Paxos和Raft协议介绍
文章来源: 陶老师运维笔记- 微信公众号
1. 背景介绍
1.1 分布式事务
分布式事务指事务的操作位于不同的分布式系统节点上,需要保证事务的 AICD 特性。 分布式事务处理的难点是必须有一种方法可以知道事务在任何地方所做的所有动作,提交或回滚事务的决定必须产生统一的结果(全部提交或全部回滚)
解决这种分布式一致性问题:其中比较著名的有二阶提交协议(Two Phase Commitment Protocol)、三阶提交协议(Tree Phase Commitment Protocol)和Paxos算法。
1.2 二阶段提交
在分布式系统中,每个节点虽然可以知晓自己的操作时成功或者失败,却无法知道其他节点的操作的成功或失败。当一个事务跨越多个节点时,为了保持事务的ACID特性,需要引入一个作为协调者的组件来统一掌控所有节点(称作参与者)的操作结果并最终指示这些节点是否要把操作结果进行真正的提交(比如将更新后的数据写入磁盘等等)。
因此,二阶段提交的算法思路可以概括为: 参与者将操作成败通知协调者,再由协调者根据所有参与者的反馈情报决定各参与者是否要提交操作还是中止操作。 2PC顾名思义分为两个阶段,其实施思路可概括为:
-
- 投票阶段(voting phase):参与者将操作结果通知协调者;
-
- 提交阶段(commit phase):收到参与者的通知后,协调者再向参与者发出通知,根据反馈情况决定各参与者是否要提交还是回滚;
2. Paxos协议
PAXOS可以用来解决分布式环境下,设置某一个值的问题。 分布式系统中有多个节点就会存在节点间通信的问题,Paxos是基于消息传递的通讯模型的。它的假设前提是,在分布式系统中进程之间的通信会出现丢失、延迟、重复等现象,但不会出现传错的现象。Paxos算法就是为了保证在这样的系统中进程间基于消息传递就某个值达成一致。
2.1 角色
Paxos是第一个被证明的共识算法,原理基于两阶段提交并进行扩展。算法中将节点分为三种类型:
- 倡议者proposer:提交一个提案,等待大家批准为结案,往往是客户端担任。提案信息包括提案编号和提议的value。
- 接受者acceptor:负责对提案进行投票,往往服务器担任。若提案获得多数Acceptors的接受,则称该提案被批准(chosen)。
