0, size)
}
/**
* 移除不在指定集合中的所有元素
*/
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
return batchRemove(c, true, 0, size)
}
boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement, final int from, final int end) {
Objects.requireNonNull(c)
final Object[] es = elementData
int r
// Optimize for initial run of survivors
for (r = from
if (r == end)
return false
if (c.contains(es[r]) != complement)
break
}
int w = r++
try {
for (Object e
if (c.contains(e = es[r]) == complement)
es[w++] = e
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection,
// even if c.contains() throws.
System.arraycopy(es, r, es, w, end - r)
w += end - r
throw ex
} finally {
modCount += end - w
shiftTailOverGap(es, w, end)
}
return true
}
/**
* 序列化操作
*/
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// Write out element count, and any hidden stuff
int expectedModCount = modCount
s.defaultWriteObject()
// Write out size as capacity for behavioral compatibility with clone()
s.writeInt(size)
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (int i=0
s.writeObject(elementData[i])
}
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException()
}
}
/**
* 反序列化操作
*/
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in size, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject()
// Read in capacity
s.readInt()
if (size > 0) {
// like clone(), allocate array based upon size not capacity
SharedSecrets.getJavaObjectInputStreamAccess().checkArray(s, Object[].class, size)
Object[] elements = new Object[size]
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
for (int i = 0
elements[i] = s.readObject()
}
elementData = elements
} else if (size == 0) {
elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
} else {
throw new java.io.InvalidObjectException("Invalid size: " + size)
}
}
/**
* 创建一个迭代器对象
*/
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index)
return new ListItr(index)
}
/**
* 创建迭代器对象
*/
public ListIterator<E> listIterator() {
return new ListItr(0)
}
/**
* 创建迭代器对象
*/
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr()
}
/**
* 实现一个迭代器模式
*/
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor
int lastRet = -1
int expectedModCount = modCount
// prevent creating a synthetic constructor
Itr() {}
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification()
int i = cursor
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException()
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException()
cursor = i + 1
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException()
checkForComodification()
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet)
cursor = lastRet
lastRet = -1
expectedModCount = modCount
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException()
}
}
@Override
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action)
final int size = ArrayList.this.size
int i = cursor
if (i < size) {
final Object[] es = elementData
if (i >= es.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException()
for (
action.accept(elementAt(es, i))
// update once at end to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i
lastRet = i - 1
checkForComodification()
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException()
}
}
/**
* 又一个迭代器模式
*/
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> {
ListItr(int index) {
super()
cursor = index
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification()
int i = cursor - 1
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException()
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException()
cursor = i
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException()
checkForComodification()
try {
ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e)
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException()
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification()
try {
int i = cursor
ArrayList.this.add(i, e)
cursor = i + 1
lastRet = -1
expectedModCount = modCount
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException()
}
}
}
/**
* Returns a view of the portion of this list between the specified
* {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, and {@code toIndex}, exclusive. (If
* {@code fromIndex} and {@code toIndex} are equal, the returned list is
* empty.) The returned list is backed by this list, so non-structural
* changes in the returned list are reflected in this list, and vice-versa.
* The returned list supports all of the optional list operations.
*
* <p>This method eliminates the need for explicit range operations (of
* the sort that commonly exist for arrays). Any operation that expects
* a list can be used as a range operation by passing a subList view
* instead of a whole list. For example, the following idiom
* removes a range of elements from a list:
* <pre>
* list.subList(from, to).clear()
* </pre>
* Similar idioms may be constructed for {@link
* {@link
* {@link Collections} class can be applied to a subList.
*
* <p>The semantics of the list returned by this method become undefined if
* the backing list (i.e., this list) is <i>structurally modified</i> in
* any way other than via the returned list. (Structural modifications are
* those that change the size of this list, or otherwise perturb it in such
* a fashion that iterations in progress may yield incorrect results.)
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size)
return new SubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex)
}
// A tiny bit set implementation
private static long[] nBits(int n) {
return new long[((n - 1) >> 6) + 1]
}
private static void setBit(long[] bits, int i) {
bits[i >> 6] |= 1L << i
}
private static boolean isClear(long[] bits, int i) {
return (bits[i >> 6] & (1L << i)) == 0
}
/**
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
return removeIf(filter, 0, size)
}
/**
* Removes all elements satisfying the given predicate, from index
* i (inclusive) to index end (exclusive).
*/
boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter, int i, final int end) {
Objects.requireNonNull(filter)
int expectedModCount = modCount
final Object[] es = elementData
// Optimize for initial run of survivors
for (
// Tolerate predicates that reentrantly access the collection for
// read (but writers still get CME), so traverse once to find
// elements to delete, a second pass to physically expunge.
if (i < end) {
final int beg = i
final long[] deathRow = nBits(end - beg)
deathRow[0] = 1L
for (i = beg + 1
if (filter.test(elementAt(es, i)))
setBit(deathRow, i - beg)
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException()
modCount++
int w = beg
for (i = beg
if (isClear(deathRow, i - beg))
es[w++] = es[i]
shiftTailOverGap(es, w, end)
return true
} else {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException()
return false
}
}
@Override
public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {
replaceAllRange(operator, 0, size)
modCount++
}
private void replaceAllRange(UnaryOperator<E> operator, int i, int end) {
Objects.requireNonNull(operator)
final int expectedModCount = modCount
final Object[] es = elementData
for (
es[i] = operator.apply(elementAt(es, i))
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException()
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
final int expectedModCount = modCount
Arrays.sort((E[]) elementData, 0, size, c)
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException()
modCount++
}
void checkInvariants() {
// assert size >= 0
// assert size == elementData.length || elementData[size] == null
}
}