背景
最近收到小伙伴的一个吐槽:“项目里的某个函数是同步阻塞的,无法确定其运行时间,某些情况下,可能出现长时间阻塞导致应用无法响应”。为了解决这个问题,他尝试过用子线程+定时器的方式去异步处理,如果超时,则重新调用,但该函数会被频繁调用,意味着每次调用都要创建一个定时器。听到这个场景后,下意识想起之前看到的一篇文章:时间轮片(Timing Wheel)实现心跳机制。该文章主要描述了使用时间轮片的方式去处理TCP心跳连接,从而避免每个连接都要开启一个计时器。明确了时间轮片方式的优势后,便尝试着手实现一个通用的基于时间轮片方式处理超时任务的框架。
时间轮
简单来说,时间轮就是一个循环列表,每个列表中包含一个称为槽的结构,这个结构通常也可以是一个列表,且每隔一定时间就会将指针向前移动。
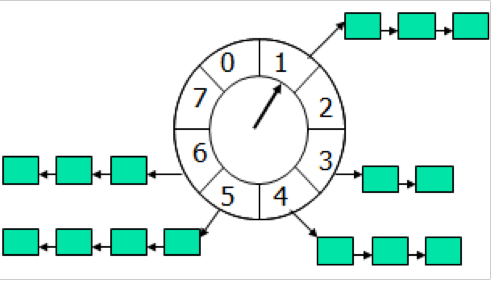
iOS 时间轮实现方案
可以使用一个嵌套数组的形式来定义时间轮结构,并用定时器去定时遍历列表中的元素。
class TimeWheel {
private var capacity: Int
private var interval: TimeInterval
private var timeWheel: [[Any]]
var index: Int
private var timer: Timer?
weak var delegate: TimeWheelDelegate?
}
- 初始化时,我们需要建立N个空槽,用于存取数据
init(_ capacity: Int, _ interval: TimeInterval) {
self.capacity = capacity
self.interval = interval
self.index = 0
timeWheel = []
for _ in 0 ..< capacity { //先填充空数组,创建若干个“空槽”
self.timeWheel.append([])
}
}
- 添加任务时,如未启动定时器,则启动定时器,并把元素添加到当前槽位中
func addObject(_ task: Any) {
if timer == nil {
timer = Timer.scheduledTimer(timeInterval: 1.0, target: self, selector: #selector(detectTimeoutItem(_:)), userInfo: nil, repeats: true)
RunLoop.current.add(timer!, forMode: .common)
}
if index < timeWheel.count {
var arr = timeWheel[index]
arr.append(task)
timeWheel[index] = arr
}
}
- 定时检查,先将位置移动到下一位,然后将对应槽位的元素传递给外部,最后清除该槽位的元素
@objc
private func detectTimeoutItem(_ timer: Timer) {
moveToNextTimeSlot()
delegate?.timeoutItems(self.currentObjects(), self)
removeExpiredObjects()
}
完整代码
protocol TimeWheelDelegate : class {
func timeoutItems(_ items: [Any]?, _ timeWheel: TimeWheel)
}
class TimeWheel {
private var capacity: Int
private var interval: TimeInterval
private var timeWheel: [[Any]]
var index: Int
private var timer: Timer?
weak var delegate: TimeWheelDelegate?
init(_ capacity: Int, _ interval: TimeInterval) {
self.capacity = capacity
self.interval = interval
self.index = 0
timeWheel = []
for _ in 0 ..< capacity { //先填充空数组,创建若干个“空槽”
self.timeWheel.append([])
}
}
func addObject(_ task: Any) {
if timer == nil {
timer = Timer.scheduledTimer(timeInterval: 1.0, target: self, selector: #selector(detectTimeoutItem(_:)), userInfo: nil, repeats: true)
RunLoop.current.add(timer!, forMode: .common)
}
if index < timeWheel.count {
var arr = timeWheel[index]
arr.append(task)
timeWheel[index] = arr
}
}
func currentObjects() -> [Any]? {
if index < timeWheel.count {
return timeWheel[index]
}
return nil
}
func cleanup() {
self.timeWheel.removeAll()
if timer != nil {
timer?.invalidate()
timer = nil
}
}
private func removeExpiredObjects() {
if index < timeWheel.count {
var arr = timeWheel[index]
arr.removeAll()
}
}
private func moveToNextTimeSlot() {
index = (index + 1) % timeWheel.count
}
@objc
private func detectTimeoutItem(_ timer: Timer) {
moveToNextTimeSlot()
delegate?.timeoutItems(self.currentObjects(), self)
removeExpiredObjects()
}
}
任务管理
- 定义一个任务协议,用于定义其通用行为
protocol Task {
associatedtype T
func taskKey() -> String //任务对应的唯一key,用于区分任务
func doTask() -> T // 实现任务行为
var completion: ((_ result: T?, _ timeout: Bool) -> Void)? {get set} //返回的异步结果
}
- 定义一个具体的
Task
class NetworkTask: Task {
typealias T = String
var completion: ((String?, Bool) -> Void)?