- 学习者learner:被告知提案结果,只能“学习”被批准的提案。不参与投票过程。客户端和服务端都可担任。
每个节点在协议中可以担任多个角色。
2.2 Paxos算法
Paxos的特点:
- 一个或多个节点可以提出提议
- 系统针对所有提案中的某个提案必须达成一致
- 最多只能对一个确定的提案达成一致
- 只要超过半数的节点存活且可互相通信,整个系统一定能达成一致状态。



2.2.1 Paxos表决
- 首先proposers将value发送给Acceptors。
- Acceptors对value进行接受(accept)。acceptor可以回应接受或拒绝。
- 一旦节点中的大多数回应接受,共识就能达成,接受的value成为正式的决议(称为“批准”决议)。
整个过程(一个事务或一个Round)分为两个阶段:
-
phase1(准备阶段) a)Proposer向超过半数(n/2+1)Acceptor发起prepare消息(发送编号) b)如果prepare符合协议规则Acceptor回复promise消息,否则拒绝
-
phase2(决议阶段或投票阶段) a)如果超过半数Acceptor回复promise,Proposer向Acceptor发送accept消息(此时包含真实的值) b)Acceptor检查accept消息是否符合规则,消息符合则批准accept请求
根据上述过程当一个proposer发现存在编号更大的提案时将终止提案。这意味着提出一个编号更大的提案会终止之前的提案过程。有可能陷入活锁,违背了Progress的要求。这种情况下的解决方案是选举出一个leader,仅允许leader提出提案。注意一个learner可能兼任proposer。
2.2.2 决议的发布
一个显而易见的方法是当acceptors批准一个value时,将这个消息发送给所有learner。但是这个方法会导致消息量过大。可将accept消息发送给learners的一个子集,然后由这些learners去通知所有learners。
但是由于消息传递的不确定性,可能会没有任何learner获得了决议批准的消息。当learners需要了解决议通过情况时,可以让一个proposer重新进行一次提案。
