前言
在《ViewGroup事件分发总结-TouchTarget》中对事件派发过程中TouchTarget的作用做了总结,TouchTarget中有一个成员变量pointerIdBits用于保存该child上的触摸点ID集合,ViewGroup在实际派发过程中会根据这个ID集合进行一些特殊处理。
当两个及以上的手指触摸屏幕时,会产生多点触摸事件传递给ViewGroup,该MotionEvent中除了会存储事件类型和坐标位置等信息外,还会保存一组触摸点信息。当触摸点落于ViewGroup中的不同child上时,需要对MotionEvent进行事件拆分,再将拆分后的事件派发给对应child。
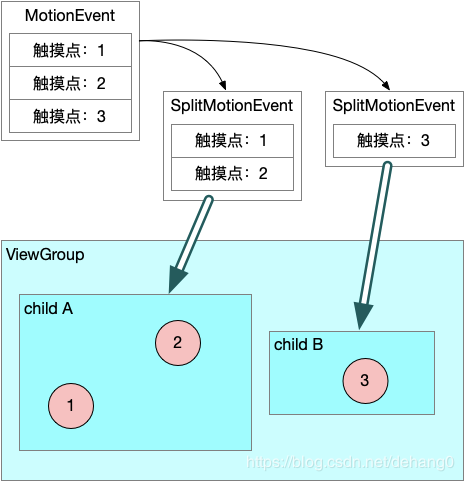
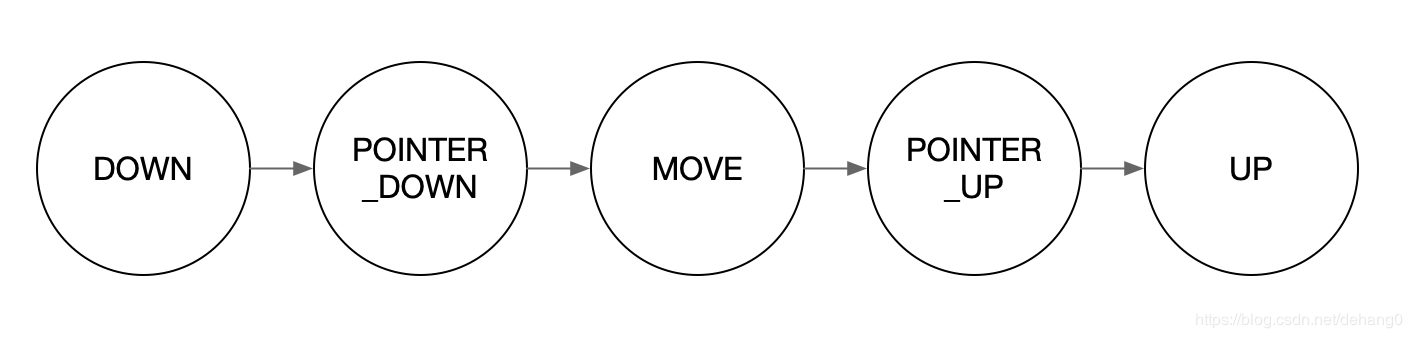
一次完整的派发事件序列是从ACTION_DOWN开始,ACTION_UP/ACTION_CANCEL结束,当中间出现ACTION_POINTER_DOWN或ACTION_POINTER_UP时,说明产生触摸点数量变动。
源码探究
文中源码基于Android 9.0
结合ViewGroup事件派发流程来看看事件拆分在其中的作用场景,首先分析下代表触摸事件的类MotionEvent。
MotionEvent说明
ViewGroup在事件派发前,会先从 MotionEvent中获取中获取action。该action为int型,高8位存储触摸点索引集合,低8位才是存储动作类型(ACTION_DOWN时索引都是0)。当处于多点触摸情况下,需要通过索引集合中的索引找到触摸点信息,再从触摸点信息中获取触摸点ID。
例如当第二个触摸点落于ViewGroup时,此时传递进来的 MotionEvent的action低8位是ACTION_POINTER_DOWN,高8位是该触摸点的索引。同时 MotionEvent中会携带当前ViewGroup上的所有触摸点信息集合。
获取触摸点索引
-> MotionEvent.java
public static final int ACTION_POINTER_INDEX_MASK = 0xff00;
public static final int ACTION_POINTER_INDEX_SHIFT = 8;
// Pointer to the native MotionEvent object that contains the actual data.
