netty的自我学习(一)—BIO、NIO、AIO的简单介绍学习这件事,不在乎有没有人督促你,最重要的是在于你自己有没有觉悟和恒心。
温习中,会以笔记的形式记录下自我学习的过程。预计1月底之前更新完毕,请关注。
文章部分图片来源于视频笔记!!非我自画!!
netty的自我学习(四)—NIO的Selector(选择器)
netty的自我学习(六)—Reactor模型以及Netty模型介绍
NIO的channel基本介绍
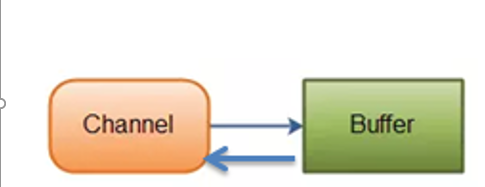
- NIO的通道与流的区别:
-
BIO 中的 stream 是单向的,例如 FileInputStream 对象只能进行读取数据的操作,而 NIO 中的通道(Channel)是双向的,可以读操作,也可以写操作。
-
通道可以实现异步读写数据
-
通道可以从缓冲读数据,也可以写数据到缓冲
- Channel在NIO中是一个接口
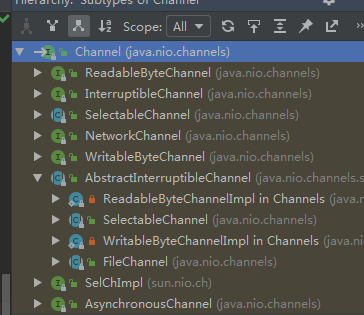
- FileChannel 用于文件的数据读写
- DatagramChannel 用于 UDP 的数据读写
- ServerSocketChannel 和 SocketChannel 用于 TCP 的数据读写。
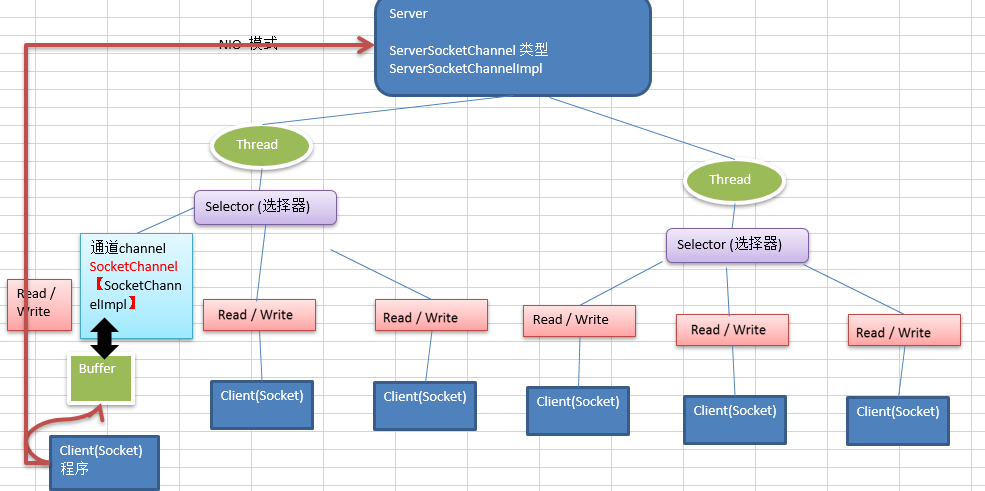
FileChannel-Demo
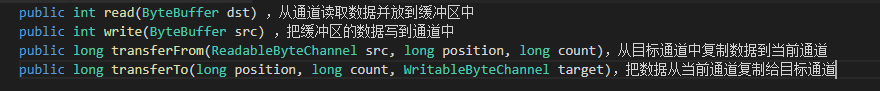
FileChannel主要用来对本地文件进行 IO 操作,常见的方法有
write-数据写入到本地文件
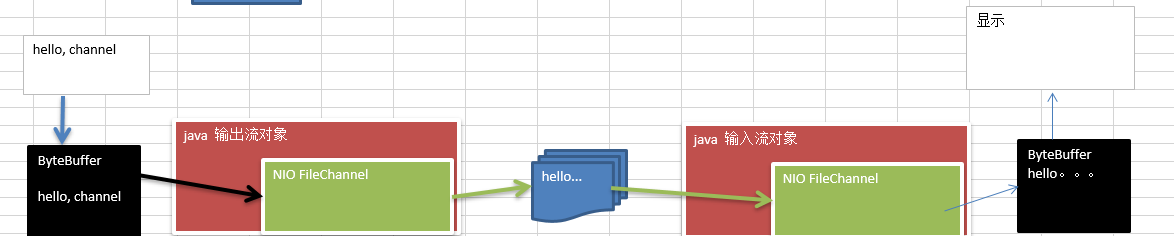
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String str = "hello,channel";
/**
* 1 创建一个输出流->channel
*/
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\1.txt");
/**
* 2 通过 fileOutputStream 获取 对应的 FileChannel
* 这个 fileChannel 真实 类型是 FileChannelImpl
*/
FileChannel fileChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
/**
* 3
* 创建一个缓冲区 ByteBuffer
*/
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
/**
* 4
* 将 str 放入 byteBuffer
*/
byteBuffer.put(str.getBytes());
/**
* 5
* 对byteBuffer 进行flip
*/
byteBuffer.flip();
/**
* 6
* 通过write方法将byteBuffer 数据写入到 fileChannel
*/
fileChannel.write(byteBuffer);
fileOutputStream.close();
}
read-读取数据
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建文件的输入流
File file = new File("d:\\1.txt");
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
//通过fileInputStream 获取对应的FileChannel
FileChannel fileChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
//创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate((int) file.length());
//将 通道的数据读入到Buffer
fileChannel.read(byteBuffer);
//将byteBuffer 的 字节数据 转成String
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array()));
fileInputStream.close();
}
文件读取,注意clear方法
public void copyFile() throws Exception{
/**
* 需求 把文件1的数据 copy到文件2
*/
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("d:\\1.txt");
FileChannel channel001 = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\2.txt");
FileChannel channel002 = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while(true){
/**
* 取到buffer里
*/
int read = channel001.read(byteBuffer);
if(read == -1 ){
break;
}
byteBuffer.flip();
channel002.write(byteBuffer);
/**
* public final Buffer clear() {
* position = 0;
* limit = capacity;
* mark = -1;
* return this;
* }
* 为什么调用clear()?
* 第一次读玩了 pos=limit
* 那么下次循环在读的时候,read就一直是0,无限循环,因为读不到数据
*
*/
byteBuffer.clear(); //清空buffer
}
//关闭相关的流
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
文件拷贝
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建相关流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("d:\\1.jpg");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\2.jpg");
//获取各个流对应的filechannel
FileChannel sourceCh = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileChannel destCh = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
//使用transferForm完成拷贝
destCh.transferFrom(sourceCh,0,sourceCh.size());
//关闭相关通道和流
sourceCh.close();
destCh.close();
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
互相讨论、共同进步
文章笔记如有失误,请指出。
持之以恒!