2.3 Paxos与2PC
在Paxos算法中,如果我们指定集群中同一时间只能有一个leader,并且要求所有节点都要投票呢?是的,我们就得到了2PC。2PC是Paxos的一个特例
两个阶段分别是准备(prepare)和提交(commit)。准备阶段解决大家对哪个提案进行投票的问题,提交阶段解决确认最终值的问题。
3. Raft协议
3.1 Raft角色
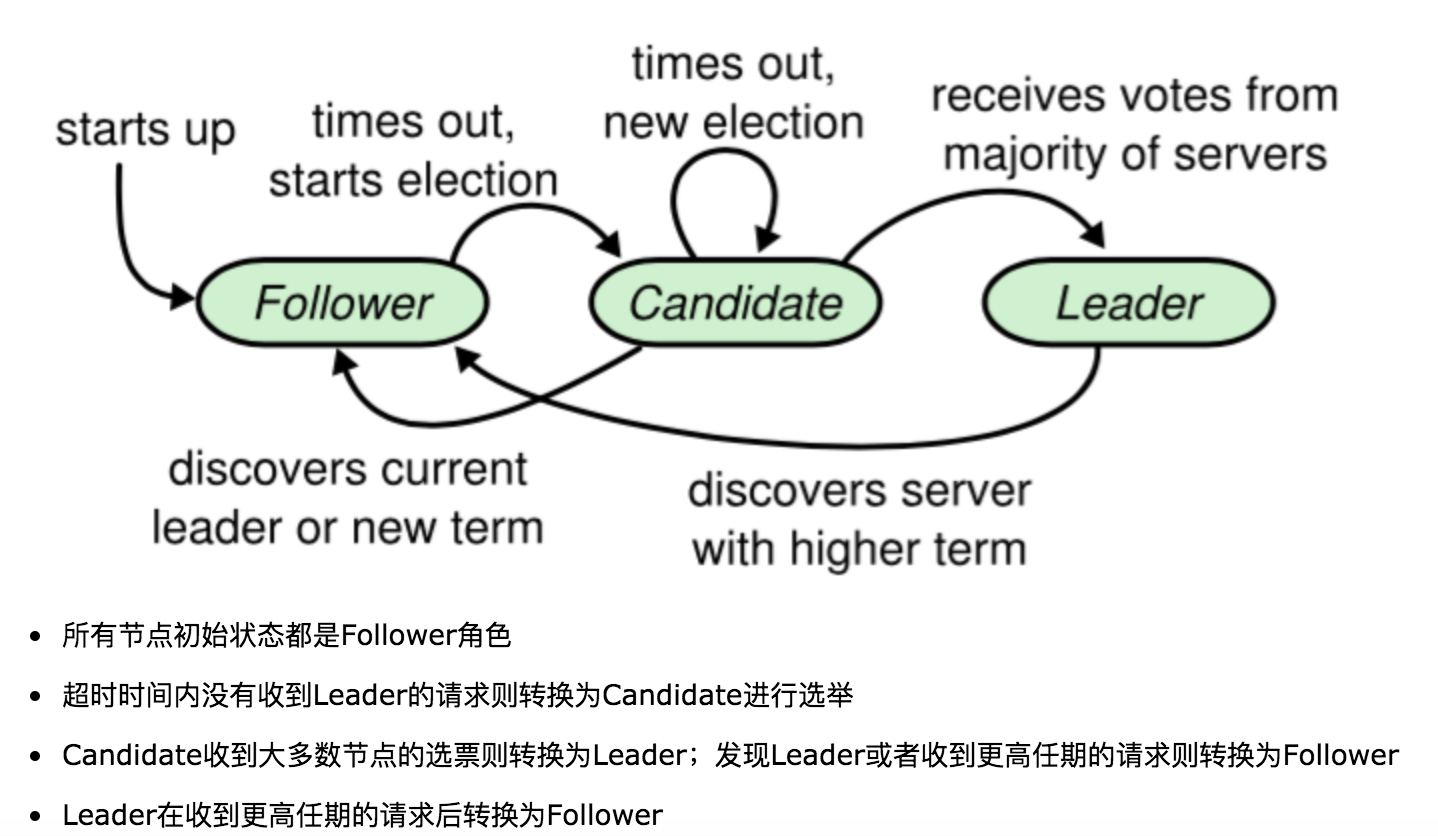
Raft算法是Paxos算法的一种简化实现。包括三种角色:leader,candidate和follower。
- follow:所有节点都以follower的状态开始,如果没有收到leader消息则会变成candidate状态。
- candidate:会向其他节点拉选票,如果得到大部分的票则成为leader,这个过程是Leader选举。
- leader:所有对系统的修改都会先经过leader。
3.2 Raft算法
Raft有两个基本过程:
- Leader选举: 每个candidate随机经过一定时间都会提出选举方案,最近阶段中的票最多者被选为leader。
- 同步log: leader会找到系统中log(各种事件的发生记录)最新的记录,并强制所有的follow来刷新到这个记录。
Raft算法过程: 有三种状态:leader,candidate和follower。
最开始都是follower状态.
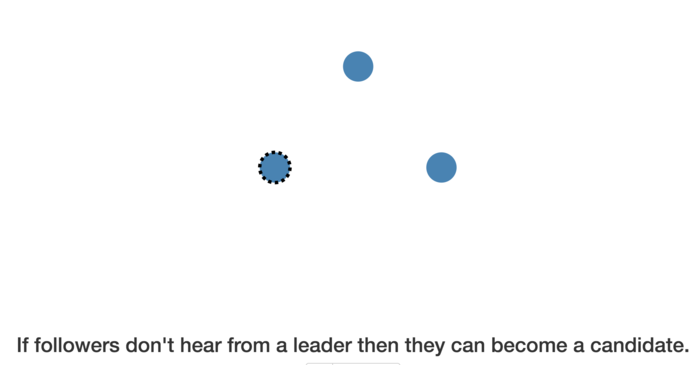
followers没有听到leader就变成candidate
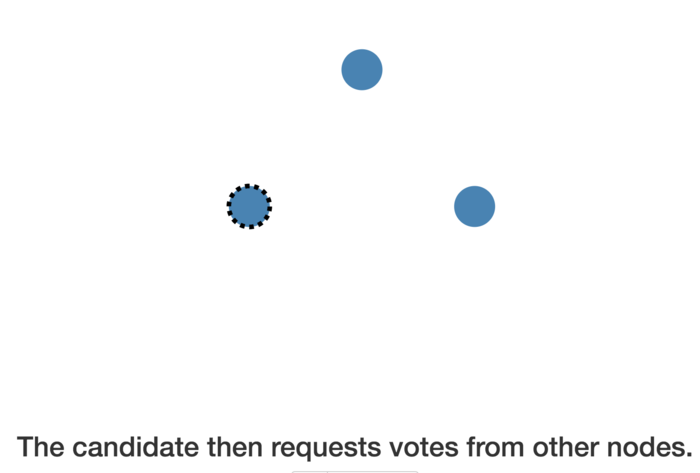
candidate then requests votes from other nodes
nodes will reply with their vote
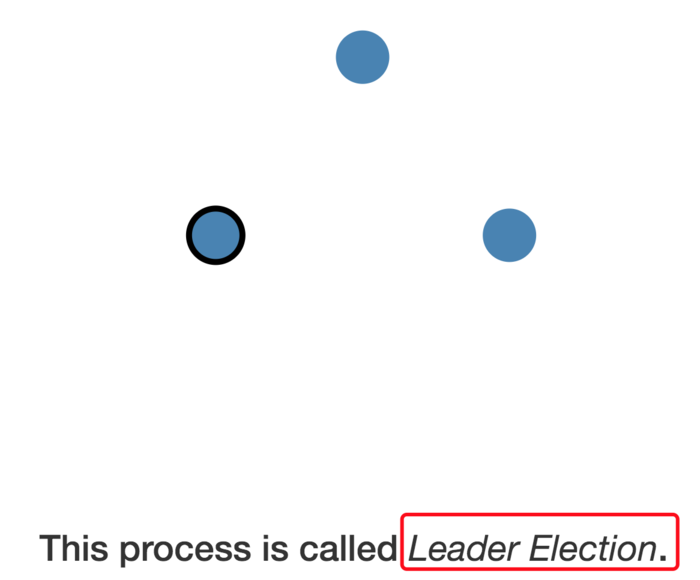
Candidate becomes the leader if it gets votes from a majority of nodes
This process is called Leader Election.
