在我们前端开发过程中,写css(包括sass, less, stylus这样的预处理器)进行设计稿的样式还原是一项重要的工作,而其中,关于页面布局的部分,又是书写样式代码时候的重点和难点,这篇文章就尽可能的去总结常见的一些页面布局实现方案(并不是全部,布局实现方法太多了),希望能够对大家有所帮助。
在开始正题之前,有一点要说明:css布局中遇到的一个绕不开的问题就是浏览器兼容性,下面方案会遇到类似transform, flex等的兼容性问题,且由于grid布局兼容性问题,暂不涉及grid布局内容,在不同场景,大家选择合适的布局实现方案即可。
1. 居中相关的布局
1.1 水平居中布局
效果图如下:
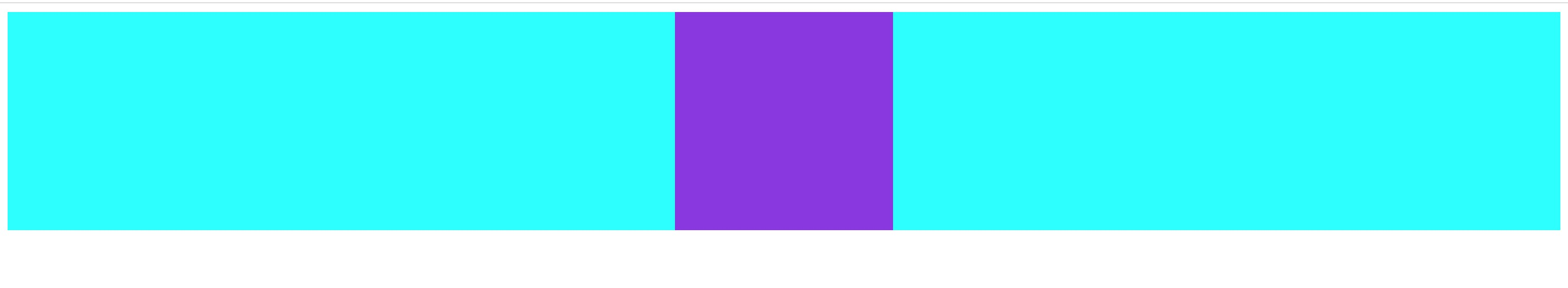

方案一. inline-block + text-align
分析:display设置为inline-block的元素,具有文本元素的性质,其父元素可以通过设置文本对齐属性text-align来控制其在行内的对齐方式,text-align: center即为水平对齐
注意:text-align属性是具有继承性的,会导致自己元素内部的文本也是居中显示的,需要自身设置text-align覆盖
<style>
.wrap {
width: 100%;
height: 200px;
background-color: aqua;
text-align: center;
}
.content {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: blueviolet;
display: inline-block;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="wrap">
<div class="content"></div>
</div>
</body>
方案二. 定位 + transform
分析:父元素开启定位(relative,absolute,fixed都可以)后,子元素设置绝对定位absolute后,left设置为50%,再使用transform: translateX(-50%)将子元素往反方向移动自身宽度的50%,便完成水平居中。
注意:父级元素是否脱离文档流,不影响子元素水平居中效果,但是transform是css3属性,存在浏览器兼容问题
<style>
.wrap {
position: relative;
width: 100%;
height: 200px;
background-color: aqua;
}
.content {
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
transform: translateX(-50%);
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: blueviolet;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="wrap">
<div class="content"></div>
</div>
</body>
方案三. display: block + margin: 0 auto
分析: 这个方法只需要对子元素进行设置就可以实现水平居中,margin设置auto表示浏览器会自动分配,实现来外边距等分效果。
注意: 这里子元素设置display为block或者table都是可以的,如果子元素脱离文档流(浮动,定位),会导致margin属性的值无效。
<style>
.wrap {
width: 100%;
height: 200px;
background-color: aqua;
}
.content {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: blueviolet;
display: table;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="wrap">
