SpringMVC执行流程图
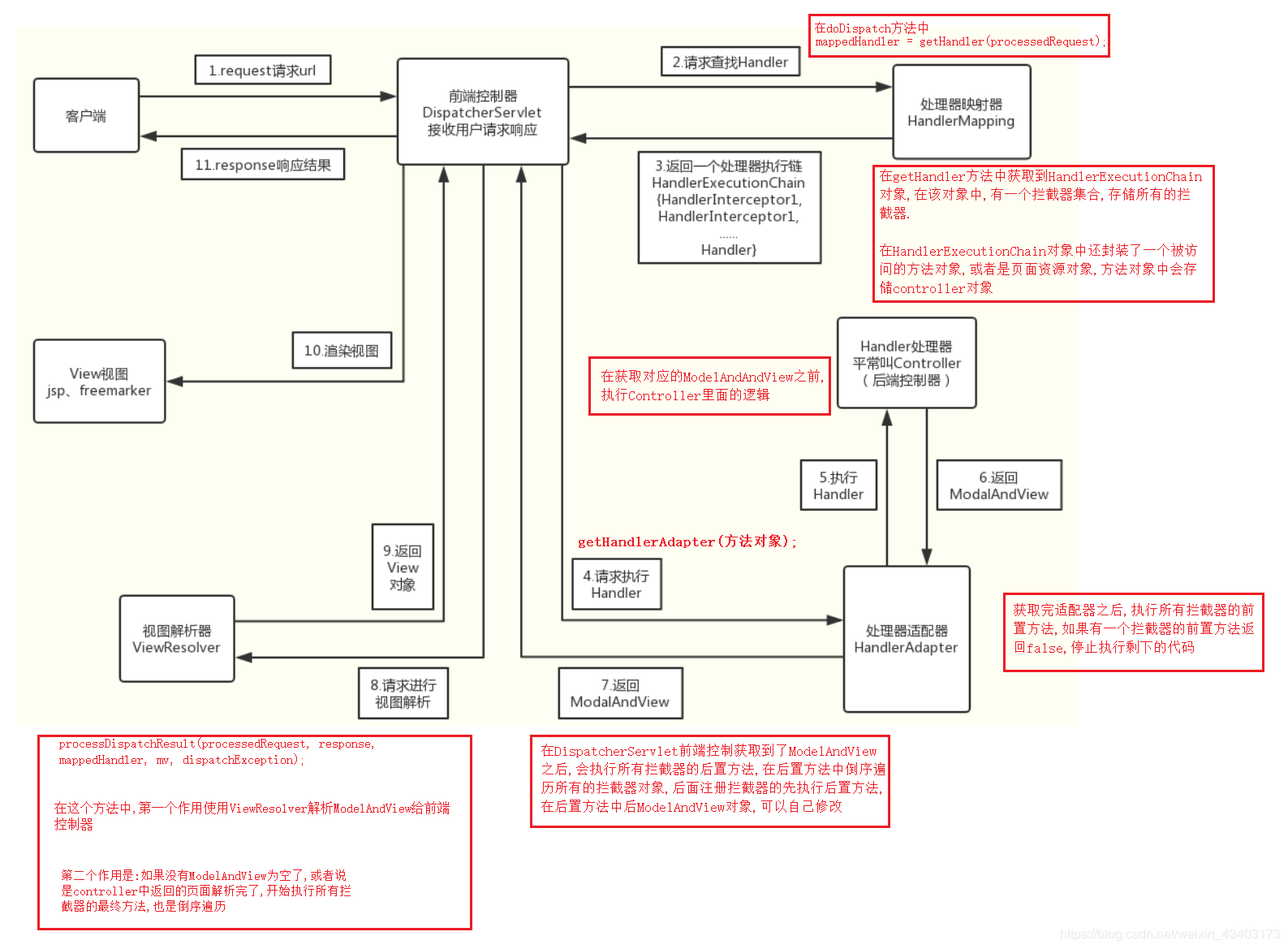
在前端控制器中最最重要的方法是 doDispatch,在这个方法中 ,起到委派模式中委派者的角色,负责把 任务分发给各个角色做处理
分发的主要任务:
-
获取处理器映射器
-
根据处理器映射器获取处理器适配器
-
根据处理器适配器获取视图ModelAndView
-
使用视图解析解解析视图
-
渲染视图
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
//把request对象赋值给 processedRequest
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
//定义 HandlerExecutionChain 如果是访问controller方法的话,封装方法对象(方法对象中封装了controller对象), HandlerExecutionChain还将封装所有的拦截器
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
//将会通过 ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); 获取 ModelAndView
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
// 1.尝试将当前请求转换为MultipartHttpServletRequest
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 2.查找当前请求对应的handler,包括Handler(控制器也就是controller本身)本身和Handler拦截器
//当遍历到requestMappingHandlerMapping时 在requestMappingHandlerMapping中其实存储了 所有拦截器的对象
/**
* 这个方法一路千辛万苦,一路封装,满载而归
* 1.首先是调用AbstractHandlerMapping的getHandler方法,然后调用 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的getHandlerInternal方法
* 然后重新创建创建对象 new HandlerMethod(this, handler) 把controller对象(从工厂中获取) 赋值 给方法对象HandlerMethod
* 所以第一步就是: 把controller对象赋值给方法对象
*
* 2.然后调用AbstractHandlerMapping.getHandlerExecutionChain 转换为 HandlerExecutionChain 对象
* 遍历拦截器集合 把所有的拦截器对象赋值给HandlerExecutionChain对象
* 所以第二步就是: 把方法对象转换为HandlerExecutionChain对象并把所有的拦截器赋值到其中
*
*/
//根据请求request对象,调用处理器映射器寻找处理器,其实就是 HandlerExecutionChain 对象
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
/**
* 此时的 mappedHandler 即为 HandlerExecutionChain 对象
* HandlerExecutionChain 对象中 封装了浏览器访问的方法对应的方法对象,方法对象中封装了对象的controller对象,HandlerExecutionChain封装了所有的拦截器
*/
// 未能找到对应的handler,抛出NoHandlerFoundException异常并返回404
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
// 3.查找当前请求对应的HandlerAdapter
//把方法对象传进去,获取到一个适配器
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
// 4.处理last-modified请求头,如果当前请求支持的话
//获取方法的请求方法
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 5.应用前置拦截器
// 如果有拦截器返回false,则表明该拦截器已经处理了返回结果,直接返回;
//注意: 此时的 processedRequest 其实就是request 对象
//就是在判断定义所有的拦截器 的前置方法,返回的到底是true,还是false
//如果有一个前置返回的是false,那么停止执行下面的代码, 只有所有的拦截器的前置方法返回的true才可以
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
// 6.调用HandlerAdapter的handler方法,真正开始处理Controller
//在以上的所有步骤中, ModelAndView都还没有返回
//这个方法尝试获取 ModelAndView 对象 把request对象 ,response对象 和方法对象传进去
//进入到RequestMappingHandlerAdaper适配器的handleInternal
//准备获取ModelAndView对象 同时在方法里面执行了controller方法的内容
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
//此时ModelAndView对象的view值为跳转的路径
// 7.如果当前请求是并发处理,直接返回
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
// 8. 如果当前返回值中不包含视图名的话,为返回值设定默认视图名,
//意思如果你没有设置跳转路径的话,这个方法默认给你加跳转路径
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 9.应用已注册拦截器的后置方法。
//倒着遍历所有的拦截器 先注册的后执行
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