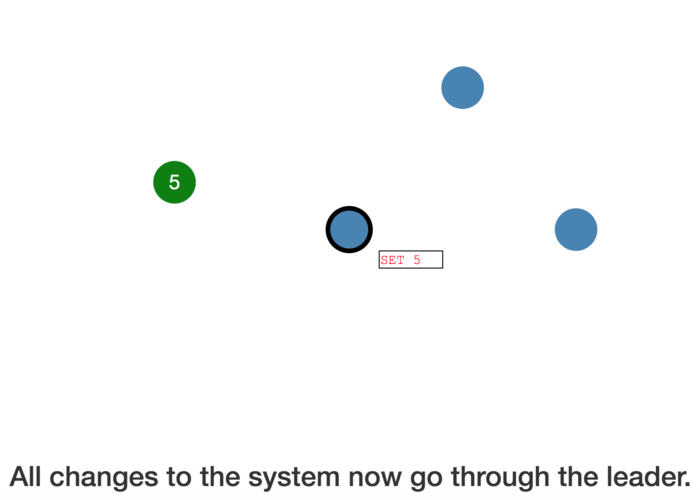
All changes to the system now go through the leader.
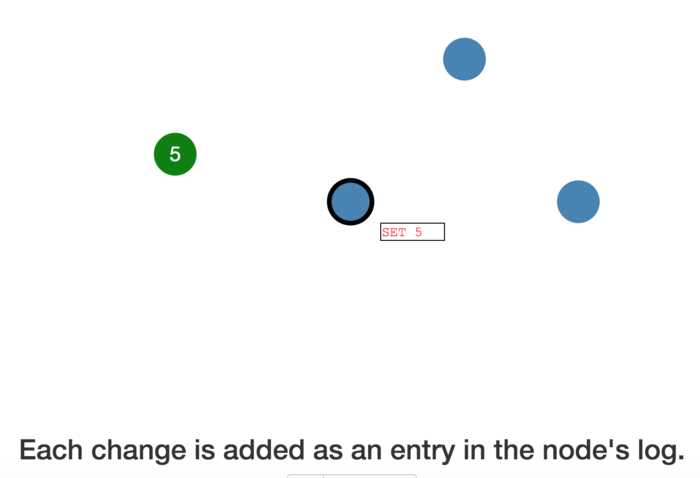
Each change is added as an entry in the node's log.