var hostName: String
init(_ name: String) {
hostName = name
}
func taskKey() -> String {
return hostName
}
func doTask() -> String {
Thread.sleep(forTimeInterval: Double.random(in: 1...20)) //模拟耗时任务
return "\(hostName)'s result"
}
}
- 任务管理
为了保证任务的独立允许,需要创建一个并发队列,且使用字典存储已添加的任务,以便确认任务是按时完成回调的,还是超时导致回调的。
class TaskManager<T: Task> : TimeWheelDelegate {
private var timeWheel: TimeWheel?
private var timeInterval: TimeInterval
private var timeoutSeconds: Int
private var queue: DispatchQueue
private var callbackDict: Dictionary<String, T>
init(_ timeout: Int, _ timeInterval: TimeInterval) {
timeoutSeconds = timeout
self.timeInterval = timeInterval
queue = DispatchQueue(label: "com.task.queue", qos: .default, attributes: .concurrent, autoreleaseFrequency: .workItem, target: nil)
callbackDict = [:]
}
}
- 添加任务:开启时间轮,且将任务提交到队列中
func appendTask(_ task: T, _ completion:@escaping (_ result: T.T?, _ timeout: Bool) -> (Void)) {
if timeWheel == nil {
timeWheel = TimeWheel(timeoutSeconds, timeInterval)
timeWheel?.delegate = self
}
var task = task
task.completion = completion
self.callbackDict[task.taskKey()] = task
self.timeWheel?.addObject(task) //将任务添加到对应的时间轮槽位中
self.queue.async {
let result = task.doTask()
DispatchQueue.main.async { //保证数据的一致性
let key = task.taskKey()
if let item = self.callbackDict[key] {
item.completion?(result, false) //返回按时完成任务的结果
self.callbackDict.removeValue(forKey: key)
}
}
}
}
- 处理超时任务:通过定时轮返回的过期数据,将任务超时回调返回。
func timeoutItems(_ items: [Any]?, _ timeWheel: TimeWheel) {
if let callbacks = items {
for callback in callbacks {
if let item = callback as? T, let task = self.callbackDict[item.taskKey()] {
task.completion?(nil, true)
self.callbackDict.removeValue(forKey: task.taskKey())
}
}
}
}
完整代码
class TaskManager<T: Task> : TimeWheelDelegate {
private var timeWheel: TimeWheel?
private var timeInterval: TimeInterval
private var timeoutSeconds: Int
private var queue: DispatchQueue
private var callbackDict: Dictionary<String, T>
init(_ timeout: Int, _ timeInterval: TimeInterval) {
timeoutSeconds = timeout
self.timeInterval = timeInterval
queue = DispatchQueue(label: "com.task.queue", qos: .default, attributes: .concurrent, autoreleaseFrequency: .workItem, target: nil)
callbackDict = [:]
}
func appendTask(_ task: T, _ completion:@escaping (_ result: T.T?, _ timeout: Bool) -> (Void)) {
if timeWheel == nil {
timeWheel = TimeWheel(timeoutSeconds, timeInterval)
timeWheel?.delegate = self
}
var task = task
task.completion = completion
self.callbackDict[task.taskKey()] = task
self.timeWheel?.addObject(task) //将任务添加到对应的时间轮槽位中
self.queue.async {
let result = task.doTask()
DispatchQueue.main.async { //保证数据的一致性
let key = task.taskKey()
if let item = self.callbackDict[key] {
item.completion?(result, false) //返回按时完成任务的结果
self.callbackDict.removeValue(forKey: key)
}
}
}
}
func timeoutItems(_ items: [Any]?, _ timeWheel: TimeWheel) {
if let callbacks = items {
for callback in callbacks {
if let item = callback as? T, let task = self.callbackDict[item.taskKey()] {
task.completion?(nil, true)
self.callbackDict.removeValue(forKey: task.taskKey())
}
}
}
}
}
使用示例
定义任务超时时间为10s,并每1s进行检查一次。这里加了一个随机时间添加任务,以便测试到时间轮不同轮的情况。
let manager = TaskManager<NetworkTask>(10, 1)
for i in 0 ..< 5 {
let task = NetworkTask("host-\(i)")
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now()+Double.random(in: 0...20.0)) {
print("task:\(task.hostName) do task in \(Date.init())")
manager.appendTask(task) { (result, timeout) -> (Void) in
print("task:\(task.hostName), result:\(result ?? "null"), timeout:\(timeout), time:\(Date.init())")
}
}
}
结果数据:
task:host-4 do task in 2020-03-19 11:56:46 +0000
task:host-1 do task in 2020-03-19 11:56:47 +0000
task:host-2 do task in 2020-03-19 11:56:56 +0000
task:host-4, result:null, timeout:true, time:2020-03-19 11:56:56 +0000
task:host-1, result:null, timeout:true, time:2020-03-19 11:56:56 +0000
task:host-2, result:host-2's result, timeout:false, time:2020-03-19 11:57:01 +0000
task:host-3 do task in 2020-03-19 11:57:03 +0000
task:host-0 do task in 2020-03-19 11:57:03 +0000
task:host-0, result:host-0's result, timeout:false, time:2020-03-19 11:57:09 +0000
task:host-3, result:null, timeout:true, time:2020-03-19 11:57:12 +0000
根据结果,可以看到,若任务10s内能按时完成,则返回对应的任务结果,否则返回timeout为true,并返回一个空结果。
总结
通过这次的事例,实现一个基于时间轮方式来处理超时任务的简单框架,从一定程度上避免了性能的消耗。