
文章首发于 www.shaotianyu.com
一、数组和链表优缺点
1.1、数组(Array)
1.1.1 数组的优点
线性表的一种。高级数据语言中,对数组内部的元素类型没有严格的要求,这在语言中称为泛型,可以放入任何单元类型。数组的底层的硬件实现,存在一个内存管理器,每当申请一个数组的时候,计算机会在内存中开辟一段连续的地址,每一个地址可以通过内存管理器进行访问,数组访问第一个元素和其他任何一个元素的时间复杂度是相同的,都是O(1),即常数级别。由于数组可以随机访问任何一个元素,所以它的时间效率快,这是数组的优势之一。
1.1.2 数组的缺点
数组的问题出现于它增加、删除某些元素的时候。
比如现在有个数组,要在中间插入一个元素F,那么元素C、D、E就要相应的向后移动一个位置,这样一来数组插入操作的时间复杂度趋于O(1)-O(n)之间。
数组删除也是同理。
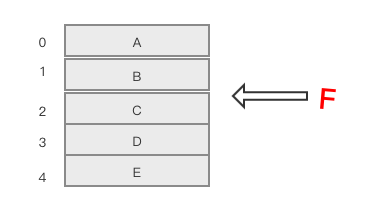
所以在增加、删除操作比较频繁的情况下,数组的缺点就会显露出来。
下面是数组中各个操作对应的时间复杂度:
| 操作 | 最大时间复杂度 |
|---|---|
| search | O(1) |
| insert | O(n) |
| remove/delete | O(n) |
| append | O(1) |
| prepend | O(1) |
1.2、链表(LinkedList)
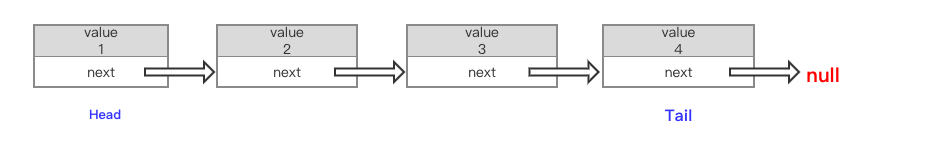
单链表
单向循环链表
1.2.1 、链表的优点
相比于数组,链表在增加节点和删除节点时候,并不会引起其他节点的群移,这样的话增加、删除操作的时间复杂度为O(1),下面是单链表插入某个节点的示意图,我们可以看到只需要更改当前节点和前置节点和的next指针,即可完成节点的插入操作。
下面是单链表的节点插入操作示意图:
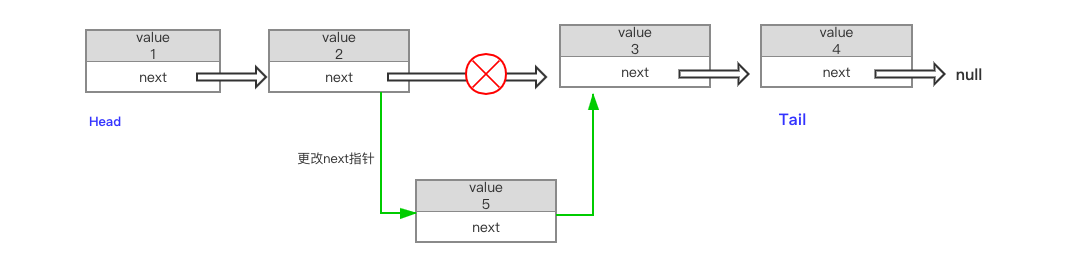
1.2.2 、链表的缺点
与数组相比,在链表中访问任一元素的位置,就没那么容易了,需要从链表的head开始,一步步的向后查询,这种情况下时间复杂度为O(1)-O(n)之间。
下面是链表中各个操作对应的时间复杂度:
| 操作 | 最大时间复杂度 |
|---|---|
| search | O(n) |
| insert | O(1) |
| remove/delete | O(1) |
| append | O(1) |
| prepend | O(1) |
1.2.3 、跳表
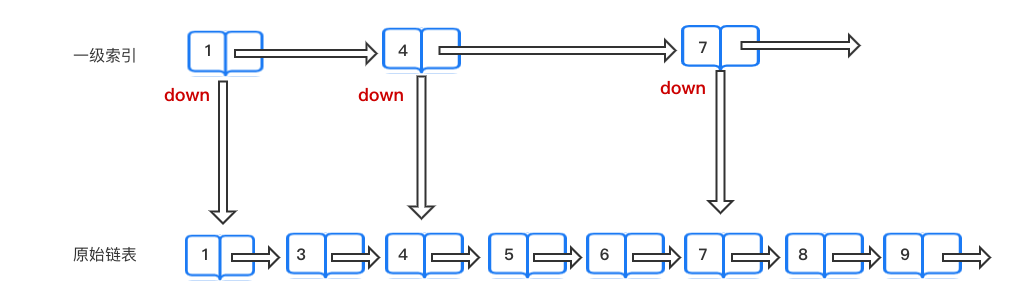
由于链表的search操作时间复杂度为O(n),为了弥补链表的缺陷,我们可以思考给链表增加多个指针去作为起始指针,这样的话search某个节点就会更有效率,从而减少search的时间复杂度。
由此引出了跳表的思想,而多个起始指针则晋升为索引的概念,通过增加维度,以空间换时间来进行时间度优化,跳表中search的时间复杂度为O(logn)。
下面是跳表中一级索引的示意图:
二、使用JS实现链表
理解了链表的几种通用形态,我们可以用js一步步实现链表这个数据结构。
2.1、单链表
实现单链表的原理在于,要不断更新节点的next指针,使整个链表串联起来。
class Node {
constructor (element) {
this.element = element
this.next = null
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor () {
// 初始化链表长度
this.length = 0
// 初始化链表第一个节点
this.head = null
}
append (element) {
let node = new Node(element)
let current
// 链表为空情况
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node
} else {
current = this.head
while (current.next) {
current = current.next
}
current.next = node
}
this.length ++
}
insert (element, point) {
if (point >=0 && point <= this.length) {
let node = new Node(element)
let current = this.head
let previous
let index = 0
if (point === 0) {
node.next = current
this.head = node
} else {
while (index++ < point) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
previous.next = node
node.next = current
}
this.length++
return true
} else {
return false
}
}
removeAt (point) {
if (point > -1 && point < this.length) {
let current = this.head
let index = 0
let previous
if (point === 0) {
this.head = current.next
} else {
while (index++ < point) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
previous.next = current.next
}
this.length--
return current.element
} else {
return null
}
}
remove (element) {
let index = this.find(element)
// 删除后返回已删除的节点
return this.removeAt(index)
}
find (element) {
let current = this.head
let index = 0
if (element == current.element){
return 0;
}
while (current.next) {
if(current.element === element) {
return index
}
index++
current = current.next
}
if (element == current.element){
return index;
}
return -1
}
isEmpty () {
return this.length === 0
}
size () {
return this.length
}
print () {
let current = this.head
let result = ''
while (current) {
result += current.element + (current.next ? '->' : '')
current = current.next
}
return result
}
}
let l1 = new LinkedList()
...
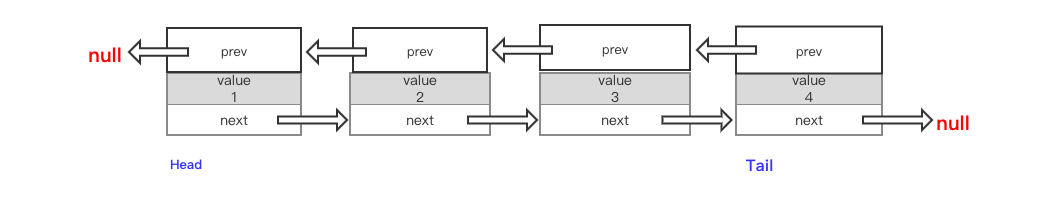
2.2、双向链表
实现双向链表的原理在于,每次更新链表要同时考虑到next和prev两个指针,并保证更新指针的指向。
class Node {
constructor (element) {
this.element = element
this.next = null
this.prev = null
}
}
class DoubleLinkedList {
constructor () {
this.length = 0
this.head = null
// 定义尾部节点
this.tail = null
}
append (element) {
let node = new Node(element)
let tail = this.tail
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node
this.tail = node
} else {
tail.next = node
node.prev = tail
this.tail = node
}
this.length++
}
insert (element, point) {
if(point >= 0 && point <= this.length) {
let node = new Node(element)
let current = this.head
let tail = this.tail
let index = 0
let previous
if (point === 0) {
if (!this.head) {
this.head = node
this.tail = node
} else {
node.next = current
current.prev = node
this.head = node
}
} else if (point === this.length) {
current = tail
current.next = node
node.prev = current
this.tail = node
} else {
while (index++ < point) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
// 将原来的链表断开,重新使用指针串接起来
node.next = current
node.prev = previous
previous.next = node
current.prev = node
}
this.length++
return true
} else {
return false
}
}
removeAt (point) {
if (point > -1 && point < this.length) {
let current = this.head
let index = 0
let previous
let tail = this.tail
if (point === 0) {
// remove第一项的情况
this.head = current.next
if (this.length === 1) {
this.tail = null
} else {
this.head.prev = null
}
} else if (point === this.length -1) {
current = tail
this.tail = current.prev
this.tail.next = null
} else {
while (index++ < point) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
previous.next = current.next
current.next.prev = previous
}
this.length--
return current.element
} else {
return null
}
}
find (element) {
let current = this.head
let index = 0
if (element == current.element){
return 0;
}
while (current.next) {
if(current.element === element) {
return index
}
index++
current = current.next
}
// 为了保证最后一位被找到
if (element == current.element){
return index;
}
return -1
}
remove (element) {
let index = this.find(element)
return this.removeAt(index)
}
isEmpty () {
return this.length === 0
}
size () {
return this.length
}
print () {
let current = this.head
let result = ''
while (current) {
result += current.element + (current.next ? '->' : '')
current = current.next
}
return result
}
}
let l1 = new DoubleLinkedList()
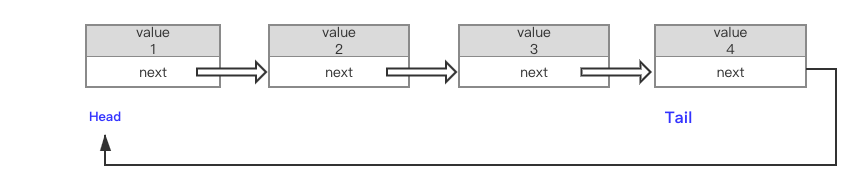
2.3、单向循环链表
单向循环链表和单链表大致相同,唯一区别是,尾节点tail的next指针要指向head,使链表的头尾串联在一起,形成循环。
class Node {
constructor (element) {
this.element = element
this.next = null
}
}
class CircleLinkedList {
constructor () {
// 初始化链表长度
this.length = 0
// 初始化链表第一个节点
this.head = null
}
append (element) {
let node = new Node(element)
let head = this.head
let current
// 链表为空情况
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node
} else {
current = this.head
while (current.next && current.next !== head) {
current = current.next
}
current.next = node
}
// 保持首尾相连
node.next = head
this.length ++
}
insert (element, point) {
if (point >=0 && point <= this.length) {
let node = new Node(element)
let current = this.head
let previous
let index = 0
if (point === 0) {
node.next = current
while (current.next && current.next !== this.head) {
current = current.next
}
this.head = node
current.next = this.head
} else {
while (index++ < point) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
previous.next = node
// 首尾相连
node.next = current === null ? head : current
}
this.length++
return true
} else {
return false
}
}
removeAt (point) {
if (point > -1 && point < this.length) {
let current = this.head
let index = 0
let previous
if (point === 0) {
this.head = current.next
while (current.next && current.next !== this.head) {
current = current.next
}
current.next = this.head
} else {
while (index++ < point) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
previous.next = current.next
}
this.length--
return current.element
} else {
return null
}
}
remove (element) {
let index = this.find(element)
// 删除后返回已删除的节点
return this.removeAt(index)
}
find (element) {
let current = this.head
let index = 0
if (element == current.element){
return 0;
}
while (current.next && current.next !== this.head) {
if(current.element === element) {
return index
}
index++
current = current.next
}
if (element == current.element){
return index;
}
return -1
}
isEmpty () {
return this.length === 0
}
size () {
return this.length
}
print () {
let current = this.head
let result = ''
while (current.next && current.next !== this.head) {
result += current.element + (current.next ? '->' : '')
current = current.next
}
result += current.element
return result
}
}
let l1 = new CircleLinkedList()
2.4、双向循环链表
双向循环链表和单向循环原理上大概一致,区别在于,双向循环链表同时拥有2个指针prev和next,并在head和tail两个临界点进行指针更新处理,并保持链表的首尾相连。
三、小结
以上是我对链表数组相关数据结构的浅薄认知,如有纰漏,还望指出~~
以上代码部分参考了书籍《javascript数据结构和算法》~~
🍺🍺🍺🍺🍺