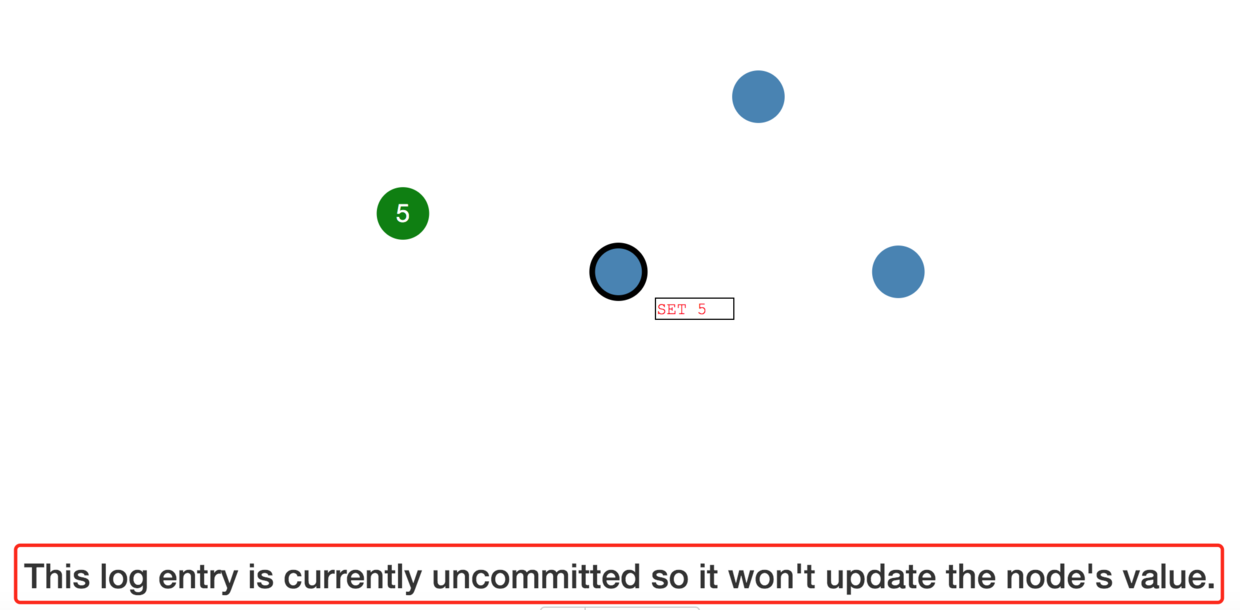
This log entry is currently uncommitted so it won't update the node's value.
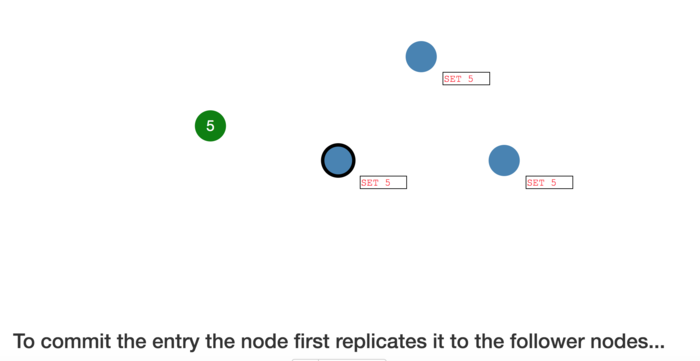
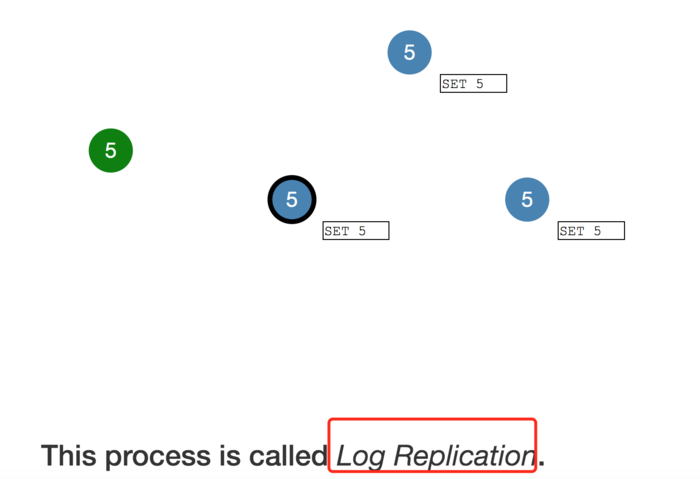
To commit the entry the node first replicates it to the follower nodes...