private long mNativePtr;
public final int getActionIndex() {
// 从native层获取该MotionEvent对应Action值,取高8位值后右移,得到索引值。
return (nativeGetAction(mNativePtr) & ACTION_POINTER_INDEX_MASK)
>> ACTION_POINTER_INDEX_SHIFT;
}
mNativePtr成员为指向包含实际数据的native层MotionEvent对象的指针。
-> android_view_MotionEvent.cpp
static jint android_view_MotionEvent_nativeGetAction(jlong nativePtr) {
// 通过java层保存的指针类型转换获得native层MotionEvent对象,详细数据都在这里面。
MotionEvent* event = reinterpret_cast<MotionEvent*>(nativePtr);
return event->getAction();
}
获取指定触摸点ID
在得到触摸点索引后,即可通过索引来获取触摸点ID。
-> MotionEvent.java
public final int getPointerId(int pointerIndex) {
// 也是通过native方法获取
return nativeGetPointerId(mNativePtr, pointerIndex);
}
-> android_view_MotionEvent.cpp
static jint android_view_MotionEvent_nativeGetPointerId(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz,
jlong nativePtr, jint pointerIndex) {
MotionEvent* event = reinterpret_cast<MotionEvent*>(nativePtr);
// 获取MotionEvent中存储的触摸点个数
size_t pointerCount = event->getPointerCount();
// 检查索引是否越界
if (!validatePointerIndex(env, pointerIndex, pointerCount)) {
return -1;
}
// 获取索引对应的触摸点ID
return event->getPointerId(pointerIndex);
}
获取所有触摸点ID
获取该MotionEvent中包含的所有触摸点ID,保存在一个int中。
-> MotionEvent.java
public final int getPointerIdBits() {
int idBits = 0;
// 获取触摸点个数
final int pointerCount = nativeGetPointerCount(mNativePtr);
for (int i = 0; i < pointerCount; i++) {
// 依次用索引获取ID,通过|=操作合并在一个int上。
idBits |= 1 << nativeGetPointerId(mNativePtr, i);
}
return idBits;
}
获取指定触摸点位置坐标
根据触摸点索引获取对应触摸点的位置坐标,以获取X坐标为例:
-> MotionEvent.java
private static final int HISTORY_CURRENT = -0x80000000;
public final float getX(int pointerIndex) {
return nativeGetAxisValue(mNativePtr, AXIS_X, pointerIndex, HISTORY_CURRENT);
}
-> android_view_MotionEvent.cpp
static const jint HISTORY_CURRENT = -0x80000000;
static jfloat android_view_MotionEvent_nativeGetAxisValue(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz,
jlong nativePtr, jint axis, jint pointerIndex, jint historyPos) {
MotionEvent* event = reinterpret_cast<MotionEvent*>(nativePtr);
size_t pointerCount = event->getPointerCount();
// 索引值校验
if (!validatePointerIndex(env, pointerIndex, pointerCount)) {
return 0;
}
// 默认相同
if (historyPos == HISTORY_CURRENT) {
// 根据坐标类型和触摸点索引获取值
return event->getAxisValue(axis, pointerIndex);
} else {
size_t historySize = event->getHistorySize();
if (!validateHistoryPos(env, historyPos, historySize)) {
return 0;
}
return event->getHistoricalAxisValue(axis, pointerIndex, historyPos);
}
}
拆分事件
根据给定的ID集合分离事件(该方法后面再详细分析)。
-> MotionEvent.java
public final MotionEvent split(int idBits) {}
实际MotionEvent数据
通过前面几个方法看到,Java层MotionEvent获取数据都是通过jni向native层的MotionEvent查询数据。
native层MotionEvent定义在:
-> Input.h
class MotionEvent : public InputEvent {
public:
// ···
inline int32_t getPointerId(size_t pointerIndex) const {
// 从mPointerProperties数组获取对应索引的触摸点信息