// 10.处理分发调用结果,如视图模型解析、返回等工作 如果以上有任何错误,把错误信息封装赋值给dispatchException 错误对象
//如果dispatchException不为空的话,打印错误信息,如果ModelAndView返回的是一个页面的话,会重新发起请求
//如果没有ModelAndView为空了 ,或者说controller返回不是一个页面了, 执行拦截器的后置方法,也是倒着遍历
//在这里面还干了一个一件事 ,那就是获取到了 view视图对象
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
//整理由多部分请求使用的任何资源。
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
聊一下比较重要的几个方法
1.获取处理器映射器
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
在doDispatch方法中找这个方法,按住Ctrl键点击进入
此一路千辛万苦,一路封装,满载而归
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//handlerMappings中有5个对象
//1. favconHandlerMapping 2.requestMappingHandlerMapping 3.beanNameHandlerMapping 4.resourceHandlerMapping 5.welcomePageHandlerMapping
//遍历这个五个对象
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
//当遍历到requestMappingHandlerMapping时 在requestMappingHandlerMapping中其实存储了 所有拦截器的对象
/**
* 这个方法一路千辛万苦,一路封装,满载而归
* 1.首先是调用AbstractHandlerMapping的getHandler方法,然后调用 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的getHandlerInternal方法
* 然后重新创建创建对象 new HandlerMethod(this, handler) 把controller对象(从工厂中获取) 赋值 给方法对象HandlerMethod
* 所以第一步就是: 把controller对象赋值给方法对象
*
* 2.然后调用AbstractHandlerMapping.getHandlerExecutionChain 转换为 HandlerExecutionChain 对象
* 遍历拦截器集合 把拦截器所有的对象赋值给HandlerExecutionChain对象的集合
* 所以第二步就是: 把方法对象转换为HandlerExecutionChain对象并把所有的拦截器赋值到其中
*
*/
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
我们再看一下
mapping.getHandler(request);方法
按住Ctrl键点击进入,发现是HandlerMapping接口 , 按住快捷键 Ctrl + Alt + B 选择AbstractHandlerMapping 这个实现类
@Override
@Nullable
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//获取Controller对象,但是获取到时对应方法的对象,方法对象中封装有controller对象
//一路获取controller对象,把controller对象封装进方法对象中,(前提是访问的是controller中的方法)
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
//把方法对象和request传进去 ,准备把所有的拦截器封装进 HandlerExecutionChain对象中
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
// 现在 HandlerExecutionChain 对象中有 方法对象 而方法对象中存储了controller对象, HandlerExecutionChain中有所有的拦截器对象
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && !request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.ASYNC)) {
logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler());
}
if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.corsConfigurationSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
2.获取处理器适配器
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
我们再回到 doDispatch方法中,找到该方法, 按住Ctrl键点击进入
//参数为对应方法对象,或者是页面资源对象
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
//handlerAdapters 有三个适配器对象
//1.RquestMappingHandlerAdapter 2.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter 3.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
//查看哪个处理器符合请求需要的,返回符合条件的处理器
if (adapter.supports(handler)) {
return adapter;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
3.获取视图ModelAndView
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