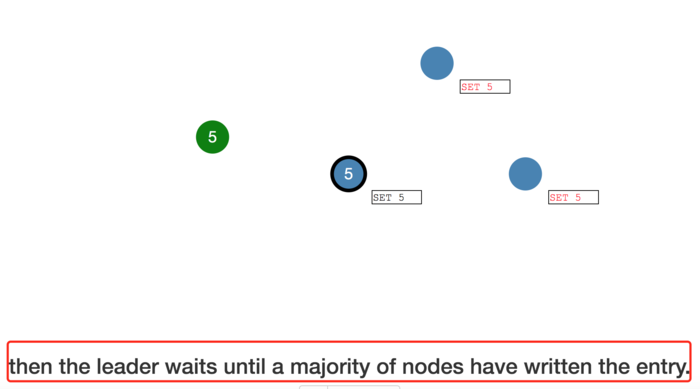
then the leader waits until a majority of nodes have written the entry.
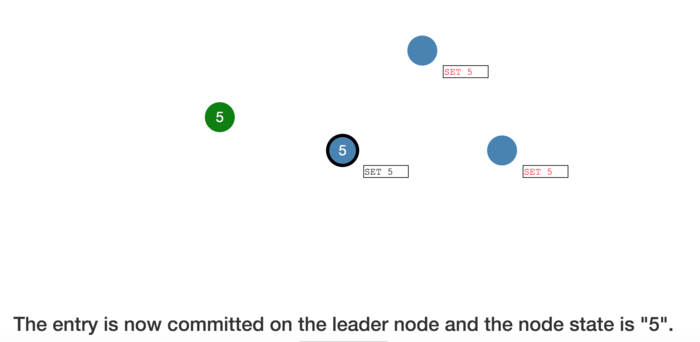
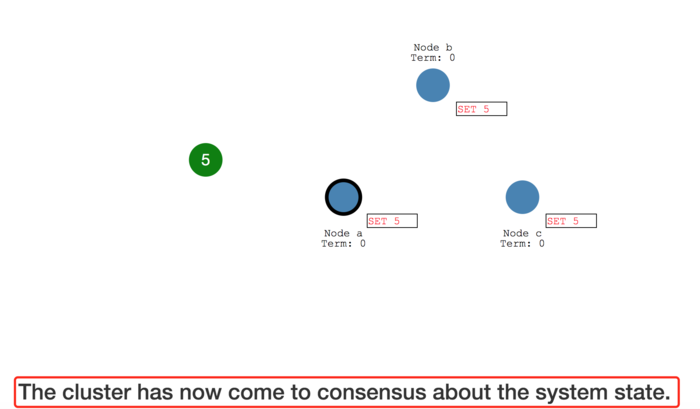
The entry is now committed on the leader node and the node state is "5".
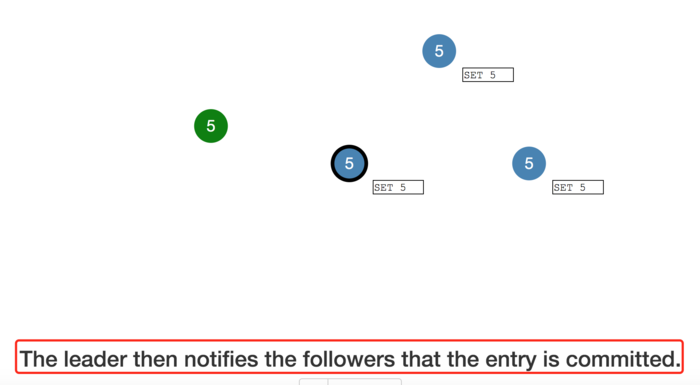
The leader then notifies the followers that the entry is committed.
The cluster has now come to consensus about the system state.
This process is called Log Replication.
3.2.1 Leader Election


3.2.2 Log Replication

参考:
- raft 演示 http://thesecretlivesofdata.com/raft/
- segmentfault.com/a/119000000…
- www.cnblogs.com/hzmark/p/pa…
- mp.weixin.qq.com/s/CmaxRM_U9…
- mp.weixin.qq.com/s/AHVMykAci…
- blog.csdn.net/westbrookli…
- juejin.cn/post/684490…
- www.jianshu.com/p/a75dec696…
- www.cnblogs.com/MaggieLXC/p…