return mPointerProperties[pointerIndex].id;
}
protected:
int32_t mAction;
int32_t mActionButton;
int32_t mFlags;
int32_t mEdgeFlags;
int32_t mMetaState;
int32_t mButtonState;
float mXOffset;
float mYOffset;
float mXPrecision;
float mYPrecision;
nsecs_t mDownTime;
// 存储触摸点ID信息
Vector<PointerProperties> mPointerProperties;
Vector<nsecs_t> mSampleEventTimes;
// 存储触摸点坐标信息
Vector<PointerCoords> mSamplePointerCoords;
};
MotionEvent中持有一个PointerProperties数组,保存着这个事件中包含的所有触摸点信息,一个PointerProperties结构体对应着一个触摸点信息,PointerProperties中的id成员即表示触摸点ID。触摸点ID的取值是从0开始,依次递增,最多不超过31。
触摸点索引和ID关系
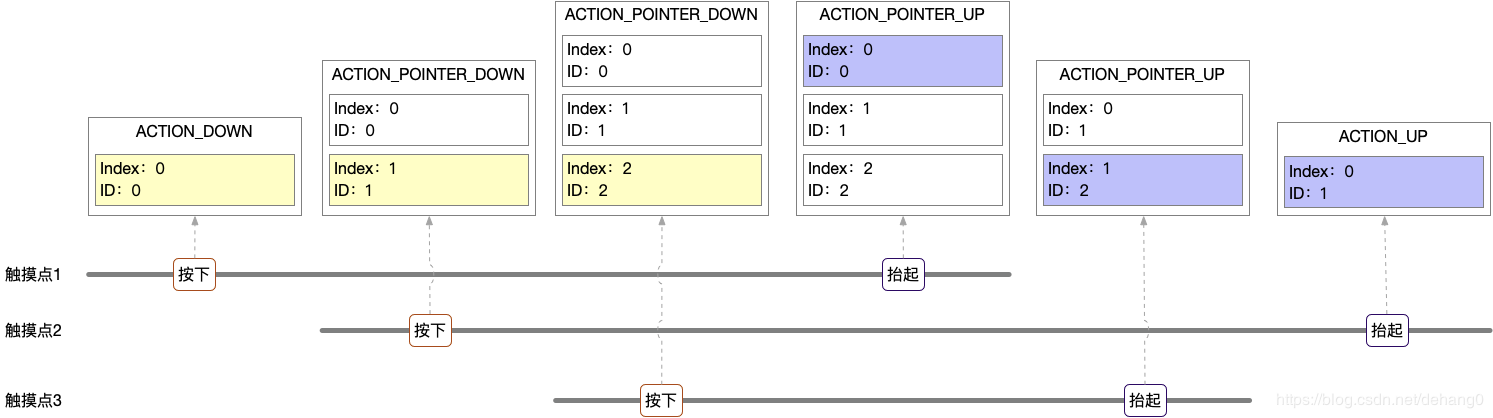
触摸点按下抬起时产生的事件中的触摸点信息中的索引和ID关系如图所示,其中索引值是会相对变化的,而ID值保持不变。
派发过程
接下来进入ViewGroup的事件派发方法。
派发目标查找
进入dispatchTouchEvent方法,派发目标确认部分: -> ViewGroup.java
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
// ···
// Update list of touch targets for pointer down, if needed.
// 标记当前ViewGroup是否启用了事件拆分
final boolean split = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_SPLIT_MOTION_EVENTS) != 0;
TouchTarget newTouchTarget = null;
boolean alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget = false;
if (!canceled && !intercepted) {
// ···
// split && actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN说明有新的触摸点产生。
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
|| (split && actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN)
|| actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_HOVER_MOVE) {
final int actionIndex = ev.getActionIndex(); // always 0 for down
// 通过触摸点索引获取触摸点ID,并将ID值保存在一个int上面,通过第x位为1来表示(x=ID)。
final int idBitsToAssign = split ? 1 << ev.getPointerId(actionIndex)
: TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS;
// Clean up earlier touch targets for this pointer id in case they
// have become out of sync.
removePointersFromTouchTargets(idBitsToAssign);
final int childrenCount = mChildrenCount;
if (newTouchTarget == null && childrenCount != 0) {
// 获取触摸点位置坐标
final float x = ev.getX(actionIndex);
final float y = ev.getY(actionIndex);
// Find a child that can receive the event.
// Scan children from front to back.
final ArrayList<View> preorderedList = buildTouchDispatchChildList();
final boolean customOrder = preorderedList == null
&& isChildrenDrawingOrderEnabled();
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = childrenCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final int childIndex = getAndVerifyPreorderedIndex(
childrenCount, i, customOrder);
final View child = getAndVerifyPreorderedView(
preorderedList, children, childIndex);
// ···
if (!canViewReceivePointerEvents(child)
|| !isTransformedTouchPointInView(x, y, child, null)) {
ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);
continue;
}
newTouchTarget = getTouchTarget(child);
if (newTouchTarget != null) {
// Child is already receiving touch within its bounds.