<div class="content"></div>
</div>
</body>
1.2 垂直居中布局
效果图如下:

方案一. 定位 + transform
这种方案和之前水平居中布局的方案二是同样的原理,不在赘述
<style>
.wrap {
position: relative;
width: 200px;
height: 600px;
background-color: aqua;
}
.content {
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
transform: translateY(-50%);
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: blueviolet;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="wrap">
<div class="content"></div>
</div>
</body>
方案二. display: table-cell + vertical-align
分析:设置display: table-cell的元素具有td元素的行为,它的子元素布局方式类似文本元素,可以在父元素使用vertical-align: middle;实现子元素的垂直居中。
注意:vertical-align属性具有继承性,导致父元素内文本也是垂直居中显示的。
<style>
.wrap {
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle;
width: 200px;
height: 600px;
background-color: aqua;
}
.content {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: blueviolet;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="wrap">
<div class="content"></div>
</div>
</body>
1.3 水平垂直居中布局
效果图如下:
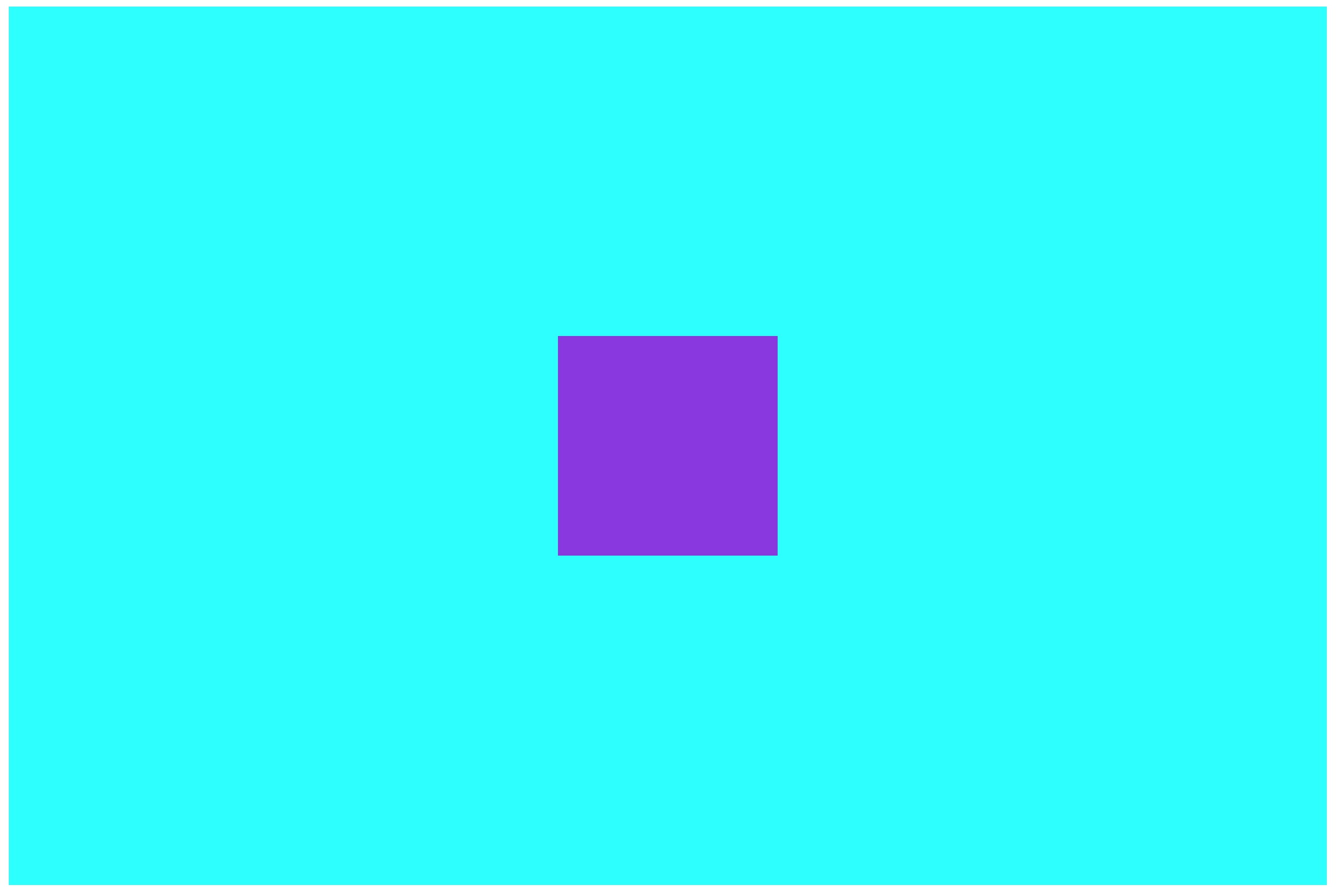
方案一.定位 + transform
<style>
.wrap {
position: relative;
width: 1200px;
height: 800px;
background-color: aqua;
}
.content {
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: blueviolet;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="wrap">
<div class="content"></div>
</div>
</body>
方案二. 结合水平布局方案三,垂直布局方案二
<style>
.wrap {
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle;
width: 1200px;
height: 800px;
background-color: aqua;
}
.content {
margin: 0 auto;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: blueviolet;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="wrap">
<div class="content"></div>
</div>
</body>
1.4 使用flex进行居中布局