我们再回到 doDispatch方法中,找到该方法, 点击进入
发现是一个HandlerAdapter接口 ,按住快捷键 Ctrl + Alt + B ,选择 AbstractHandlerMethodAdaper
按住Ctrl键点击 handleInternal 方法,发现是一个抽象的方法,再次 按住快捷键 Ctrl + Alt + B 进入到RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
@Override
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav;
checkRequest(request);
//如果需要,在同步块中执行InvokehandlerMethod。
// Execute invokeHandlerMethod in synchronized block if required.
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// No HttpSession available -> no mutex necessary
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// No synchronization on session demanded at all...
//尝试获取ModelAndView对象,如果没有HTML,则获取不到视图
//这个方法里面执行了controller的内容
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) {
if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
}
else {
prepareResponse(response);
}
}
//获取到ModelAndView对象
return mav;
}
4.解析视图
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
我们再回到 doDispatch方法中,找到该方法, 按住Ctrl键点击进入
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv,
@Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
}
else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
//处理程序是否返回要呈现的视图?
// Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
//这个方法当中会获取到视图view
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned.");
}
}
if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Concurrent handling started during a forward
return;
}
if (mappedHandler != null) {
//如果没有ModelAndView为空了 ,或者说controller返回不是一个页面了,执行拦截器的后置方法,也是倒着遍历
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}
找到 render(mv, request, response); 方法, 按住Ctrl键点击进入
protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Determine locale for request and apply it to the response.
Locale locale =
(this.localeResolver != null ? this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request) : request.getLocale());
response.setLocale(locale);
View view;
String viewName = mv.getViewName();
if (viewName != null) {
//我们需要解析视图名称
// We need to resolve the view name.
//获取到了视图
view = resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name '" + mv.getViewName() +
"' in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
else {
// No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object.
view = mv.getView();
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " +
"View object in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
// Delegate to the View object for rendering.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Rendering view [" + view + "] ");
}
try {
if (mv.getStatus() != null) {
response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value());
}
//获取到视图之后
view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "]", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
这个方法中,解析视图ModelAndView ,获取View对象