Promise 是异步编程的一种解决方案。
Promise
/**
* 属性
*/
Promise.length
Promise.prototype
/**
* 方法
*/
Promise.all(iterable) // 所有成功触发成功 任何失败触发失败
Promise.race(iterable) // 任意一个成功或失败后触发
Promise.reject(reason)
Promise.resolve(value)
/**
* 原型
*/
Promise.prototype.constructor
//方法
Promise.prototype.catch(onRejected)
Promise.prototype.then(onFulfilled, onRejected)
Promise.prototype.finally(onFinally)
Promise 有三种状态
- pending: 初始状态,既不是成功,也不是失败状态。
- resolve: 意味着操作成功完成。(resoloved)
- reject: 意味着操作失败。
pending
pending 是初始状态,执行 resolve/reject 会进入对应状态,如果不执行,责一直为 pending 状态
例如下面代码,promise 将一直在 pending 状态,不会执行 then/catch.
new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { })
.then(res => console.log(res))
.catch(err => console.log(err))
resolve
resolve 意味着操作成功完成, 如果有 .then,值会传入 .then 的第一个参数函数里。
如
new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
resolve(1)
})
.then(res => console.log(res))
then 的第一个参数是成功的回调,第一个参数的返回值会影响接下来链的去向。第一个参数的返回值一般有三种情况
- 无返回值:会去执行下一个 .then ,没有参数
- 返回值非promise:调用下一个then的函数,参数为返回值
- 返回值为promise:根据promise的执行结果,执行 下一个then/catch,如果一直是pending,则不执行下一个then/catch
例如想要在当前 then 终止,可以这样操作:
.then((res) => new Promise(() => {}))
reject
reject 意味着操作失败。
使用 .catch 会捕获到错误信息。
与代码报错(如 undefined.a)不同的是, 代码报错如果不使用 catch 捕获,会向外传递,最终传递到根结点;而 reject 属于 promise 错误,即使不使用 catch 捕获也不会对全局有影响。
用 promise 实现 fetch
先来看几个问题:
- 如果请求 code 404, 会走 then 还是 catch? (答案:then)
- 控制台能看到一行 404 的错误, 为什么还是走 then 不是 catch 呢
- 如果请求跨域失败,走 then 还是 catch?(答案:catch)
- 同样是控制台看到错误,两者有什么区别呢?
- 跨域失败的报错, 和 then 中 undefined.a 报错,如果都不 catch,后者在 react 脚手架开发环境页面会蹦,两者有什么区别?
带着这几个问题,来看看 fetch。
fetch 返回值是 promise,所以有三种状态 pending、resolve、reject.
- pending: 请求中
- resolve: 请求成功(code 200/404/500 等, 非 200 控制台输出错误)
- reject: 请求失败(跨域失败、连接超时、无网络等,控制台输出错误)
我们还发现,请求失败时,只能 catch 到最后一行错误, 如图
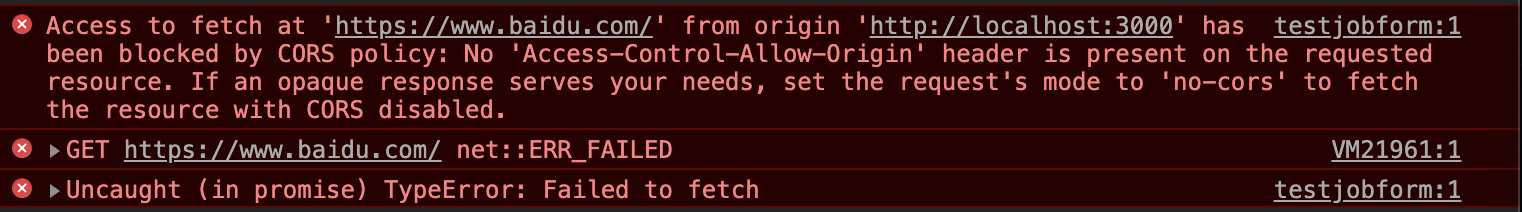
捕获后
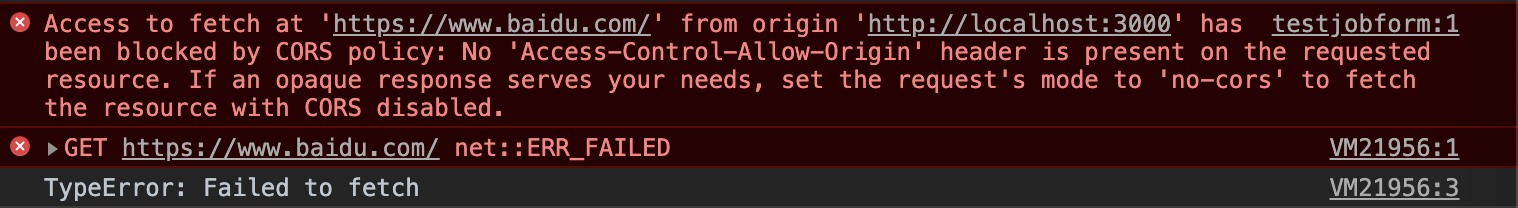
为什么 404 在控制台看到错误,还走 then, resolve 如何实现
实现有几个难点,
- throw 后面代码不会执行;
- 先报错,后执行 then;
- catch 后错误不会打印在控制台;
试了下,Promise.reject('xxx') 这样的报错方式虽然是微观任务,但是总是在.then之后才在控制台输出,更像是宏观任务。所以也加个setTImeout宏观任务调至后面。
var fetch = function () {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function () {
if ('请求成功 200') {
resolve('Response数据结构');
} else if ('请求成功 404,500等') {
Promise.reject('GET xxxxxxxx 404');
setTimeout(function () {
resolve('Response数据结构');
});
}
})
})
}
请求失败 例如跨域失败 reject 如何实现呢
同样加个 setTimeout
var fetch = function () {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function () {
if ('请求成功 200') {
resolve('Response数据结构');
} else if ('请求成功 404,500等') {
Promise.reject('GET xxxxxxxx 404');
setTimeout(function () {
resolve('Response数据结构');
});
} else if ('请求失败') {
Promise.reject('Access to fetch xxxxx with CORS disabled.');
Promise.reject('GET xxxxx net::ERR_FAILED');
setTimeout(function () {
reject('TypeError: Failed to fetch');
});
}
})
})
}
还是有些问题,我们实现的因为在promise 中,错误会有前缀 Uncaught (in promise)。浏览器客户端应该有更好的实现方式。
最后总结一下 fetch 的三种情况
- pending: 请求中
- resolve: 请求成功(code 200: 调用 resolve 返回数据; code: 404/500 等, 先抛错,再调用 resolve 返回数据。)
- reject: 请求失败(跨域失败、连接超时、无网络等,先控制台抛错,再调用 reject)
抛错均不影响代码执行,与 undefined.a 不同。