分析:使用flex,水平垂直居中会变得非常容易,默认情况下,align-items: center垂直居中(交叉轴排列方式),justify-content: center水平居中(主轴排列方式)
注意: 需要考虑浏览器兼容性问题。
<style>
.wrap {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
width: 1200px;
height: 800px;
background-color: aqua;
}
.content {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: blueviolet;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="wrap">
<div class="content"></div>
</div>
</body>
2. N列布局
2.1 两列布局
这里的两列布局指的是,其中一列是定宽元素,另一列元素宽度自适应。比如,我们实现做列定宽,右列自适应的布局。
效果图如下:
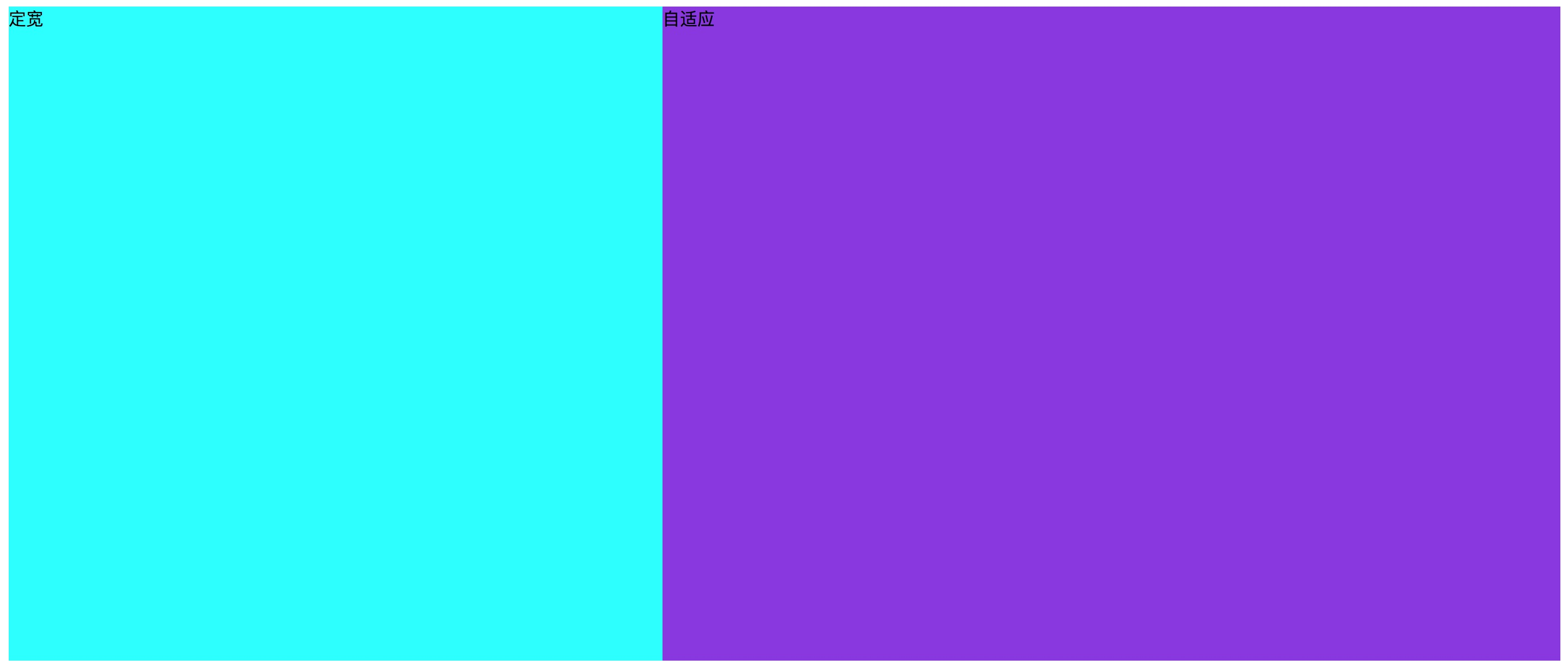

方案一. 左边元素浮动,定宽,右边元素设置margin-left
分析:一个最简单的做法,左边元素设置浮动,定宽,右边元素的margin-left设置为左边元素宽度大小,可以实现效果。
注意:我们左边元素使用了浮动,但是右边元素没有浮动
<style>
.l, .r {
height: 600px;
}
.l {
width: 400px;
background-color: aqua;
float: left;
}
.r {
background-color: blueviolet;
margin-left: 400px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="l">定宽</div>
<div class="r">自适应</div>
</body>
方案二. 左边元素浮动,定宽,右边元素设置overflow:hidden
分析: 右边元素由于设置overflow:hidden开启BFC,与外界隔离,所以能实现效果
注意:overflow:hidden的设置也使得右边元素内容超出隐藏。这里如果不设置overflow:hidden,右边元素的宽度是100%,有一部分被左边浮动元素盖住,不是我们要的结果,虽然看起来没什么区别。
<style>
.l, .r {
height: 600px;
}
.l {
width: 400px;
background-color: aqua;
float: left;
}
.r {
background-color: blueviolet;
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="l">定宽</div>
<div class="r">自适应</div>
</body>
方案三.将左右元素用一个display:table的元素包裹,左右元素设置为display: table-cell
分析:这里主要是基于表格元素,在没有设置宽度时,会自动分配宽度来实现布局的。
注意:设置为表格后,在某些浏览器可能会受到表格本身特有行为的影响,比如表格边框等等。
<style>
.w {
display: table;
table-layout: fixed;
width: 100%;
}
.l, .r {
display: table-cell;
height: 600px;
}
.l {
width: 400px;
background-color: aqua;
}
.r {
background-color: blueviolet;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="w">
<div class="l">定宽</div>
<div class="r">自适应</div>
</div>
</body>
方案四. flex布局
