1、分层绘制
类似web 端 canvas, 我们经常是采用分层的策略 例如以下游戏场景, 在打斗的过程中, 人物动作, 位移,动画等变化的频率和幅度是很大的,而背景变化的频率或幅度则相对较小(基本不变,或者缓慢变化,或者仅在某些时机变化),这个过程需要很频繁地更新和重绘人物,但是对于背景,我们也许只需要绘制一次,也许只需要隔一段时间才重绘一次
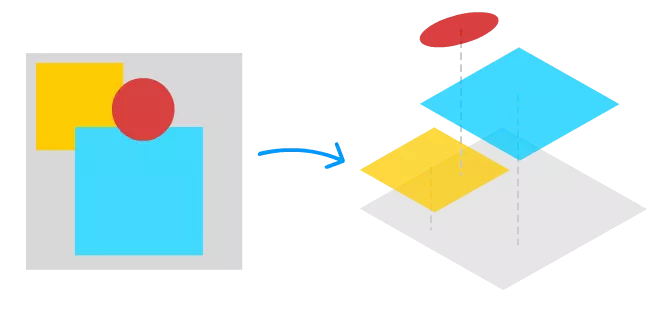
如果只在一个画布里面绘制,那人物的的频繁变化也会引起背景的绘制,因此需要需要生成多个画布独立绘制,最后再合成
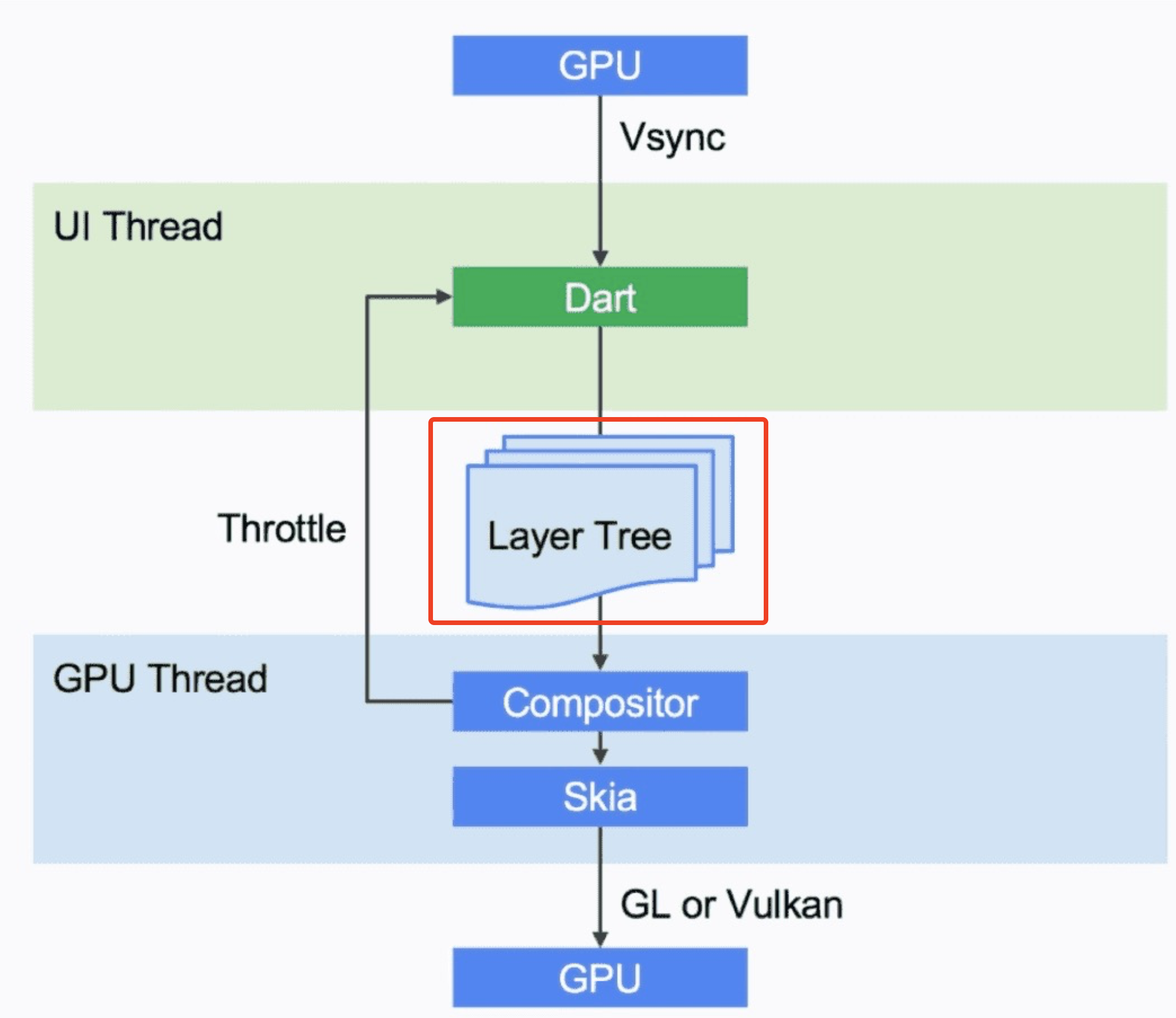
在flutter 中, 也是采用分层绘制的概念,例如下图,是Flutter框架渲染机制的一个示意图~ 在框架渲染完成之后会输出 的 一个个的 layer 形成的 layer tree,layer tree被送入engine,engine会把layer tree调度到GPU线程,在GPU线程内合成(compsite)layer tree,然后由Skia 2D渲染引擎渲染后送入GPU显示~
2、Layer 类
(1) Layer
abstract class Layer extends AbstractNode with DiagnosticableTreeMixin {
@override
ContainerLayer get parent => super.parent;
Layer get previousSibling => _previousSibling;
