前言
beego是go语言中http框架最流行的框架之一,想必大家都非常了解,其高效的工具利用使得开发web和API应用变得非常方便快捷。趁着公司最近时间段不忙打算深入去学习beego,之前也打算做的,但各种事情无法抽出时间。这篇文章主要是简单介绍一下go是如何生成自动化api文档的。
问题
一、beego是怎样来解析模块函数中的注释行的?
在parser.go中,我们看到如下代码:
```
fileSet := token.NewFileSet()
astPkgs, err := parser.ParseDir(fileSet, pkgRealpath, func(info os.FileInfo) bool {
name := info.Name()
return !info.IsDir() && !strings.HasPrefix(name, ".") && strings.HasSuffix(name, ".go")
}, parser.ParseComments)
```
其中引用了go包中的ast.ParseDir来解析./controllers包下的所有.go文件,那么问题来了,go中的ast包是用来做什么的?答案是抽象语法树。
二、什么是抽象语法树(AST)?
抽象语法树,其实就是使用树状结构表示源代码的语法结构,树的每一个节点就代表源代码中的一个结构。AST,它的全名是abstract syntax tree(抽象语法树)。可想而知go ast包就是用来解析生成go语法树的。
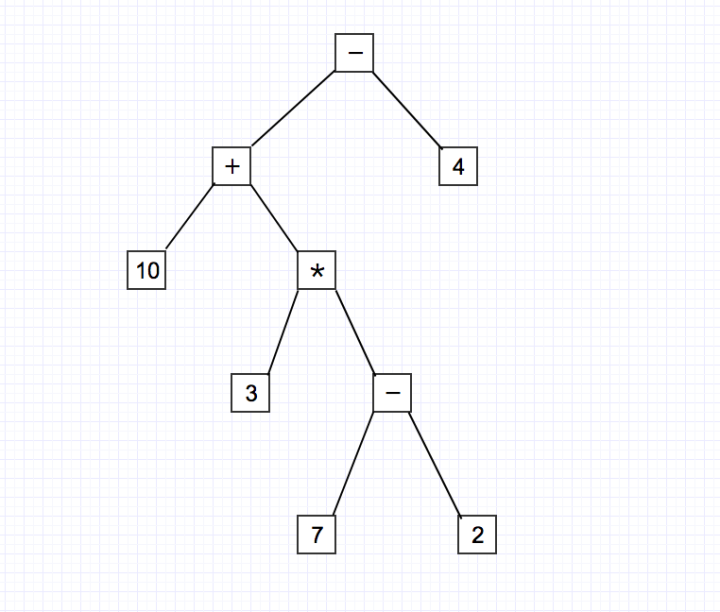
例如,表达式10+3*(7-2)-4抽象语法树为:
代码分析
- 1.解析controllers包下的所有.go文件
```
fileSet := token.NewFileSet()
astPkgs, err := parser.ParseDir(fileSet, pkgRealpath, func(info os.FileInfo) bool {
name := info.Name()
return !info.IsDir() && !strings.HasPrefix(name, ".") && strings.HasSuffix(name, ".go")
}, parser.ParseComments)
```
- 2.遍历包下的所有文件并解析函数中的注释
//遍历/controllers包下所有文件
for _, pkg := range astPkgs {
for _, fl := range pkg.Files {
for _, d := range fl.Decls {
switch specDecl := d.(type) {
case *ast.FuncDecl: //函数声明类型
if specDecl.Recv != nil {
exp, ok := specDecl.Recv.List[0].Type.(*ast.StarExpr) // Check that the type is correct first beforing throwing to parser
if ok {
parserComments(specDecl, fmt.Sprint(exp.X), pkgpath)
}
}
}
}
}
}
- 3.析获取注释中的参数,如@router等
func parseComment(lines []*ast.Comment) (pcs []*parsedComment, err error) {
pcs = []*parsedComment{}
params := map[string]parsedParam{}
filters := []parsedFilter{}
imports := []parsedImport{}
//@Param
for _, c := range lines {
t := strings.TrimSpace(strings.TrimLeft(c.Text, "//"))
if strings.HasPrefix(t, "@Param") {
...
}
}
for _, c := range lines {
t := strings.TrimSpace(strings.TrimLeft(c.Text, "//"))
if strings.HasPrefix(t, "@Import") {
...
}
for _, c := range lines {
t := strings.TrimSpace(strings.TrimLeft(c.Text, "//"))
if strings.HasPrefix(t, "@Filter") {
...