分析:父容器采用flex布局,左边元素定宽之后,右边元素,因为只有一个,所以flex属性设置为不是0的正值(也就是设置flex-grow),都会占满剩余空间。
注意:依然是,注意兼容性问题。
<style>
.p {
display: flex;
height: 600px;
}
.l {
background-color: aqua;
width: 400px;
}
.r {
flex: 1;
background-color: blueviolet;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="p">
<div class="l">定宽</div>
<div class="r">自适应</div>
</div>
</body>
2.2 三列布局
这里的三列布局,主要分三种情况介绍,第一种是普通三列布局,还有两种是比较有名的圣杯布局和双飞翼布局(两者都是实现一个两侧宽度固定,中间宽度自适应的三列布局,区别在于双飞翼布局比起圣杯布局,中间元素会多一个子元素,而左右元素需要定位relative)
2.2.1. 普通三列布局
我们这里实现的是,左中两列定宽,右边一列自适应的布局,这个实际上和前面的两列布局是类似的。
效果图如下:
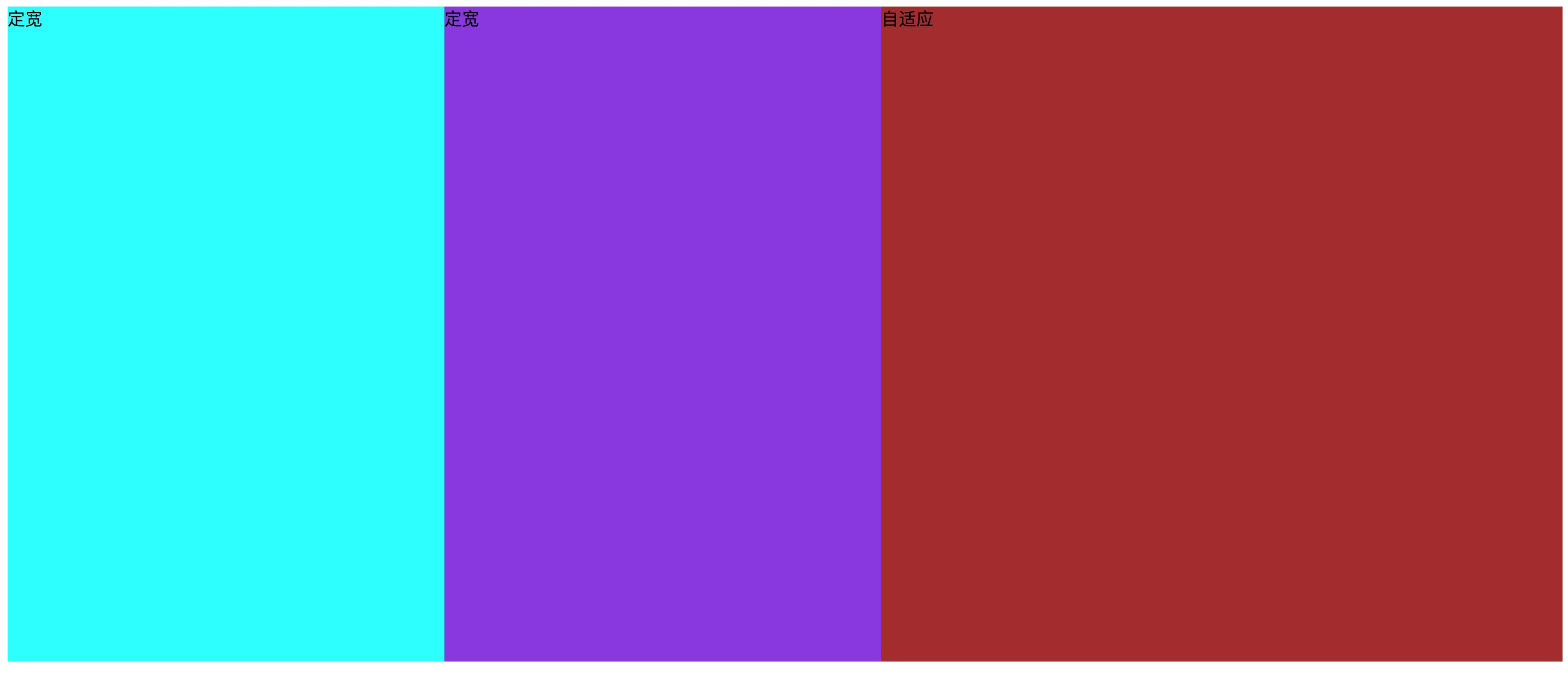
方案一. 定宽 + overflow:hidden
分析:这个方案和两列布局方案二是相同的。
<style>
.l, .c, .r {
height: 600px;
}
.l {
width: 400px;
background-color: aqua;
float: left;
}
.c {
width: 400px;
background-color: blueviolet;
float: left;
}
.r {
background-color: brown;
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="l">定宽</div>
<div class="c">定宽</div>
<div class="r">自适应</div>
</body>
方案二. flex布局
分析:这里布局原理和两列布局中flex布局方式是相同的。
<style>
.w {
display: flex;
height: 600px;
}
.l {
width: 400px;
background-color: aqua;
}
.c {
width: 400px;
background-color: blueviolet;
}
.r {
flex: 1;
background-color: brown;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="w">
<div class="l">定宽</div>
<div class="c">定宽</div>
<div class="r">自适应</div>
</div>
</body>
2.2.2. 圣杯布局
两侧宽度固定,中间宽度自适应的三列布局(中间元素不需要嵌套子元素)
效果图如下:

方案一. 左右两侧浮动,中间元素使用margin
分析:这种方法就是左右两边浮动,给定宽度,中间元素使用margin空出左右两边元素的位置,实现比较简单。
注意:这种方式,需要在书写html结构时,将右侧元素写在中间元素的前面,因为如果右侧元素在中间元素后面,由于浮动元素位置上不能高于(或平级)前面的非浮动元素,导致右侧元素会下沉。但是,中间元素一般都是页面的核心部分,放在比较后面的位置,不利于SEO。
<style>
.l, .c, .r {
height: 600px;
}
.l {
width: 400px;
background-color: aqua;
float: left;
}
.c {
background-color: blueviolet;
margin-left: 400px;
margin-right: 400px;
}
.r {
width: 400px;
