系列文章
- [Koa源码学习] Koa
- [Koa源码学习] koa-router
- [Koa源码学习] koa-bodyparser
- [Koa源码学习] koa cookie
- [Koa源码学习] koa-session
前言
HTTP是一种无状态的协议,浏览器通过引入Cookie技术,从而实现了保持状态的功能。当服务器收到HTTP请求时,服务器可以使用Set-Cookie响应头,向浏览器中设置cookie,在这之后,当浏览器再次对该服务器发起请求时,就会将cookie放到Cookie请求头中,然后连同其他信息一起发送给服务器。
Koa内部使用cookies模块,提供对cookie的支持,那么接下来,我们就来看看其内部是如何实现的。
keys & ctx.cookies
在创建Koa实例时,可以通过keys选项,设置对Cookie签名的密钥,它是一个数组的形式,默认总是使用第一个密钥对cookie进行签名,但是也可以在运行过程中调整密钥的顺序,其代码如下所示:
/* koa/lib/application.js */
module.exports = class Application extends Emitter {
constructor(options) {
// ...
// 对Cookie签名的密钥列表
if (options.keys) this.keys = options.keys;
// ...
}
};
收到请求时,在中间件中可以使用ctx.cookies设置和获取cookie,代码如下所示:
/* koa/lib/context.js */
const Cookies = require('cookies');
const COOKIES = Symbol('context#cookies');
const proto = module.exports = {
get cookies() {
if (!this[COOKIES]) {
// 创建Cookies实例
this[COOKIES] = new Cookies(this.req, this.res, {
keys: this.app.keys,
// https
secure: this.request.secure
});
}
return this[COOKIES];
},
set cookies(_cookies) {
this[COOKIES] = _cookies;
}
};
可以看到,在同一个请求上下文中,首次访问ctx.cookies时,会创建一个Cookies的实例,这里会将当前请求的req、res,连同之前配置的密钥keys传入,之后就可以通过这个实例对cookie进行设置和获取了。
Cookies
我们首先来看看Cookies的构造函数,其代码如下所示:
/* cookies/index.js */
function Cookies(request, response, options) {
if (!(this instanceof Cookies)) return new Cookies(request, response, options)
this.secure = undefined
this.request = request
this.response = response
if (options) {
// ...
// 使用Keygrip模块,进行签名和认证
this.keys = Array.isArray(options.keys) ? new Keygrip(options.keys) : options.keys
this.secure = options.secure
}
}
Cookies.prototype.get = function(name, opts) {
// ...
};
Cookies.prototype.set = function(name, value, opts) {
// ...
};
可以看到,在实例化Cookies时,除了在当前实例上保存request和response外,还创建了Keygrip的实例,它是用来对cookie进行签名和认证的,我们首先来看看它是如何使用的。
Keygrip
Keygrip的构造函数如下所示:
/* keygrip/index.js */
function Keygrip(keys, algorithm, encoding) {
// 默认哈希算法sha1,默认编码方式base64
if (!algorithm) algorithm = "sha1";
if (!encoding) encoding = "base64";
if (!(this instanceof Keygrip)) return new Keygrip(keys, algorithm, encoding)
// ...
// 根据密钥对数据进行签名
function sign(data, key) {
return crypto
.createHmac(algorithm, key)
.update(data).digest(encoding)
.replace(/\/|\+|=/g, function(x) {
return ({ "/": "_", "+": "-", "=": "" })[x]
})
}
this.sign = function(data){ return sign(data, keys[0]) }
this.verify = function(data, digest) {
return this.index(data, digest) > -1
}
this.index = function(data, digest) {
for (var i = 0, l = keys.length; i < l; i++) {
if (compare(digest, sign(data, keys[i]))) {
return i
}
}
return -1
}
}
可以看到,在Keygrip构造函数中,这里的关键方法是sign,它使用原生的crypto模块,使用sha1哈希算法和密钥key,对数据data进行hmac,生成消息摘要,然后将其编码成base64url的格式并返回,除此之外,Keygrip的实例还提供三个实例方法:
-
sign:对上面sign方法的包装,使用keys中第一个密钥对数据进行签名。 -
verify:首先对数据进行签名,然后对比传入的签名digest,如果两者相等,说明校验通过。 -
index:因为keys是一个密钥列表,在程序运行过程中,密钥的顺序可能会调整,index方法可以找到digest对应的密钥索引。
Keygrip模块就是给cookie提供了一套签名和验证的机制,那么接下来,我们就来看看如何设置和获取cookie的。
set
我们首先来看看是如何通过ctx.cookies设置cookie的,其代码如下所示:
/* cookies/index.js */
Cookies.prototype.set = function(name, value, opts) {
var res = this.response
, req = this.request
// 获取缓冲中的Set-Cookie响应头
, headers = res.getHeader("Set-Cookie") || []
, secure = this.secure !== undefined ? !!this.secure : req.protocol === 'https' || req.connection.encrypted
// 创建Cookie实例
, cookie = new Cookie(name, value, opts)
// cookie是否需要签名
, signed = opts && opts.signed !== undefined ? opts.signed : !!this.keys
if (typeof headers == "string") headers = [headers]
// ...
cookie.secure = opts && opts.secure !== undefined
? opts.secure
: secure
// ...