// Give it the new pointer in addition to the ones it is handling.
// 找到一个派发目标,给这个目标添加新的触摸点ID。
newTouchTarget.pointerIdBits |= idBitsToAssign;
break;
}
resetCancelNextUpFlag(child);
// dispatchTransformedTouchEvent方法派发,第四个参数传入上面
// 获取的触摸点ID,事件拆分在该方法中执行。
if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, false, child, idBitsToAssign)) {
// ···
// 若该child消费了事件,则新建TouchTarget保存child和触摸点ID,并添入TouchTarget链表。
newTouchTarget = addTouchTarget(child, idBitsToAssign);
alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget = true;
break;
}
// ···
}
if (preorderedList != null) preorderedList.clear();
}
if (newTouchTarget == null && mFirstTouchTarget != null) {
// Did not find a child to receive the event.
// Assign the pointer to the least recently added target.
newTouchTarget = mFirstTouchTarget;
while (newTouchTarget.next != null) {
newTouchTarget = newTouchTarget.next;
}
// 若决定派发给最早添加的TouchTarget的话,则往它添加触摸点ID。
newTouchTarget.pointerIdBits |= idBitsToAssign;
}
}
}
// ···
}
在派发目标查找阶段,若当次事件为ACTION_DOWN或ACTION_POINTER_DOWN,说明有新触摸点产生,则会获取该事件对应的触摸点ID,然后将ID添加至确定派发的TouchTarget中。
执行派发
-> ViewGroup.java
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
// ···
// Dispatch to touch targets.
if (mFirstTouchTarget == null) {
// No touch targets so treat this as an ordinary view.
// 常量ALL_POINTER_IDS值为-1,所有bit位都为1。
handled = dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, canceled, null,
TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS);
} else {
// Dispatch to touch targets, excluding the new touch target if we already
// dispatched to it. Cancel touch targets if necessary.
TouchTarget predecessor = null;
TouchTarget target = mFirstTouchTarget;
while (target != null) {
final TouchTarget next = target.next;
if (alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget && target == newTouchTarget) {
handled = true;
} else {
final boolean cancelChild = resetCancelNextUpFlag(target.child)
|| intercepted;
// 这里dispatchTransformedTouchEvent第四个参数传入各个
// TouchTarget中保存的触摸点ID集合。
if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, cancelChild,
target.child, target.pointerIdBits)) {
handled = true;
}
if (cancelChild) {
// ···
continue;
}
}
predecessor = target;
target = next;
}
}
// ···
}
在遍历TouchTarget链表依次派发过程中,会取出各个TouchTarget中保存的触摸点ID集合,表示该目标对这些触摸点上的事件感兴趣。这里将ID集合传入dispatchTransformedTouchEvent方法,在该方法中会根据ID集合对事件进行拆分。
dispatchTransformedTouchEvent
-> ViewGroup.java
// 参数desiredPointerIdBits表示child期望接收哪些触摸点上的事件
private boolean dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, boolean cancel, View child, int desiredPointerIdBits) {
final boolean handled;
// Canceling motions is a special case. We don't need to perform any transformations
// or filtering. The important part is the action, not the contents.
final int oldAction = event.getAction();
// 判断是否需要取消事件序列,若是的话则派发ACTION_CANCEL事件。
if (cancel || oldAction == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL) {
event.setAction(MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL);
// 没有派发目标的情况下,child为null,交由ViewGroup自身处理。
if (child == null) {
handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
} else {
handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
}
event.setAction(oldAction);
return handled;
}
// Calculate the number of pointers to deliver.
// 获取该事件上所有的触摸点ID
final int oldPointerIdBits = event.getPointerIdBits();
// 和期望接收的触摸点做相与操作得到新的触摸点集合。正常情况下newPointerIdBits就是
// desiredPointerIdBits,这里做这样操作的目的是一种校验目的。
final int newPointerIdBits = oldPointerIdBits & desiredPointerIdBits;
// If for some reason we ended up in an inconsistent state where it looks like we
// might produce a motion event with no pointers in it, then drop the event.