Layer _previousSibling;
}
类Layer是一个树形结构, 属性parent代表其父节点, nextSibling和previousSibling表示同一图层的前一个和后一个兄弟节点,即图层孩子节点们是用双向链表存储的
(2)AbstractNode
class AbstractNode {
int get depth => _depth;
int _depth = 0;
void redepthChildren() { }
Object get owner => _owner;
Object _owner;
/// The parent of this node in the tree.
AbstractNode get parent => _parent;
AbstractNode _parent;
void adoptChild(covariant AbstractNode child) {}
void dropChild(covariant AbstractNode child) {}
}
Layer 继承 AbstractNode,因此ayer 也是一个个普通的节点,这个节点可以是叶子节点,也可以拥有子节点
3、Layer 分类
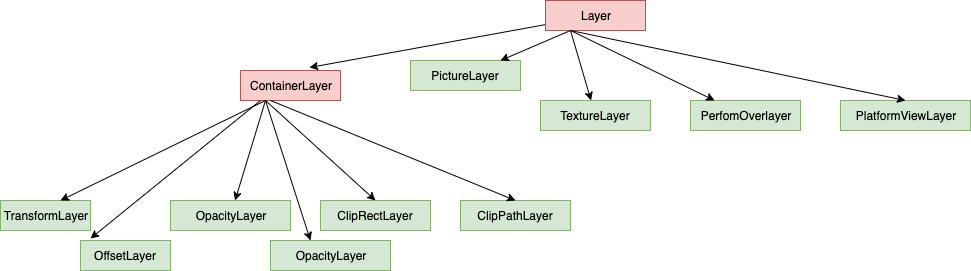
Layer 有不同的实现类,只有ContainerLayer类型及其子类的图层可以拥有孩子,其他类型的Layer子类都是叶子图层。
4、绘制流程 layer 管理
分层绘制的核心思想是实现多个 canvas, 那在 flutter 里面,什么时候会创建新的 canvas?
