使用场景
- 在一个任务需要多个线程来执行,并且是需要线程在同一时间一起开始执行,这样的话,可以使用CountDownLatch
本质
- 虽然CountDownLatch这个类并没有直接继承AbstractQueuedSynchronizer,但是他使用的一个final修饰的变量sync继承AbstractQueuedSynchronizer,所以其本质上还是使用了AQS的共享模式
- 这个类的作用实际上就是在线程开始之后设置了一个栅栏,这个栅栏将所有线程阻塞住了,只有所有线程都激活的情况下,栅栏才会消失
图解
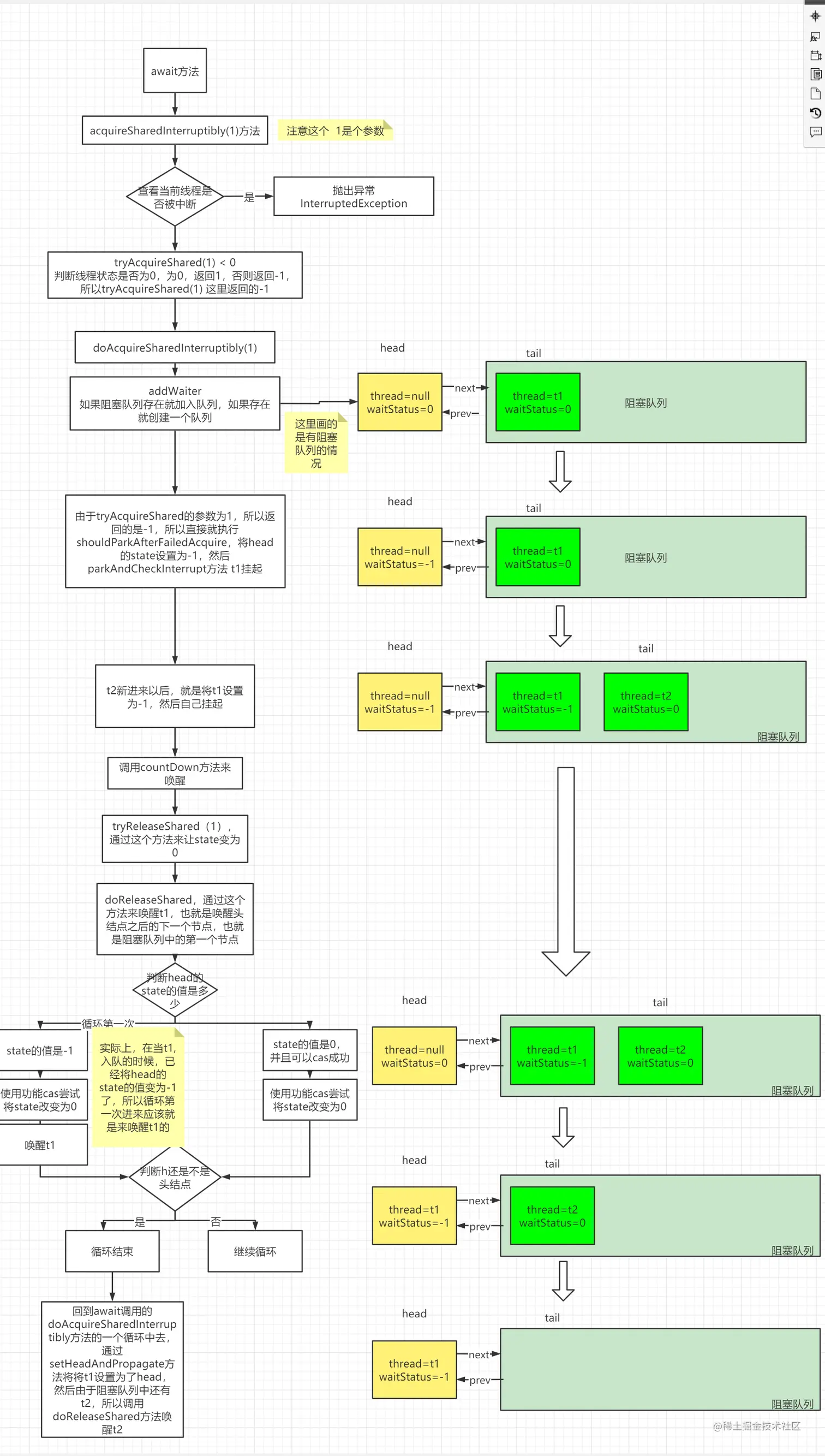
源码分析
Sync
private static final class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4982264981922014374L;
Sync(int count) {
setState(count);
}
int getCount() {
return getState();
}
tryAcquireShared
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
return (getState() == 0) ? 1 : -1;
}
tryReleaseShared
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
if (c == 0)
return false;
int nextc = c-1;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
return nextc == 0;
}
}
await
public void await() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}
acquireSharedInterruptibly
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly
private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null;
failed = false;
return;
}
}
-1
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
predecessor
final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {
Node p = prev;
if (p == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
else
return p;
}
countDown
public void countDown() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
releaseShared
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
doReleaseShared
private void doReleaseShared() {
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue;
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue;
}
if (h == head)
break;
}
}
unparkSuccessor
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
df
private void setHeadAndPropagate(Node node, int propagate) {
Node h = head;
setHead(node);
if (propagate > 0 || h == null || h.waitStatus < 0 ||
(h = head) == null || h.waitStatus < 0) {
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.isShared())
doReleaseShared();
}
}
参考链接:
- 一行一行源码分析清楚 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer (三)