树
二叉树是一种树,那树是什么呢
如图,上面那个就是树,与图中下面的有回路的图相比
树的任意两个节点只有一条唯一路径连通
二叉树
二叉树则是一种特殊的树,特点是每个节点至多只有一个左节点和一个右节点,也就是每个父亲节点最多只能有两个儿子节点
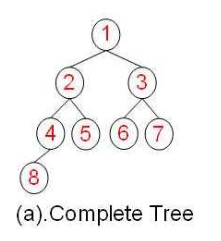
完全二叉树
深度为 h的二叉树(深度就是有几层节点),除第 h 层外,其它各层 (1~h-1) 的结点数都达到最大个数,第 h 层从右向左连续缺若干结点,就是完全二叉树。
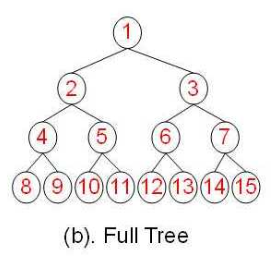
满二叉树
对一个深度为h的二叉树,节点数为2^n-1
也就是每个父亲都完美的生了两个儿子,一家子整整齐齐,是完全二叉树的升级版
二叉查找树
然后便是今天的主角了,二叉查找树(BST) 它的规则是:
- 任意左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值
- 任意右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值
之所以要这么规定,就是为了利用二分法的思想,增加查找和插入的效率
创建二叉查找树
首先我们需要定义一个Node类,存储自身的值和对两个儿子的指针
并且定义有一个插入节点的方法
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data
this.left = null
this.right = null
}
insertNode(newNode) {
if (newNode.data < this.data) {
if (this.left === null) { this.left = newNode }
else {
this.left.insertNode(newNode)
}
}
else {
if (this.right === null) { this.right = newNode }
else {
this.right.insertNode(newNode)
}
}
}
}
然后定义一个BST类,接受一个数组进行初始化
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor(arr) {
this.root = new Node(arr[0])
if (arr.length === 1) return;
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
this.root.insertNode(new Node(arr[i]))
}
}
}
通过传一个数组进去,就完成了我们的二叉查找树的初始化
var BST = new BinarySearchTree([9, 6, 11, 7, 19, 8, 20, 5])
打印出来大概长这样

插入
当想插入新的节点的时候,直接这么调用就可以了
this.root.insertNode(new Node(data))
广度遍历
广度遍历就是一层一层进行遍历,从上到下,从左至右
最后返回一个数组
breadthTraversal() {
var queue = [this.root]
var node
var arr = []
while (queue.length > 0) {
node = queue.shift()
arr.push(node.data)
if (node.left) queue.push(node.left)
if (node.right) queue.push(node.right)
}
return arr
}
深度遍历(递归)
深度遍历分为三种,前序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历
这里需要强调的是,它们其实在遍历的走向上是一样的,只是什么时候才算真正遍历到了这个元素上有所分歧,可以看一下这篇文章的动画,瞬间理解
juejin.cn/post/684490…
首先我们很容易想到的是递归
//前序遍历
preOrder(arr = [], node = this.root) {
if (node === null) return arr;
arr.push(node.data)
this.preOrder(arr, node.left)
this.preOrder(arr, node.right)
return arr;
}
那么中序遍历和后序遍历呢?
回想一下,他们三个唯一的区别只是在何时把节点的值加入数组
那么其实只要改一下arr.push(node.data)这句话的位置即可
//中序遍历
inOrder(arr = [], node = this.root) {
if (node === null) return arr;
this.inOrder(arr, node.left)
arr.push(node.data)
this.inOrder(arr, node.right)
return arr;
}
//后序遍历
postOrder(arr, node = this.root) {
if (node === null) return arr;
this.postOrder(arr, node.left)
arr.push(node.data)
this.postOrder(arr, node.right)
return arr;
}
不过这也未免太简单了吧,我要是面试官我肯定不考这个
而且递归做法,在数据量很大的时候有爆栈的可能
所以下面我们要研究非递归的解法
深度遍历(非递归)
这里的关键是,我们要自己创建一个栈 var stack=[]
使用两个while循环,大循环保证遍历到所有节点,小循环是不断进行向左深入
//前序遍历
preOrder2() {
var node = this.root
var arr = []
var stack = []
while (node !== null || stack.length > 0) {
while (node !== null) {
stack.push(node)
arr.push(node.data)
node = node.left
}
//出来的时候node的左树已经遍历完了,此时是null
if (stack.length > 0) {
node = stack.pop()
node = node.right
}
//出来后回到大循环的开始,又进入第一个小循环遍历左树
}
return arr
}
中序遍历的思想与其类似,我们也是只要改变arr.push(node.data)的位置即可
//中序遍历
inOrder2() {
var node = this.root
var stack = []
while (node !== null || stack.length > 0) {
while (node !== null) {
stack.push(node)
node = node.left
}
//出来的时候node的左树已经遍历完了,此时是null
if (stack.length > 0) {
node = stack.pop()
arr.push(node.data)
node = node.right
}
//出来后回到大循环的开始,又进入第一个小循环遍历左树
}
return arr
}
最难的是后序遍历,这里不是改变那句话的位置那么简单了
我们要改变一下思想了
想一想每个节点到底是什么时候算是被遍历到了的
就是在所有儿子都被遍历完了后,所以我们越先接触到的节点,就会越出现在最终的数组的末尾部分
所以我们只要把前序遍历的arr.push改成arr.unshift即可!