needsCompositing
isRepaintBoundary
我们先看 needsCompositing 在监听 Vsync 信号调用 drawFrame, (1) drawFrame
@protected
void drawFrame() {
pipelineOwner.flushLayout();
pipelineOwner.flushCompositingBits();
pipelineOwner.flushPaint();
renderView.compositeFrame(); // this sends the bits to the GPU
pipelineOwner.flushSemantics(); // this also sends the semantics to
}
在调用 flushPaint 进行绘制之前,会先调用 flushCompositingBits
(2) flushCompositingBits
void flushCompositingBits() {
_nodesNeedingCompositingBitsUpdate.sort((RenderObject a, RenderObject b) => a.depth - b.depth);
for (RenderObject node in _nodesNeedingCompositingBitsUpdate) {
if (node._needsCompositingBitsUpdate && node.owner == this)
node._updateCompositingBits();
}
_nodesNeedingCompositingBitsUpdate.clear();
}
这个函数中,主要是遍历 _nodesNeedingCompositingBitsUpdate 节点集合,调用 _updateCompositingBits
(3) _updateCompositingBits
void _updateCompositingBits() {
if (!_needsCompositingBitsUpdate)
return;
final bool oldNeedsCompositing = _needsCompositing;
_needsCompositing = false;
visitChildren((RenderObject child) {
child._updateCompositingBits();
if (child.needsCompositing)
_needsCompositing = true;
});
if (isRepaintBoundary || alwaysNeedsCompositing)
_needsCompositing = true;
if (oldNeedsCompositing != _needsCompositing) {
// 如果 oldNeedsCompositing != _needsCompositing, 则说明节点所在的图层发生了改变,则需要重新绘制
markNeedsPaint();
}
_needsCompositingBitsUpdate = false;
}
在这个函数中,遍历子节点,如果子节点 的 needsCompositing 为true, 则需要将该节点的 needsCompositing 设置为 true
上述代码 (2) 中,_nodesNeedingCompositingBitsUpdate 节点集合怎么来的? 追踪代码、则发现在 markNeedsCompositingBitsUpdate 函数中有相关处理
(4) markNeedsCompositingBitsUpdate
void markNeedsCompositingBitsUpdate() {
if (_needsCompositingBitsUpdate)
return;
_needsCompositingBitsUpdate = true;
if (parent is RenderObject) {
final RenderObject parent = this.parent;
if (parent._needsCompositingBitsUpdate)
return;
if (!isRepaintBoundary && !parent.isRepaintBoundary) {
parent.markNeedsCompositingBitsUpdate();
return;
}
}
if (owner != null)
owner._nodesNeedingCompositingBitsUpdate.add(this);
}
在该代码段中会将该 renderObject 加入 _nodesNeedingCompositingBitsUpdate 集合中,同时向上遍历父节点的 markNeedsCompositingBitsUpdate 方法,
(5)markNeedsCompositingBitsUpdate 何时调用? renderObject 一般在 添加,删除孩子时调用 markNeedsCompositingBitsUpdate
//添加孩子
@override
void adoptChild(RenderObject child) {
markNeedsCompositingBitsUpdate();
}
//删除孩子
@override
void dropChild(RenderObject child) {
super.dropChild(child);
markNeedsCompositingBitsUpdate();
}
needsCompositing有哪些应用场景
(6) needsCompositing
在绘制时,如果 needsCompositing 这个属性值 为 true, 则意味着需要新增一个 layer
ClipRectLayer pushClipRect(bool needsCompositing, Offset offset, Rect clipRect, PaintingContextCallback painter, { Clip clipBehavior = Clip.hardEdge, ClipRectLayer oldLayer }) {
final Rect offsetClipRect = clipRect.shift(offset);
if (needsCompositing) {
final ClipRectLayer layer = oldLayer ?? ClipRectLayer();
layer
..clipRect = offsetClipRect
..clipBehavior = clipBehavior;
pushLayer(layer, painter, offset, childPaintBounds: offsetClipRect);
return layer;
} else {
clipRectAndPaint(offsetClipRect, clipBehavior, offsetClipRect, () => painter(this, offset));
return null;
}
}