background-color: brown;
float: right;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="l">定宽</div>
<div class="r">定宽</div>
<div class="c">自适应</div>
</body>
方案二. 父容器使用margin,左中右元素均浮动,利用定位和margin移动到正确位置
分析:这种方法将中间元素c放置在最前面,有利于SEO。
注意:实现细节在参考下面代码中的注释。
<style>
.w {
/* margin-left对应左边元素l的宽度,margin-right对应右边元素r的宽度 */
margin-left: 400px;
margin-right: 400px;
}
.l, .c, .r {
height: 600px;
float: left;
}
.l {
width: 400px;
background-color: aqua;
position: relative;
/* 为了让l元素从当前行移动到第一行同一位置*/
margin-left: -100%;
/* 移动到中间元素左侧正确位置 */
left: -400px;
}
.c {
width: 100%;
background-color: blueviolet;
}
.r {
width: 400px;
background-color: brown;
position: relative;
/* 为了让l元素从当前行移动到上一行*/
margin-left: -400px;
right: -400px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="w">
<div class="c">自适应</div>
<div class="l">定宽</div>
<div class="r">定宽</div>
</div>
</body>
2.2.3. 双飞翼布局
两侧宽度固定,中间宽度自适应的三列布局(中间元素内部增加子元素用于放置内容)
效果图如下:

方案一. 中间元素子元素设置margin,左中右元素均设置浮动,左右元素通过margin移动到正确位置
分析:这种方法为中间元素增加子元素作为内容区域,通过子元素设置margin完成。
注意:和圣杯布局对照,有相似处,也有不同,实现的结果是一样的。
<style>
.l, .c, .r {
height: 600px;
float: left;
}
.l {
width: 400px;
background-color: aqua;
/* 为了让l元素从当前行移动到第一行同一位置*/
margin-left: -100%;
}
.c {
width: 100%;
background-color: blue;
}
.i {
height: 600px;
background-color: blueviolet;
margin-left: 400px;
margin-right: 400px;
}
.r {
width: 400px;
background-color: brown;
/* 为了让r元素移动到第一行*/
margin-left: -400px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="c">
<div class="i">自适应</div>
</div>
<div class="l">定宽</div>
<div class="r">定宽</div>
</body>
2.2.4. flex布局实现(中间自适应,左右等宽)
分析: flex实现就很简单了,可以参照普通三列布局flex实现。
注意:还是要注意浏览器兼容性问题。
<style>
.w {
display: flex;
height: 600px;
}
.l {
width: 400px;
background-color: aqua;
}
.c {
flex: 1;