//后序遍历
postOrder2() {
var node = this.root
var stack = []
while (node !== null || stack.length > 0) {
while (node !== null) {
stack.push(node)
arr.unshift(node.data) //最先接触到的节点最后才会被插入数组
node = node.left
}
//出来的时候node的左树已经遍历完了,此时是null
if (stack.length > 0) {
node = stack.pop()
node = node.right
}
//出来后回到大循环的开始,又进入第一个小循环遍历左树
}
return arr
}
查找最大最小节点
最小其实就是最左边那个节点,最大是最右边那个节点
searchMin(node = this.root) {
if (node.left === null) return node;
else {
return this.searchMin(node.left)
}
}
searchMax(node = this.root) {
if (node.right === null) return node;
else {
return this.searchMax(node.right)
}
}
查找指定节点
这个就是二叉查找树的强项了,基于二分思想的查找
hasNode(data, node = this.root) {
if (node === null) return false;
if (data === node.data) return true;
else if (data < node.data) {
return this.hasNode(data, node.left)
}
else {
return this.hasNode(data, node.right)
}
}
删除指定节点
这个分三种情况
- 叶子节点(没有儿子了)
- 节点只有左子树或右子树
- 节点既有左子树又有右子树
前两种好解决
第一种只要把叶子节点变成null即可
第二种就把它变成它的子树
第三种稍微麻烦一点,要先找到待删除节点A的右子树中最小的那个节点B(也可以在左子树中找最大的),B就是整个右子树中最接近A的数值的了,然后令A.data=B.data,再把B节点删掉即可
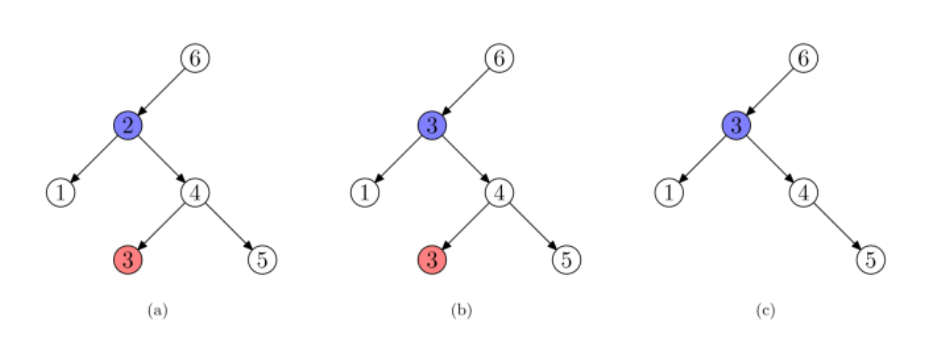
delNode(data, node = this.root) {
if (node === null) return 'not found';
//找到了
if (data === node.data) {
//是叶子节点
if (node.left === null && node.right === null) {
node = null
}
//只有左子树或者右子树
else if (node.left === null && node.right !== null) {
node = node.right
}
else if (node.right === null && node.left !== null) {
node = node.left
}
//左右子树都有
else {
var replaceNode = this.searchMin(node.right)
node.data = replaceNode.data //掉包掉好了,接下去就是删除那个最小节点
return this.delNode(node.data, node.right)
}
}
//没找到,继续向下找
else if (data < node.data) {
return this.delNode(data, node.left)
}
else {
return this.delNode(data, node.right)
}
}
最大深度
返回当前二叉树的最大深度
使用分治思想,先向下不断分,再由底向上返回汇总
maxDepth(node = this.root) {
if (node === null) return 0;
return Math.max(this.maxDepth(node.left), this.maxDepth(node.right)) + 1
}
总结
学好二叉树不止是为了面试,从中也能更好得理解递归与分治的思想,并感受数据结构的魅力
这是我的个人网站,记录下前端学习的点滴,欢迎大家参观
www.ssevenk.com