Reactor
BIO 模式
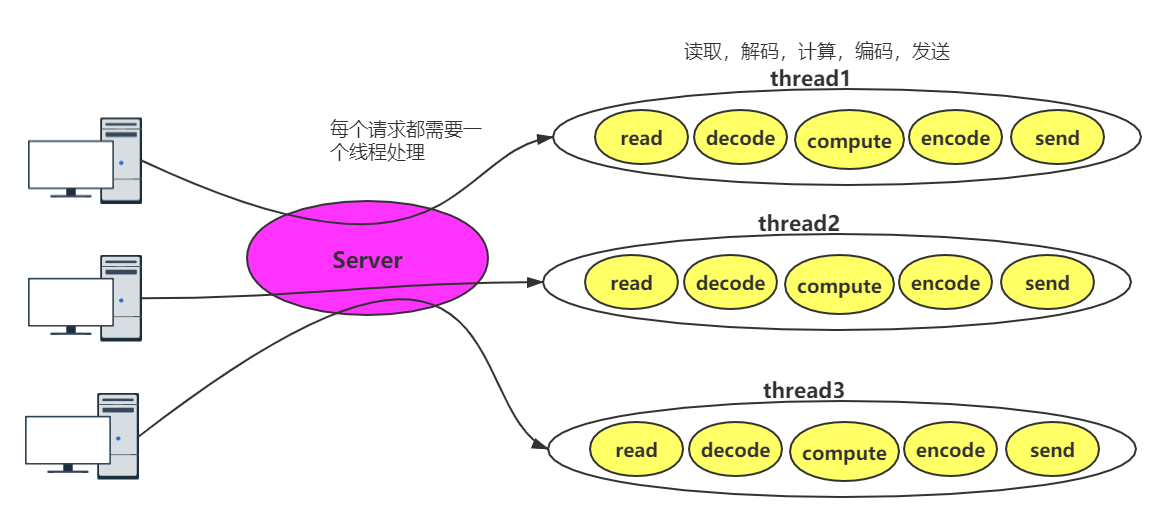
BIO模式是最简单的,也是最符合人类思维模式的,但是效率太低,为什么呢?
- BIO的核心是每个请求对应一个线程处理,因此严重依赖线程,线程是Java虚拟机中非常宝贵的资源,一旦并发访问量过大,会导致服务端性能急剧下降
- 服务端 accept 阶段由于网速、IO等原因是会阻塞的,如果有大量请求阻塞,会导致线程资源紧张,最终影响服务端性能
Reactor 模式
Reactor模式的目的主要是提高系统的吞吐量,在有限的资源下处理更多的事情
在单核的机器上,多线程并不能提高系统的性能,除非在有一些阻塞的情况发生。否则线程切换的开销会使处理的速度变慢。就像你一个人做两件事情,1、削一个苹果。2、切一个西瓜。那你可以一件一件的做,我想你也会一件一件的做。如果这个时候你使用多线程,一会儿削苹果,一会切西瓜,可以相像究竟是哪个速度快。这也就是说为什么在单核机上多线程来处理可能会更慢。
但当有阻碍操作发生时,多线程的优势才会显示出来,现在你有另外两件事情去做,1、削一个苹果。2、烧一壶开水。我想没有人会去做完一件再做另一件,你肯定会一边烧水,一边就把苹果削了。
Reactor实际上采用了分而治之和事件驱动的思想
分而治之: 一个完整的网络处理过程一般分为 accept,read,decode,process,encode,send这几步。Reactor模式将每个步骤映射为 一个Task,服务端线程执行的最小逻辑单元不再是一个完整的网络请求,而是 Task,且采用非阻塞方式执行
事件驱动: 每个Task 对应特定的网络事件,当Task 准备就绪时,Reactor 收到对应的网络事件通知,并将Task 分发给绑定了对应网络事件的 Handler 执行
Reactor 单线程模型
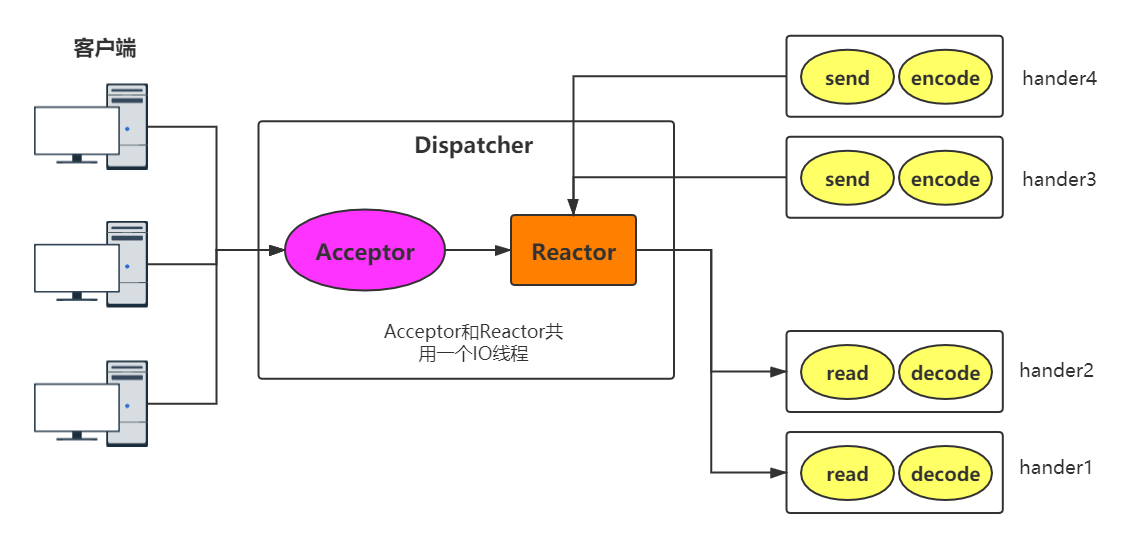
Reactor单线程模型,是指所有的IO操作都在同一个NIO线程上面完成
缺点:当其中某个Handler阻塞时,会导致其他Client 的Handler 都不能执行,更严重的情况会导致整个服务不能接收新的Client 请求
Reactor 多线程模型
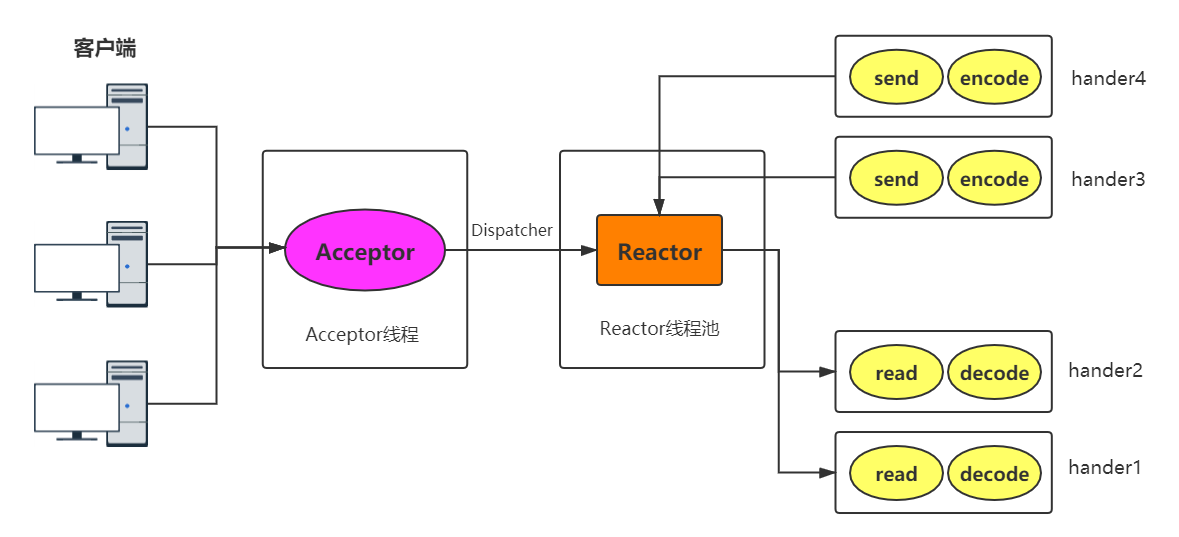
- 一个专有线程,即Acceptor 线程用于监听Client 的TCP 连接请求
- Client 的IO 操作都由一个特定的NIO 线程池负责,负责消息的读取、解码、编码和发送
- Client连接有很多,但是NIO 线程数是比较少的,一个NIO 线程可以同时绑定到多个Client,同时一个Client只能对应一个线程,避免出现线程安全问题
在绝大多数情况下,Reactor 多线程模型可以满足高并发的网络请求
当并发量达到百万或者client连接需要进行验证且验证消耗很大时,单个 Acceptor线程可能会存在性能不足的问题
Reactor 主从多线程模型
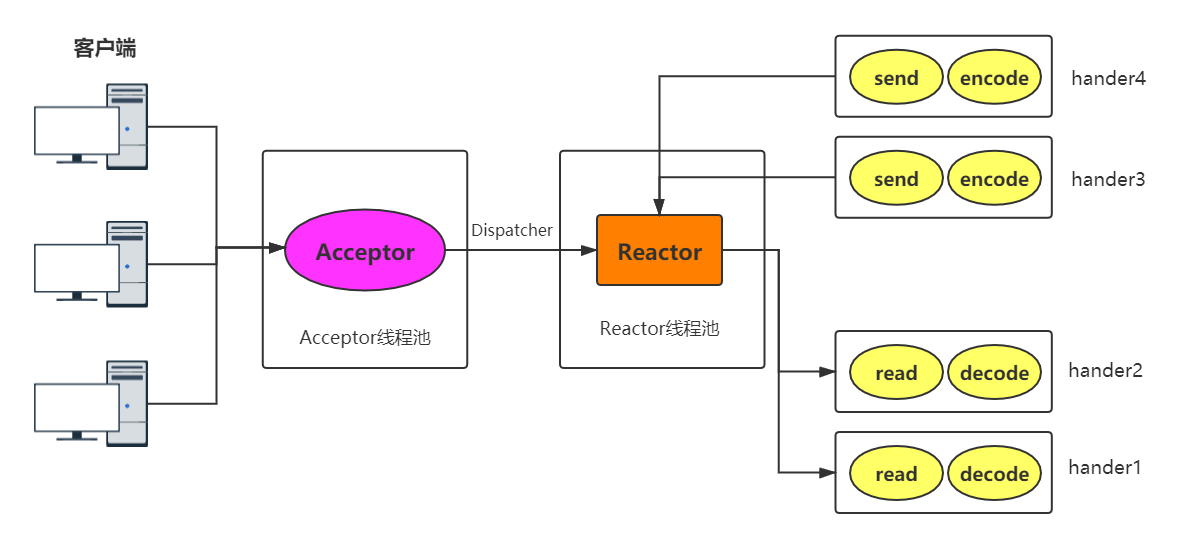
Reactor主从多线程模型和多线程模型的区别:服务端用于接收客户端连接的不再是一个单独的NIO线程,而是一个独立的NIO线程池
Netty
什么是Netty?Netty是一个基于Java NIO 的网络应用框架
不选择Java原生NIO编程的原因
- NlO的类库和API繁杂,使用麻烦,需要熟练掌握 Selector、 ServerSocketChannel、 SocketChannel、 ByteBuffer的使用
- NIO编程涉及到 Reactor模式,对开发者的并发编程能力有一定的要求
- 如果要保证通信的可靠性,开发会遇到很大的困难。例如客户端面临断连重连、网络闪断、半包读写、失败缓存、网络拥塞和异常码流的处理等问题,需要进行大量的调试和修改
- Java原生NIO存在BUG,例如臭名昭著的 epoll bug,它会导致 Selector空轮询,最终导致CPU100%
选择Netty的优势
- API使用简单,开发门槛低
- 功能强大,预置了多种编解码功能,支持多种主流协议
- 定制能力强,可以通过实现ChannelHandler接口进行灵活地扩展
- 性能高,通过与其他业界主流的NO框架对比,Netty的综合性能最优
- 成熟稳定, Netty修复了原生NIO存在的BUG
- 经历了大规模的商业应用考验,质量得到验证
Netty 线程模型
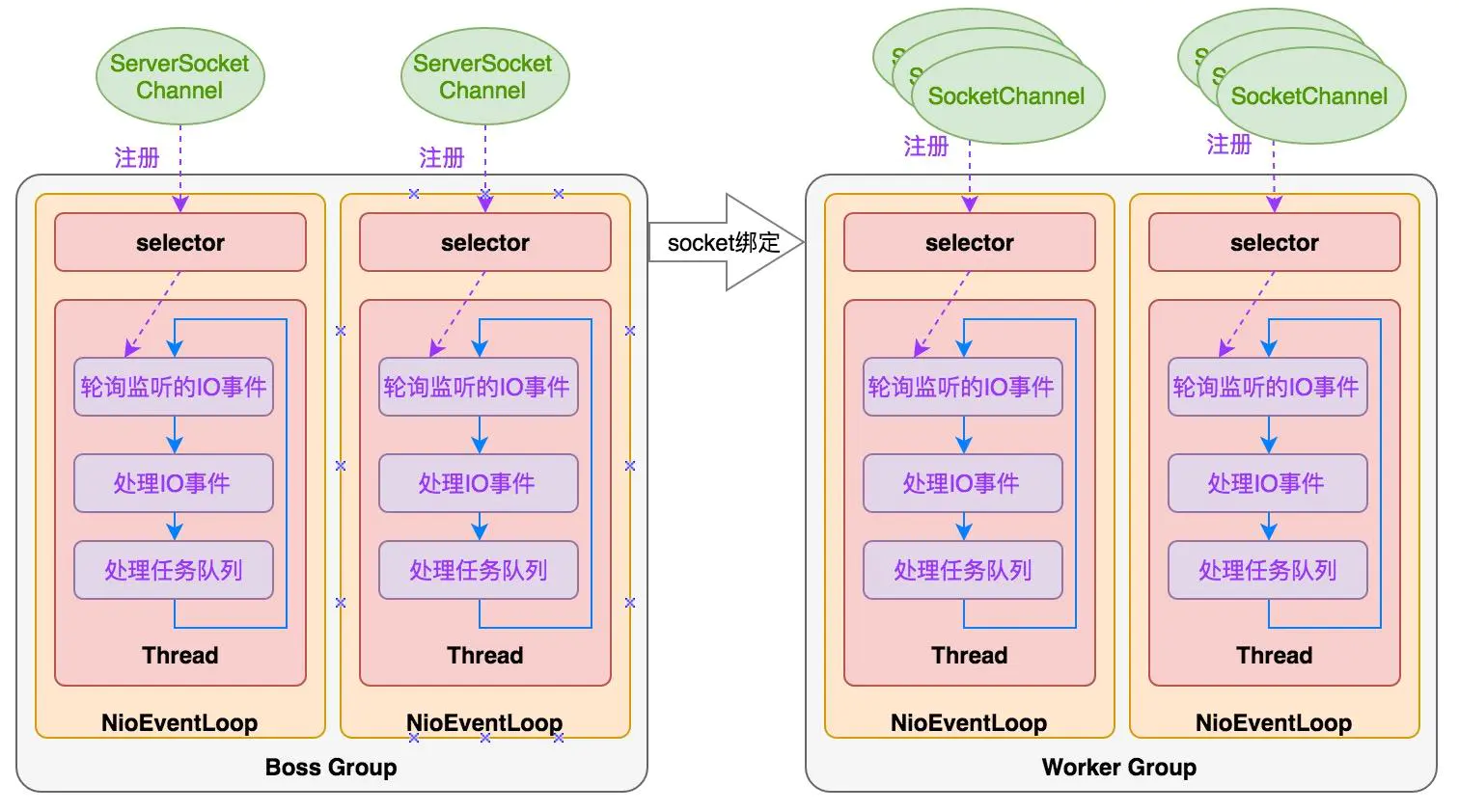
TCP粘包/拆包
TCP是一个"流"的协议,传输的最小单位为一个报文段(segment),为了提高性能,避免频繁的连接请求,发送端会先将需要发送的数据放到缓冲区,等缓存区占满后,再将缓冲区的数据发送给接收方,同样接收方也存在用来接收数据的缓冲区
在这种情况下,会存在一些问题
- 如果缓冲区存在两组不同的请求数据,会被当做一组数据发送,导致解析出错,发生粘包问题
- 如果缓冲区较小,数据包一次无法完整发送,会被拆分成多个部分发送,产生拆包问题
解决方案
- 消息定长,例如每个报文的大小为固定长度200字节,如果不够,空位补空格
- 将回车换行符(或者其它特殊字符)作为消息结束符,进行分割,例如FTP协议
- 将消息分为消息头和消息体,消息头中包含表示消息总长度(或者消息体长度)的字段,通常设计思路为消息头的第一个字段使用int32来表示消息的总长度
Netty 解决方案
FixedLengthFrameDecoder
FixedLengthFrameDecoder是固定长度解码器,按照指定长度进行解码,从而解决TCP粘包/拆包问题
// 添加解码器
pipeline.addLast("frameDecoder",new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(20));
Netty 只提供了固定长度的解码器,对应的编码器需要我们手工实现
public class FixedLengthFrameDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
// 长度
private final int frameLength;
public FixedLengthFrameDecoder(int frameLength) {
// 校验 frameLength 不能小于等于0
checkPositive(frameLength, "frameLength");
this.frameLength = frameLength;
}
@Override
protected final void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
Object decoded = decode(ctx, in);
if (decoded != null) {
out.add(decoded);
}
}
protected Object decode(
@SuppressWarnings("UnusedParameters") ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in) throws Exception {
// 小于指定长度, 不读取
if (in.readableBytes() < frameLength) {
return null;
} else {
// 只返回指定长度的数据
return in.readRetainedSlice(frameLength);
}
}
}
LineBasedFrameDecoder与DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder
同样,Netty 只提供了通过特殊字符作为消息结束符分割的解码器,对应的编码器需要我们手工实现
LineBasedFrameDecoder:通过换行符(\n或者\r\n)对数据进行处理
// 现在最大长度1024
pipeline.addLast("frameDecoder",new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024));
DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder:通过用户指定的分隔符对数据进行处理
// 指定分隔符
ByteBuf delimiters = Unpooled.wrappedBuffer("_$".getBytes());
pipeline.addLast("frameDecoder",new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(1024,delimiters));
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder与LengthFieldPrepender
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder与LengthFieldPrepender需要配合起来使用,LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder负责解码,LengthFieldPrepender负责编码;解决TCP粘包/拆包问题的原理是在生成的数据包中添加一个长度字段,用于记录当前数据包的长度。
LengthFieldPrepender会在响应的数据前面添加指定的字节数据,这个字节数据中保存了当前消息体的整体字节数据长度
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder会按照参数指定的长度偏移量数据对接收到的数据进行解码,从而得到目标消息体数据
/* 解码器 入参有5个
* maxFrameLength:框架的最大长度。如果帧的长度大于此值,则将抛出TooLongFrameException。
* lengthFieldOffset:长度字段的偏移量:即对应的长度字段在整个消息数据中得位置
* lengthFieldLength:长度字段的长度:如:长度字段是int型表示,那么这个值就是4(long型就是8)
* lengthAdjustment:要添加到长度字段值的补偿值
* initialBytesToStrip:从解码帧中去除的第一个字节数
*/
pipeline.addLast("frameDecoder", new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, 4, 0, 4));
// 编码器
pipeline.addLast("frameEncoder", new LengthFieldPrepender(4));
缓存ByteBuf
在NIO中主要使用ByteBuffer作为数据缓冲,ByteBuffer存在一些缺点
- ByteBuffer长度固定,容量不能动态扩展和伸缩
- ByteBuffer只有一个标识位置的指针 position,读写的时候需要手工调用flip()或rewind()
- ByteBuffer的API功能有限,一些高级和实用的特性不支持
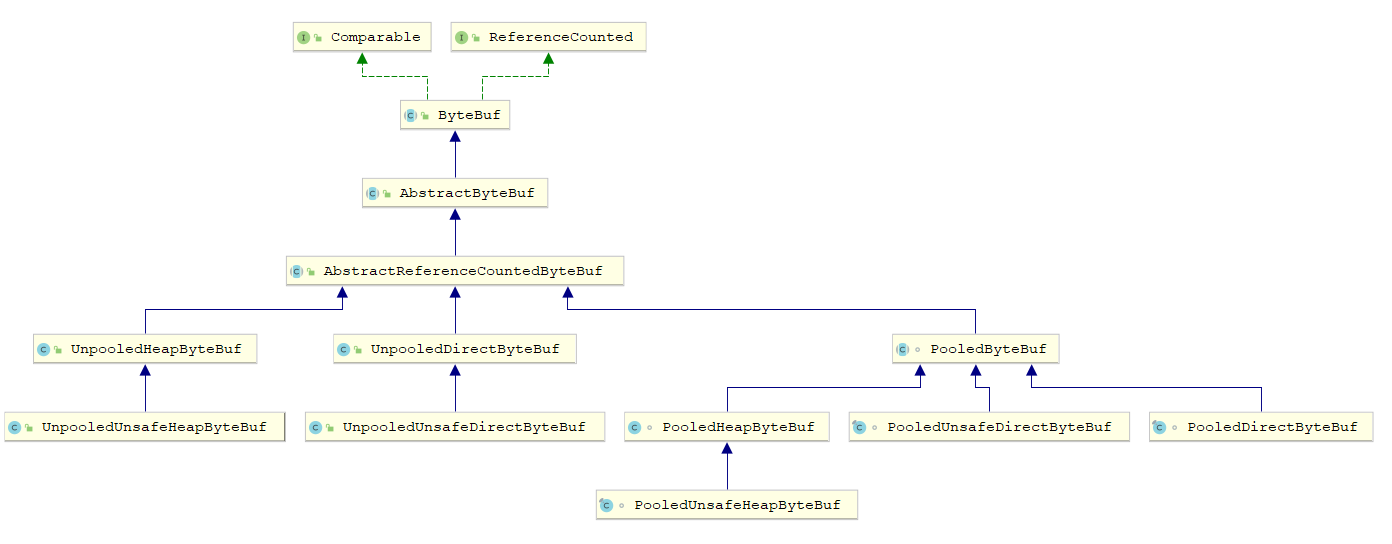
从内存分配的角度看, ByteBuf可以分为两类
- 堆内存( HeapByteBuf)字节缓冲区:特点是内存的分配和回收速度快,可以被JVM自动回收;缺点就是如果进行 Socket的IO读写,需要额外做一次内存复制,将堆内存对应的缓冲区复制到内核 Channel中,性能会有一定程度的下降
- 直接内存( DirectByteBuf)字节缓冲区:非堆内存,它在堆外进行内存分配,相比于堆内存,它的分配和回收速度会慢一些,但是将它写入或者从 Socket channel中读取时,由于少了一次内存复制,速度比堆内存快
正是因为各有利弊,所以Netty提供了多种 ByteBuf供开发者使用,经验表明,ByteBuf的最佳实践是在IO通信线程的读写缓冲区使用 DirectByteBuf,后端业务消息的编解码模块使用 HeapByteBuf,这样组合可以达到性能最优
从内存回收角度看,ByteBuf也分为两类
- 基于对象池的 ByteBuf
- 普通 ByteBuf
主要区别 :基于对象池的 ByteBuf可以重用 ByteBuf对象,内部维护了一个内存池,可以循环利用已创建的 ByteBuf,提升内存的使用效率,降低由于高负载导致的频繁GC。测试表明使用内存池后的Nety在高负载、大并发的冲击下内存和GC更加平稳
AbstractByteBuf
public abstract class AbstractByteBuf extends ByteBuf {
// 读索引
int readerIndex;
// 写索引
int writerIndex;
// mark 之后的读索引
private int markedReaderIndex;
// mark 之后的写索引
private int markedWriterIndex;
// 最大容量
private int maxCapacity;
// 构造方法
protected AbstractByteBuf(int maxCapacity) {
checkPositiveOrZero(maxCapacity, "maxCapacity");
this.maxCapacity = maxCapacity;
}
}
读操作
@Override
public ByteBuf readBytes(byte[] dst, int dstIndex, int length) {
// 检查ByteBuf 读取的长度是否越界,
// 如果 readerIndex + length > writerIndex 说明读取的数据越界
checkReadableBytes(length);
// 获取数据 抽象方法子类实现
getBytes(readerIndex, dst, dstIndex, length);
readerIndex += length;
return this;
}
写操作
@Override
public ByteBuf writeBytes(ByteBuf src, int srcIndex, int length) {
// 判断没有越界,并进行扩容
// writerIndex + length > capacity 说明写入的数据越界,需要扩容
ensureWritable(length);
// 写入数据 抽象方法子类实现
setBytes(writerIndex, src, srcIndex, length);
writerIndex += length;
return this;
}
ensureWritable
final void ensureWritable0(int minWritableBytes) {
final int writerIndex = writerIndex();
final int targetCapacity = writerIndex + minWritableBytes;
// 小于当前容量 直接返回
if (targetCapacity <= capacity()) {
ensureAccessible();
return;
}
// 大于最大容量,抛出异常
if (checkBounds && targetCapacity > maxCapacity) {
ensureAccessible();
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(String.format(
"writerIndex(%d) + minWritableBytes(%d) exceeds maxCapacity(%d): %s",
writerIndex, minWritableBytes, maxCapacity, this));
}
final int fastWritable = maxFastWritableBytes();
// 计算新数组需要的容量
int newCapacity = fastWritable >= minWritableBytes ? writerIndex + fastWritable
: alloc().calculateNewCapacity(targetCapacity, maxCapacity);
// 扩容, 子类实现
capacity(newCapacity);
}
计算容量
/**
* minNewCapacity 需要的支持的最小容量(写索引+当前写入字节)
* maxCapacity 最大容量
*/
@Override
public int calculateNewCapacity(int minNewCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
// 校验参数
checkPositiveOrZero(minNewCapacity, "minNewCapacity");
if (minNewCapacity > maxCapacity) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format(
"minNewCapacity: %d (expected: not greater than maxCapacity(%d)",
minNewCapacity, maxCapacity));
}
// 容量计算阈值
// 如果 Buffer 容量小于4M,则每次都扩容2倍,大于4M,则每次扩容4M
final int threshold = CALCULATE_THRESHOLD; // 4 MiB page
if (minNewCapacity == threshold) {
return threshold;
}
// 如果 minNewCapacity 超过 threshold
if (minNewCapacity > threshold) {
int newCapacity = minNewCapacity / threshold * threshold;
// 如果扩容后超过最大值, 直接赋值为 maxCapacity
if (newCapacity > maxCapacity - threshold) {
newCapacity = maxCapacity;
} else {
// 每次扩容4M
newCapacity += threshold;
}
return newCapacity;
}
// 不超过 threshold 阈值 则每次扩容两倍, 64起步
int newCapacity = 64;
while (newCapacity < minNewCapacity) {
newCapacity <<= 1;
}
return Math.min(newCapacity, maxCapacity);
}
重用缓冲区
discardReadBytes 就相当于 NIO ByteBuffer 中的 compact() 方法,情况已经读取的数据,从而可以在缓冲区中写更多的数据
@Override
public ByteBuf discardReadBytes() {
// 如果 readerIndex = 0,说明没有已经读取过的数据,不需要 discard
if (readerIndex == 0) {
ensureAccessible();
return this;
}
// 如果 readerIndex != writerIndex 调整读写索引位置,并移动数据
if (readerIndex != writerIndex) {
// 把readerIndex和writerIndex 之间的数据 复制 到 0 ~ writerIndex - readerIndex的位置
setBytes(0, this, readerIndex, writerIndex - readerIndex);
writerIndex -= readerIndex;
// 调整 读标记 和 写标记
adjustMarkers(readerIndex);
// readerIndex 重置为0 , 清除了之前0 ~ readerIndex的数据
readerIndex = 0;
}
// 如果读写索引相等,说明没有要读取的数据,则直接把 读写索引重置为0, 相当于清空索引
else {
ensureAccessible();
// 调整 读标记 和 写标记
adjustMarkers(readerIndex);
// 读写索引重置为0
writerIndex = readerIndex = 0;
}
return this;
}
AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf
对引用进行计数,类似于JVM内存回收的对象引用计数器,用于跟踪对象的分配和销毁,做自动内存回收
public abstract class AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf extends AbstractByteBuf {
// 它用于标识 refCnt 字段在 AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf 中的内存地址
private static final long REFCNT_FIELD_OFFSET =
ReferenceCountUpdater.getUnsafeOffset(AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf.class, "refCnt");
// AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater 通过原子操作对成员变量进行更新等操作,以实现线程安全,消除锁
private static final AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf> AIF_UPDATER =
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf.class, "refCnt");
// 通过 ReferenceCountUpdater 实现引用计数的记录
private static final ReferenceCountUpdater<AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf> updater =
new ReferenceCountUpdater<AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf>() {
@Override
protected AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf> updater() {
return AIF_UPDATER;
}
@Override
protected long unsafeOffset() {
return REFCNT_FIELD_OFFSET;
}
};
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
// refCnt 用于跟踪对象的引用次数, volatile是为了解决多线程并发访问的可见性问题
// 不直接使用,通过unsafe直接操作内存
private volatile int refCnt = updater.initialValue();
// 引用计数 +1, 通过ReferenceCountUpdater实现
@Override
public ByteBuf retain() {
return updater.retain(this);
}
// 引用计数 -1, 通过ReferenceCountUpdater实现
@Override
public boolean release() {
return handleRelease(updater.release(this));
}
}
UnpooledHeapByteBuf
UnpooledHeapByteBuf基于堆内存进行内存分配的缓冲区。没有基于对象池技术实现,每次IO操作都要创建一个新的UnpooledHeapByteBuf,频繁的进行大块的堆内存分配和回收对性能有一定影响
public class UnpooledHeapByteBuf extends AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf {
// 内存分配
private final ByteBufAllocator alloc;
// byte数组,用于缓存
byte[] array;
// ByteBuffer 与 ByteBuf 内部转换使用
private ByteBuffer tmpNioBuf;
}
扩容
@Override
public ByteBuf capacity(int newCapacity) {
// newCapacity 新数组的容量
checkNewCapacity(newCapacity);
byte[] oldArray = array;
int oldCapacity = oldArray.length;
if (newCapacity == oldCapacity) {
return this;
}
int bytesToCopy;
if (newCapacity > oldCapacity) {
bytesToCopy = oldCapacity;
} else {