background-color: blueviolet;
}
.r {
width: 400px;
background-color: brown;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="w">
<div class="l">定宽</div>
<div class="c">自适应</div>
<div class="r">定宽</div>
</div>
</body>
2.3 多列等分布局
所谓多列等分布局,就是若干列在容器中自适应等分宽度,我们以五列等分布局为例。
效果图如下:
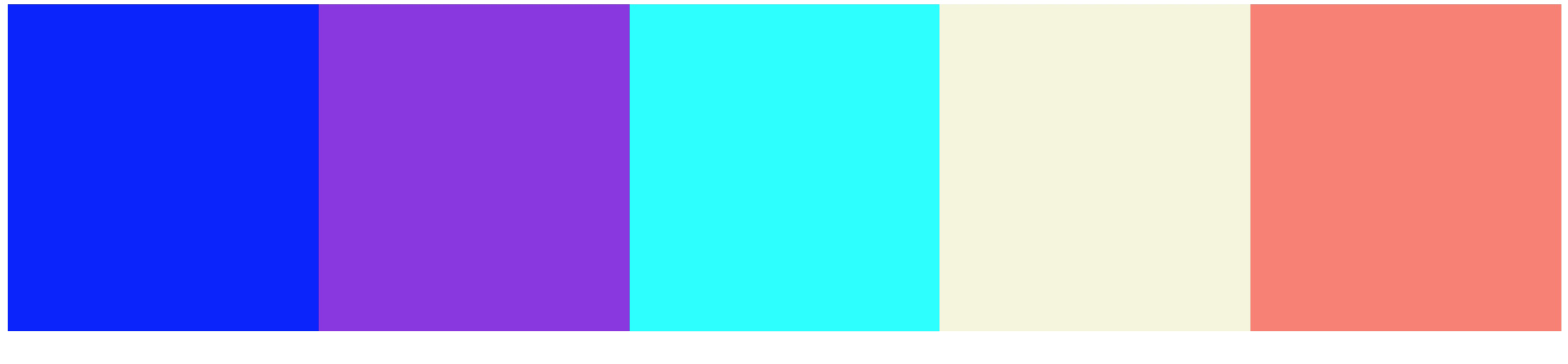
方案一. 浮动 + 百分数平分
分析: 这种方案就是每一列浮动,之后按照百分比平分宽度,实现简单。
<style>
.col {
float: left;
width: 20%;
height: 300px;
}
.col1 {
background-color: blue;
}
.col2 {
background-color: blueviolet;
}
.col3 {
background-color: aqua;
}
.col4 {
background-color: beige;
}
.col5 {
background-color: salmon;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="w">
<div class="col col1"></div>
<div class="col col2"></div>
<div class="col col3"></div>
<div class="col col4"></div>
<div class="col col5"></div>
</div>
</body>
方案二. 使用display: table布局
分析:父容器指定display: table,设置布局行为table-layout: fixed,指定每个表格等宽。
注意: table-layout: fixed是需要设置的,默认情况下,列宽度由单元格内容设定,设置之后,列宽由表格宽度和列宽度设定。
<style>
.w {
display: table;
/* 列宽由表格宽度和列宽度设定 */
table-layout: fixed;
width: 100%;
}
.col {
display: table-cell;
height: 300px;
}
.col1 {
background-color: blue;
}
.col2 {
background-color: blueviolet;
}
.col3 {
background-color: aqua;
}
.col4 {
background-color: beige;
}
.col5 {
background-color: salmon;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="w">
<div class="col col1"></div>
<div class="col col2"></div>
<div class="col col3"></div>
<div class="col col4"></div>
<div class="col col5"></div>
</div>
</body>
方案三. 使用column布局
分析:使用column布局,指定内容区域需要分为5列即可。
注意:浏览器兼容性问题。
<style>
.w {
/* 指定列数 */
column-count: 5;
/* 指定列与列之间的间隙,默认1em */
column-gap: 0;
}
.col {
height: 300px;
}
.col1 {
background-color: blue;
}
.col2 {
background-color: blueviolet;
}
.col3 {
background-color: aqua;
}
