建议PC端观看,移动端代码高亮错乱
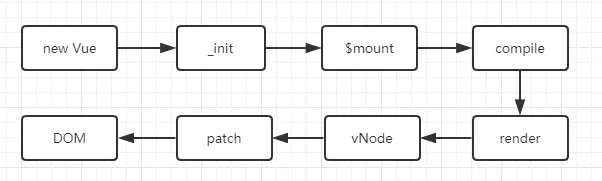
new Vue发生了什么
我们来一步步找到Vue的核心定义,以web-full-esm为例
// scripts/config.js
const builds = {
// ...
// Runtime+compiler ES modules build (for bundlers)
'web-full-esm': {
entry: resolve('web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js'),
dest: resolve('dist/vue.esm.js'),
format: 'es',
alias: { he: './entity-decoder' },
banner
},
}src/platforms/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js(入口)- —>
src/platforms/web/runtime/index.js - —>
src/core/index.js - —>
src/core/instance/index.js(核心)
Vue 构造函数定义就在src/core/instance/index.js中
// src/core/instance/index.js
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
this._init(options)
}
initMixin(Vue)
stateMixin(Vue)
eventsMixin(Vue)
lifecycleMixin(Vue)
renderMixin(Vue)
export default VueinitMixin(Vue):就做了一件事,定义_init方法。stateMixin(Vue):定义数据相关的方法$set,$delete,$watch方法。eventsMixin(Vue):定义事件相关的方法$on,$once,$off,$emit。lifecycleMixin(Vue):定义_update,及生命周期相关的$forceUpdate和$destroy。renderMixin(Vue):定义$nextTick,_render将render函数转为vnode。
可以看到 new Vue 主要就是调用了 _init 方法
_init方法
this._init方法在执行 initMixin 时绑定的,在src/core/instance/init.js中:
export function initMixin (Vue) {
Vue.prototype._init = function (options) {
const vm = this
// uid
vm._uid = uid++
// a flag to avoid this being observed
vm._isVue = true
if (options && options._isComponent) {
// 优化内部组件实例化,因为动态选项合并非常慢,并且没有内部组件选项需要特殊处理。
initInternalComponent(vm, options)
} else {
// 合并options
vm.$options = mergeOptions(
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),
options || {},
vm
)
}
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
initProxy(vm)
} else {
vm._renderProxy = vm
}
// expose real self
vm._self = vm
initLifecycle(vm)
initEvents(vm)
initRender(vm)
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
initState(vm)
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
callHook(vm, 'created')
// 挂载
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)
}
}
}Vue 初始化主要就干了几件事情:
mergeOptions合并配置initLifecycle初始化生命周期initEvents初始化事件中心initRender初始化渲染,比如定义vm._c和vm.$createElementinitState初始化data、props、computed、watcher等等。
这些内容在后续的章节都会介绍到,这里只需要了解做了什么事情即可。
数据代理
不知道大家有没有好奇过,为什么我们的数据定义在data中,可是却可以通过 this.xxx 访问
export default {
data() {
return {
name: 'l1shu'
}
},
mounted() {
console.log(this.name) // l1shu
}
}
其中的奥秘就在 _init 的 initState 中,src/core/instance/state.js:
// src/core/instance/state.js
export function initState (vm) {
// ...
if (opts.data) {
initData(vm) // 执行 initData 方法
} else {
observe(vm._data = {}, true /* asRootData */)
}
// ...
}从 $options 中读取 data,并执行 initData方法:
// src/core/instance/state.js
function initData (vm) {
let data = vm.$options.data
data = vm._data = typeof data === 'function'
? getData(data, vm)
: data || {}
if (!isPlainObject(data)) {
data = {}
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
'data functions should return an object:\n' +
'https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/components.html#data-Must-Be-a-Function',
vm
)
}
// proxy data on instance
const keys = Object.keys(data)
const props = vm.$options.props
const methods = vm.$options.methods
let i = keys.length
while (i--) {
const key = keys[i]
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
// 判断是否和 methods 同名冲突
if (methods && hasOwn(methods, key)) {
warn(
`Method "${key}" has already been defined as a data property.`,
vm
)
}
}
// 判断是否和 props 同名冲突
if (props && hasOwn(props, key)) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
`The data property "${key}" is already declared as a prop. ` +
`Use prop default value instead.`,
vm
)
} else if (!isReserved(key)) {
// 数据代理
proxy(vm, `_data`, key)
}
}
// 响应式处理
observe(data, true /* asRootData */)
}首先判断 data 是否为一个函数,是的话就执行 getData,此函数定义如下:
export function getData (data: Function, vm: Component): any {
// #7573 disable dep collection when invoking data getters
// https://github.com/vuejs/vue/issues/7573
pushTarget()
try {
return data.call(vm, vm)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, vm, `data()`)
return {}
} finally {
popTarget()
}
}可以看到 getData 函数逻辑非常简单,关于 pushTarget 和 popTarget 在之后的响应式章节会介绍。
回到 initData 函数:
- 遍历
keys,判断定义的字段是否和props,methods同名冲突,冲突的话则在开发模式下抛出警告 isReserved判断是否为保留字段,不能以_或者$开头proxy实现数据代理 (核心)observe实现响应式处理,这个我们以后再说
最后看下 proxy 函数是怎么实现数据代理的:
// src/core/instance/state.js
const sharedPropertyDefinition = {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: noop,
set: noop
}
export function proxy (target: Object, sourceKey: string, key: string) {
sharedPropertyDefinition.get = function proxyGetter () {
return this[sourceKey][key]
}
sharedPropertyDefinition.set = function proxySetter (val) {
this[sourceKey][key] = val
}
Object.defineProperty(target, key, sharedPropertyDefinition)
}使用 Object.defineProperty 给 vm 添加指定的 key,通过 set 和 get 方法修改或读取 this._data。
看到这里我们理解了,当我们调用this.message时候,实际上我们调用了this._data.message
总结
Vue 的初始化逻辑写的非常清楚,把不同的功能逻辑拆成一些单独的函数执行,让主线逻辑一目了然
由于我们这一章的目标是弄清楚模板和数据如何渲染成最终的 DOM,所以各种初始化逻辑我们先不看。
在初始化的最后,检测到如果有 el 属性,则调用 vm.$mount 方法挂载 vm,挂载的目标就是把模板渲染成最终的 DOM,那么接下来我们来分析 Vue 的挂载过程。