// 由于某些异常原因导致desiredPointerIdBits不存在于oldPointerIdBits,出现
// newPointerIdBits为0。此种情况下没有找到有效触摸点,则丢弃该事件。
if (newPointerIdBits == 0) {
return false;
}
// If the number of pointers is the same and we don't need to perform any fancy
// irreversible transformations, then we can reuse the motion event for this
// dispatch as long as we are careful to revert any changes we make.
// Otherwise we need to make a copy.
// transformedEvent用于保存事件副本
final MotionEvent transformedEvent;
// 判断触摸点是否产生变化,例如有新的触摸点按下或旧触摸点抬起。
if (newPointerIdBits == oldPointerIdBits) {
// 触摸点ID集合无变化,则不需要进行事件拆分。
if (child == null || child.hasIdentityMatrix()) {
if (child == null) {
handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
} else {
// 坐标系偏移以适应子view坐标系
final float offsetX = mScrollX - child.mLeft;
final float offsetY = mScrollY - child.mTop;
event.offsetLocation(offsetX, offsetY);
// 派发给child
handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
// 恢复坐标偏移
event.offsetLocation(-offsetX, -offsetY);
}
return handled;
}
// 若child需要计算变化矩阵,这里获取一个事件副本
transformedEvent = MotionEvent.obtain(event);
} else {
// 触摸点ID有变化,进行事件拆分,保存拆分事件副本
transformedEvent = event.split(newPointerIdBits);
}
// Perform any necessary transformations and dispatch.
if (child == null) {
handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent);
} else {
final float offsetX = mScrollX - child.mLeft;
final float offsetY = mScrollY - child.mTop;
transformedEvent.offsetLocation(offsetX, offsetY);
if (! child.hasIdentityMatrix()) {
transformedEvent.transform(child.getInverseMatrix());
}
// 使用事件副本进行派发给child
handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent);
}
// Done.
transformedEvent.recycle();
return handled;
}
当MotionEvent中的触摸点ID集合和当前即将进行派发的TouchTarget中的ID集合完全一致时,就不需要进行事件拆分。否则会根据TouchTarget中的ID集合从MotionEvent中拆分出仅包含TouchTarget期望处理的触摸点的事件的副本,将事件副本派发给该TouchTarget。
事件拆分规则
拆分规则在MotionEvent的split方法中:
-> MotionEvent.java
// 参数idBits表示TouchTarget感兴趣的那些触摸点(即落于TouchTarget中的触摸点),
// 期望拆分出仅包含这些触摸点的事件
public final MotionEvent split(int idBits) {
// 从对象缓存池获取一个MotionEvent作为副本
MotionEvent ev = obtain();
synchronized (gSharedTempLock) {
// 获取该事件中的触摸点个数
final int oldPointerCount = nativeGetPointerCount(mNativePtr);
// 初始化gSharedTempPointerProperties、gSharedTempPointerCoords、gSharedTempPointerIndexMap数组。
ensureSharedTempPointerCapacity(oldPointerCount);
final PointerProperties[] pp = gSharedTempPointerProperties;
final PointerCoords[] pc = gSharedTempPointerCoords;
final int[] map = gSharedTempPointerIndexMap;
// 获取事件动作类型
final int oldAction = nativeGetAction(mNativePtr);
final int oldActionMasked = oldAction & ACTION_MASK;
// 获取触摸点索引,当前按下或抬起的那个触摸点的索引
final int oldActionPointerIndex = (oldAction & ACTION_POINTER_INDEX_MASK)
>> ACTION_POINTER_INDEX_SHIFT;
// 若当前按下或抬起的那个触摸点是TouchTarget感兴趣的,则单独记录这个触摸点索引
int newActionPointerIndex = -1;
// TouchTarget感兴趣的触摸点个数
int newPointerCount = 0;
// TouchTarget感兴趣的触摸点ID集合
int newIdBits = 0;
// 遍历MotionEvent中携带的所有触摸点信息
for (int i = 0; i < oldPointerCount; i++) {
// 将native层中的信息保存至Java层
nativeGetPointerProperties(mNativePtr, i, pp[newPointerCount]);
// 获取触摸点ID
final int idBit = 1 << pp[newPointerCount].id;
if ((idBit & idBits) != 0) {
// 该触摸点是TouchTarget感兴趣的
if (i == oldActionPointerIndex) {
// 且该触摸点是引发当前事件的那个触摸点,特别记录下它的索引
newActionPointerIndex = newPointerCount;
}
// 缓存记录
map[newPointerCount] = i;
newPointerCount += 1;
newIdBits |= idBit;
}
}
// 安全检查
if (newPointerCount == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("idBits did not match any ids in the event");
}
// 用于记录事件拆分后新的动作类型
final int newAction;
// 仅对ACTION_POINTER_DOWN和ACTION_POINTER_UP进行类型调整
if (oldActionMasked == ACTION_POINTER_DOWN || oldActionMasked == ACTION_POINTER_UP) {
if (newActionPointerIndex < 0) {
// An unrelated pointer changed.
