DPOS原理
DPOS全称Delegated proof of Stake,中文是委托权益证明。
可以理解为整个区块链网络有许多节点,我们需要选出一些节点作为代表来维护整个区块链网络,这些代表需要保证区块链的安全和性能,不需要通过POS算力竞争了,节约能源。
DPOS规则
他们可以生产区块,如果不称职就会被踢出代表列表重新选举。这里的选举最少需要整个网络一半的节点通过则证明去中心化的有效投票。
DPOS算法要求随机指定代表列表的顺序,不按照顺序生成区块的是无效的,每个周期会重新洗牌一次,打乱原有顺序。代表之间不存在争夺情况,不会遗漏区块,定时会出现一个区块,这就使共识达成的时间周期大大缩短,这也是相对于POS,POW的优点所在。
DPOS奖励机制
DPOS因为每秒可以处理确认比POW和POS大上几个数量级的交易量,会将一部分交易作为奖励给网络维护节点和投票者,作为代表选举维护的奖励,让更多的节点参与进来。
Golang实现DPOS算法
包引入
package main
import (
"crypto/sha256"
"encoding/hex"
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"sort"
"time"
)
区块结构体定义
type Block struct {
Index int
TimeStamp string
BPM int
Hash string
PrevHash string
Delegate string
}
创建新区块
func generateBlock(oldBlock Block, _BMP int , address string)(Block, error){
var newBlock Block
t := time.Now()
newBlock.Index = oldBlock.Index + 1
newBlock.TimeStamp = t.String()
newBlock.BPM = _BMP
newBlock.PrevHash = oldBlock.Hash
newBlock.Hash = createBlockHash(newBlock)
newBlock.Delegate = address
fmt.Println("NewBlock: ", newBlock)
return newBlock, nil
}
生成区块的hash
func createBlockHash(block Block) string{
record := string(block.Index) + block.TimeStamp + string(block.BPM) + block.PrevHash
sha3 := sha256.New()
sha3.Write([] byte(record))
hash := sha3.Sum(nil)
fmt.Println("NewHash: ",hex.EncodeToString(hash))
return hex.EncodeToString(hash)
}
检查新区块是否合法
func isBlockValid(newBlock, oldBlock Block) bool{
if oldBlock.Index + 1 != newBlock.Index{
fmt.Println("失败!!index非法")
return false
}
if newBlock.PrevHash != oldBlock.Hash{
fmt.Println("失败!!PrevHash非法")
return false
}
fmt.Println("合法")
return true
}
定义区块链,代表,代表列表
var blockChain []Block
type Trustee struct{
name string
votes int
}
type trusteeList [] Trustee
代表排序