.col4 {
background-color: beige;
}
.col5 {
background-color: salmon;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="w">
<div class="col col1"></div>
<div class="col col2"></div>
<div class="col col3"></div>
<div class="col col4"></div>
<div class="col col5"></div>
</div>
</body>
方案四. 使用flex布局
分析:使用flex布局十分简单,指定每一列所占空间相同即可
<style>
.w {
display: flex;
}
.col {
height: 300px;
flex: 1;
}
.col1 {
background-color: blue;
}
.col2 {
background-color: blueviolet;
}
.col3 {
background-color: aqua;
}
.col4 {
background-color: beige;
}
.col5 {
background-color: salmon;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="w">
<div class="col col1"></div>
<div class="col col2"></div>
<div class="col col3"></div>
<div class="col col4"></div>
<div class="col col5"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
2.4 多列等高布局
所谓多列等高布局,就是多类内容可能不一样,但是保证每一列的高度是相同的,这个高度应该由内容最多的那一列决定。
效果图如下:

方案一. 使用display: table布局
分析:父元素设置display: table,子元素设置display: table-cell,这样布局就是按照表格行为布局,表格单元格默认等高。
<style>
.w {
display: table;
}
.col {
display: table-cell;
width: 20%;
}
.col1 {
background-color: blue;
}
.col2 {
background-color: blueviolet;
}
.col3 {
background-color: aqua;
}
.col4 {
background-color: beige;
}
.col5 {
background-color: salmon;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="w">
<div class="col col1">啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊</div>
<div class="col col2">啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊</div>
<div class="col col3">啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊</div>
<div class="col col4"></div>
<div class="col col5">啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊</div>
</div>
</body>
方案二. 使用flex布局
分析: 默认情况下,display: flex的元素align-items属性值为stretch,如果项目未设置高度或设为auto,将占满整个容器的高度。