}
for _, c := range lines {
if strings.HasPrefix(t, "@router") {
...
}
return
}
- 4.根据获取到的参数生成路由信息
//生成要注册的路由信息
for _, parsedComment := range parsedComments {
if parsedComment.routerPath != "" {
key := pkgpath + ":" + controllerName
cc := ControllerComments{}
//方法名
cc.Method = f.Name.String()
cc.Router = parsedComment.routerPath
cc.AllowHTTPMethods = parsedComment.methods
cc.MethodParams = buildMethodParams(f.Type.Params.List, parsedComment)
cc.FilterComments = buildFilters(parsedComment.filters)
cc.ImportComments = buildImports(parsedComment.imports)
genInfoList[key] = append(genInfoList[key], cc)
}
}
// ControllerComments store the comment for the controller method
type ControllerComments struct {
Method string //对应函数名
Router string //对应路径
Filters []*ControllerFilter
ImportComments []*ControllerImportComments
FilterComments []*ControllerFilterComments
AllowHTTPMethods []string //允许http的访问方式 get/post/put等
Params []map[string]string //相关参数
MethodParams []*param.MethodParam
}
- 5.根据路由信息生成自定义格式的代码
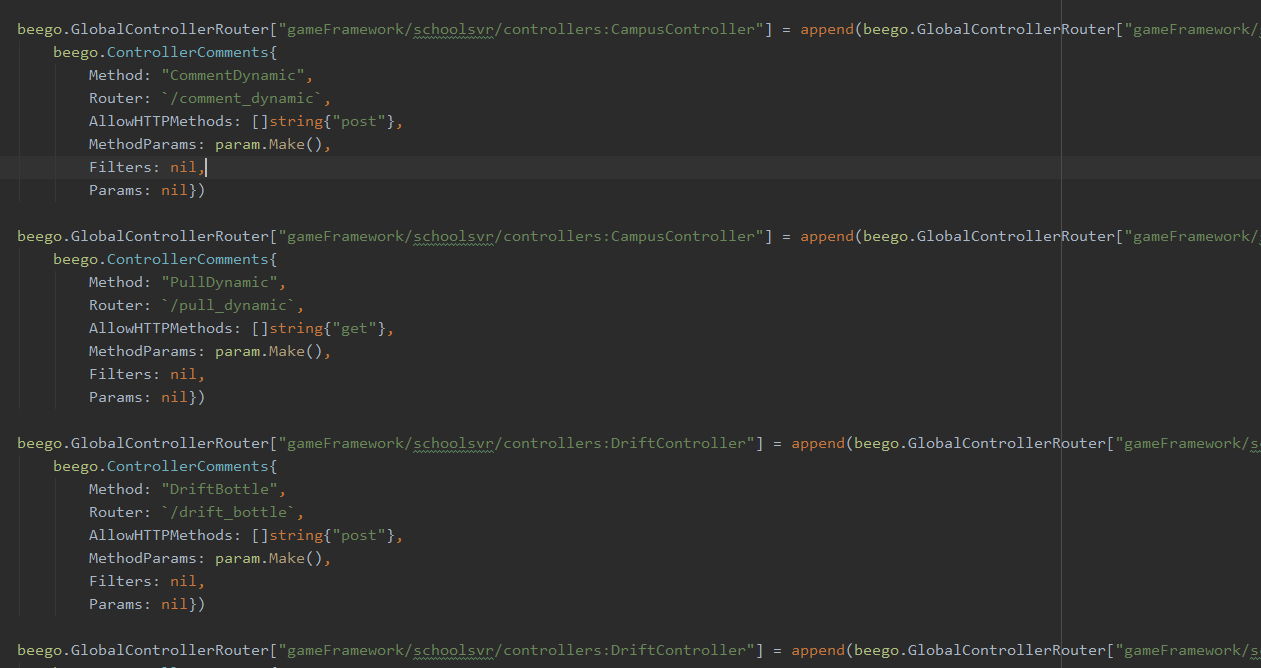
genRouterCode(pkgRealpath string) {
....
globalinfo = globalinfo + `
beego.GlobalControllerRouter["` + k + `"] = append(beego.GlobalControllerRouter["` + k + `"],
beego.ControllerComments{
Method: "` + strings.TrimSpace(c.Method) + `",
` + "Router: `" + c.Router + "`" + `,
AllowHTTPMethods: ` + allmethod + `,
MethodParams: ` + methodParams + `,
Filters: ` + filters + `,
Params: ` + params + `})
....
}
最终生成代码示例