Happens-Before 规则
1. 程序的顺序性规则
该规则指的是在一个线程中,如果前面的操作执行Happens-Before 后面的任意操作。如下面代码,在一个线程中,int i=2操作一定发生在int j=2操作前。
int i=1;
int j=2;
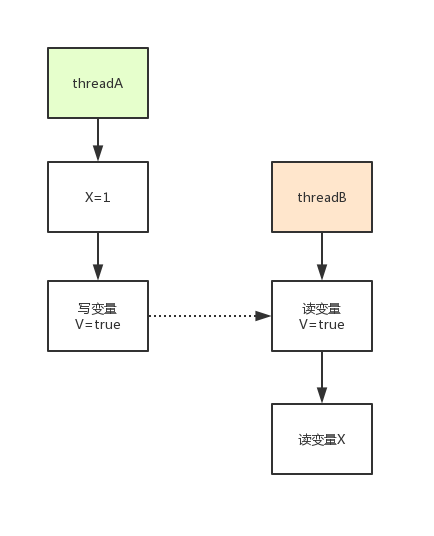
2. volatile 变量规则
这条规则是指对一个 volatile 变量的写操作, Happens-Before 于后续对这个 volatile 变量的读操作。
3、传递性规则
如果操作A Happens-Before 操作B,操作B Happens-Before 操作C,那么操作A一定Happens-Before操作C。 Demo
class VolatileExample {
int x = 0;
volatile boolean v = false;
public void writer() {
x = 1;
v = true;
}
public void reader() {
if (v == true) {
System.out.println("x="+x);
// x=1
}
}
}
public class VolatileExampleMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
VolatileExample volatileExample = new VolatileExample();
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
volatileExample.writer();
});
threadA.start();
Thread threadB = new Thread(() -> {
volatileExample.reader();
});
threadB.start();
}
}
运行结果
4、管程中锁的规则
该规则说的是一个对锁的解锁操作Happens-Before后续对该锁的加锁操作。
管程是一种通用的同步原语,在 Java 中指的就是 synchronized,synchronized 是 Java 里对管程的实现。 如下代码所示: x 的初始值是 1,线程 A 执行完代码块后 x 的值会变成 12(执行完自动释放锁),线程 B 进入代码块时,能够看到线程 A 对 x 的写操作,也就是线程 B 能够看到 x的值12。
public class SynchronizedExample {
int x = 1;
public synchronized void updateValue() {
if (this.x < 12) {
this.x = 12;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SynchronizedExample synchronizedExample = new SynchronizedExample();
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> synchronizedExample.updateValue());
threadA.start();
Thread threadB = new Thread(() -> synchronizedExample.updateValue());
threadB.start();
}
}
5、线程start规则
该规则说明的是主线程在调用子线程的start方法后,子线程能够看到主线程在启动子线程前的操作。 如下代码,data的初始值为1,调用threadB.start()方法前,data的值为77。根据该规则,子线程threadB能够看到data的值为77。
public class ThreadExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Data data = new Data();
data.setValue(1);
Thread threadB = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(data.getValue());
}
});
data.setValue(77);
threadB.start();
}
static class Data {
private int value;
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
}
6、线程 join() 规则
这条是关于线程等待的。它是指主线程 A 等待子线程 B 完成(主线程 A 通过调用子线程 B 的 join() 方法实现),当子线程 B 完成后(主线程 A 中 join() 方法返回),主线程能够看到子线程的操作。
public class JoinExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
final Data data = new Data();
data.setValue(1);
Thread threadB = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
data.setValue(77);
}
});
threadB.start();
threadB.join();
System.out.println("Main Thread data.value="+data.getValue());
}
static class Data {
private int value;
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
}