<style>
.w {
display: flex;
}
.col {
flex: 1;
}
.col1 {
background-color: blue;
}
.col2 {
background-color: blueviolet;
}
.col3 {
background-color: aqua;
}
.col4 {
background-color: beige;
}
.col5 {
background-color: salmon;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="w">
<div class="col col1">啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊</div>
<div class="col col2">啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊</div>
<div class="col col3">啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊</div>
<div class="col col4"></div>
<div class="col col5">啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊</div>
</div>
</body>
3. 全屏布局
所谓全屏布局,就是实现经典的头部,内容区,底部三大区域占满全屏的布局,这种布局很常见。
实现效果如下:
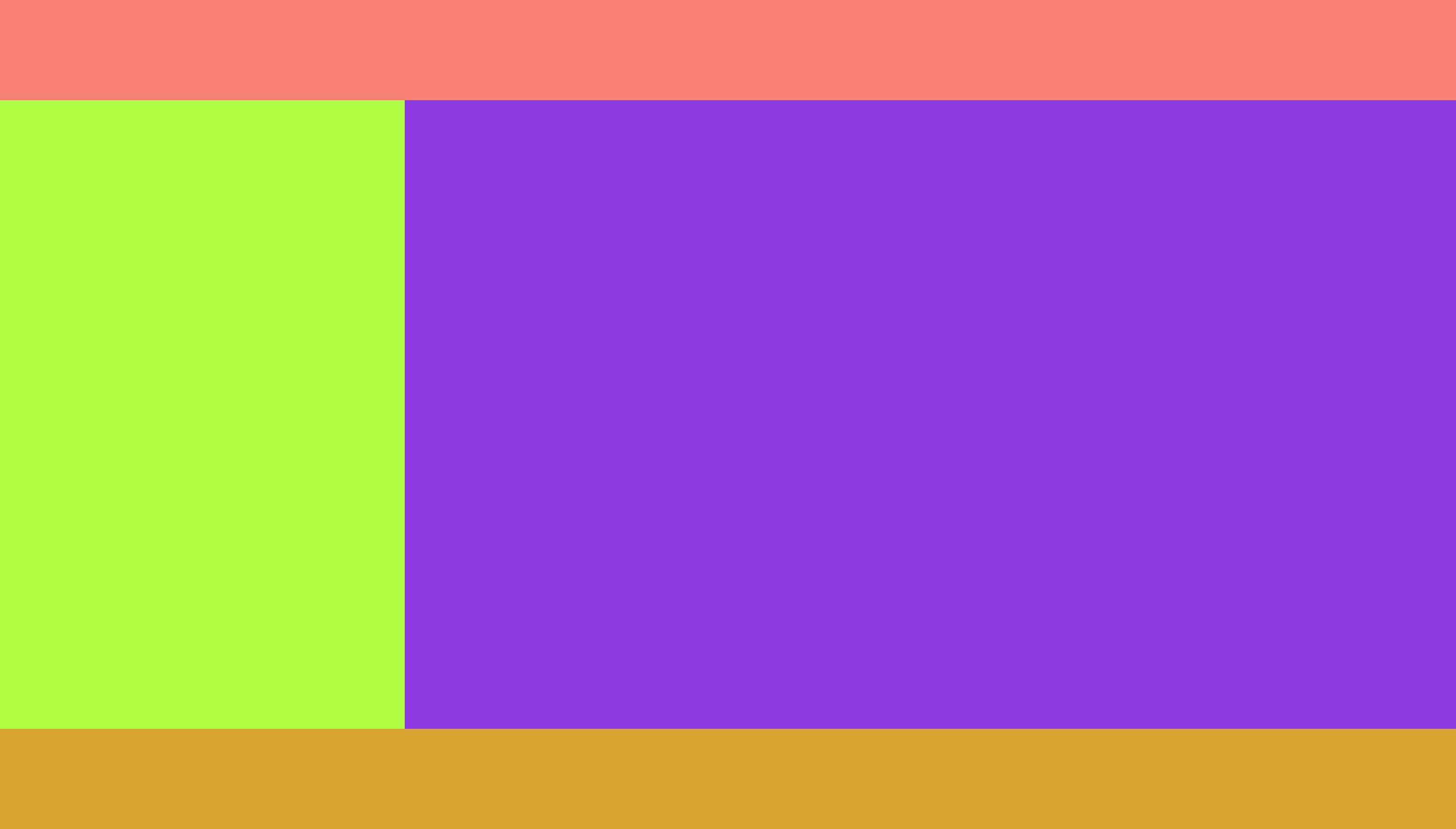

分析: 这里采用的方案是,头部底部使用fixed定位,中间使用之前讲到的两列布局技术。
注意: 头部底部可以使用header, footer标签,内容区域结构与布局都是多种多样的。
<style>
html, body {
margin: 0;
overflow: hidden;
}
.header {
position: fixed;
left: 0;
top: 0;
right: 0;
height: 100px;
background-color: salmon;
}
.w {
position: fixed;
left: 0;
right: 0;
top: 100px;
bottom: 100px;
overflow: auto;
background-color: palevioletred;
}
.w .l {
width: 400px;
/* height: 100%; */
position: fixed;
left: 0;
top: 100px;
bottom: 100px;
background-color: greenyellow;
}
.w .r {
position: fixed;
left: 400px;
right: 0;
top: 100px;
bottom: 100px;
background-color: blueviolet;
}
.footer {
position: fixed;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
height: 100px;
background-color: goldenrod;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="header"></div>
<div class="w">
<div class="l"></div>
<div class="r"></div>
</div>
<div class="footer"></div>
</body>
本篇文章总结了一些常见布局的实现方案,css布局的实现方案很多,需要我们平时多去积累,选择合适的方案。
最后,希望随着时间的推移,兼容性不再成为我们技术实现的障碍,愿世界越来越美好。