// 将cookie添加到headers数组中
pushCookie(headers, cookie)
// 如果cookie需要签名,创建一条新的cookie,添加到headers数组中
if (opts && signed) {
if (!this.keys) throw new Error('.keys required for signed cookies');
// name=value的消息摘要,cookie.name携带.sig后缀
cookie.value = this.keys.sign(cookie.toString())
cookie.name += ".sig"
pushCookie(headers, cookie)
}
var setHeader = res.set ? http.OutgoingMessage.prototype.setHeader : res.setHeader
// 设置Set-Cookie响应头
setHeader.call(res, 'Set-Cookie', headers)
return this
};
可以看到,在cookies.set方法中,首先会创建一条新的Cookie实例,其代码如下所示:
/* cookies/index.js */
function Cookie(name, value, attrs) {
// ...
this.name = name
this.value = value || ""
for (var name in attrs) {
this[name] = attrs[name]
}
// 设置expires,让浏览器删除对应的cookie
if (!this.value) {
this.expires = new Date(0)
this.maxAge = null
}
// ...
}
// 原型上的默认属性,会被传入的attrs覆盖
Cookie.prototype.path = "/";
Cookie.prototype.expires = undefined;
Cookie.prototype.domain = undefined;
Cookie.prototype.httpOnly = true;
Cookie.prototype.sameSite = false;
Cookie.prototype.secure = false;
Cookie.prototype.overwrite = false;
可以看到,对于每一个Cookie实例,里面包含着所有与cookie相关的配置,通过这些配置信息,可以控制cookie在浏览器中的行为。
回到上面的cookies.set方法中,接着就会调用pushCookie,将cookie添加到headers数组中,其代码如下所示:
/* cookies/index.js */
function pushCookie(headers, cookie) {
// overwrite选项用来覆盖同名cookie
if (cookie.overwrite) {
for (var i = headers.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (headers[i].indexOf(cookie.name + '=') === 0) {
headers.splice(i, 1)
}
}
}
headers.push(cookie.toHeader())
}
Cookie.prototype.toString = function() {
return this.name + "=" + this.value
};
Cookie.prototype.toHeader = function() {
// 生成name=value
var header = this.toString()
// 根据配置选项,生成cookie相关的配置,控制cookie的行为
if (this.maxAge) this.expires = new Date(Date.now() + this.maxAge);
if (this.path ) header += "; path=" + this.path
if (this.expires ) header += "; expires=" + this.expires.toUTCString()
if (this.domain ) header += "; domain=" + this.domain
if (this.sameSite ) header += "; samesite=" + (this.sameSite === true ? 'strict' : this.sameSite.toLowerCase())
if (this.secure ) header += "; secure"
if (this.httpOnly ) header += "; httponly"
return header
};
可以看到,pushCookie方法就是根据cookie的配置,生成对应的字符串,然后将其添加到headers数组中。
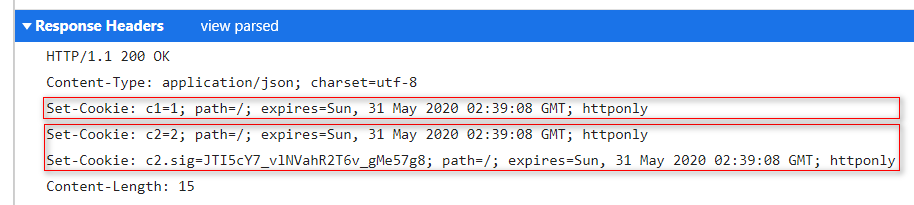
回到上面的cookies.set方法中,如果检测到本条cookie需要签名,就使用keys.sign方法,对name=value进行消息摘要,然后继续使用pushCookie方法,创建一条新的cookie,其cookie名称为原始名称后面加上.sig,然后同样将签名后的cookie添加到headers中,所以对于需要签名的cookie来说,服务器会为其创建两条cookie,一条对应原始的,一条对应签名的。
在cookies.set的最后,通过setHeader方法,将所有的cookie设置到Set-Cookie响应头中,此时,设置cookie的工作就完成了。
get
在收到请求时,可以通过cookies.get方法,从请求头中获取cookie,其代码如下所示:
/* cookies/index.js */
Cookies.prototype.get = function(name, opts) {
var sigName = name + ".sig"
, header, match, value, remote, data, index
, signed = opts && opts.signed !== undefined ? opts.signed : !!this.keys
// cookie请求头
header = this.request.headers["cookie"]
if (!header) return
// 根据name取出对应的cookie
match = header.match(getPattern(name))
if (!match) return
// 如果不需要校验,则直接返回cookie的值
value = match[1]
if (!opts || !signed) return value
// 如果需要校验,就再次调用get方法,通过[name].sig,获取消息摘要
remote = this.get(sigName)
if (!remote) return
// 使用keys.index方法,对cookie进行校验,返回在密钥列表中的索引
data = name + "=" + value
if (!this.keys) throw new Error('.keys required for signed cookies');
index = this.keys.index(data, remote)
if (index < 0) {
// cookie可能被篡改,删除[name].sig
this.set(sigName, null, {path: "/", signed: false })
} else {
// index>0,则说明密钥的顺序做过修改,重新使用第一个密钥进行签名,最后返回cookie的值
index && this.set(sigName, this.keys.sign(data), { signed: false })
return value
}
};
可以看到,在cookies.get方法中,首先从请求头中获取cookie,然后根据name找到对应的值value,如果不需要校验,则直接返回value即可;如果需要校验,就需要再次调用get方法,通过[name].sig,从cookie中获取上一次的消息摘要,然后使用keys.index方法,对cookie进行校验,如果校验通过,则说明此cookie没有被篡改,那么就返回value,如果校验失败,说明此cookie无效,无需返回。
总结
Koa通过cookies模块,提供对cookie的支持,在中间件中可以通过ctx.cookies接口,设置和获取cookie,同时在其内部使用Keygrip模块,提供对cookie进行签名和验证的机制。