// 引发当前事件的那个触摸点不是TouchTarget感兴趣的,则将类型调整为
// ACTION_MOVE,对于该TouchTarget来说,当作普通的滑动事件处理。
newAction = ACTION_MOVE;
} else if (newPointerCount == 1) {
// The first/last pointer went down/up.
// 引发当前事件的那个触摸点是该TouchTarget感兴趣的,且TouchTarget
// 感兴趣的个数为1。说明该TouchTarget仅对当前这一个触摸点感兴趣(单点触摸),那么
// 对于该TouchTarget来说,将是一个全新序列的开始或结束。
// 将动作类型调整为ACTION_DOWN或ACTION_UP。
newAction = oldActionMasked == ACTION_POINTER_DOWN
? ACTION_DOWN : ACTION_UP;
} else {
// A secondary pointer went down/up.
// 到了这个case,意味着该触摸点是该TouchTarget上的多点触摸事件,沿用
// 动作类型,并组合上触摸点索引。
newAction = oldActionMasked
| (newActionPointerIndex << ACTION_POINTER_INDEX_SHIFT);
}
} else {
// Simple up/down/cancel/move or other motion action.
newAction = oldAction;
} // 事件动作类型调整完毕
// 初始化MotionEvent副本
final int historySize = nativeGetHistorySize(mNativePtr);
for (int h = 0; h <= historySize; h++) {
final int historyPos = h == historySize ? HISTORY_CURRENT : h;
for (int i = 0; i < newPointerCount; i++) {
nativeGetPointerCoords(mNativePtr, map[i], historyPos, pc[i]);
}
final long eventTimeNanos = nativeGetEventTimeNanos(mNativePtr, historyPos);
if (h == 0) {
// 使用原对象数据初始化native层对象,并返回对象指针,这里传入了调整后的动作类型。
ev.mNativePtr = nativeInitialize(ev.mNativePtr,
nativeGetDeviceId(mNativePtr), nativeGetSource(mNativePtr),
newAction, nativeGetFlags(mNativePtr),
nativeGetEdgeFlags(mNativePtr), nativeGetMetaState(mNativePtr),
nativeGetButtonState(mNativePtr),
nativeGetXOffset(mNativePtr), nativeGetYOffset(mNativePtr),
nativeGetXPrecision(mNativePtr), nativeGetYPrecision(mNativePtr),
nativeGetDownTimeNanos(mNativePtr), eventTimeNanos,
newPointerCount, pp, pc);
} else {
nativeAddBatch(ev.mNativePtr, eventTimeNanos, pc, 0);
}
}
return ev;
}
}
split方法中主要根据传入的idBits调整事件的Action,这么做的原因是什么呢?这里以一个图示为例:
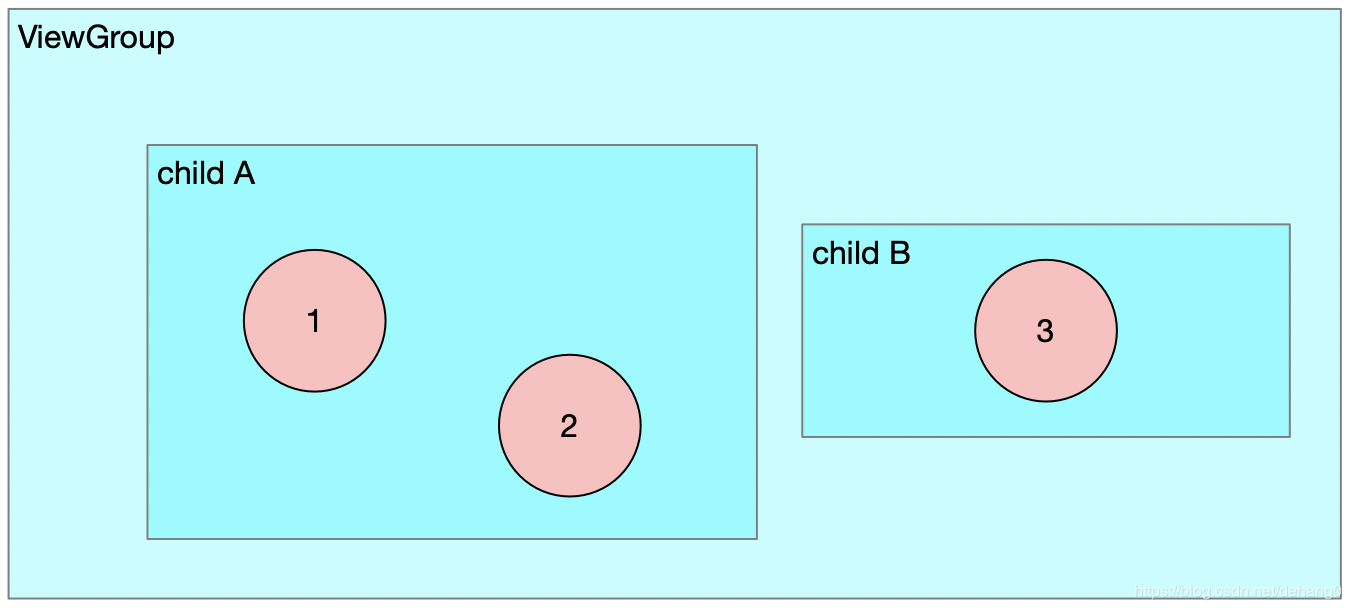
- 当触摸点3按下时,ViewGroup会收到ACTION_POINTER_DOWN事件,该触摸点是child B感兴趣的。此时对于child B来说是一个全新的事件序列开始,因此在派发给child B时,需要将类型调整为ACTION_DOWN。但是对于child A来说,并不是它感兴趣的,因此在派发给child A时要调整为ACTION_MOVE。
- 当触摸点2抬起时,ViewGroup会收到ACTION_POINTER_UP事件。该事件是child A感兴趣的,但是child A上仍有触摸点1,因此派发给child A的事件类型依旧是ACTION_POINTER_UP。而在派发给child B时,将调整为ACTION_MOVE。
触摸点ID的移除
在派发流程的末尾,当判断有触摸点抬起时,会移除相应的触摸点ID: -> ViewGroup.java
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
// ···
// Update list of touch targets for pointer up or cancel, if needed.
if (canceled
|| actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP
|| actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_HOVER_MOVE) {
resetTouchState();
} else if (split && actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_UP) {
// 事件类型为ACTION_POINTER_UP
final int actionIndex = ev.getActionIndex();
// 通过索引获取引发当前事件的触摸点ID
final int idBitsToRemove = 1 << ev.getPointerId(actionIndex);
// 移除该触摸点ID
removePointersFromTouchTargets(idBitsToRemove);
}
// ···
}
接着看removePointersFromTouchTargets方法: -> ViewGroup.java
// 参数pointerIdBits为将被移除的触摸点ID
private void removePointersFromTouchTargets(int pointerIdBits) {
TouchTarget predecessor = null;
TouchTarget target = mFirstTouchTarget;
// 遍历TouchTarget链表
while (target != null) {
final TouchTarget next = target.next;
if ((target.pointerIdBits & pointerIdBits) != 0) {
// 若该TouchTarget上有该ID,则从中移除ID
target.pointerIdBits &= ~pointerIdBits;
if (target.pointerIdBits == 0) {
// 若TouchTarget移除ID后,没有任何ID了,则从链表中移除该TouchTarget
if (predecessor == null) {
mFirstTouchTarget = next;
} else {
predecessor.next = next;
}
target.recycle();
target = next;
continue;
}
}
predecessor = target;
target = next;
}
}
总结
事件拆分是为了在多点触摸情况下更准确的将事件传递给子view,在派发流程中,ViewGroup不会原样把MotionEvent派发给子view,而是根据落于子view上的触摸点,调整MotionEvent中的事件类型和触摸点信息后生成新的MotionEvent副本,再用这个MotionEvent副本派发给对应子view。