Stack在flutter笔记 Demo篇(模拟登录)中出现过,这里来详细了解一下这个Widget,类似于css中的position: relative,但是会强制子Widget层叠显示,Positioned类似于css中的position: absolute,可以设置坐标。
Stack
Stack({
Key key,
AlignmentGeometry alignment: AlignmentDirectional.topStart,
TextDirection textDirection,
StackFit fit: StackFit.loose,
Overflow overflow: Overflow.clip,
List<Widget> children: const[]
})
先看一个只有children的demo
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return new MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body: Stack(
children: <Widget>[
Text('1'),
Text('2'),
Text('3')
],
)
)
);
}
}

Text换成Container再看一下,
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return new MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body: Stack(
children: <Widget>[
Container(
width: 100,
height: 100,
color: Colors.red
),
Container(
width: 50,
height: 50,
color: Colors.green
)
],
)
)
);
}
}

css里一样,后写的在上。
alignment
子Widget的对齐方式
AlignmentDirectional.topStart (默认值)、AlignmentDirectional.topCenter、AlignmentDirectional.topEnd、AlignmentDirectional.centerStart、AlignmentDirectional.center、AlignmentDirectional.centerEnd、AlignmentDirectional.bottomStart、AlignmentDirectional.bottomCenter、AlignmentDirectional.bottomEnd。
简单易懂,看个demo。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return new MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body: Stack(
alignment: AlignmentDirectional.bottomCenter,
children: <Widget>[
Container(
width: 100,
height: 100,
color: Colors.red
),
Container(
width: 50,
height: 50,
color: Colors.green
),
Container(
width: 30,
height: 30,
color: Colors.blue
)
],
)
)
);
}
}
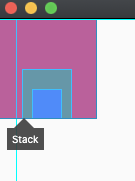
textDirection
子Widget的排列方式,默认值是TextDirection.ltr,从左往右,当设置为TextDirection.rtl时效果如下:

fit
子Widget中未定位元素的大小,只有两个值:
StackFit.loose:不对其大小进行约束(默认值)
StackFit.expand:最大
StackFit.passthrough:父级的约束直接传递给子Widgert
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return new MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body: Container(
width: 200,
height: 200,
child: Stack(
fit: StackFit.passthrough,
children: <Widget>[
Container(
width: 50,
height: 50,
color: Colors.red
)
],
)
)
)
);
}
}
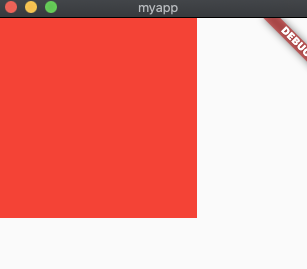
fit值如果不是默认值StackFit.loose,子Widget设置的尺寸将失去作用。
overflow
和css里效果一样,只有两个值
Overflow.clip:溢出将被剪切
Overflow.visible:不对溢出的部分做处理
Positioned
定位元素,用于Stack的子Widget
Positioned({
Key key,
double left,
double top,
double right,
double bottom,
double width,
double height,
@required Widget child
})
都是基础属性,left、top、right、bottom是相对于父级的坐标。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return new MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body: Stack(
children: <Widget>[
Positioned(
width: 100,
height: 100,
left: 100,
bottom: 100,
child: Container(
color: Colors.red
)
)
],
)
)
);
}
}
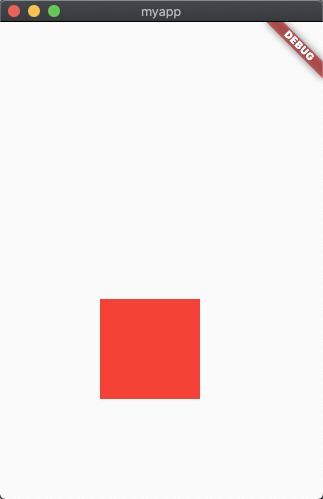
Align
这个更简单一点,只是设定子Widget相对于Align的位置。
Align({
Key key,
AlignmentGeometry alignment: Alignment.center,
double widthFactor,
double heightFactor,
Widget child
})
alignment
子Widget相对于Align的位置。
widthFactor & heightFactor
这两个相当于是系数,乘以子Widget的宽高,就是Align的尺寸。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return new MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body: Align(
widthFactor: 2,
heightFactor: 2,
alignment: Alignment.bottomRight,
child: Container(
width: 50,
height: 50,
color: Colors.blue
)
)
)
);
}
}
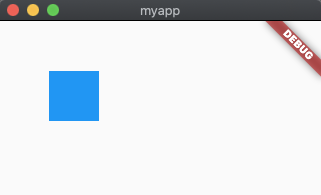
Align的父级设有宽高widthFactor和heightFactor将市区作用,大小为最大。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return new MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body: Container(
width: 300,
height: 300,
color: Colors.red,
child: Align(
widthFactor: 2,
heightFactor: 2,
alignment: Alignment.bottomRight,
child: Container(
width: 50,
height: 50,
color: Colors.blue
)
)
)
)
);
}
}