trimIndicesToCapacity(newCapacity);
bytesToCopy = newCapacity;
}
// 新建数组
byte[] newArray = allocateArray(newCapacity);
// 把旧数组的数据复制给新数组
System.arraycopy(oldArray, 0, newArray, 0, bytesToCopy);
// this.array重新赋值为新数组
setArray(newArray);
freeArray(oldArray);
return this;
}
byte数组复制
@Override
public ByteBuf setBytes(int index, byte[] src, int srcIndex, int length) {
// 检查越界
checkSrcIndex(index, length, srcIndex, src.length);
// 把src数据复制到array
System.arraycopy(src, srcIndex, array, index, length);
return this;
}
转换成ByteBuffer
@Override
public ByteBuffer nioBuffer(int index, int length) {
ensureAccessible();
// 调用ByteBuffer.wrap 把 array 转换为ByteBuffer
return ByteBuffer.wrap(array, index, length).slice();
}
UnpooledDirectByteBuf
UnpooledDirectByteBuf主要通过NIO提供的DirectByteBuffer实现直接内存控制
public class UnpooledDirectByteBuf extends AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf {
// 内存分配
private final ByteBufAllocator alloc;
// ByteBuffer 通过 DirectByteBuffer 实现直接内存
ByteBuffer buffer;
// ByteBuf 和 ByteBuffer 内部转换使用
private ByteBuffer tmpNioBuf;
// 容量
private int capacity;
// 是否释放
private boolean doNotFree;
}
扩容
@Override
public ByteBuf capacity(int newCapacity) {
// newCapacity 新数组的容量 检查
checkNewCapacity(newCapacity);
int oldCapacity = capacity;
if (newCapacity == oldCapacity) {
return this;
}
int bytesToCopy;
if (newCapacity > oldCapacity) {
bytesToCopy = oldCapacity;
} else {
trimIndicesToCapacity(newCapacity);
bytesToCopy = newCapacity;
}
ByteBuffer oldBuffer = buffer;
// 新建 DirectByteBuffer
ByteBuffer newBuffer = allocateDirect(newCapacity);
oldBuffer.position(0).limit(bytesToCopy);
newBuffer.position(0).limit(bytesToCopy);
// 把旧ByteBuffer的数据复制给新ByteBuffer
newBuffer.put(oldBuffer).clear();
// 重新赋值 buffer, 释放旧ByteBuffer
setByteBuffer(newBuffer, true);
return this;
}
setByteBuffer
void setByteBuffer(ByteBuffer buffer, boolean tryFree) {
if (tryFree) {
ByteBuffer oldBuffer = this.buffer;
if (oldBuffer != null) {
if (doNotFree) {
doNotFree = false;
} else {
// 释放 oldBuffer
freeDirect(oldBuffer);
}
}
}
// 重新赋值
this.buffer = buffer;
tmpNioBuf = null;
// 容量
capacity = buffer.remaining();
}
转换成ByteBuffer
@Override
public ByteBuffer nioBuffer(int index, int length) {
// 检查是否越界
checkIndex(index, length);
// 通过 DirectByteBuffer 的方法复制一份新的ByteBuffer
return ((ByteBuffer) buffer.duplicate().position(index).limit(index + length)).slice();
}
PooledByteBuf
todo
PooledHeapByteBuf
todo
PooledDirectByteBuf
todo
EventLoopGroup和EventLoop
EventLoopGroup
Netty线程模型基于主从Reactor模型;Channel会绑定一个线程模型(EventLoopGroup),与该通道的读,写等事件都在一个EventLoopGroup中执行,避免了Handler执行的线程安全问题。
EventLoopGroup由对应的EventLoop组合而成,内部持有EventLoop数组
NioEventLoopGroup
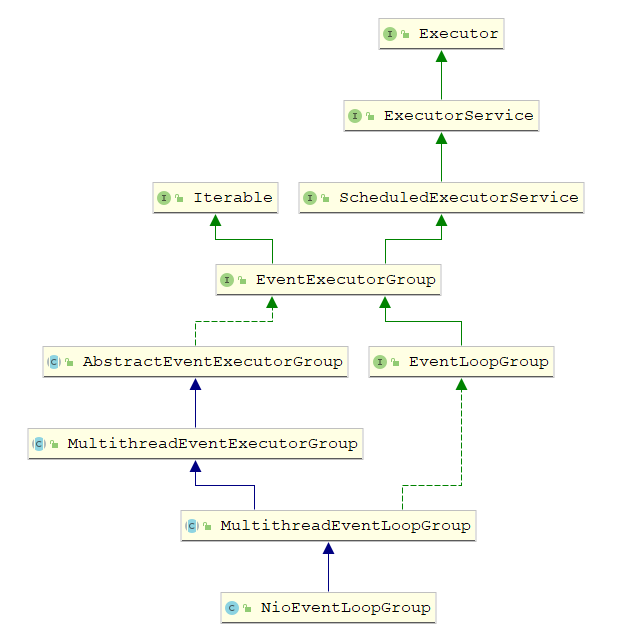
public class NioEventLoopGroup extends MultithreadEventLoopGroup {
// 构造方法,线程数0
public NioEventLoopGroup() {
this(0);
}
// 构造方法,指定线程数
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads) {
this(nThreads, (Executor) null);
}
/**
* 最终构造方法
* @param nThreads 线程数
* @param executor 线程池
* @param selectorProvider 默认 DefaultSelectorProvider
* @param selectStrategyFactory 默认 DefaultSelectStrategyFactory
*/
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, final SelectorProvider selectorProvider,
final SelectStrategyFactory selectStrategyFactory) {
// 调用父类
super(nThreads, executor, selectorProvider, selectStrategyFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandlers.reject());
}
}
// 父类
public abstract class MultithreadEventLoopGroup extends MultithreadEventExecutorGroup
implements EventLoopGroup {
protected MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, Object... args) {
// 如果线程数为0,默认 可用的处理器个数*2
super(nThreads == 0 ? DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS : nThreads, executor, args);
}
}
MultithreadEventExecutorGroup
public abstract class MultithreadEventExecutorGroup extends AbstractEventExecutorGroup {
// EventExecutor数组,长度固定,等于构造线程数
private final EventExecutor[] children;
// EventExecutor数组的副本,只读
private final Set<EventExecutor> readonlyChildren;
// EventExecutor 中断的数量
private final AtomicInteger terminatedChildren = new AtomicInteger();
private final Promise<?> terminationFuture = new DefaultPromise(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE);
// EventExecutor 选择器, 选择使用哪个 EventExecutor 去执行任务,
// 需要保证每个 EventExecutor 均匀执行任务, 类似轮询机制
private final EventExecutorChooserFactory.EventExecutorChooser chooser;
// 构造方法
protected MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, Object... args) {
// 如果线程数为0,默认 可用的处理器个数*2
super(nThreads == 0 ? DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS : nThreads, executor, args);
}
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor,
EventExecutorChooserFactory chooserFactory, Object... args) {
// 线程数 <= 0 异常
if (nThreads <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("nThreads: %d (expected: > 0)", nThreads));
}
if (executor == null) {
// 创建线程池 ThreadPerTaskExecutor
executor = new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(newDefaultThreadFactory());
}
// 根据线程数创建对应大小的 EventExecutor 数组
children = new EventExecutor[nThreads];
// 遍历创建 EventExecutor
for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; i ++) {
boolean success = false;
try {
// newChild 抽象方法, 子类创建对应的 EventExecutor
children[i] = newChild(executor, args);
success = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("failed to create a child event loop", e);
} finally {
// 如果创建EventExecutor失败,关闭资源
if (!success) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
children[j].shutdownGracefully();
}
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
EventExecutor e = children[j];
try {
while (!e.isTerminated()) {
e.awaitTermination(Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
} catch (InterruptedException interrupted) {
// 线程中断
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
break;
}
}
}
}
}
// 创建 选择器
chooser = chooserFactory.newChooser(children);
// 创建一个future的监听器用于监听终止结果
final FutureListener<Object> terminationListener = new FutureListener<Object>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<Object> future) throws Exception {
// EventExecutor 关闭会进入该方法
if (terminatedChildren.incrementAndGet() == children.length) {
// 如果 所有Children的EventExecutor 都关闭, 需要发起关闭通知
terminationFuture.setSuccess(null);
}
}
};
// 遍历children 为每个EventExecutor添加监听
for (EventExecutor e: children) {
e.terminationFuture().addListener(terminationListener);
}
// 创建一个children的副本
Set<EventExecutor> childrenSet = new LinkedHashSet<EventExecutor>(children.length);
Collections.addAll(childrenSet, children);
// unmodifiableSet 设置只读
readonlyChildren = Collections.unmodifiableSet(childrenSet);
}
protected abstract EventExecutor newChild(Executor executor, Object... args) throws Exception;
}
DefaultEventExecutorChooserFactory
EventExecutorChooserFactory目的是创建对应的选择器EventExecutorChooser
EventExecutorChooser 的目的是从EventExecutor数组中选择一个EventExecutor执行任务,需要保证均匀分配;采用原子递增和取模(2的次幂为与运算)实现均匀分配
public final class DefaultEventExecutorChooserFactory implements EventExecutorChooserFactory {
public static final DefaultEventExecutorChooserFactory INSTANCE =
new DefaultEventExecutorChooserFactory();
private DefaultEventExecutorChooserFactory() { }
// 创建对应的选择器EventExecutorChooser
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public EventExecutorChooser newChooser(EventExecutor[] executors) {
// 判断是否2的次幂
if (isPowerOfTwo(executors.length)) {
return new PowerOfTwoEventExecutorChooser(executors);
} else {
return new GenericEventExecutorChooser(executors);
}
}
// 判断是否2的次幂
private static boolean isPowerOfTwo(int val) {
return (val & -val) == val;
}
// 2的次幂 选择器
private static final class PowerOfTwoEventExecutorChooser implements EventExecutorChooser {
private final AtomicInteger idx = new AtomicInteger();
private final EventExecutor[] executors;
PowerOfTwoEventExecutorChooser(EventExecutor[] executors) {
this.executors = executors;
}
@Override
public EventExecutor next() {
// 2的次幂 可以用 & 取哈希位置(类似 % 求余), 保证 任务均匀分配
return executors[idx.getAndIncrement() & executors.length - 1];
}
}
// 非2的次幂 选择器
private static final class GenericEventExecutorChooser implements EventExecutorChooser {
private final AtomicInteger idx = new AtomicInteger();
private final EventExecutor[] executors;
GenericEventExecutorChooser(EventExecutor[] executors) {
this.executors = executors;
}
@Override
public EventExecutor next() {
// 非2的次幂 只能使用 % 求余 取哈希位置, 保证 任务均匀分配
return executors[Math.abs(idx.getAndIncrement() % executors.length)];
}
}
}
创建对应的EventLoop
public class NioEventLoopGroup extends MultithreadEventLoopGroup {
@Override
protected EventLoop newChild(Executor executor, Object... args) throws Exception {
EventLoopTaskQueueFactory queueFactory = args.length == 4 ?
(EventLoopTaskQueueFactory) args[3] : null;
// 创建 NioEventLoop
return new NioEventLoop(this, executor, (SelectorProvider) args[0],
((SelectStrategyFactory) args[1]).newSelectStrategy(),
(RejectedExecutionHandler) args[2], queueFactory);
}
}
EventLoop
每一个 NioEventLoop 开启一个线程,线程启动时会调用 NioEventLoop 的 run 方法,执行I/O任务和非I/O任务
I/O任务
I/O 任务就是处理 Nio 中 Selector 中注册的 4 种事件
SelectionKey.OP_READ SelectionKey.OP_WRITE SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT
非IO任务
系统 Task:通过调用 NioEventLoop 的 excute(Runnable task) 方法实现, Netty 有很多系统 Task,创建它们的主要原因:当 I/O 线程和用户线程同时操作网络资源时,为了防止并发操作导致的锁竞争,将用户线程操作封装成 Task 放入消息队列中,由 NioEventLoop 线程执行,由同一个线程执行,不需要考虑多线程并发问题。
定时任务:通过调用 NioEventLoop 的 schedule(Runnable command,long delay,TimeUnit unit) 方法实现。
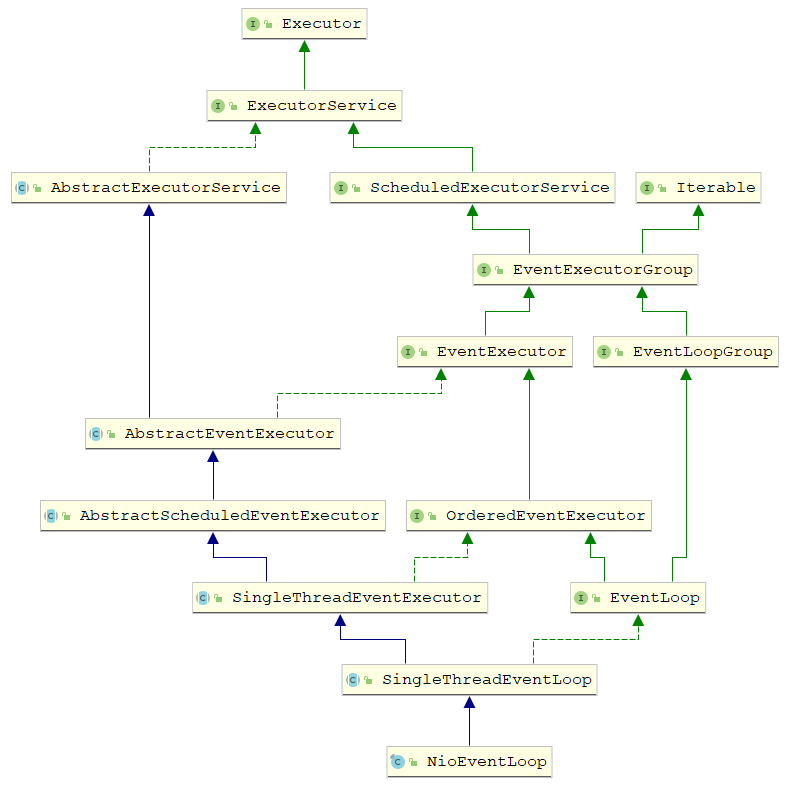
NioEventLoop
public final class NioEventLoop extends SingleThreadEventLoop {
// NIO-API 多路复用器selector
private Selector selector;
private Selector unwrappedSelector;
// SelectionKey的Set集合
private SelectedSelectionKeySet selectedKeys;
// NIO-API 默认 DefaultSelectorProvider
private final SelectorProvider provider;
// 构造方法
NioEventLoop(NioEventLoopGroup parent, Executor executor, SelectorProvider selectorProvider,
SelectStrategy strategy, RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler,
EventLoopTaskQueueFactory queueFactory) {
// newTaskQueue 创建任务队列
super(parent, executor, false, newTaskQueue(queueFactory), newTaskQueue(queueFactory),
rejectedExecutionHandler);
// SelectorProvider NIO API; 默认 DefaultSelectorProvider
this.provider = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(selectorProvider, "selectorProvider");
// 多路复用策略 提供控制选择循环行为的能力。例如,如果有事件要立即处理,则可以完全延迟或跳过阻塞选择操作。
this.selectStrategy = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(strategy, "selectStrategy");
// 创建 Selector
final SelectorTuple selectorTuple = openSelector();
// 赋值 Selector
this.selector = selectorTuple.selector;
this.unwrappedSelector = selectorTuple.unwrappedSelector;
}
}
openSelector
调用NIO 的API创建Selector
/**
* 获取 Selector
* @return
*/
private SelectorTuple openSelector() {
final Selector unwrappedSelector;
try {
// NIO-API 创建selector 等价于 Selector.open();
unwrappedSelector = provider.openSelector();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException("failed to open a new selector", e);
}
// 2、判断是否开启优化开关,默认false 直接返回 unwrappedSelector
if (DISABLE_KEY_SET_OPTIMIZATION) {
return new SelectorTuple(unwrappedSelector);
}
// 用特权访问方式 加载SelectorImpl.class
Object maybeSelectorImplClass = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
try {
return Class.forName( "sun.nio.ch.SelectorImpl", false,
PlatformDependent.getSystemClassLoader());
} catch (Throwable cause) {
return cause;
}
}
});
// ... 省略
// 通过反射创建 SelectorImpl
final Class<?> selectorImplClass = (Class<?>) maybeSelectorImplClass;
// ... 省略
}
run
当 NioEventLoop 初始化后,开始运行会调用 run() 方法
@Override
protected void run() {
int selectCnt = 0;
for (;;) {
try {
int strategy;
try {
// 获取 多路复用策略
// 存在 task 调用 selectNowSupplier.get()
strategy = selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks());
switch (strategy) {
case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:
continue;
case SelectStrategy.BUSY_WAIT:
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:
long curDeadlineNanos = nextScheduledTaskDeadlineNanos();
if (curDeadlineNanos == -1L) {
curDeadlineNanos = NONE;
}
nextWakeupNanos.set(curDeadlineNanos);
try {
if (!hasTasks()) {
// select 轮询
strategy = select(curDeadlineNanos);
}
} finally {
nextWakeupNanos.lazySet(AWAKE);
}
default:
}
} catch (IOException e) {
rebuildSelector0();
selectCnt = 0;
handleLoopException(e);
continue;
}
// select 次数 + 1
selectCnt++;
cancelledKeys = 0;
needsToSelectAgain = false;
// 处理IO事件所需的时间和花费在处理 task 时间的比例 默认为 50%
final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;
boolean ranTasks;
if (ioRatio == 100) {
try {
// 如果 IO 比例是100,表示每次都处理完IO事件后,才执行所有的task
if (strategy > 0) {
// 处理IO事件
processSelectedKeys();
}
} finally {
// 执行 task 任务
ranTasks = runAllTasks();
}
} else if (strategy > 0) {
// 记录处理 IO 开始的执行时间
final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();
try {
// 处理IO事件
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
// 计算处理 IO 所花费的时间
final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;
// 执行 task 任务,判断执行 task 任务时间是否超过配置的比例,如果超过则停止执行 task 任务
ranTasks = runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);
}
} else {
ranTasks = runAllTasks(0);
}
if (ranTasks || strategy > 0) {
selectCnt = 0;
} else if (unexpectedSelectorWakeup(selectCnt)) {
// unexpectedSelectorWakeup 解决 空轮询bug
selectCnt = 0;
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
try {
if (isShuttingDown()) {
closeAll();
if (confirmShutdown()) {
return;
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
}
}
// io.netty.channel.DefaultSelectStrategy#calculateStrategy
public int calculateStrategy(IntSupplier selectSupplier, boolean hasTasks) throws Exception {
//如果 hasTask 没有任务则调用则返回 SelectStrategy.SELECT,否则调用 selectNow
return hasTasks ? selectSupplier.get() : SelectStrategy.SELECT;
}
// io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop#selectNowSupplier
private final IntSupplier selectNowSupplier = new IntSupplier() {
@Override
public int get() throws Exception {
// selectNow轮询: 非阻塞的,返回可操作的 Channel 的个数,如果没有返回 0 。
return selectNow();
}
};
空轮询bug
空轮询Bug:即使select返回的事件数是0,本应阻塞的select还是在不断轮询
最新版的Netty修改了解决空轮询Bug的方法,在EventLoop的run()方法中进行处理
- 每次执行任务时 run()方法 都会 selectCnt++,通过该次数可以判断是否触发了NIO中的 Selector 空轮询 bug
- 如果selectCnt 超过SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD(默认512),重新创建 Selector,并把原 Selector 上注册的 Channel 迁移到新的 Selector 上
- 将新的 Selector 替换掉原来的 Selector
private boolean unexpectedSelectorWakeup(int selectCnt) {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
return true;
}
// selector自动重建阈值 SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD 默认512
if (SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD > 0 &&
selectCnt >= SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD) {
// 重新创建 Selector,并把原 Selector 上注册的 Channel 迁移到新的 Selector 上
rebuildSelector();
return true;
}
return false;
}
rebuildSelector
重新创建 Selector,并把原 Selector 上注册的 Channel 迁移到新的 Selector 上,将新的 Selector 替换掉原来的 Selector
private void rebuildSelector0() {
final Selector oldSelector = selector;
final SelectorTuple newSelectorTuple;
if (oldSelector == null) {
return;
}
try {
// 创建新的 Selector
newSelectorTuple = openSelector();
} catch (Exception e) {
return;
}
int nChannels = 0;
// 循环原 Selector 上注册的所有的 SelectionKey
for (SelectionKey key: oldSelector.keys()) {
Object a = key.attachment();
try {
if (!key.isValid() || key.channel().keyFor(newSelectorTuple.unwrappedSelector) != null) {
continue;
}
int interestOps = key.interestOps();
key.cancel();
SelectionKey newKey = key.channel().register(newSelectorTuple.unwrappedSelector, interestOps, a);
if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) {
((AbstractNioChannel) a).selectionKey = newKey;
}
nChannels ++;
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("Failed to re-register a Channel to the new Selector.", e);
if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) {
AbstractNioChannel ch = (AbstractNioChannel) a;
ch.unsafe().close(ch.unsafe().voidPromise());
} else {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
NioTask<SelectableChannel> task = (NioTask<SelectableChannel>) a;
invokeChannelUnregistered(task, key, e);
}
}
}
// 将新的 Selector 替换 原 Selector
selector = newSelectorTuple.selector;
unwrappedSelector = newSelectorTuple.unwrappedSelector;
try {
// 关闭 旧的Selector
oldSelector.close();
} catch (Throwable t) {
}
}
select轮询
private int select(long deadlineNanos) throws IOException {
// NIO-API 调用 selector.select()
if (deadlineNanos == NONE) {
return selector.select();
}
// 超时机制
long timeoutMillis = deadlineToDelayNanos(deadlineNanos + 995000L) / 1000000L;
return timeoutMillis <= 0 ? selector.selectNow() : selector.select(timeoutMillis);
}
处理IO事件
private void processSelectedKeys() {
if (selectedKeys != null) {
processSelectedKeysOptimized();
} else {
// selectedKeys == null 重新获取selectedKeys
processSelectedKeysPlain(selector.selectedKeys());
}
}
processSelectedKeysOptimized
这个方法经过优化,
private void processSelectedKeysOptimized() {
// 遍历 selectedKeys
for (int i = 0; i < selectedKeys.size; ++i) {
final SelectionKey k = selectedKeys.keys[i];
selectedKeys.keys[i] = null;
// attachment 变量,通过源码分析我们发现,attachment在注册阶段进行赋值,有两个来源
// 1. AbstractNioChannel.doRegister() 注册 AbstractNioChannel
// 2. NioEventLoop.register0() 注册 NioTask
final Object a = k.attachment();
if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) {
// 处理 channel
processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a);
} else {
// 处理 NioTask
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
NioTask<SelectableChannel> task = (NioTask<SelectableChannel>) a;
processSelectedKey(k, task);
}
// 再次select
if (needsToSelectAgain) {
selectedKeys.reset(i + 1);
selectAgain();
i = -1;
}
}
}
processSelectedKeysPlain
private void processSelectedKeysPlain(Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys) {
if (selectedKeys.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
Iterator<SelectionKey> i = selectedKeys.iterator();
// 不停的执行,可能在遍历过程中,会有新的channel
for (;;) {
final SelectionKey k = i.next();
final Object a = k.attachment();
i.remove();
if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) {
// 处理 channel
processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a);
} else {
// 处理 NioTask
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
NioTask<SelectableChannel> task = (NioTask<SelectableChannel>) a;
processSelectedKey(k, task);
}
// SelectionKey 跳出循环
if (!i.hasNext()) {
break;
}
// 再次select
if (needsToSelectAgain) {
selectAgain();
selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
if (selectedKeys.isEmpty()) {
break;
} else {
i = selectedKeys.iterator();
}
}
}
}
处理 channel
通过unsafe完成channel的连接,读写
private void processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) {
final AbstractNioChannel.NioUnsafe unsafe = ch.unsafe();
if (!k.isValid()) {
final EventLoop eventLoop;
try {
eventLoop = ch.eventLoop();
} catch (Throwable ignored) {
return;
}
if (eventLoop == this) {
unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
}
return;
}
try {
// 获取channel状态
int readyOps = k.readyOps();
// OP_CONNECT 事件 相当于 k.isConnectable()
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) {
// 修改状态
int ops = k.interestOps();
// 这个算法会使得 原来状态是 OP_CONNECT 会清0,其他状态不变
ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;
k.interestOps(ops);
// 完成连接
unsafe.finishConnect();
}
// OP_WRITE 事件, flush写数据
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) {
// 强制flush写入,一旦全部写入,更新为read状态
ch.unsafe().forceFlush();
}
// OP_READ 或 OP_ACCEPT 事件 调用 unsafe.read() 进行读取数据
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException ignored) {
unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
}
}
SingleThreadEventLoop
public abstract class SingleThreadEventLoop extends SingleThreadEventExecutor implements EventLoop {
// 队尾 任务队列
private final Queue<Runnable> tailTasks;
// 构造方法
protected SingleThreadEventLoop(EventLoopGroup parent, Executor executor,
boolean addTaskWakesUp, Queue<Runnable> taskQueue, Queue<Runnable> tailTaskQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler) {
super(parent, executor, addTaskWakesUp, taskQueue, rejectedExecutionHandler);
// 赋值
tailTasks = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(tailTaskQueue, "tailTaskQueue");
}
}
SingleThreadEventExecutor
public abstract class SingleThreadEventExecutor extends AbstractScheduledEventExecutor
implements OrderedEventExecutor {
// 任务队列 默认LinkedBlockingQueue 阻塞队列
private final Queue<Runnable> taskQueue;
// 线程
private volatile Thread thread;
// 构造方法
protected SingleThreadEventExecutor(EventExecutorGroup parent, Executor executor,
boolean addTaskWakesUp, Queue<Runnable> taskQueue, RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedHandler) {
super(parent);
this.addTaskWakesUp = addTaskWakesUp;
this.maxPendingTasks = DEFAULT_MAX_PENDING_EXECUTOR_TASKS;
// 创建 executor 线程执行器 对NioEventLoop executor = ThreadPerTaskExecutor
// 这里会创建新线程
this.executor = ThreadExecutorMap.apply(executor, this);
// 创建 任务队列 长度为maxPendingTasks的LinkedBlockingQueue
this.taskQueue = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(taskQueue, "taskQueue");
this.rejectedExecutionHandler = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(rejectedHandler, "rejectedHandler");
}
}
executor
这里的executor是一个抽象类
// 创建 executor 线程执行器 对NioEventLoop executor = ThreadPerTaskExecutor()
this.executor = ThreadExecutorMap.apply(executor, this);
ThreadExecutorMap
public final class ThreadExecutorMap {
public static Executor apply(final Executor executor, final EventExecutor eventExecutor) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(executor, "executor");
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(eventExecutor, "eventExecutor");
// 返回一个抽象类Executor, 实际预先交给executor(ThreadPerTaskExecutor)
return new Executor() {
@Override
public void execute(final Runnable command) {
executor.execute(apply(command, eventExecutor));
}
};
}
}
ThreadPerTaskExecutor
// 创建线程池 ThreadPerTaskExecutor
executor = new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(newDefaultThreadFactory());
protected ThreadFactory newDefaultThreadFactory() {
return new DefaultThreadFactory(getClass());
}
ThreadPerTaskExecutor在创建时,会指定ThreadFactory
当执行execute方法时,ThreadFactory会创建对应的线程并启动
public final class ThreadPerTaskExecutor implements Executor {
private final ThreadFactory threadFactory;
// threadFactory 默认 DefaultThreadFactory
public ThreadPerTaskExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
this.threadFactory = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(threadFactory, "threadFactory");
}
// 在这里创建并启动新线程
@Override
public void execute(Runnable command) {
threadFactory.newThread(command).start();
}
}
DefaultThreadFactory
最终创建的线程是FastThreadLocalThread,FastThreadLocalThread继承了Thread
public class DefaultThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
// 自动设置线程name
Thread t = newThread(FastThreadLocalRunnable.wrap(r), prefix + nextId.incrementAndGet());
try {
if (t.isDaemon() != daemon) {
t.setDaemon(daemon);
}
if (t.getPriority() != priority) {
t.setPriority(priority);
}
} catch (Exception ignored) {
// Doesn't matter even if failed to set.
}
return t;
}
protected Thread newThread(Runnable r, String name) {
return new FastThreadLocalThread(threadGroup, r, name);
}
}
public class FastThreadLocalThread extends Thread {
}
execute
执行task
private void execute(Runnable task, boolean immediate) {
boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop();
// 添加任务
addTask(task);
// 如果当前线程 不等于 当前EventLoop持有的线程
if (!inEventLoop) {
// 启动线程
startThread();
// 正在关闭
if (isShutdown()) {
boolean reject = false;
try {
if (removeTask(task)) {
reject = true;
}
} catch (UnsupportedOperationException e) {
}
// 拒绝任务
if (reject) {
reject();
}
}
}
if (!addTaskWakesUp && immediate) {
wakeup(inEventLoop);
}
}
startThread
启动线程,excutor.execute在执行时,会创建对应的线程并启动
private void startThread() {
if (state == ST_NOT_STARTED) {
// CAS 修改更新状态
if (STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, ST_NOT_STARTED, ST_STARTED)) {
boolean success = false;
try {
// 启动线程
doStartThread();
success = true;
} finally {
if (!success) {
STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, ST_STARTED, ST_NOT_STARTED);
}
}
}
}
}
private void doStartThread() {
assert thread == null;
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 获取当前线程
thread = Thread.currentThread();
if (interrupted) {
thread.interrupt();
}
boolean success = false;
updateLastExecutionTime();
try {
// 执行run() 方法 NioEventLoop 具体实现
SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run();
success = true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Unexpected exception from an event executor: ", t);
} finally {
// ... 省略
}
}
});
}
Channel
io. netty channel. Channel是Netty网络操作抽象类,实现了以下功能:
- IO读、写,客户端发起连接,主动关闭连接,链路关闭,获取通信双方的网络地址
- 获取该 Channel的 Eventloop,获取缓冲分配器 ByteBufAllocator和 pipeline
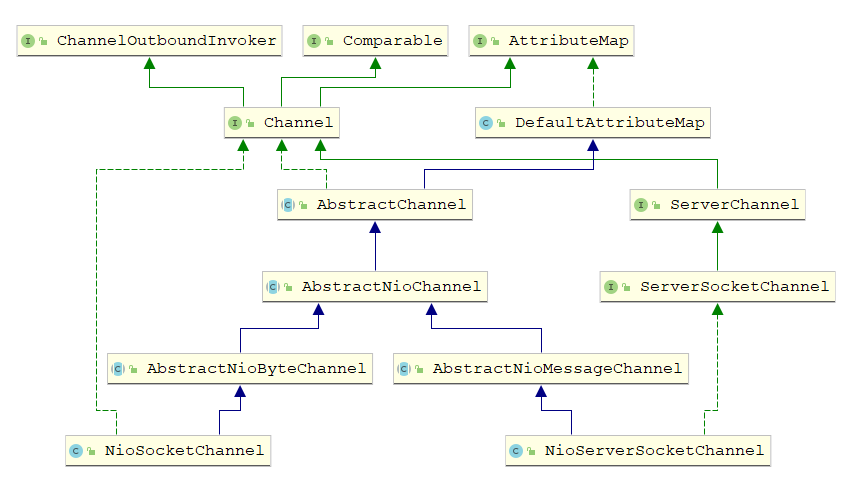
AbstractChannel
public abstract class AbstractChannel extends DefaultAttributeMap implements Channel {
// 代表父类 Channel
private final Channel parent;
// 采用默认方式生成的全局唯一ID
private final ChannelId id;
// Unsafe实例, 封装 ByteBuf 的读写操作
private final Unsafe unsafe;
// 当前 Channel 关联的 Pipeline 对象 DefaultChannelPipeline
private final DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline;
private final VoidChannelPromise unsafeVoidPromise = new VoidChannelPromise(this, false);
private final CloseFuture closeFuture = new CloseFuture(this);
// 本地地址
private volatile SocketAddress localAddress;
// 远端地址
private volatile SocketAddress remoteAddress;
// 当前 Channel注册的 EventLoop, 内部封装了Selector
private volatile EventLoop eventLoop;
// 是否注册
private volatile boolean registered;
// 是否发起关闭
private boolean closeInitiated;
// 导致关闭的异常
private Throwable initialCloseCause;
// 构造方法
protected AbstractChannel(Channel parent) {
this.parent = parent;
id = newId();
// 创建 Unsafe 抽象方法 NioMessageUnsafe
unsafe = newUnsafe();
// 创建 ChannelPipeline 默认 DefaultChannelPipeline
pipeline = newChannelPipeline();
}
}
IO操作
通过源码我们发现,Channel所有的IO操作都是交给DefaultChannelPipeline完成的
// 当前 Channel 关联的 Pipeline 对象 DefaultChannelPipeline
private final DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline;
// 绑定指定的本地Socket地址 localAddress
@Override
public ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress) {
return pipeline.bind(localAddress);
}
// 向服务端地址 remoteAddress 发起连接请求
@Override
public ChannelFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress) {
return pipeline.connect(remoteAddress);
}
@Override
public ChannelFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress) {
return pipeline.connect(remoteAddress, localAddress);
}
// 从当前的 Channel中读取数据 到第一个 inbound缓冲区中
// 如果数据被成功读取,触发 ChannelInboundHandler.channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) 事件。
@Override
public Channel read() {
pipeline.read();
return this;
}
// 请求将当前的msg通过 ChannelPipeline 写入到目标 Channel 中
// 只有调用flush才会发送信息
@Override
public ChannelFuture write(Object msg) {
return pipeline.write(msg);
}
@Override
public ChannelFuture write(Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) {
return pipeline.write(msg, promise);
}
// 向Channel写入消息并发送 等价于 write + flush
@Override
public ChannelFuture writeAndFlush(Object msg) {
return pipeline.writeAndFlush(msg);
}
// 将之前写入的消息写入到Channel中,然后发送
@Override
public Channel flush() {
pipeline.flush();
return this;
}
AbstractNioChannel
public abstract class AbstractNioChannel extends AbstractChannel {
// 抽象了 SocketChannel 和 ServerSocketChannel 的公共的父类
// 是 AbstractNioChannel 可以在客户端和服务端共用
private final SelectableChannel ch;
// NIO API 中的 SelectionKey.OP_READ, 读事件
protected final int readInterestOp;
// NIO API SelectionKey: 注册到 selector 上返回的 SelectionKey
volatile SelectionKey selectionKey;
// 是否还有待读的数据
boolean readPending;
// 任务 清除待读数据
private final Runnable clearReadPendingRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
clearReadPending0();
}
};
// 连接操作的结果
private ChannelPromise connectPromise;
// 定时任务 定时处理超时连接
private ScheduledFuture<?> connectTimeoutFuture;
// 客户端地址
private SocketAddress requestedRemoteAddress;
// 构造方法
protected AbstractNioChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch, int readInterestOp) {
super(parent);
this.ch = ch;
// 状态 readInterestOp = OP_ACCEPT
this.readInterestOp = readInterestOp;
try {
// 设置为非阻塞
ch.configureBlocking(false);
} catch (IOException e) {
try {
ch.close();
} catch (IOException e2) {
}
throw new ChannelException("Failed to enter non-blocking mode.", e);
}
}
}
doRegister
将Channel注册到Selector上
/**
* 将 SelectableChannel 注册到 当前 eventLoop(主线程)的 Selector 上
* 不监听任何事件,仅完成注册操作
* 覆盖父类的方法 在AbstractUnsafe.register 中调用
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void doRegister() throws Exception {
boolean selected = false;
for (;;) {
try {
// 将 SelectableChannel(SocketChannel 和 ServerSocketChannel 的公共的父类)
// 注册到 当前 eventLoop(主线程)的 Selector 上
// ops == 0 不监听任何事件,仅完成注册操作
selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().unwrappedSelector(), 0, this);
return;
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
// 第一次失败 selected == false, 会重新尝试注册
if (!selected) {
eventLoop().selectNow();
selected = true;
} else {
// 第二次之后抛出异常
throw e;
}
}
}
}
doBeginRead
注册读事件,等价于NIO中的channel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
/**
* 修改 selectionKey 为 读状态
* 等价于注册读事件 channel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
final SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;
// 判断 selectionKey 是否可用
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) {
return;
}
readPending = true;
final int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
// 如果当前状态 位运算与 读状态 等于0
// 则说明该 Channel 没有在 selelctor 上注册读事件
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) == 0) {
// 修改 selectionKey 为 读状态
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | readInterestOp);
}
}
AbstractNioMessageChannel
public abstract class AbstractNioMessageChannel extends AbstractNioChannel {
// 是否关闭 Channel
boolean inputShutdown;
// 构造方法
protected AbstractNioMessageChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch, int readInterestOp) {
// readInterestOp = OP_ACCEPT
super(parent, ch, readInterestOp);
}
// newUnsafe
@Override
protected AbstractNioUnsafe newUnsafe() {
return new NioMessageUnsafe();
}
// 注册读事件
@Override
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
if (inputShutdown) {
return;
}
// 调用 父类方法
super.doBeginRead();
}
}
doWrite
@Override
protected void doWrite(ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception {
// 获取 SelectionKey
final SelectionKey key = selectionKey();
// SelectionKey 的状态
final int interestOps = key.interestOps();
for (;;) {
// 从 ChannelOutboundBuffer 中弹出一条消息进行处理
Object msg = in.current();
// 如果消息为空,说明发送缓冲区为空,所有消息都已经被发送完成
if (msg == null) {
// 清除写状态
if ((interestOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) {
key.interestOps(interestOps & ~SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
break;
}
try {
// 消息是否全部发送
boolean done = false;
for (int i = config().getWriteSpinCount() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// doWriteMessage 判断消息是否发送成功
if (doWriteMessage(msg, in)) {
done = true;
break;
}
}
// 如果消息发送成功,将消息从缓冲数组中移除
if (done) {
in.remove();
} else {
// 没有发送成功, 重新设置为写状态
if ((interestOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) == 0) {
key.interestOps(interestOps | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
break;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (continueOnWriteError()) {
in.remove(e);
} else {
throw e;
}
}
}
}
NioServerSocketChannel
NioServerSocketChannel是通过Constructor反射创建的
public class NioServerSocketChannel extends AbstractNioMessageChannel
implements io.netty.channel.socket.ServerSocketChannel {
// 默认 DefaultSelectorProvider
private static final SelectorProvider DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER = SelectorProvider.provider();
// 配置信息
private final ServerSocketChannelConfig config;
private static ServerSocketChannel newSocket(SelectorProvider provider) {
try {
// 打开Channel通道
return provider.openServerSocketChannel();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException("Failed to open a server socket.", e);
}
}
// 构造方法
public NioServerSocketChannel() {
this(newSocket(DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER));
}
public NioServerSocketChannel(ServerSocketChannel channel) {
// ACCEPT 状态
super(null, channel, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
// 配置信息赋值
config = new NioServerSocketChannelConfig(this, javaChannel().socket());
}
}
doReadMessages
获取客户端的连接,读取客户端的消息
@Override
protected int doReadMessages(List<Object> buf) throws Exception {
// NIO-API ServerSocketChannel.accept() 获取客户端的连接
SocketChannel ch = SocketUtils.accept(javaChannel());
try {
// 如果 SocketChannel(客户端连接)不为空
if (ch != null) {
// 创建新的NioSocketChannel, 放入计划buf中
buf.add(new NioSocketChannel(this, ch));
// 返回1,表示服务端消息读取成功
return 1;
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
try {
ch.close();
} catch (Throwable t2) {
}
}
return 0;
}
doBind
绑定地址和端口
@SuppressJava6Requirement(reason = "Usage guarded by java version check")
@Override
protected void doBind(SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
if (PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 7) {
// NIO-API ServerSocketChannel.bind 绑定监听端口
javaChannel().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
} else {
javaChannel().socket().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
}
}
isActive
@Override
public boolean isActive() {
// channel 打开 且 绑定了地址
return isOpen() && javaChannel().socket().isBound();
}
AbstractNioByteChannel
public abstract class AbstractNioByteChannel extends AbstractNioChannel {
// 任务 负责flush发送缓存中的数据
private final Runnable flushTask = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
((AbstractNioUnsafe) unsafe()).flush0();
}
};
protected AbstractNioByteChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch) {
// 调用父类构造方法
super(parent, ch, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
}
doWrite
@Override
protected void doWrite(ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception {
// 获取循环发送的次数 默认 16
int writeSpinCount = config().getWriteSpinCount();
do {
// 从 ChannelOutboundBuffer 中弹出一条消息进行处理
Object msg = in.current();
// 如果消息为空,说明发送缓冲区为空,所有消息都已经被发送完成
if (msg == null) {
// 清除写状态
clearOpWrite();
return;
}
// 写入消息, 减少循环次数
writeSpinCount -= doWriteInternal(in, msg);
} while (writeSpinCount > 0);
// 完成写入
incompleteWrite(writeSpinCount < 0);
}
// 清除写状态
protected final void clearOpWrite() {
final SelectionKey key = selectionKey();
if (!key.isValid()) {
return;
}
// 清除写状态
final int interestOps = key.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) {
key.interestOps(interestOps & ~SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
}
// 发送消息
private int doWriteInternal(ChannelOutboundBuffer in, Object msg) throws Exception {
// ByteBuf 类型的消息
if (msg instanceof ByteBuf) {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
// 判断 buf 是否可读
if (!buf.isReadable()) {
// 不可读,将消息从缓冲数组中移除
in.remove();
return 0;
}
// 调用 doWriteBytes() 方法发送消息,返回发送的字节数
final int localFlushedAmount = doWriteBytes(buf);
if (localFlushedAmount > 0) {
// 如果发送的字节数大于0,调用 in.progress() 更新消息发送的进度
in.progress(localFlushedAmount);
// 如果发送成功,将消息从缓冲数组中移除
if (!buf.isReadable()) {
in.remove();
}
return 1;
}
} else if (msg instanceof FileRegion) {
FileRegion region = (FileRegion) msg;
if (region.transferred() >= region.count()) {
in.remove();
return 0;
}
long localFlushedAmount = doWriteFileRegion(region);
if (localFlushedAmount > 0) {
in.progress(localFlushedAmount);
if (region.transferred() >= region.count()) {
in.remove();
}
return 1;
}
} else {
throw new Error();
}
return WRITE_STATUS_SNDBUF_FULL;
}
protected final void incompleteWrite(boolean setOpWrite) {
// 消息未发送完成, 设置为 写状态
if (setOpWrite) {
setOpWrite();
} else {
// 清除写状态
clearOpWrite();
// 执行flush任务
eventLoop().execute(flushTask);
}
}
NioSocketChannel
public class NioSocketChannel extends AbstractNioByteChannel implements io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel {
// NIO API 默认 DefaultSelectorProvider
private static final SelectorProvider DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER = SelectorProvider.provider();
// 配置信息
private final ServerSocketChannelConfig config;
private static SocketChannel newSocket(SelectorProvider provider) {
try {
// 打开Channel通道
return provider.openSocketChannel();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException("Failed to open a socket.", e);
}
}
// 构造方法
public NioSocketChannel() {
this(DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER);
}
public NioSocketChannel(SelectorProvider provider) {
this(newSocket(provider));
}
public NioSocketChannel(SocketChannel socket) {
this(null, socket);
}
public NioSocketChannel(Channel parent, SocketChannel socket) {
// 父类构造方法
super(parent, socket);
// 配置信息赋值
config = new NioSocketChannelConfig(this, socket.socket());
}
}
doConnect
连接远程地址 remoteAddress
@Override
protected boolean doConnect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
if (localAddress != null) {
// 绑定 本地IP
doBind0(localAddress);
}
boolean success = false;
try {
// 发起连接,连接到remoteAddress
boolean connected = SocketUtils.connect(javaChannel(), remoteAddress);
if (!connected) {
// 没有连接成功, 修改状态为 OP_CONNECT, 之后会再次连接
selectionKey().interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}
success = true;
return connected;
} finally {
if (!success) {
doClose();
}
}
}
// 绑定 地址
private void doBind0(SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
if (PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 7) {
// NIO-API SocketChannel.bind 绑定监听端口
SocketUtils.bind(javaChannel(), localAddress);
} else {
SocketUtils.bind(javaChannel().socket(), localAddress);
}
}
doReadBytes
@Override
protected int doReadBytes(ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = unsafe().recvBufAllocHandle();
// 尝试读取数据
// byteBuf.writableBytes() 可已写入的字节数
allocHandle.attemptedBytesRead(byteBuf.writableBytes());
// 传输数据到缓冲区
return byteBuf.writeBytes(javaChannel(), allocHandle.attemptedBytesRead());
}
doWrite
@Override
protected void doWrite(ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception {
SocketChannel ch = javaChannel();
// 获取循环发送的次数 默认 16
int writeSpinCount = config().getWriteSpinCount();
do {
// 消息发送缓冲区为空,所有消息都已经被发送完成
if (in.isEmpty()) {
// 清除写状态,取消写事件
clearOpWrite();
return;
}
int maxBytesPerGatheringWrite = ((NioSocketChannelConfig) config).getMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite();
// ByteBuffer数组
ByteBuffer[] nioBuffers = in.nioBuffers(1024, maxBytesPerGatheringWrite);
// 获取 ChannelOutboundBuffer 中 ByteBuf 的数量 
int nioBufferCnt = in.nioBufferCount();
switch (nioBufferCnt) {
case 0:
// 个数为0,可能是其他内容的数据
writeSpinCount -= doWrite0(in);
break;
case 1: {
// 只有一个 ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer buffer = nioBuffers[0];
int attemptedBytes = buffer.remaining();
// NIO-API 写入 buffer
final int localWrittenBytes = ch.write(buffer);
if (localWrittenBytes <= 0) {
// 完成写入
incompleteWrite(true);
return;
}
adjustMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite(attemptedBytes, localWrittenBytes,
maxBytesPerGatheringWrite);
in.removeBytes(localWrittenBytes);
--writeSpinCount;
break;
}
default: {
// 有多个 ByteBuffer
long attemptedBytes = in.nioBufferSize();
// NIO-API 写入 ByteBuffer数组 nioBuffers
final long localWrittenBytes = ch.write(nioBuffers, 0, nioBufferCnt);
if (localWrittenBytes <= 0) {
incompleteWrite(true);
return;
}
adjustMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite((int) attemptedBytes, (int) localWrittenBytes,
maxBytesPerGatheringWrite);
in.removeBytes(localWrittenBytes);
--writeSpinCount;
break;
}
}
} while (writeSpinCount > 0);
// 完成写入
incompleteWrite(writeSpinCount < 0);
}
isActive
@Override
public boolean isActive() {
SocketChannel ch = javaChannel();
// channel 打开 且 处于连接状态
return ch.isOpen() && ch.isConnected();
}
Unsafe
Unsafe接口是 Channel接口的辅助接口,是一个内部接口。所有IO读写操作都是由 Channel直接或间接调用Unsafe接口完成的
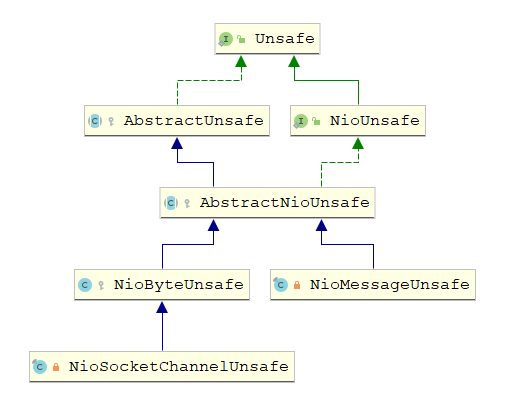
AbstractUnsafe
protected abstract class AbstractUnsafe implements Unsafe {
// Netty 向外输出数据的过程统一通过 ChannelOutboundBuffer 类进行封装
private volatile ChannelOutboundBuffer outboundBuffer = new ChannelOutboundBuffer(AbstractChannel.this);
}
register
注册 channel
@Override
public final void register(EventLoop eventLoop, final ChannelPromise promise) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(eventLoop, "eventLoop");
// 已注册
if (isRegistered()) {
// 返回异常结果
promise.setFailure(new IllegalStateException("registered to an event loop already"));
return;
}
if (!isCompatible(eventLoop)) {
// 返回异常结果
promise.setFailure(new IllegalStateException("incompatible event loop type: "
+ eventLoop.getClass().getName()));
return;
}
AbstractChannel.this.eventLoop = eventLoop;
// 如果当前线程和eventLoop的线程相同,直接执行
if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) {
register0(promise);
} else {
// 否则, 交给对应eventLoop执行
try {
eventLoop.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
register0(promise);
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
}
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
boolean firstRegistration = neverRegistered;
// 将channel注册到selector, 抽象方法,对应的Channel实现
doRegister();
neverRegistered = false;
registered = true;
// SocketChannel首次注册到selector后,对应的pipeline的invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded方法
// AbstractChannelHandlerContext.callHandlerAdded() =>ChannelHandler.handlerAdded()
pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded();
safeSetSuccess(promise);
pipeline.fireChannelRegistered();
// channel 是否active
if (isActive()) {
// firstRegistration 首次注册标识
if (firstRegistration) {
// 首次注册 触发 ChannelActive 事件
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
} else if (config().isAutoRead()) {
// 触发一次读操作
beginRead();
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
@Override
public final void beginRead() {
assertEventLoop();
if (!isActive()) {
return;
}
try {
// 抽象方法,对应的Channel实现
doBeginRead();
} catch (final Exception e) {
invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.fireExceptionCaught(e);
}
});
close(voidPromise());
}
}
bind
bind方法主要用于绑定指定的端口
- 服务端:用于绑定监听端口
- 客户端:用于指定客户端 Channel的Socket地址
@Override
public final void bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
assertEventLoop();
if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
// 是否激活状态(服务端: 开启状态且已绑定; 客户端: channel 打开且处于连接状态)
boolean wasActive = isActive();
try {
// 抽象方法,对应的Channel实现
doBind(localAddress);
} catch (Throwable t) {
// 返回失败信息
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
closeIfClosed();
return;
}
// 如果之前未激活,绑定后激活
if (!wasActive && isActive()) {
// 触发 ChannelActive 事件
invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
}
});
}
// 返回成功
safeSetSuccess(promise);
}
disconnect
disconnect用于客户端或者服务端主动关闭连接
@Override
public final void disconnect(final ChannelPromise promise) {
assertEventLoop();
if (!promise.setUncancellable()) {
return;
}
// 是否激活状态(服务端: 开启状态且已绑定; 客户端: channel 打开且处于连接状态)
boolean wasActive = isActive();
try {
// 抽象方法,对应的Channel实现
doDisconnect();
// Reset remoteAddress and localAddress
remoteAddress = null;
localAddress = null;
} catch (Throwable t) {
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
closeIfClosed();
return;
}
// 如果之前激活,断开连接未激活
if (wasActive && !isActive()) {
// 触发 ChannelInactive 事件,调用 ChannelInboundHandler.channelInactive()
invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.fireChannelInactive();
}
});
}
safeSetSuccess(promise);
closeIfClosed();
}
write
write方法实际上将消息添加到ChannelOutboundBuffer 中,并不是真正的写入 Channel
@Override
public final void write(Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) {
assertEventLoop();
// 每个 Channel 的 Unsafe 都有一个绑定的 ChannelOutboundBuffer
// Netty 向外输出数据都是通过 ChannelOutboundBuffer 类进行的
ChannelOutboundBuffer outboundBuffer = this.outboundBuffer;
// 如果outboundBuffer为空,说明Channel已关闭,因此需要立即失败
if (outboundBuffer == null) {
safeSetFailure(promise, newClosedChannelException(initialCloseCause));
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
return;
}
int size;
try {
msg = filterOutboundMessage(msg);
size = pipeline.estimatorHandle().size(msg);
if (size < 0) {
size = 0;
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
return;
}
// 把消息放入outboundBuffer的链表中
outboundBuffer.addMessage(msg, size, promise);
}
flush
flush方法负责将发送缓冲区中待发送的消息全部写入到 Channel中,并发送给通信方
@Override
public final void flush() {
assertEventLoop();
ChannelOutboundBuffer outboundBuffer = this.outboundBuffer;
if (outboundBuffer == null) {
return;
}
// 调用该方法,记录了flushedEntry指针的位置和需要flush的链表长度(flushed字段)
outboundBuffer.addFlush();
// 真正的flush方法,把数据发送到channel
flush0();
}
protected void flush0() {
// 正在flush
if (inFlush0) {
return;
}
final ChannelOutboundBuffer outboundBuffer = this.outboundBuffer;
if (outboundBuffer == null || outboundBuffer.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
inFlush0 = true;
// 如果channel未激活, 则将所有待处理的写请求标记为失败
if (!isActive()) {
try {
if (isOpen()) {
outboundBuffer.failFlushed(new NotYetConnectedException(), true);
} else {
// Do not trigger channelWritabilityChanged because the channel is closed already.
outboundBuffer.failFlushed(newClosedChannelException(initialCloseCause), false);
}
} finally {
inFlush0 = false;
}
return;
}
try {
// 写入数据 AbstractChannel.doWrite 抽象方法,对应的Channel实现
doWrite(outboundBuffer);
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (t instanceof IOException && config().isAutoClose()) {
initialCloseCause = t;
close(voidPromise(), t, newClosedChannelException(t), false);
} else {
try {
shutdownOutput(voidPromise(), t);
} catch (Throwable t2) {
initialCloseCause = t;
close(voidPromise(), t2, newClosedChannelException(t), false);
}
}
} finally {
inFlush0 = false;
}
}
AbstractNioUnsafe
AbstractNioUnsafe是 AbstractUnsafe类的NlO实现,主要实现了 connect、 finishConnect等方法
connect
发起远程连接
public final void connect(
final SocketAddress remoteAddress, final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
try {
if (connectPromise != null) {
throw new ConnectionPendingException();
}
// 是否激活状态(开启状态且已绑定)
boolean wasActive = isActive();
// 连接成功:AbstractNioChannel.doConnect 抽象方法,对应的Channel实现
if (doConnect(remoteAddress, localAddress)) {
// 返回连接结果promise
fulfillConnectPromise(promise, wasActive);
} else {
// 连接失败设置定时任务
connectPromise = promise;
requestedRemoteAddress = remoteAddress;
// Schedule connect timeout.
int connectTimeoutMillis = config().getConnectTimeoutMillis();
if (connectTimeoutMillis > 0) {
// 添加定时任务
connectTimeoutFuture = eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 返回异常
ChannelPromise connectPromise = AbstractNioChannel.this.connectPromise;
ConnectTimeoutException cause =
new ConnectTimeoutException("connection timed out: " + remoteAddress);
// 释放资源
if (connectPromise != null && connectPromise.tryFailure(cause)) {
close(voidPromise());
}
}
}, connectTimeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
// 添加连接结果监听器
promise.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
// 连接关闭
if (future.isCancelled()) {
if (connectTimeoutFuture != null) {
// 取消定时任务
connectTimeoutFuture.cancel(false);
}
// 释放资源
connectPromise = null;
close(voidPromise());
}
}
});
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
promise.tryFailure(annotateConnectException(t, remoteAddress));
closeIfClosed();
}
}
finishConnect
@Override
public final void finishConnect() {
assert eventLoop().inEventLoop();
try {
// 是否激活状态(服务端: 开启状态且已绑定; 客户端: channel 打开且处于连接状态)
boolean wasActive = isActive();
// 抽象方法,对应的channel实现
doFinishConnect();
// 返回连接结果promise
fulfillConnectPromise(connectPromise, wasActive);
} catch (Throwable t) {
fulfillConnectPromise(connectPromise, annotateConnectException(t, requestedRemoteAddress));
} finally {
if (connectTimeoutFuture != null) {
connectTimeoutFuture.cancel(false);
}
connectPromise = null;
}
}
NioByteUnsafe
主要负责数据读取,AbstractNioByteChannel的内部类,对应客户端
protected class NioByteUnsafe extends AbstractNioUnsafe {
@Override
public final void read() {
// 配置信息
final ChannelConfig config = config();
if (shouldBreakReadReady(config)) {
clearReadPending();
return;
}
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
// 用于ByteBuf内存分配
final ByteBufAllocator allocator = config.getAllocator();
// 内存分配处理
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.reset(config);
ByteBuf byteBuf = null;
boolean close = false;
try {
do {
// 分配内存给ByteBuf,用于接收通道中的数据
byteBuf = allocHandle.allocate(allocator);
// doReadBytes 从channel中读取数据 抽象方法子类实现
allocHandle.lastBytesRead(doReadBytes(byteBuf));
if (allocHandle.lastBytesRead() <= 0) {
byteBuf.release();
byteBuf = null;
close = allocHandle.lastBytesRead() < 0;
if (close) {
// There is nothing left to read as we received an EOF.
readPending = false;
}
break;
}
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(1);
readPending = false;
// 触发ChannelRead事件,最终调用 ChannelInboundHandler.channelRead
pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf);
byteBuf = null;
} while (allocHandle.continueReading());
allocHandle.readComplete();
// 触发ChannelReadComplete事件,最终调用 ChannelInboundHandler.channelReadComplete
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
if (close) {
closeOnRead(pipeline);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleReadException(pipeline, byteBuf, t, close, allocHandle);
} finally {
if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) {
// 移除读状态
removeReadOp();
}
}
}
}
NioMessageUnsafe
主要负责数据读取,AbstractNioMessageChannel的内部类,对应服务端
private final class NioMessageUnsafe extends AbstractNioUnsafe {
// 数据列表
private final List<Object> readBuf = new ArrayList<Object>();
@Override
public void read() {
assert eventLoop().inEventLoop();
// 配置信息
final ChannelConfig config = config();
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
// 用于ByteBuf内存分配的处理
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = unsafe().recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.reset(config);
boolean closed = false;
Throwable exception = null;
try {
try {
do {
// / doReadMessages 从channel中读取数据 模板方法子类实现
int localRead = doReadMessages(readBuf);
if (localRead == 0) {
break;
}
if (localRead < 0) {
closed = true;
break;
}
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(localRead);
} while (allocHandle.continueReading());
} catch (Throwable t) {
exception = t;
}
int size = readBuf.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
readPending = false;
// 触发ChannelRead事件,最终调用 ChannelInboundHandler.channelRead
pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i));
}
readBuf.clear();
allocHandle.readComplete();
// 触发ChannelReadComplete事件,最终调用 ChannelInboundHandler.channelReadComplete
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
if (exception != null) {
closed = closeOnReadError(exception);
pipeline.fireExceptionCaught(exception);
}
if (closed) {
inputShutdown = true;
if (isOpen()) {
close(voidPromise());
}
}
} finally {
if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) {
// 移除读状态
removeReadOp();
}
}
}
}
ChannelOutboundBuffer
每个 Channel 的 Unsafe 都有一个绑定的 ChannelOutboundBuffer,Netty 向外输出数据都是通过 ChannelOutboundBuffer 类进行的,调用 write 的时候,数据并没有写到 SocketChannel,而是写到了 ChannelOutboundBuffer 这里,当调用 flush 的时候,才真正写入到SocketChannel,完成数据传输
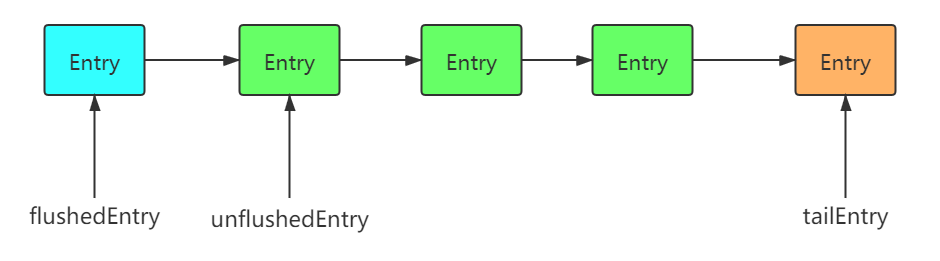
public final class ChannelOutboundBuffer {
// 对应的 channel
private final Channel channel;
// 缓存链表中被flush的第一个元素
private Entry flushedEntry;
// 缓存链表中中第一个未flush的元素
private Entry unflushedEntry;
// 缓存链表中的尾元素
private Entry tailEntry;
// flush但还没有写入到 channel 的数量
private int flushed;
// nioBuffer的个数
private int nioBufferCount;
// nioBuffer的字节大小
private long nioBufferSize;
}
Entry
静态内部类,Entry 是链表的结点,封装了待写入的 ByteBuf
static final class Entry {
// 使用对象池
private static final ObjectPool<Entry> RECYCLER = ObjectPool.newPool(new ObjectCreator<Entry>() {
@Override
public Entry newObject(Handle<Entry> handle) {
return new Entry(handle);
}
});
// 负责回收 Entry
private final Handle<Entry> handle;
// next 结点
Entry next;
// 消息内容 ByteBuf
Object msg;
// 一般情况,一个 ByteBuf 底层对应一个 ByteBuffer
// bufs 多数时候为空, 只有 buf 会被赋值
ByteBuffer[] bufs;
ByteBuffer buf;
// 回调结果,promise 是可写的 future
ChannelPromise promise;
// ByteBuf 中已写入的字节数
long progress;
// ByteBuf 可读的字节数
long total;
int pendingSize;
int count = -1;
boolean cancelled;
private Entry(Handle<Entry> handle) {
this.handle = handle;
}
static Entry newInstance(Object msg, int size, long total, ChannelPromise promise) {
// 通过对象池创建
Entry entry = RECYCLER.get();
entry.msg = msg;
entry.pendingSize = size + CHANNEL_OUTBOUND_BUFFER_ENTRY_OVERHEAD;
entry.total = total;
entry.promise = promise;
return entry;
}
}
addMessage
向ChannelOutboundBuffer中添加消息,新建一个Entry 加入链表尾部
public void addMessage(Object msg, int size, ChannelPromise promise) {
// 创建一个 新的Entry
Entry entry = Entry.newInstance(msg, size, total(msg), promise);
if (tailEntry == null) {
flushedEntry = null;
} else {
Entry tail = tailEntry;
tail.next = entry;
}
// 将新添加的 Entry 设置为 链表的 tailEntry
tailEntry = entry;
if (unflushedEntry == null) {
unflushedEntry = entry;
}
// 使用 CAS 修改 totalPendingSize
incrementPendingOutboundBytes(entry.pendingSize, false);
}
addFlush
当 addMessage 成功添加进 ChannelOutboundBuffer 后,就需要 flush 到 channel 中,但是addFlush并没有flush数据,而是记录了flushedEntry指针的位置和需要flush的链表长度(flushed字段)
public void addFlush() {
// 拿到未flush的头结点
Entry entry = unflushedEntry;
if (entry != null) {
// flushedEntry 被flush的结点为空
if (flushedEntry == null) {
// 设置未当前结点 entry
flushedEntry = entry;
}
do {
flushed ++;
if (!entry.promise.setUncancellable()) {
int pending = entry.cancel();
decrementPendingOutboundBytes(pending, false, true);
}
entry = entry.next;
} while (entry != null);
// 清空unflushedEntry
unflushedEntry = null;
}
}
remove
移除已flush的Entry
public boolean remove() {
Entry e = flushedEntry;
if (e == null) {
// 清空 NioBuffers
clearNioBuffers();
return false;
}
Object msg = e.msg;
ChannelPromise promise = e.promise;
int size = e.pendingSize;
// 从链表中移除 已flush的Entry
removeEntry(e);
if (!e.cancelled) {
ReferenceCountUtil.safeRelease(msg);
safeSuccess(promise);
decrementPendingOutboundBytes(size, false, true);
}
// 回收entry, GC
e.recycle();
return true;
}
// 从链表中移除 Entry
private void removeEntry(Entry e) {
if (-- flushed == 0) {
// processed everything
flushedEntry = null;
if (e == tailEntry) {
tailEntry = null;
unflushedEntry = null;
}
} else {
flushedEntry = e.next;
}
}
ChannelPipeline和 ChannelHandler
Netty的 ChannelPipeline和 ChannelHandler机制类似于 Servlet和 Filter过滤器,这类拦截器实际上是职责链模式的一种变形,主要是为了方便事件的拦截和用户业务逻辑的定制
ChannelPipeline
ChannelPipeline 是 ChannelHandler 的容器,负责 ChannelHandler 的管理和事件的拦截与调度
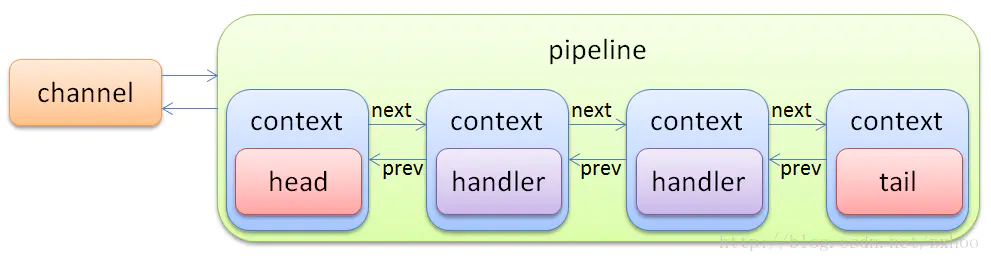
public class DefaultChannelPipeline implements ChannelPipeline {
// 双向链表的头结点和尾结点
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext head;
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext tail;
private final Channel channel;
// Future 和 Promise
private final ChannelFuture succeededFuture;
private final VoidChannelPromise voidPromise;
protected DefaultChannelPipeline(Channel channel) {
this.channel = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(channel, "channel");
// 创建 Future 和 Promise
succeededFuture = new SucceededChannelFuture(channel, null);
voidPromise = new VoidChannelPromise(channel, true);
// 默认创建双向链表
tail = new TailContext(this);
head = new HeadContext(this);
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
}
ChannelHandler链表
ChannelPipeline 对外提供了 增删改查 的功能,这样对开发来说也有更多的操作空间
addLast: 链表尾部添加结点
@Override
public final ChannelPipeline addLast(EventExecutorGroup group, String name, ChannelHandler handler) {
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext newCtx;
// 锁住当前对象,保证线程安全
synchronized (this) {
checkMultiplicity(handler);
// 创建 DefaultChannelHandlerContext 分钟
newCtx = newContext(group, filterName(name, handler), handler);
// 加入链表 放到tail前一位
addLast0(newCtx);
if (!registered) {
// 设置状态: 即将调用handlerAdded()
newCtx.setAddPending();
callHandlerCallbackLater(newCtx, true);
return this;
}
EventExecutor executor = newCtx.executor();
if (!executor.inEventLoop()) {
// 调用ChannelHandler.handlerAdded()方法,交给executor处理
callHandlerAddedInEventLoop(newCtx, executor);
return this;
}
}
// 调用ChannelHandler.handlerAdded()方法
callHandlerAdded0(newCtx);
return this;
}
private void addLast0(AbstractChannelHandlerContext newCtx) {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext prev = tail.prev;
newCtx.prev = prev;
newCtx.next = tail;
prev.next = newCtx;
tail.prev = newCtx;
}
addFirst: 链表头部添加结点
@Override
public final ChannelPipeline addFirst(EventExecutorGroup group, String name, ChannelHandler handler) {
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext newCtx;
synchronized (this) {
// 检查 ChannelHandler @Sharable 注解
// 如果是 @Sharable 类型的就可以添加到多个 ChannelPipeline 中
// 如果不是 @Sharable 类型添加到多个ChannelPipeline 中就会抛出 ChannelPipelineException
checkMultiplicity(handler);
// 设置name
name = filterName(name, handler);
// 创建 DefaultChannelHandlerContext
newCtx = newContext(group, name, handler);
// 插入链表
addFirst0(newCtx);
if (!registered) {
// 设置状态: 即将调用handlerAdded()
newCtx.setAddPending();
callHandlerCallbackLater(newCtx, true);
return this;
}
EventExecutor executor = newCtx.executor();
if (!executor.inEventLoop()) {
// 调用ChannelHandler.handlerAdded()方法,交给executor处理
callHandlerAddedInEventLoop(newCtx, executor);
return this;
}
}
// 调用ChannelHandler.handlerAdded()方法
callHandlerAdded0(newCtx);
return this;
}
private void addFirst0(AbstractChannelHandlerContext newCtx) {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext nextCtx = head.next;
newCtx.prev = head;
newCtx.next = nextCtx;
head.next = newCtx;
nextCtx.prev = newCtx;
}
addBefore: 指定结点前添加结点
addAfter: 指定结点后添加结点
remove: 移除结点
ChannelHandlerContext
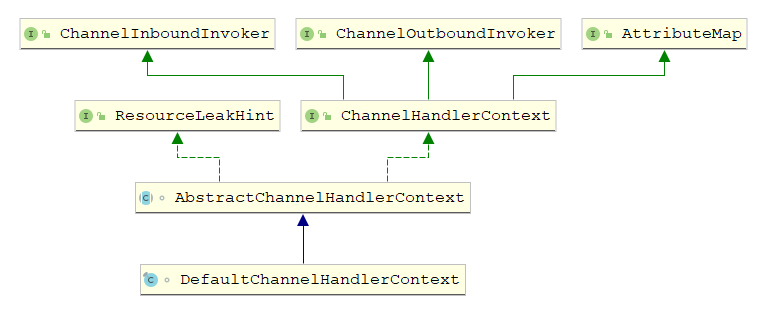
AbstractChannelHandlerContext
abstract class AbstractChannelHandlerContext implements ChannelHandlerContext, ResourceLeakHint {
// 后继结点
volatile AbstractChannelHandlerContext next;
// 前驱结点
volatile AbstractChannelHandlerContext prev;
// HANDLER 状态
private static final AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<AbstractChannelHandlerContext> HANDLER_STATE_UPDATER =
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(AbstractChannelHandlerContext.class, "handlerState");
// 状态: 即将调用handlerAdded()
private static final int ADD_PENDING = 1;
// 状态: 已调用handlerAdded()
private static final int ADD_COMPLETE = 2;
// 状态: 已调用handlerRemoved()
private static final int REMOVE_COMPLETE = 3;
// 状态: 初始状态
private static final int INIT = 0;
private final DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline;
// Handler 名称
private final String name;
private final boolean ordered;
private final int executionMask;
// 执行器
final EventExecutor executor;
// 执行结果
private ChannelFuture succeededFuture;
private Tasks invokeTasks;
// Handler 状态
private volatile int handlerState = INIT;
}
Inbound的IN事件
- Inbound 事件是通知事件,当某件事情已经就绪后,通知上层
- Inbound 事件发起者是 unsafe,处理者是 Channel
- 如果用户没有实现自定义的处理方法,Inbound 事件默认的处理者是 TailContext, 并且其处理方法是空实现
- Inbound 事件在 Pipeline 中传输方向是 head -> tail
public interface ChannelInboundInvoker {
// Channel注册
ChannelInboundInvoker fireChannelRegistered();
// Channel取消注册
ChannelInboundInvoker fireChannelUnregistered();
// Channel激活
ChannelInboundInvoker fireChannelActive();
// Channel取消激活
ChannelInboundInvoker fireChannelInactive();
// 捕获异常
ChannelInboundInvoker fireExceptionCaught(Throwable cause);
// 用户事件触发
ChannelInboundInvoker fireUserEventTriggered(Object event);
// channelRead事件
ChannelInboundInvoker fireChannelRead(Object msg);
// channelRead完成事件
ChannelInboundInvoker fireChannelReadComplete();
// channel可写性修改事件
ChannelInboundInvoker fireChannelWritabilityChanged();
}
findContextInbound
根据事件标记mask,在链表中找到下一个mask事件的结点
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext findContextInbound(int mask) {
// ctx初始化为指向当前context, 也就是this
AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx = this;
do {
// 然后指向ctx的next指针
ctx = ctx.next;
} while ((ctx.executionMask & mask) == 0);
// (ctx.executionMask & mask) != 0 表示 ctx.executionMask = mask
return ctx;
}
以fireChannelRegistered为例,调用过程都是相似的
@Override
public ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelRegistered() {
// 找到下一个REGISTERED事件结点,触发事件
invokeChannelRegistered(findContextInbound(MASK_CHANNEL_REGISTERED));
return this;
}
static void invokeChannelRegistered(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next) {
// 获取执行器EventLoop
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
// 如果当前线程和eventLoop的线程相同,直接执行
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
next.invokeChannelRegistered();
} else {
// 否则交给executor执行
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
next.invokeChannelRegistered();
}
});
}
}
private void invokeChannelRegistered() {
// 检查是否已经调用了handlerAdded()
if (invokeHandler()) {
try {
// 调用 ChannelInboundHandler.channelRegistered
((ChannelInboundHandler) handler()).channelRegistered(this);
} catch (Throwable t) {
notifyHandlerException(t);
}
} else {
// 重新触发
fireChannelRegistered();
}
}
Outbound的Out事件
- Outbound 事件是请求事件(由 Connect 发起一个请求,并最终由 unsafe 处理这个请求)
- Outbound 事件的发起者是 Channel,处理者是 unsafe
- Outbound 事件在 Pipeline 中的传输方向是 tail -> head
public interface ChannelOutboundInvoker {
// 绑定地址
ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress);
// 通过ChannelPromise可以获取返回结果
ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise);
// 连接远程地址
ChannelFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress);
ChannelFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress);
// 通过ChannelPromise可以获取返回结果
ChannelFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, ChannelPromise promise);
ChannelFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise);
// 断开连接
ChannelFuture disconnect();
// 通过ChannelPromise可以获取返回结果
ChannelFuture disconnect(ChannelPromise promise);
// channel关闭
ChannelFuture close();
// 通过ChannelPromise可以获取返回结果
ChannelFuture close(ChannelPromise promise);
// channel注销
ChannelFuture deregister();
// 通过ChannelPromise可以获取返回结果
ChannelFuture deregister(ChannelPromise promise);
// 从channel获取到对应的ChannelOutboundInvoker
ChannelOutboundInvoker read();
// 写入信息msg,通过ChannelPromise可以获取返回结果
ChannelFuture write(Object msg);
ChannelFuture write(Object msg, ChannelPromise promise);
// flush 发送数据
ChannelOutboundInvoker flush();
// 写入并 flush 信息msg
ChannelFuture writeAndFlush(Object msg, ChannelPromise promise);
ChannelFuture writeAndFlush(Object msg);
// 返回一个新建的ChannelPromise
ChannelPromise newPromise();
ChannelProgressivePromise newProgressivePromise();
ChannelPromise voidPromise();
// 返回一个新建的ChannelFuture(成功或失败结果)
ChannelFuture newSucceededFuture();
ChannelFuture newFailedFuture(Throwable cause);
}
findContextOutbound
根据事件标记mask,在链表中找到下一个mask事件的结点
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext findContextOutbound(int mask) {
// ctx初始化为指向当前context, 也就是this
AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx = this;
do {
// 然后指向ctx的prev指针
ctx = ctx.prev;
} while ((ctx.executionMask & mask) == 0);
// (ctx.executionMask & mask) != 0 表示 ctx.executionMask = mask
return ctx;
}
以bind为例,调用过程都是相似的
@Override
public ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress) {
return bind(localAddress, newPromise());
}
@Override
public ChannelFuture bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(localAddress, "localAddress");
if (isNotValidPromise(promise, false)) {
// cancelled
return promise;
}
// 找到下一个BIND事件结点,触发事件
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = findContextOutbound(MASK_BIND);
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
// 如果当前线程和eventLoop的线程相同,直接执行
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
next.invokeBind(localAddress, promise);
} else {
// 否则交给executor执行
safeExecute(executor, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
next.invokeBind(localAddress, promise);
}
}, promise, null, false);
}
return promise;
}
private void invokeBind(SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
// 检查是否已经调用了handlerAdded()
if (invokeHandler()) {
try {
// 调用 ChannelOutboundHandler.bind
((ChannelOutboundHandler) handler()).bind(this, localAddress, promise);
} catch (Throwable t) {
notifyOutboundHandlerException(t, promise);
}
} else {
// 重新触发事件
bind(localAddress, promise);
}
}
DefaultChannelHandlerContext
final class DefaultChannelHandlerContext extends AbstractChannelHandlerContext {
// 处理接口
private final ChannelHandler handler;
// 构造方法
DefaultChannelHandlerContext(
DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline, EventExecutor executor, String name, ChannelHandler handler) {
super(pipeline, executor, name, handler.getClass());
this.handler = handler;
}
@Override
public ChannelHandler handler() {
return handler;
}
}
ChannelHandler
ChannelHandler类似于 Servlet的 Filter过滤器,负责对IO事件或者I/O操作进行拦截和处理
ChannelHandler支持注解,目前支持的注解有两种.
- @Sharable: 多个 ChannelPipeline共用同一个 ChannelHandler;
- @Skip: 被Skip注解的方法不会被调用,直接被忽略.
ChannelHandler做下面一些事情:
- 传输数据时,将数据从一种格式转换到另一种格式
- 异常通知
- Channel变为有效或无效时获得通知
- Channel被注册或从EventLoop中注销时获得通知
- 通知用户特定事件
ChannelInitializer
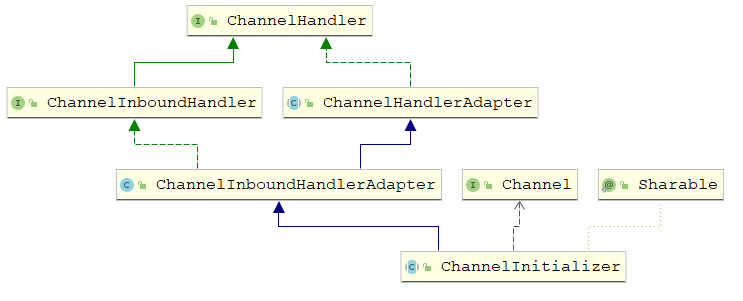
ChannelInitializer继承了ChannelHandlerAdapter,是一个比较特殊的handler, 当一个Channel被注册到它的EventLoop时,提供一个简单的方式用于初始化。它的实现类通常在Bootstrap.handler(ChannelHandler)/ServerBootstrap.handler(ChannelHandler)和ServerBootstrap.childHandler(ChannelHandler)的上下文中使用,用于构建channel的ChannelPipeline
ChannelInitializer在完成初始化工作后会从pipeline中移除,只会初始化一次
public abstract class ChannelInitializer<C extends Channel> extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
// ChannelHandlerContext 集合
private final Set<ChannelHandlerContext> initMap = Collections.newSetFromMap(
new ConcurrentHashMap<ChannelHandlerContext, Boolean>());
// 当前 handler 加入ChannelHandler链表时触发
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 已注册
if (ctx.channel().isRegistered()) {
// 初始化Channel
if (initChannel(ctx)) {
// 成功初始化,移除ctx
removeState(ctx);
}
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private boolean initChannel(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 向集合中添加ctx
if (initMap.add(ctx)) { // Guard against re-entrance.
try {
// 模板方法
initChannel((C) ctx.channel());
} catch (Throwable cause) {
exceptionCaught(ctx, cause);
} finally {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ctx.pipeline();
if (pipeline.context(this) != null) {
pipeline.remove(this);
}
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 模板方法
protected abstract void initChannel(C ch) throws Exception;
}
Promise与Future
Future用于获取异步操作的结果
promise 是可写的 future,因为 future 不支持写操作接口,netty 使用 promise 扩展了 future, 可以对异步操作结果进行设置
AbstractFuture
public abstract class AbstractFuture<V> implements Future<V> {
// 获取异步结果
@Override
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
// 阻塞等到 调用完成,失败或返回结果
await();
// 获取失败异常信息
Throwable cause = cause();
// 如果异常信息为null,直接获取响应结果
if (cause == null) {
return getNow();
}
//异常不为null,抛出异常
if (cause instanceof CancellationException) {
throw (CancellationException) cause;
}
throw new ExecutionException(cause);
}
// 带超时机制的异步结果
@Override
public V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException,
ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
// 带超时的阻塞
if (await(timeout, unit)) {
Throwable cause = cause();
if (cause == null) {
return getNow();
}
if (cause instanceof CancellationException) {
throw (CancellationException) cause;
}
throw new ExecutionException(cause);
}
// 超时异常
throw new TimeoutException();
}
}
DefaultPromise
public class DefaultPromise<V> extends AbstractFuture<V> implements Promise<V> {
// 返回结果result的原子更新器
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
private static final AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<DefaultPromise, Object> RESULT_UPDATER =
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater.newUpdater(DefaultPromise.class, Object.class, "result");
// 常量: 成功返回标记
private static final Object SUCCESS = new Object();
// 常量: 不可取消标记
private static final Object UNCANCELLABLE = new Object();
// 常量: 异常返回
private static final CauseHolder CANCELLATION_CAUSE_HOLDER =
new CauseHolder(ThrowableUtil.unknownStackTrace(
new CancellationException(), DefaultPromise.class, "cancel(...)"));
private static final StackTraceElement[] CANCELLATION_STACK =
CANCELLATION_CAUSE_HOLDER.cause.getStackTrace();
// 返回结果 volatile 修饰
private volatile Object result;
// 执行任务的线程 一般是 EventLoop
private final EventExecutor executor;
// 事件监听器 单个或多个 类型为 DefaultFutureListeners(列表) 或 GenericFutureListener(单个)
private Object listeners;
// wait线程的数量
private short waiters;
// true 表示正在进行通知Listeners, false 表示通知结束, 防止并发
private boolean notifyingListeners;
}
设置执行结果
// 设置成功结果
@Override
public Promise<V> setSuccess(V result) {
if (setSuccess0(result)) {
return this;
}
throw new IllegalStateException("complete already: " + this);
}
private boolean setSuccess0(V result) {
return setValue0(result == null ? SUCCESS : result);
}
// 设置失败结果
@Override
public Promise<V> setFailure(Throwable cause) {
if (setFailure0(cause)) {
return this;
}
throw new IllegalStateException("complete already: " + this, cause);
}
// 设置失败标志
private boolean setFailure0(Throwable cause) {
return setValue0(new CauseHolder(checkNotNull(cause, "cause")));
}
// 更新result
private boolean setValue0(Object objResult) {
// 通过CAS更新result结果
if (RESULT_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, null, objResult) ||
RESULT_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, UNCANCELLABLE, objResult)) {
if (checkNotifyWaiters()) {
// 唤醒所有阻塞线程
notifyListeners();
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
await
@Override
public Promise<V> await() throws InterruptedException {
if (isDone()) {
return this;
}
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
throw new InterruptedException(toString());
}
checkDeadLock();
synchronized (this) {
while (!isDone()) {
// 执行wait()之前,waiters加1
incWaiters();
try {
wait();
} finally {
// wait()结束之后,waiters减1
decWaiters();
}
}
}
return this;
}
notify
// 检查waiter线程
private synchronized boolean checkNotifyWaiters() {
if (waiters > 0) {
// 通知全部wait线程
notifyAll();
}
return listeners != null;
}
private void notifyListeners() {
EventExecutor executor = executor();
// 当前线程 等于 当前EventLoop持有的线程
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
final InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocals = InternalThreadLocalMap.get();
final int stackDepth = threadLocals.futureListenerStackDepth();
if (stackDepth < MAX_LISTENER_STACK_DEPTH) {
threadLocals.setFutureListenerStackDepth(stackDepth + 1);
try {
notifyListenersNow();
} finally {
threadLocals.setFutureListenerStackDepth(stackDepth);
}
return;
}
}
// 交给EventLoop持有的线程执行
safeExecute(executor, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
notifyListenersNow();
}
});
}
private void notifyListenersNow() {
Object listeners;
synchronized (this) {
// 正在执行通知
if (notifyingListeners || this.listeners == null) {
return;
}
notifyingListeners = true;
listeners = this.listeners;
// 通知完之后就置空,不再通知第二次
this.listeners = null;
}
// 循环执行
for (;;) {
if (listeners instanceof DefaultFutureListeners) {
notifyListeners0((DefaultFutureListeners) listeners);
} else {
notifyListener0(this, (GenericFutureListener<?>) listeners);
}
synchronized (this) {
// 不存在新的 listeners, 执行结束
if (this.listeners == null) {
notifyingListeners = false;
return;
}
// 存在新的 listeners, 重新循环
listeners = this.listeners;
this.listeners = null;
}
}
}
获取结果
@Override
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
Object result = this.result;
// 如果没有执行完毕
if (!isDone0(result)) {
// 阻塞等到await()调用完成
await();
result = this.result;
}
if (result == SUCCESS || result == UNCANCELLABLE) {
return null;
}
// 获取异常信息
Throwable cause = cause0(result);
if (cause == null) {
return (V) result;
}
if (cause instanceof CancellationException) {
throw (CancellationException) cause;
}
throw new ExecutionException(cause);
}
private static boolean isDone0(Object result) {
return result != null && result != UNCANCELLABLE;
}
编解码器
利用Netty提供的半包编码和解码器LengthFieldPrepender和LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder,可以轻松的解决TCP粘包和半包问题
Decoder(解码器)
- 解码字节到消息(ByteToMessageDecoder 和 ReplayingDecoder)
- 解码消息到消息(MessageToMessageDecoder)
Encoder(编码器)
- 编码从消息到字节(MessageToByteEncoder)
- 编码从消息到消息(MessageToMessageEncoder)
Bootstrap
Bootstrap类是Netty提供的一个可以通过简单配置来设置或"引导"程序的一个很重要的类。
- Bootstrap用来连接远程主机,有1个EventLoopGroup
- ServerBootstrap用来绑定本地端口,有2个EventLoopGroup
AbstractBootstrap
public abstract class AbstractBootstrap<B extends AbstractBootstrap<B, C>, C extends Channel>
implements Cloneable {
// 这里的EventLoopGroup 对应 Reactor模式的 Acceptor 线程, 负责处理客户端的请求接入
volatile EventLoopGroup group;
// 创建 Channel 的工厂 根据传入的class 通过反射创建 对应的Channel
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
private volatile ChannelFactory<? extends C> channelFactory;
// 用来绑定的地址
private volatile SocketAddress localAddress;
// 记录 Channel 的配置信息
private final Map<ChannelOption<?>, Object> options = new LinkedHashMap<ChannelOption<?>, Object>();
private final Map<AttributeKey<?>, Object> attrs = new ConcurrentHashMap<AttributeKey<?>, Object>();
// ChannelHandler 负责处理 Channel 的IO事件
private volatile ChannelHandler handler;
}
group
绑定线程
public B group(EventLoopGroup group) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(group, "group");
if (this.group != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("group set already");
}
// 绑定一个 EventLoopGroup,对应 Reactor模式的 Acceptor 线程
this.group = group;
return self();
}
channel
设置对应的Channel,Netty通过ChannelFactory创建不同的Channel
- 服务端: NioServerSocketChannel.class
- 客户端: NioSocketChannel.class
public B channel(Class<? extends C> channelClass) {
// 创建反射工厂ReflectiveChannelFactory, ReflectiveChannelFactory 通过反射创建 对应的Channel
return channelFactory(new ReflectiveChannelFactory<C>(
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(channelClass, "channelClass")
));
}
public B channelFactory(io.netty.channel.ChannelFactory<? extends C> channelFactory) {
return channelFactory((ChannelFactory<C>) channelFactory);
}
@Deprecated
public B channelFactory(ChannelFactory<? extends C> channelFactory) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(channelFactory, "channelFactory");
if (this.channelFactory != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("channelFactory set already");
}
// 记录 channelFactory,通过ChannelFactory创建对应的Channnel
this.channelFactory = channelFactory;
return self();
}
ReflectiveChannelFactory
通过ReflectiveChannelFactory创建对应的Channnel
public class ReflectiveChannelFactory<T extends Channel> implements ChannelFactory<T> {
// 记录Channel的 Constructor
private final Constructor<? extends T> constructor;
// 构造方法
public ReflectiveChannelFactory(Class<? extends T> clazz) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(clazz, "clazz");
try {
this.constructor = clazz.getConstructor();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
}
// 通过Constructor反射创建对应 Channel
@Override
public T newChannel() {
try {
return constructor.newInstance();
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new ChannelException();
}
}
}
option
设置一些Channel相关参数
// 记录 Channel 的配置信息
private final Map<ChannelOption<?>, Object> options = new LinkedHashMap<ChannelOption<?>, Object>();
// 设置参数
public <T> B option(ChannelOption<T> option, T value) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(option, "option");
synchronized (options) {
if (value == null) {
// 如果value为null则删除该key
options.remove(option);
} else {
options.put(option, value);
}
}
return self();
}
handler
设置Handler,一般是客户端使用,服务端使用childHandler
public B handler(ChannelHandler handler) {
this.handler = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(handler, "handler");
return self();
}
bind
绑定端口,对该端口进行监听
public ChannelFuture bind(int inetPort) {
return bind(new InetSocketAddress(inetPort));
}
public ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress) {
// 校验
validate();
return doBind(ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(localAddress, "localAddress"));
}
doBind
private ChannelFuture doBind(final SocketAddress localAddress) {
// 创建并注册Channel
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();
// 注册异常,返回移除信息
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
return regFuture;
}
// 是否注册成功
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise();
// 绑定 交给EventLoop执行
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
return promise;
} else {
final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
// 返回错误信息
promise.setFailure(cause);
} else {
promise.registered();
// 绑定
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
}
}
});
return promise;
}
}
initAndRegister
创建并注册Channel
final ChannelFuture initAndRegister() {
Channel channel = null;
try {
// channelFactory 反射创建 对应的Channel
channel = channelFactory.newChannel();
// 初始化 模板方法,子类实现
init(channel);
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (channel != null) {
// 如果出错, 强行关闭这个channel
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
return new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
// 返回失败信息
return new DefaultChannelPromise(new FailedChannel(), GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
// acceptor 线程 注册 channel
ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel);
// 注册出错
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
if (channel.isRegistered()) {
channel.close();
} else {
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
}
}
return regFuture;
}
doBind0
执行真正的bind操作,交给Reactor线程(服务端)执行
private static void doBind0(
final ChannelFuture regFuture, final Channel channel,
final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
channel.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 检查注册是否成功
if (regFuture.isSuccess()) {
// 绑定localAddress到channel, 添加监听-> bind失败关闭channel
channel.bind(localAddress, promise).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
} else {
// 返回失败信息
promise.setFailure(regFuture.cause());
}
}
});
}
ServerBootstrap
ServerBootstrap是服务端的启动类,内部采用了Reactor模式
public class ServerBootstrap extends AbstractBootstrap<ServerBootstrap, ServerChannel> {
// 记录 worker Channel 的配置信息
private final Map<ChannelOption<?>, Object> childOptions = new LinkedHashMap<ChannelOption<?>, Object>();
private final Map<AttributeKey<?>, Object> childAttrs = new ConcurrentHashMap<AttributeKey<?>, Object>();
// 配置信息
private final ServerBootstrapConfig config = new ServerBootstrapConfig(this);
// 记录 worker 线程(Reactor模式的从线程)
private volatile EventLoopGroup childGroup;
// worker 线程 对应的 Handler
private volatile ChannelHandler childHandler;
}
group
绑定线程,采用Reactor模式,需要绑定boss线程(Acceptor线程)和 worker 线程(Reactor 线程)
public class ServerBootstrap extends AbstractBootstrap<ServerBootstrap, ServerChannel> {
public ServerBootstrap group(EventLoopGroup parentGroup, EventLoopGroup childGroup) {
// 设置 boss 线程
super.group(parentGroup);
if (this.childGroup != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("childGroup set already");
}
// worker 线程
this.childGroup = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(childGroup, "childGroup");
return this;
}
}
childHandler
对于服务端而言,由于采用了Reactor模式,有两种Channel需要处理
- ServerSocketChannel:用于处理客户端连接的accept操作
- SocketChannel:对应客户端连接请求
childHandler用于处理客户端的请求
public ServerBootstrap childHandler(ChannelHandler childHandler) {
// childHandler 赋值
this.childHandler = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(childHandler, "childHandler");
return this;
}
init
init是一个模板方法,父类doBind() -> initAndRegister() -> init()
@Override
void init(Channel channel) {
// 设置 Channel 选项配置 和 attrs 配置
setChannelOptions(channel, newOptionsArray(), logger);
setAttributes(channel, attrs0().entrySet().toArray(EMPTY_ATTRIBUTE_ARRAY));
// 获取 channel 的 pipeline
ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline();
// worker 从线程和 从线程对应的 Handler
final EventLoopGroup currentChildGroup = childGroup;
final ChannelHandler currentChildHandler = childHandler;
final Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object>[] currentChildOptions;
synchronized (childOptions) {
currentChildOptions = childOptions.entrySet().toArray(EMPTY_OPTION_ARRAY);
}
final Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object>[] currentChildAttrs =
childAttrs.entrySet().toArray(EMPTY_ATTRIBUTE_ARRAY);
//3 为NioServerSocketChannel设置通过handler方法指定的处理器
p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(final Channel ch) {
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
// config.handler() => bootstrap.handler()
// 这里将 boss 线程(acceptor 线程)对应的 handler 添加到 ChannelPipeline 的双向链表中
ChannelHandler handler = config.handler();
if (handler != null) {
pipeline.addLast(handler);
}
// 添加一个默认的处理器ServerBootstrapAcceptor 用于接收客户端的连接请求
// 对应 Reactor 模式的 acceptor 线程, 接收请求并转发
ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));
}
});
}
});
}
ServerBootstrapAcceptor
private static class ServerBootstrapAcceptor extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
// worker 线程
private final EventLoopGroup childGroup;
// worker 线程处理器
private final ChannelHandler childHandler;
private final Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object>[] childOptions;
private final Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object>[] childAttrs;
private final Runnable enableAutoReadTask;
// 构造方法
ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
final Channel channel, EventLoopGroup childGroup, ChannelHandler childHandler,
Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object>[] childOptions, Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object>[] childAttrs) {
this.childGroup = childGroup;
this.childHandler = childHandler;
this.childOptions = childOptions;
this.childAttrs = childAttrs;
enableAutoReadTask = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
channel.config().setAutoRead(true);
}
};
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
// 将客户端传入的对象转成Channel对象
final Channel child = (Channel) msg;
// 客户端的连接 添加 childHandler
child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler);
// 设置 channel参数
setChannelOptions(child, childOptions, logger);
setAttributes(child, childAttrs);
try {
// worker 线程注册 channel, 交给childGroup(Reactor 线程)处理
childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
// 强制关闭
forceClose(child, future.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
// 强制关闭
forceClose(child, t);
}
}
}
Bootstrap
connect
客户端连接服务的远程地址
public ChannelFuture connect(InetAddress inetHost, int inetPort) {
return connect(new InetSocketAddress(inetHost, inetPort));
}
public ChannelFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(remoteAddress, "remoteAddress");
validate();
// 连接
return doResolveAndConnect(remoteAddress, config.localAddress());
}
doResolveAndConnect
private ChannelFuture doResolveAndConnect(final SocketAddress remoteAddress,final SocketAddress localAddress) {
// 创建并注册Channel
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();
// 是否注册完成
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
// 注册失败,返回
if (!regFuture.isSuccess()) {
return regFuture;
}
// 远程连接
return doResolveAndConnect0(channel, remoteAddress, localAddress, channel.newPromise());
} else {
final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
// 返回错误信息
promise.setFailure(cause);
} else {
promise.registered();
// 远程连接
doResolveAndConnect0(channel, remoteAddress, localAddress, promise);
}
}
});
return promise;
}
}
init
init是一个模板方法,doResolveAndConnect() -> initAndRegister() -> init()
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
void init(Channel channel) {
// 取channel的ChannelPipeline
ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline();
// 增加当前Bootstrap的handler 到ChannelPipeline中
p.addLast(config.handler());
// 实在 Options 配置 和 attrs
setChannelOptions(channel, newOptionsArray(), logger);
setAttributes(channel, attrs0().entrySet().toArray(EMPTY_ATTRIBUTE_ARRAY));
}
doResolveAndConnect0
private ChannelFuture doResolveAndConnect0(final Channel channel, SocketAddress remoteAddress,
final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
final EventLoop eventLoop = channel.eventLoop();
final AddressResolver<SocketAddress> resolver = this.resolver.getResolver(eventLoop);
if (!resolver.isSupported(remoteAddress) || resolver.isResolved(remoteAddress)) {
// 连接远程地址
doConnect(remoteAddress, localAddress, promise);
return promise;
}
final Future<SocketAddress> resolveFuture = resolver.resolve(remoteAddress);
if (resolveFuture.isDone()) {
final Throwable resolveFailureCause = resolveFuture.cause();
if (resolveFailureCause != null) {
// Failed to resolve immediately
channel.close();
// 设置失败信息
promise.setFailure(resolveFailureCause);
} else {
// 连接远程地址
doConnect(resolveFuture.getNow(), localAddress, promise);
}
return promise;
}
// 添加监听,等待完成连接
resolveFuture.addListener(new FutureListener<SocketAddress>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<SocketAddress> future) throws Exception {
// 连接失败
if (future.cause() != null) {
// 关闭 channel 设置失败信息
channel.close();
promise.setFailure(future.cause());
} else {
doConnect(future.getNow(), localAddress, promise);
}
}
});
} catch (Throwable cause) {
promise.tryFailure(cause);
}
return promise;
}
doConnect
private static void doConnect(final SocketAddress remoteAddress, final SocketAddress localAddress,
final ChannelPromise connectPromise) {
final Channel channel = connectPromise.channel();
// 取当前channel的eventLoop, 执行连接任务
channel.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 调用DefaultChannelPipeline.connect
if (localAddress == null) {
channel.connect(remoteAddress, connectPromise);
} else {
channel.connect(remoteAddress, localAddress, connectPromise);
}
// 添加监听, 返回失败关闭Channel
connectPromise.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
}
});
}