每个进程都有一个当前工作目录,此目录是搜索所有相对路径名的起点。比如,当用户登录到unix系统时,其当前工作目录通常是口令文件在/etc/passwd中。当前工作目录是进程的一个属性,起始目录是登录名的一个属性。
在C语言中,可以有多个函数可以用于获取目录的操作。
getcwd获取当前工作目录
我们需要一个函数,它从当前工作目录(.)开始,用..找到其上一级目录,然后读其目录项,直到该目录项中的i节点编号与工作目录i节点编号相同,这样地就找到了其对应的文件名。
按照这种方法。就得到了当前工作目录完整的绝对路径名。
#include <unistd.h>
char *getcwd(char *buf, size_t size);
使用getcwd必须向函数传递两个参数,一个是缓冲区地址buf,另一个是缓冲区的长度size。缓冲区必须有足够的长度以容纳绝对路径名,不然返回出错。
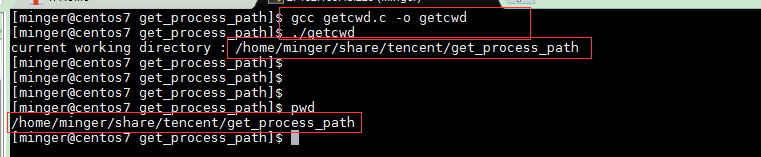
下面来实现一个获取当前目录绝对路径的小例子。
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv){
char buf[256] = {0};
getcwd(buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("current working directory : %s\n", buf);
return 0;
}
编译运行:
#include <unistd.h>
char *getwd(char *buf);
char *get_current_dir_name(void);
这里就不对它们进行介绍了哈 。
另一种获取工作目录方式(readlink)
#include <unistd.h>
ssize_t readlink(const char *restrict path, char *restrict buf,
size_t bufsize);
readlink()函数用于读取相关路径下的连接符号,并将其存储于buf中。
下面获取当前目录工作路径,用readlink函数。这种方法最可靠,可用于开机启动程序获取自身目录。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_PATH_LEN 256
#define ERR_ERROR -1
#define ERR_SUCCESS 0
//
int get_process_path(char *process_path){
char *p = NULL;
int n = 0;
memset(process_path,0x00,MAX_PATH_LEN);
n = readlink("/proc/self/exe",process_path,MAX_PATH_LEN);
if (NULL != (p = strrchr(process_path,'/'))){
*p = '\0';
}else{
printf("wrong process path");
return ERR_ERROR;
}
return ERR_SUCCESS;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv){
char path[MAX_PATH_LEN];
// printf("process path = %d \n",get_process_path(path));
if (get_process_path(path)){
printf("get process path error!\n");
return ERR_ERROR;
}
printf("%s\n",path);
return 0;
}
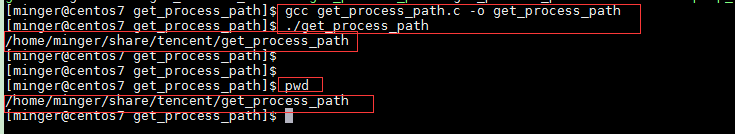
编译运行:
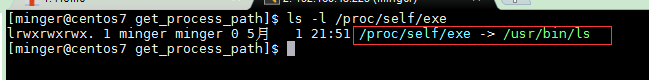
可以用ls -l /proc/self/exe查看文件和目录的软连接路径。
readlink("/proc/self/exe",process_path,MAX_PATH_LEN);
执行结果,buf中存在字符结果为/usr/bin/ls
这种方法的原理在于linux系统中的符号链接:/proc/self/exe代表当前程序,所以可以用readlink读取它的源路径就可以获取当前程序的绝对路径。
总结
getcwd系统调用可以获取用户的工作目录。readlink也是获取当前程序的运行路径,用readlink函数。这种方法最可靠,可用于开机启动程序获取自身目录。

欢迎关注公众号【程序猿编码】,添加本人微信号(17865354792),回复:领取学习资料。或者回复:进入技术交流群。网盘资料有如下: