此时webpack版本为v4.42.0.
介绍
学习过程中的demo已上传gitee,点击跳转地址
为什么使用
前端网页功能丰富,尤其是spa技术流行后, 打包:JavaScript的复杂度增加和需要一大堆依赖包
转换编译:Sass、less、ES6/ES7等的编译
优化:页面复杂之后,性能也会遇到问题,而webpack也可以做到优化
原理
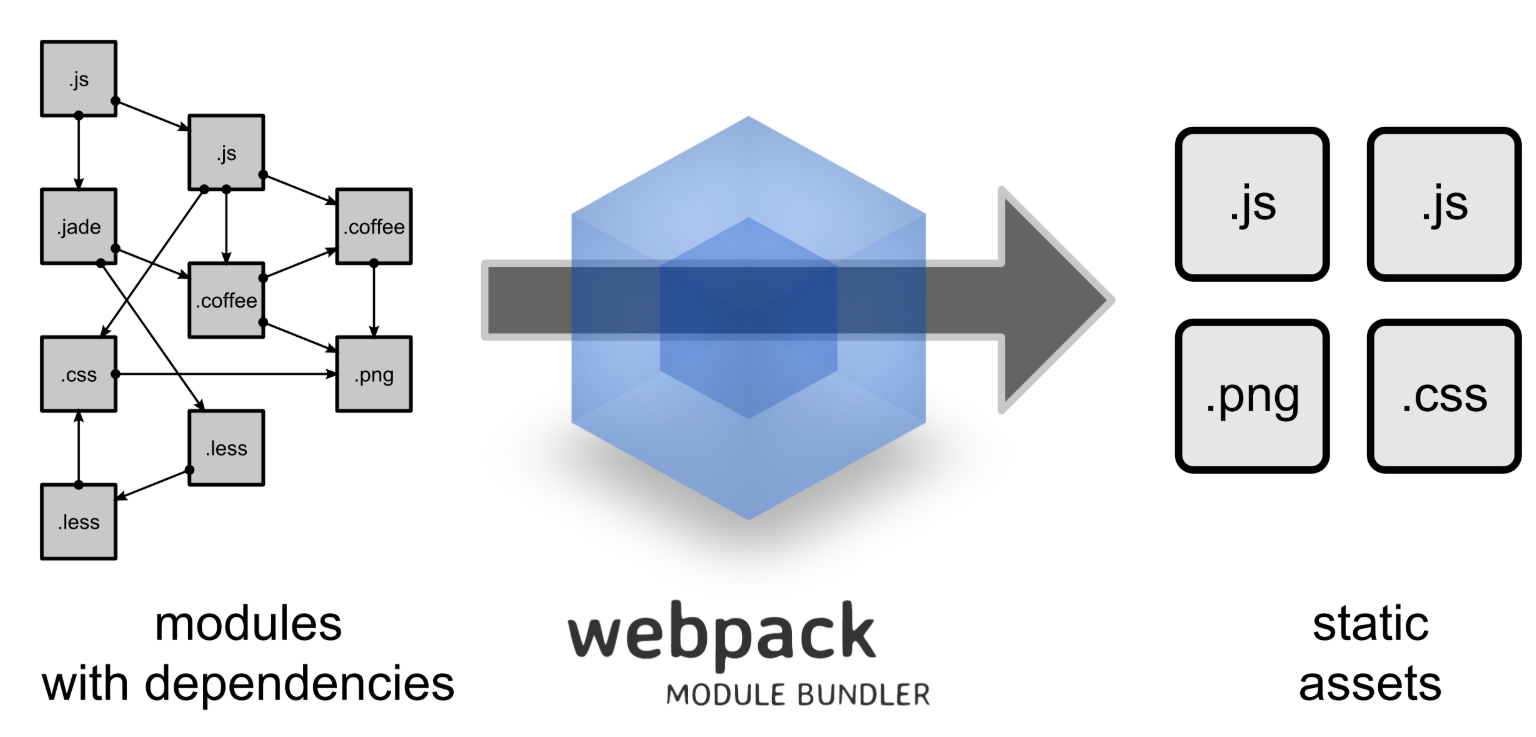
安装
//全局安装
npm install -g webpack
// 初始化
npm init
// 安装webpack
npm install --save-dev webpack webpack-dev-server webpack-cli
使用
单文件入口
// webpack.base.js 根目录下新建
const path = require('path');
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: 'bundle.js',
},
};
// 打包
npm run build
多文件入口
const path = require('path');
module.exports = {
entry: {
entry: './src/index.js',
second: './src/second.js',
},
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: '[name].js',
publicPath: 'static',
},
// chunkFilename: '',
};
// 结果
dist/entry.js dist/second.js
配置项
mode
告知 webpack使用相应模式的内置优化。
production: 注重模块大小(默认值),进行脚本压缩
development: 调试,热更新
webpack会根据mode生成一个process.env.NODE_ENV变量,是webpack.DefinedPlugin中定义的全局变量,允许根据不同环境执行不同代码,例如:
if (process.env.NODE_ENV==='development') {
// 开发环境执行
} else {
// 生产环境执行
}
生产环境下,uglify打包代码时会自动删除不可达代码,也就是说生产环境压缩后最终的代码为:
// 生产环境执行
热更新HMR
在开发环境中,我们需要快速调试代码,因此需要本地服务器访问webpack打包后的静态文件
优点:
- 保留在完全重新加载页面时丢失的应用程序状态
- 只更新变更内容,以节省时间
- 调整样式更加快速,几乎相当于在浏览器调试器中更改样式
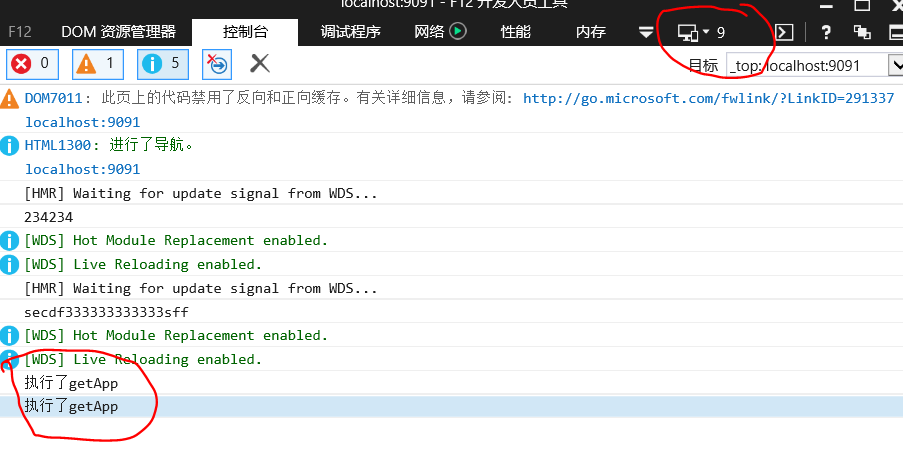
监听之后,热更新并不会生成实际打包文件,只是存在内存中,没有磁盘IO,速度更快
webpack-dev-server是webpack官方提供的工具,当mode为development时可开启热更新,实时预览修改后的代码。
首先我们已经安装了webpack-dev-server,接下来需要在package.json中配置scripts,
scripts: {
dev: 'webpack-dev-server --mode development --config webpack.base.js',
}
// webpack.base.js
const path = require('path');
const distSrc = path.resolve(__dirname, '../dist');
module.exports = {
entry: {
entry: path.resolve(__dirname, '../src/index.js'),
second: path.resolve(__dirname, '../src/second.js'),
},
output: {
path: distSrc,
filename: '[name].js',
},
devServer: {
contentBase: distSrc,
port: '9091', // 本地访问端口号
compress: true, // 是否开启压缩
hot: true, // 开启热更新
},
};
devServer
常用参数:
host - default:'localhost'
hot - 启动热更新
hotOnly- 只有包含HMR的模块会启动热更新
在应用中,
在编辑器中,
在模块中,如果模块内实现了HMR接口,到HMR接收到更新,会使用更新替换旧的。然而并不是所有模块都需要HMR接口,当一个模块没有实现HMR接口时,那么他的更新会冒泡,意味着一个简单的处理函数能对整个模块树进行更新。
在这样的模块中,一个单独的模块更新,整个依赖块会被重新加载。
在HMR Runtime中
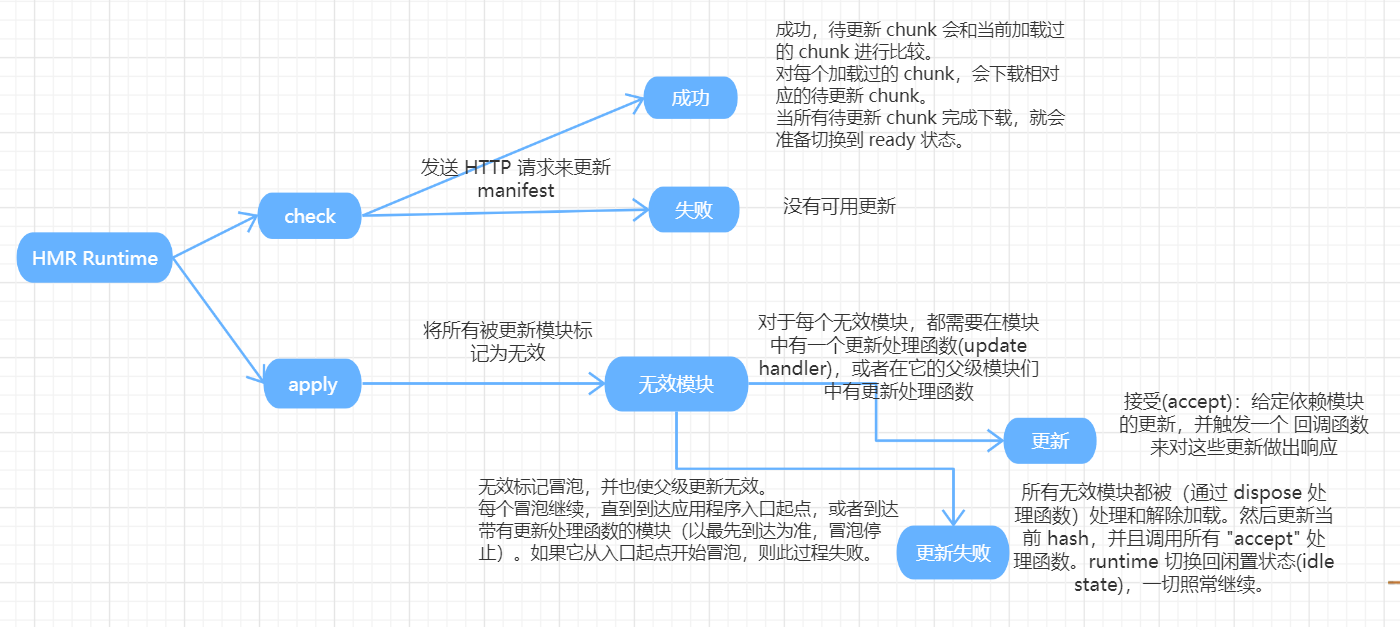
loader
loader用于对源代码进行转换。可以将不同的语言转换为JavaScript。可以预处理import或加载模块时预处理文件。loader可以将内联图像转化为data URL,甚至允许直接在JavaScript中import css文件、
loader的三个参数:
test:匹配处理文件的扩展名
use:loader名称,要使用的模块的名称
include/exclude:添加必须处理的文件或屏蔽不需要处理的文件
query:为loaders提供额外的设置选项。
css-loader: The css-loader interprets @import and url() like import/require() and will resolve them.
主要是为了处理 CSS 中的依赖,例如 @import 和 url() 等引用外部文件的声明
style-loader: Inject CSS into the DOM.
会将 css-loader 解析的结果转变成 JS 代码,运行时动态插入 style 标签来让 CSS 代码生效。
url-loader/file-loader: 用来处理jpg/png/gif等文件格式
sass-loader node-sass 用来解析scss文件
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.(css|less)$/,
use: [
{
loader: 'style-loader'
},
{
loader: 'css-loader',
options: {
importLoaders: 1,
},
},
{
loader: 'postcss-loader',
options: {
ident: 'postcss',
plugins: (loader) => [
require('postcss-import')({ root: loader.resourcePath }),
require('postcss-cssnext')(),
require('autoprefixer')(),
require('cssnano')(),
],
},
},
{
loader: 'less-loader',
options: {
importLoaders: 1,
},
},
],
},
{
test: /\.(png|jpg|gif)/,
use: {
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 1024,
fallback: {
loader: 'file-loader',
options: {
name: 'img/[name].[hash:8].[ext]',
},
},
},
},
}
],
},
或
rules: [
{ test: '', use: '' }
],
babel
目前低版本浏览器不支持es6/es7语法,需要转成es5语法。
打包之后:

// 可解决箭头函数等,但无法解决promise,symbol等内建对象
npm install -D babel-loader @babel/core @babel/preset-env
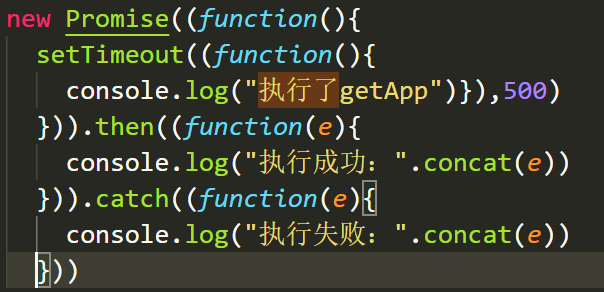
引入babel-polyfill,需要在生产环境中使用
npm intall --save babel-polyfill
未引入babel-polyfill
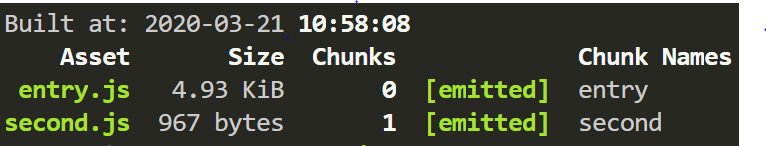
引入之后
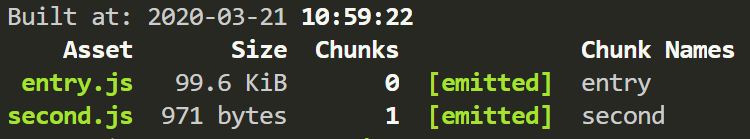
可以很明显发现 entry.js 体积大了很多,因为 babel-polyfill 会污染全局环境,将 promise 添加为全局变量。此时就需要 plugin-transform-runtime
优点:
不会污染全局变量 多次使用只会打包一次 依赖统一按需引入,无重复引入,无多余引入
{
test: /\.js$/,
use: {
loader: 'babel-loader',
options: {
presets: ['@babel/preset-env'],
plugins: ['@babel/plugin-transform-runtime'],
},
},
}
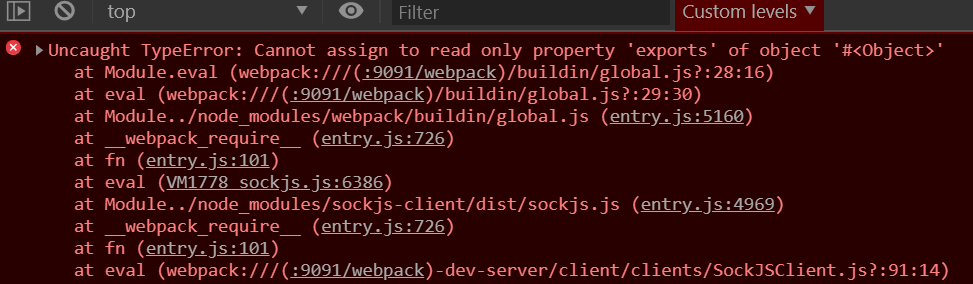
// error
Uncaught TypeError: Cannot assign to read only property 'exports' of object '#<Object>'
使用@babel/plugin-transform-runtime这个插件的时候,同时你又在某个commonJS写的文件里使用这个插件时,babel会默认你这个文件是ES6的文件,然后就使用import导入了这个插件,从而产生了import和module.exports混用的错误。解决方法是在babel.config.js里配置unambiguous设置,让babel和webpack一样严格区分commonJS文件和ES6文件。
{
test: /\.js$/,
use: {
loader: 'babel-loader',
options: {
presets: ['@babel/preset-env'],
plugins: ['@babel/plugin-transform-runtime'],
sourceType: 'unambiguous',
},
},
},
plugin
在 webpack 构建过程中,plugin 用户处理更多其他构建任务,loader 用来转换语言,更好的兼容。
分块、压缩、优化
自从webpack升级到4以来,号称零配置。代码会自动分割、压缩、优化,同时 webpack也会自动帮你 Scope hoisting 和 Tree-shaking。
当多个 bundle共享一些相同的依赖,需要提取这些依赖到共享的 bundle 中,来避免重复打包。CommonsChunkPlugin在webpack4.0被移除了,取而代之的是optimization.splitChunks and optimization.runtimeChunk
内置代码分隔策略:
新的chunk是否被共享或者来自node_modules的模块
新的chunk体积在压缩前是否大于30kb
按需加载chunk的并发请求数量小于等于5
页面初始加载时的并发请求数量小于等于3
chunk分析插件
npm install --save-dev webpack-bundle-analyzer
// vue.config.js or webpack.base.js
const { BundleAnalyzerPlugin } = require('webpack-bundle-analyzer');
plugins: [
new BundleAnalyzerPlugin({
analyzerMode: 'server',
// analyzerHost: '127.0.0.1',
analyzerPort: 7777,
reportFilename: 'index.html',
defaultSizes: 'parsed',
openAnalyzer: true,
generateStatsFile: false,
statsFilename: 'stats.json',
statsOptions: null,
logLevel: 'info',
}),
],
// package.json
scripts: {
"analyze": "NODE_ENV=production npm_config_report=true npm run build"
},
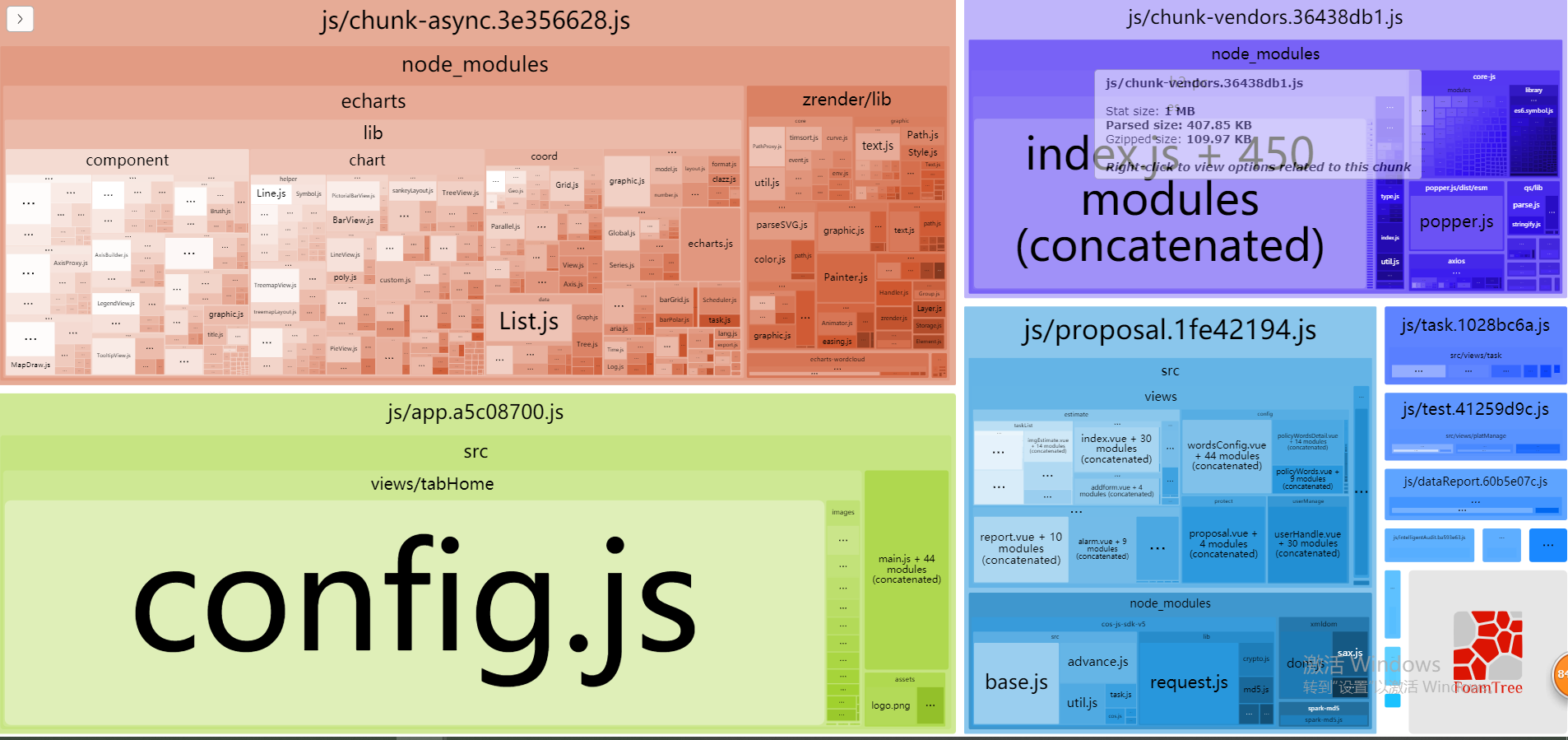
DefinePlugin
允许创建一个在编译时可以使用的全局变量。
分离css
mini-css-extract-plugin
npm install --save-dev mini-css-extract-plugin
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require('mini-css-extract-plugin');
output: {
filename: '[name].js',
// 解决html里img的路径问题,都改为
publicPath: 'http://localhost:9091',
},
plugins: [
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({
filename: 'css/[name].js',
chunkFilename: '[id].css',
}),
],
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.(css|less)$/,
use: [
MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader,
css-loader,
less-loader,
],
}
],
}
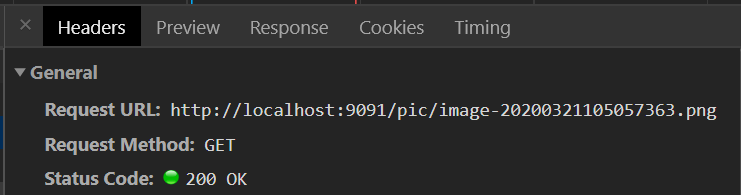
html中引入的图片:
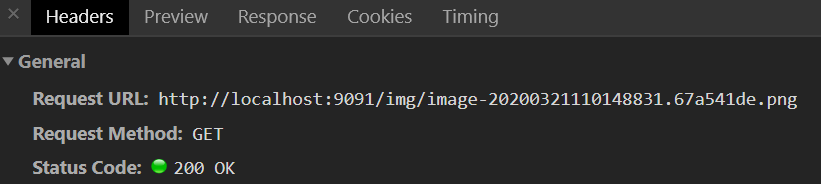
css中引入的图片:
自动添加css属性前缀
为css加前缀autoprefixer。前面在写到css-loader时,有为css添加postcss-loader,其中包括autoprefixer插件
rules: [
{
test: /\.(css|less)$/,
use: [
MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader,
'css-loader',
'post-loader',
],
}
],
// 在根目录添加文件 postcss.config.js
module.exports = {
plugins: {
autoprefixer: {},
},
};
// 在根目录添加文件 .browserslistrc(推荐)
> 1%
last 2 versions
not ie <= 8
// 或 在package.json中添加(不推荐)
"browserslist": [
"last 1 version",
"> 1%",
"IE 10"
]
忽略模块打包
IgnorePlugin:忽略某些特定模块,让webpack不把这些特定模块打包进去。
module.exports = {
// ...
plugins: [
new webpack.IgnorePlugin(/^\.\/locale$/, /moment$/)
]
}
IgnorePlugin配置的参数有两个,第一个是匹配引入模块路径的正则表达式,第二个是匹配模块的对应上下文,即所在目录名。
在vue-cli中忽略打包模块的配置:
module.exports = {
chainWebpack: (config) => {
config.externals({
'element-ui': 'ElEMENT',
'moment': 'moment',
}),
}
};
这些被忽略不打包的文件,可以通过script形式引入。
<script src="<%= BASE_URL %>element-ui@2.13.0.js"></script>
<script src="<%= BASE_URL %>moment.min@2.22.2.js"></script>
分离代码文件
为了实现减小打包后的代码体积,利用缓存来加速静态资源访问,需要将不同且互不影响的代码块分离出来,plugin中说过可以使用mini-css-extract-plugin来对css文件进行分离,除此之外,建议将公共使用的第三方类库显式的配置为公共的部分。因为在第三方库的实际开发中,几乎不会改变,可以避免因公共chunk的频繁变更而导致缓存失效。
hash: 每次构建都会重新全部生成,所有文件hash值相同,无论是否修改都会重新生成,起不到缓存效果
chunkhash:根据不同入口文件进行依赖文件解析,构建对应chunk,生成对应的hash,不改变代码就不需重新构建。
contenthash: 因css和js用的同一个chunkhash,所以只改变js时,css也会重新生成。所以css使用contenthash
module.exports = {
entry: {
vendor: ["react", "lodash", "angular", ...], // 指定公共使用的第三方类库
},
optimization: {
splitChunks: {
cacheGroups: {
vendor: {
chunks: "initial",
test: "vendor",
name: "vendor", // 使用 vendor 入口作为公共部分
enforce: true,
},
},
},
},
// ... 其他配置
}
// 或者
module.exports = {
optimization: {
splitChunks: {
cacheGroups: {
vendor: {
test: /react|angluar|lodash/, // 直接使用 test 来做路径匹配
chunks: "initial",
name: "vendor",
enforce: true,
},
},
},
},
}
// 或者
module.exports = {
optimization: {
splitChunks: {
cacheGroups: {
vendor: {
chunks: "initial",
test: path.resolve(__dirname, "node_modules") // 路径在 node_modules 目录下的都作为公共部分
name: "vendor", // 使用 vendor 入口作为公共部分
enforce: true,
},
},
},
},
}...
vue-cli中的vue.config.js
module.exports = {
chainWebpack: (config) => {
config.optimization.splitChunks(Object.assign({}, splitOptions, {
name: false,
cacheGroups: {
default: false,
vendors: {
name: 'chunk-vendors',
test: /[\\/]node_modules|plat-utils[\\/]/,
minChunks: 2,
priority: 11,
chunks: 'all',
reuseExistingChunk: true,
},
betterScroll: {
test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]better-scroll[\\/]/,
name: 'better-scroll',
priority: 12,
chunks: 'all',
reuseExistingChunk: true,
enforce: true,
},
vueRouter: {
test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]vue-router[\\/]/,
name: 'vue-router',
enforce: true,
priority: 12,
chunks: 'all',
reuseExistingChunk: true,
},
vueLazyload: {
test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]vue-lazyload[\\/]/,
name: 'vueLazyload',
enforce: true,
priority: 12,
chunks: 'all',
reuseExistingChunk: true,
},
},
}));
}
};
resolve.alias
module.exports = {
resolve: {
alias: {
utils: path.resolve(__dirname, 'src/utils'),
},
},
};
引用时:
// 原引用方式
import cookie from './utils/cookie';
// alias之后
import cookit form 'utils/cookie';
vue-cli中的vue.config.js
module.exports = {
configureWebpack: {
resolve: {
alias: {
'utils': path.resolve('utils'), // 配置别名
},
},
},
chainWebpack: (config) => {
config.resolve.alias.set('utils', path.resolve(__dirname, 'src/components'));
}
};
引用:
笔记是之前记录的,最近在复习,顺便发下,有理解不对的地方欢迎指正。
优化问题
待更新