func (_trusteeList trusteeList) Len() int{
return len(_trusteeList)
}
func (_trusteeList trusteeList) Swap(i,j int){
_trusteeList[i],_trusteeList[j] = _trusteeList[j],_trusteeList[i]
}
func (_trusteeList trusteeList) Less(i,j int) bool{
return _trusteeList[j].votes < _trusteeList[i].votes
}
代表列表生成
func selecTrustee()([]Trustee){
_trusteeList := []Trustee{
{"node1", rand.Intn(100)},
{"node2", rand.Intn(100)},
{"node3", rand.Intn(100)},
{"node4", rand.Intn(100)},
{"node5", rand.Intn(100)},
{"node6", rand.Intn(100)},
{"node7", rand.Intn(100)},
{"node8", rand.Intn(100)},
{"node9", rand.Intn(100)},
{"node10", rand.Intn(100)},
{"node11", rand.Intn(100)},
{"node12", rand.Intn(100)},
}
sort.Sort(trusteeList(_trusteeList))
result := _trusteeList[:5]
_trusteeList = result[1:]
_trusteeList = append(_trusteeList, result[0])
fmt.Println("当前超级节点代表列表是:",_trusteeList)
return _trusteeList
}
main函数部分
func main(){
t := time.Now()
//模拟创世块的生成,实际要复杂一些
genesisBlock := Block{0, t.String(),0,createBlockHash(Block{}),"",""}
fmt.Println("创世块block: ", genesisBlock)
blockChain = append(blockChain, genesisBlock)
var trustee Trustee
for _, trustee = range selecTrustee(){
_BPM := rand.Intn(100)
blockHeight := len(blockChain)
oldBlock := blockChain[blockHeight-1]
newBlock,err := generateBlock(oldBlock, _BPM, trustee.name)
if err!=nil{
fmt.Println("新生成区块失败:",err)
continue
}
if isBlockValid(newBlock, oldBlock){
blockChain = append(blockChain, newBlock)
fmt.Println("当前操作区块节点为:", trustee.name)
fmt.Println("当前区块数:", len(blockChain))
fmt.Println("当前区块信息:", blockChain[len(blockChain)-1])
}
}
}
运行截图
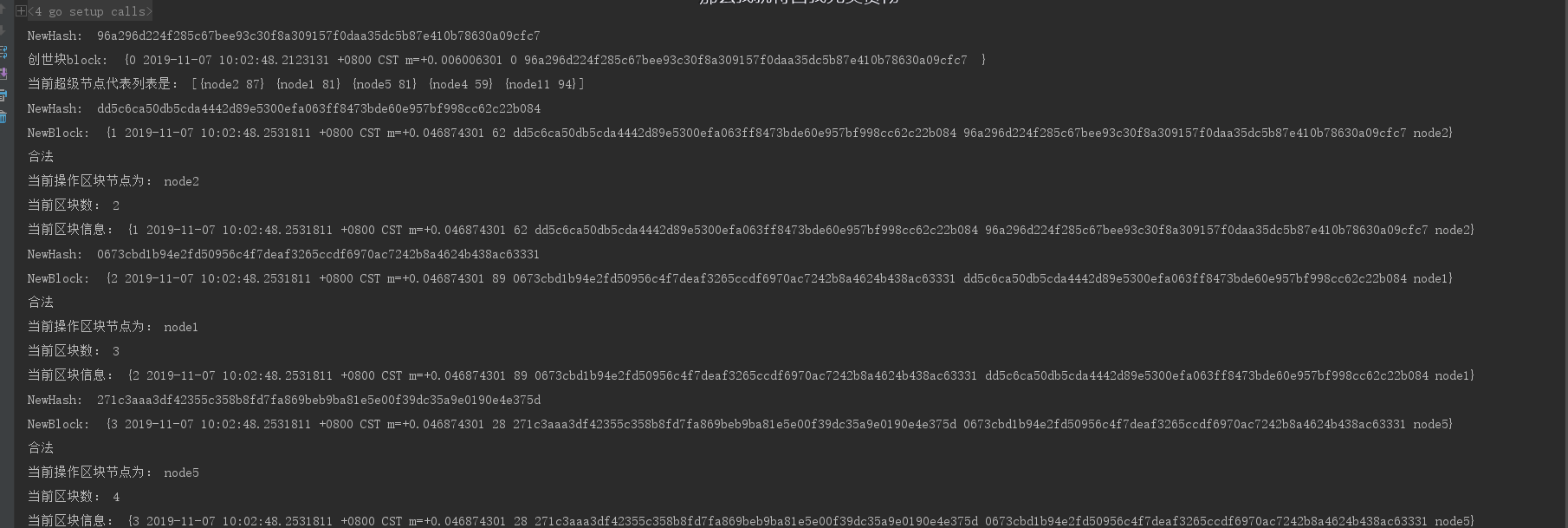
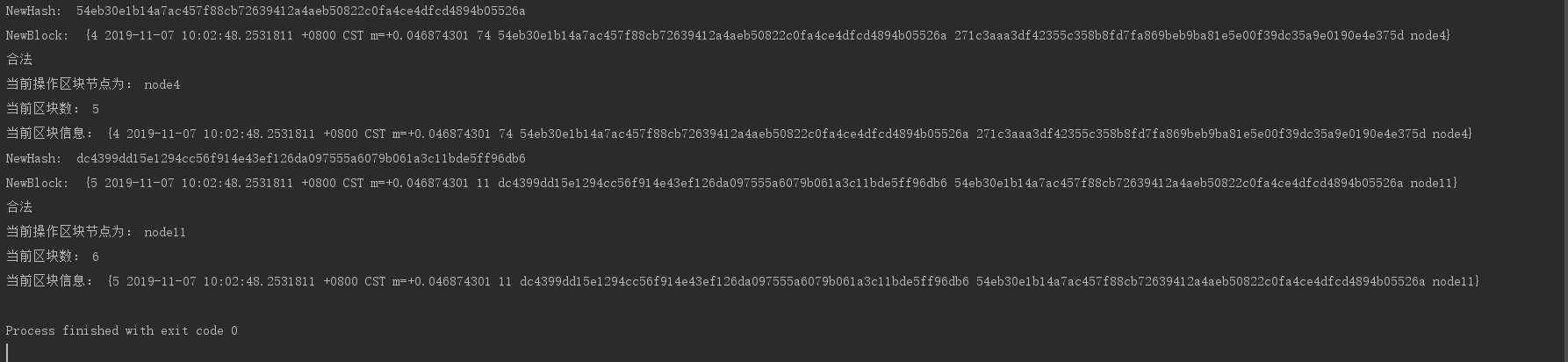
结尾
大家也可以试试,区块链还是很有意思的啊~~~~~